2010 JAGUAR XFR sensor
[x] Cancel search: sensorPage 2610 of 3039

1 Occupant classification system pressure pad (NAS only) 2 Safety belt tension sensor (NAS only) 3 Occupant detection system pad (all, except NAS) 4 Occupant classification system control module (NAS only) 5 RH side impact sensor (pressure sensor) 6 RH rear impact sensor 7 LH rear impact sensor 8 Passenger airbag deactivation LED (light emitting diode) 9 Driver's seat position sensor 10 LH side impact sensor (pressure sensor) 11 Instrument cluster 12 LH front impact sensor 13 RH front impact sensor
Page 2611 of 3039

Published: 30-May-2012
Supplemental Restraint System - Air Bag and Safety Belt Pretensioner
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) - Overview
Description and Operation
OVERVIEW
WARNING: All pyrotechnic devices are dangerous. Before performing any procedures on any pyrotechnic device, read all
information contained within the Standard Workshop Practices section of this manual.
Refer to: Standard Workshop Practices (100-00 General Information, Description and Operation).
The SRS (supplemental restraint system) provides additional protection for the vehicle occupants in certain impact conditions.
The system is controlled by the RCM (restraints control module), which is mounted beneath the floor console. The system
includes twin stage drivers and front passenger airbags.
The RCM receives inputs from various sensors around the vehicle and determines which, if any, airbags should be deployed.
The SRS features an occupant detection system. The occupant detection system comprises a mat fitted inside the front passenger seat. By monitoring the condition of the mat, the RCM can determine if the front passenger seat is occupied. It uses this information to determine which airbags to deploy in the event of an impact. This information is also used to illuminate the
safety belt instrument cluster warning lamp if the front passenger seat is occupied and the safety belt is not engaged.
North American Specification (NAS) vehicles also feature an occupant classification system. The occupant classification system
comprises a control module, pressure pad and safety belt tension sensor. The system can determine the size and weight of the
front seat passenger. This information is transmitted to the RCM over the high speed CAN (controller area network) bus. The RCM uses this information to help determine which airbags to deploy in the event of an impact.
Page 2612 of 3039
Published: 26-Jun-2012
Supplemental Restraint System - Air Bag and Safety Belt Pretensioner
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) - System Operation and Component Description
Description and Operation
Control Diagram
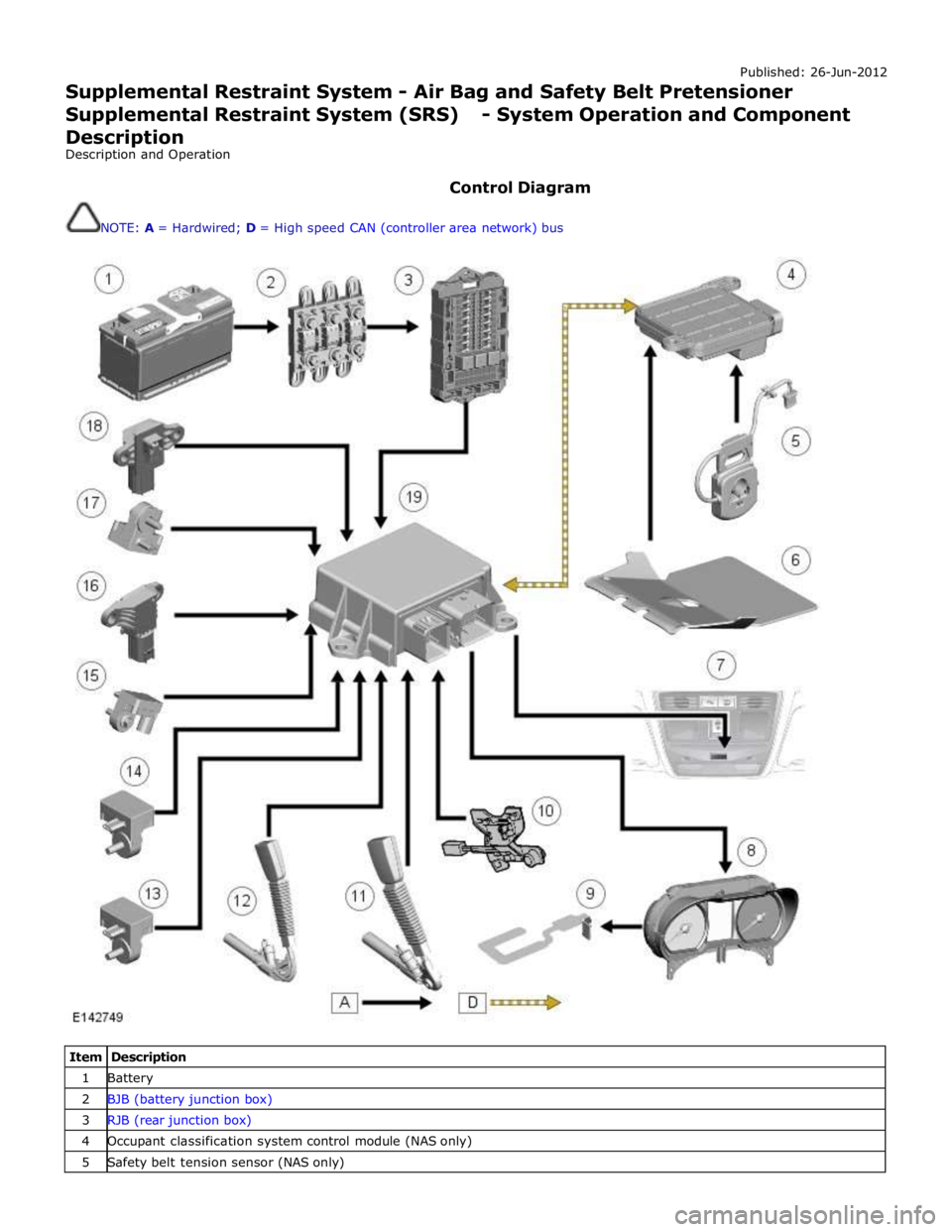
NOTE: A = Hardwired; D = High speed CAN (controller area network) bus
Item Description 1 Battery 2 BJB (battery junction box) 3 RJB (rear junction box) 4 Occupant classification system control module (NAS only) 5 Safety belt tension sensor (NAS only)
Page 2613 of 3039
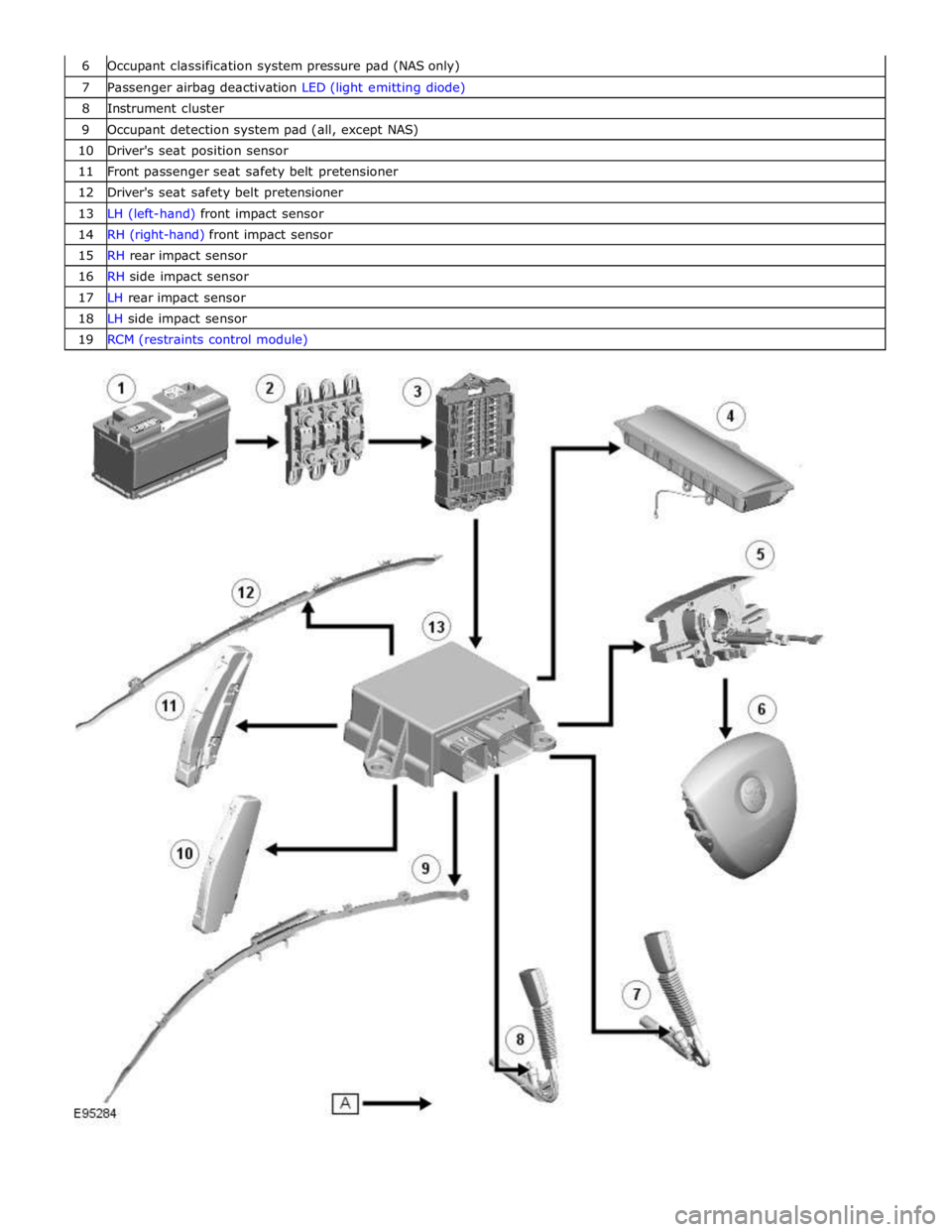
6 Occupant classification system pressure pad (NAS only) 7 Passenger airbag deactivation LED (light emitting diode) 8 Instrument cluster 9 Occupant detection system pad (all, except NAS) 10 Driver's seat position sensor 11 Front passenger seat safety belt pretensioner 12 Driver's seat safety belt pretensioner 13 LH (left-hand) front impact sensor 14 RH (right-hand) front impact sensor 15 RH rear impact sensor 16 RH side impact sensor 17 LH rear impact sensor 18 LH side impact sensor 19 RCM (restraints control module)
Page 2614 of 3039
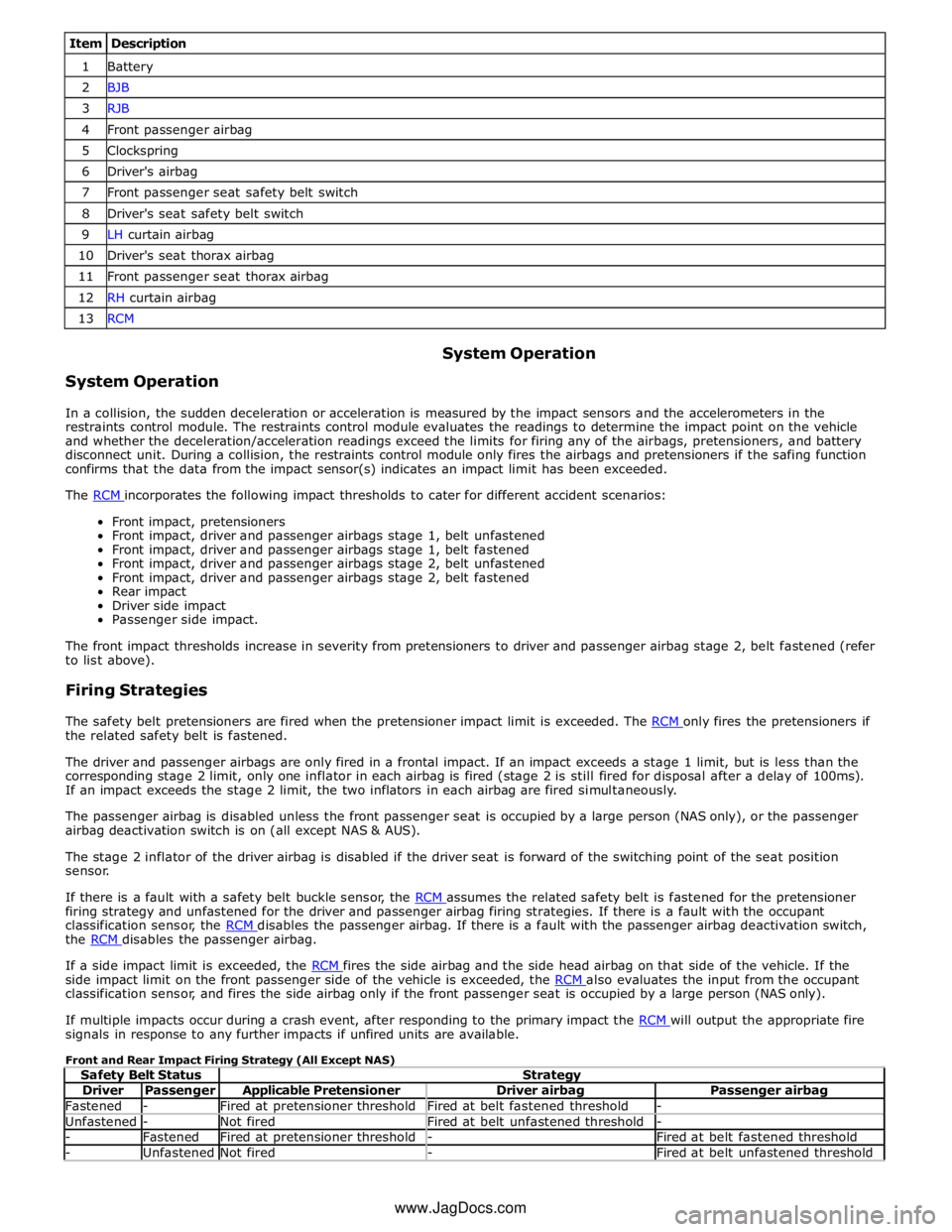
Item Description 1 Battery 2 BJB 3 RJB 4 Front passenger airbag 5 Clockspring 6 Driver's airbag 7 Front passenger seat safety belt switch 8 Driver's seat safety belt switch 9 LH curtain airbag 10 Driver's seat thorax airbag 11 Front passenger seat thorax airbag 12 RH curtain airbag 13 RCM
System Operation System Operation
In a collision, the sudden deceleration or acceleration is measured by the impact sensors and the accelerometers in the
restraints control module. The restraints control module evaluates the readings to determine the impact point on the vehicle
and whether the deceleration/acceleration readings exceed the limits for firing any of the airbags, pretensioners, and battery
disconnect unit. During a collision, the restraints control module only fires the airbags and pretensioners if the safing function
confirms that the data from the impact sensor(s) indicates an impact limit has been exceeded.
The RCM incorporates the following impact thresholds to cater for different accident scenarios: Front impact, pretensioners
Front impact, driver and passenger airbags stage 1, belt unfastened
Front impact, driver and passenger airbags stage 1, belt fastened
Front impact, driver and passenger airbags stage 2, belt unfastened
Front impact, driver and passenger airbags stage 2, belt fastened
Rear impact
Driver side impact
Passenger side impact.
The front impact thresholds increase in severity from pretensioners to driver and passenger airbag stage 2, belt fastened (refer
to list above).
Firing Strategies
The safety belt pretensioners are fired when the pretensioner impact limit is exceeded. The RCM only fires the pretensioners if the related safety belt is fastened.
The driver and passenger airbags are only fired in a frontal impact. If an impact exceeds a stage 1 limit, but is less than the
corresponding stage 2 limit, only one inflator in each airbag is fired (stage 2 is still fired for disposal after a delay of 100ms).
If an impact exceeds the stage 2 limit, the two inflators in each airbag are fired simultaneously.
The passenger airbag is disabled unless the front passenger seat is occupied by a large person (NAS only), or the passenger
airbag deactivation switch is on (all except NAS & AUS).
The stage 2 inflator of the driver airbag is disabled if the driver seat is forward of the switching point of the seat position
sensor.
If there is a fault with a safety belt buckle sensor, the RCM assumes the related safety belt is fastened for the pretensioner firing strategy and unfastened for the driver and passenger airbag firing strategies. If there is a fault with the occupant
classification sensor, the RCM disables the passenger airbag. If there is a fault with the passenger airbag deactivation switch, the RCM disables the passenger airbag.
If a side impact limit is exceeded, the RCM fires the side airbag and the side head airbag on that side of the vehicle. If the side impact limit on the front passenger side of the vehicle is exceeded, the RCM also evaluates the input from the occupant classification sensor, and fires the side airbag only if the front passenger seat is occupied by a large person (NAS only).
If multiple impacts occur during a crash event, after responding to the primary impact the RCM will output the appropriate fire signals in response to any further impacts if unfired units are available.
Front and Rear Impact Firing Strategy (All Except NAS)
Safety Belt Status Strategy Driver Passenger Applicable Pretensioner Driver airbag Passenger airbag Fastened - Fired at pretensioner threshold Fired at belt fastened threshold - Unfastened - Not fired Fired at belt unfastened threshold - - Fastened Fired at pretensioner threshold - Fired at belt fastened threshold - Unfastened Not fired - Fired at belt unfastened threshold www.JagDocs.com
Page 2616 of 3039
and the safety belt buckle sensor. Based on this data, the RCM decides which level of airbag module deployment is required and forwards the information to the second area, the deployment handler.
The deployment handler evaluates the status of the seat track position sensor and safety belt buckle sensors before a decision
is made about which restraints should finally be deployed.
Data from the side crash sensors is used by the RCM in conjunction with acceleration data from the RCM internal accelerometer to make a deployment decision. The RCM processes the acceleration data and subject to an impact being of high enough severity, decides whether the side airbag module should be deployed.
On board testing of the airbag modules, front safety belt pretensioner firing circuits, warning indicator circuits and module
status (the crash and side impact sensors perform basic self-tests) is performed by the RCM together with the storing of fault codes.
The RCM drives the SRS indicator on the instrument pack via a CAN signal. If the warning lamp fails, a fault code is recorded and a warning tone is sounded in place of the lamp if a further fault occurs. It also provides a temporary back-up power supply
to operate the airbag modules in the event that in crash conditions, the battery supply is lost. In the event of a crash, it
records certain data which can be accessed via the diagnostic connector.
A safing sensor in the RCM provides confirmation of an impact to verify if airbag and pretensioner activation is necessary. A roll-over sensor monitors the lateral attitude of the vehicle. Various firing strategies are employed by the RCM to ensure that during an accident only the appropriate airbags and pretensioners are fired. The firing strategy used also depends on the
inputs from the safety belt switches and the occupant monitoring system.
An energy reserve in the RCM ensures there is always a minimum of 150 milliseconds of stored energy available if the power supply from the ignition switch is disrupted during a crash. The stored energy is sufficient to produce firing signals for the
driver airbag, the passenger airbag and the safety belt pretensioners.
When the ignition is switched on, the RCM performs a self-test and then performs cyclical monitoring of the system. If a fault is detected the RCM stores a related fault code and illuminates the airbag warning indicator. The faults can be retrieved by the recommended Jaguar diagnostic tool over the CAN bus. If a fault that could cause a false fire signal is detected, the RCM disables the respective firing circuit, and keeps it disabled during a crash event.
Clock Spring
The clockspring is installed on the steering column to provide the electrical interface between the fixed wiring harness of the
steering column and the components that rotate with the steering wheel, i.e. the driver airbag, the horn and the steering
wheel switch packs.
The clockspring consists of a plastic cassette which incorporates an outer cover fixed to the steering column and an inner rotor
which turns with the steering wheel. Four securing lugs attach the cover to the multifunction switch on the steering column.
The rotor is keyed to the steering wheel by a drive peg. A lug on the underside of the rotor operates the self-cancelling feature
of the turn signal indicator switch. A ribbon lead, threaded on rollers in the rotor, links two connectors on the cover to two
connectors on the rotor. Link leads for the driver airbag are installed in one of the connectors on the rotor.
To prevent damage to the ribbon lead, both the steering and the clockspring must be centralized when removing and installing
the clockspring or the steering wheel. The clockspring is centralized when the drive peg is at six o'clock and 50 - 100% of a
yellow wheel is visible in the viewing window.
Replacement clocksprings are fitted with a stopper, which locks the cover to the rotor, in the central position. The stopper must
be broken off when the replacement clockspring is installed.
Page 2619 of 3039
provides the interface connection through which the side impact sensor communicates with the RCM using serial data messages. Acceleration is evaluated by the microchip and transmitted to the restraints control module, which then makes the
decision on whether or not to activate the airbags and pretensioners.
When the ignition is switched on, the RCM supplies power to the impact sensors, which perform a self-test. After satisfactory self tests the impact sensors continually output 'digital acceleration' messages to the restraints control module. If a fault is
detected the relevant impact sensor sends a fault message, instead of the digital acceleration message, to the restraints
control module. The RCM then stores a related fault code and illuminates the airbag warning indicator. Faults can be retrieved by the Jaguar approved diagnostic system from the RCM via the high speed CAN bus connection. www.JagDocs.com
Page 2620 of 3039
position sensor consists of a Hall effect sensor attached to the driver seat frame. While the ignition is on, the RCM supplies the sensor with power, and monitors the return current. When the seat frame moves forwards, the sensor moves over the edge
of the seat track, which changes the reluctance of the sensor. The change of current is detected by the RCM and used as a switching point. The switching point is when the center of the sensor is 3 ± 4 mm from the leading edge of the seat track.
When the driver seat is forward of the switching point, the RCM increases the time delay between firing the two stages of the inflator in the driver airbag. When the driver seat is rearward of the switching point, the RCM uses the normal time delay between firing the two stages.
Safety Belt Sensor
A safety belt switch is installed in the buckle of each front safety belt to provide the RCM with a status signal of the related safety belt(s). When the safety belt is unfastened the switch outputs a low current to the RCM. When the safety belt is fastened the switch outputs a high current to the RCM.
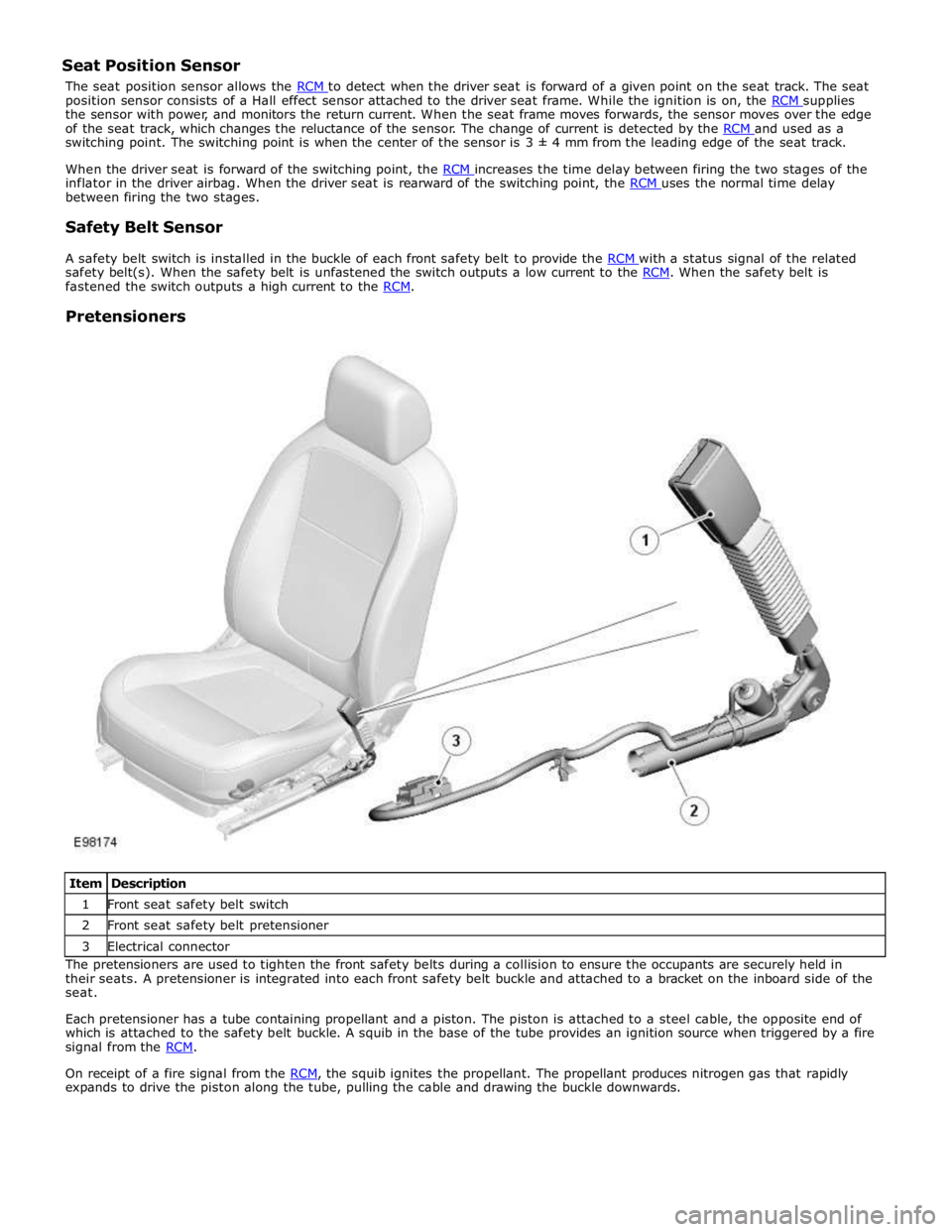
Pretensioners
Item Description 1 Front seat safety belt switch 2 Front seat safety belt pretensioner 3 Electrical connector The pretensioners are used to tighten the front safety belts during a collision to ensure the occupants are securely held in
their seats. A pretensioner is integrated into each front safety belt buckle and attached to a bracket on the inboard side of the
seat.
Each pretensioner has a tube containing propellant and a piston. The piston is attached to a steel cable, the opposite end of
which is attached to the safety belt buckle. A squib in the base of the tube provides an ignition source when triggered by a fire
signal from the RCM.
On receipt of a fire signal from the RCM, the squib ignites the propellant. The propellant produces nitrogen gas that rapidly expands to drive the piston along the tube, pulling the cable and drawing the buckle downwards.