2010 JAGUAR XFR Module
[x] Cancel search: ModulePage 557 of 3039

Installation
1. Torque: 11 Nm
2. CAUTIONS:
Make sure that the mating faces are clean and free of
foreign material.
Apply a continuous bead of silicone gasket sealant
(Loctite 5999) as shown on the illustration. The application
of the sealant must be 4mm diameter. Install the
component immediately after applying the sealant without
smearing the sealant.
NOTE: New units must be configured using the
Programmable Module Installation Routine in the diagnostic
tool.
Torque: 11 Nm Apply a suitable amount of approved sealant to one
of the mating faces.
Page 582 of 3039

Brake System - General Information - Brake System
Diagnosis and Testing
Principle of Operation Published: 11-May-2011
For a detailed description of the brake system, refer to the relevant Description and Operation sections in the workshop
manual. REFER to:
Front Disc Brake (206-03, Description and Operation),
Front Disc Brake (206-03, Description and Operation),
Front Disc Brake (206-03, Description and Operation),
Rear Disc Brake (206-04, Description and Operation),
Rear Disc Brake (206-04, Description and Operation),
Rear Disc Brake (206-04, Description and Operation),
Parking Brake (206-05 Parking Brake and Actuation, Description and Operation), Parking Brake (206-05 Parking Brake and Actuation, Description and Operation), Parking Brake (206-05 Parking Brake and Actuation, Description and Operation), Hydraulic Brake Actuation (206-06 Hydraulic Brake Actuation, Description and Operation), Hydraulic Brake Actuation (206-06 Hydraulic Brake Actuation, Description and Operation), Hydraulic Brake Actuation (206-06 Hydraulic Brake Actuation, Description and Operation), Brake Booster (206-07 Power Brake Actuation, Description and Operation), Brake Booster (206-07 Power Brake Actuation, Description and Operation), Brake Booster (206-07, Description and Operation).
Inspection and Verification
Visually examine the front and rear wheel and tire assemblies for damage such as uneven wear patterns, tread worn out or
sidewall damage. Verify the tires are the same size, type and, where possible, same manufacturer. Replace the damaged
wheel or excessively worn tire.
Wheels and tires must be cleared of any foreign matter and tire pressures adjusted to the correct specification.
If the tires exhibit uneven wear or feathering, the cause must be corrected. Check the steering and suspension components for
damage or wear and, if necessary, check and adjust front wheel alignment. REFER to: (204-00 Suspension System - General
Information)
Specifications (Specifications), Front Toe Adjustment (General Procedures).
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical
Brake master cylinder
Brake caliper piston(s)
Brake discs
Wheel bearings
Brake pads
Power brake booster
Brake pedal linkage
Brake booster vacuum hose
Tires
Debris
Parking brake actuator
Parking brake module
Parking brake switch
Damaged or corroded wiring harness
Brake master cylinder fluid level switch Road Test
Carry out a road test to compare actual vehicle braking performance with the performance standards expected by the driver.
The ability of the test driver to make valid comparisons and detect performance deficiencies will depend on experience.
The driver should have a thorough knowledge of brake system operation and accepted general performance guidelines to make
good comparisons and detect performance concerns.
An experienced brake technician will always establish a route that will be used for all brake diagnosis road tests. The roads
selected will be reasonably smooth and level. Gravel or bumpy roads are not suitable because the surface does not allow the
tires to grip the road equally. Crowned roads should be avoided because of the large amount of weight shifted to the low set
of wheels on this type of road. Once the route is established and consistently used, the road surface variable can be
eliminated from the test results.
Before a road test, obtain a complete description of the customer concerns or suspected condition. From the description, the
technician's experience will allow the technician to match possible causes with symptoms. Certain components will be tagged
as possible suspects while others will be eliminated by the evidence. More importantly, the customer description can reveal
unsafe conditions which should be checked or corrected before the road test. The description will also help form the basic
approach to the road test by narrowing the concern to specific components, vehicle speed or conditions.
Begin the road test with a general brake performance check. Keeping the description of the concern in mind, test the brakes at
different vehicle speeds using both light and heavy pedal pressure. To determine if the concern is in the front or rear braking
system, use the brake pedal and then use the parking brake control. If the condition (pull, vibration, pulsation) occurs only
with the parking brake, the concern is in the rear brake system.
Page 644 of 3039

Parking brake module retaining bolts 4 - 35 Parking brake release actuator retaining bolts 20 15 -
Page 645 of 3039
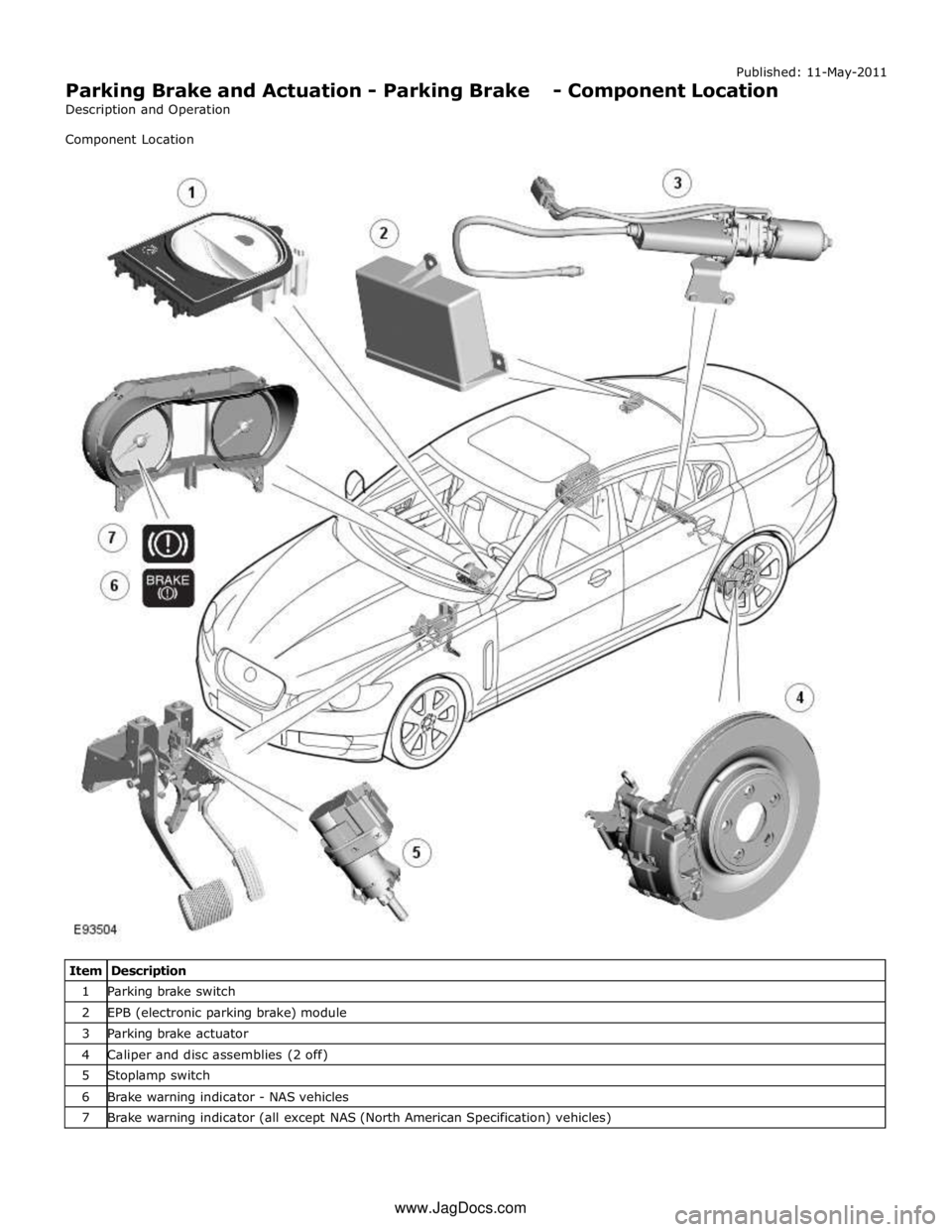
Published: 11-May-2011
Parking Brake and Actuation - Parking Brake - Component Location
Description and Operation
Component Location
Item Description 1 Parking brake switch 2 EPB (electronic parking brake) module 3 Parking brake actuator 4 Caliper and disc assemblies (2 off) 5 Stoplamp switch 6 Brake warning indicator - NAS vehicles 7 Brake warning indicator (all except NAS (North American Specification) vehicles) www.JagDocs.com
Page 647 of 3039
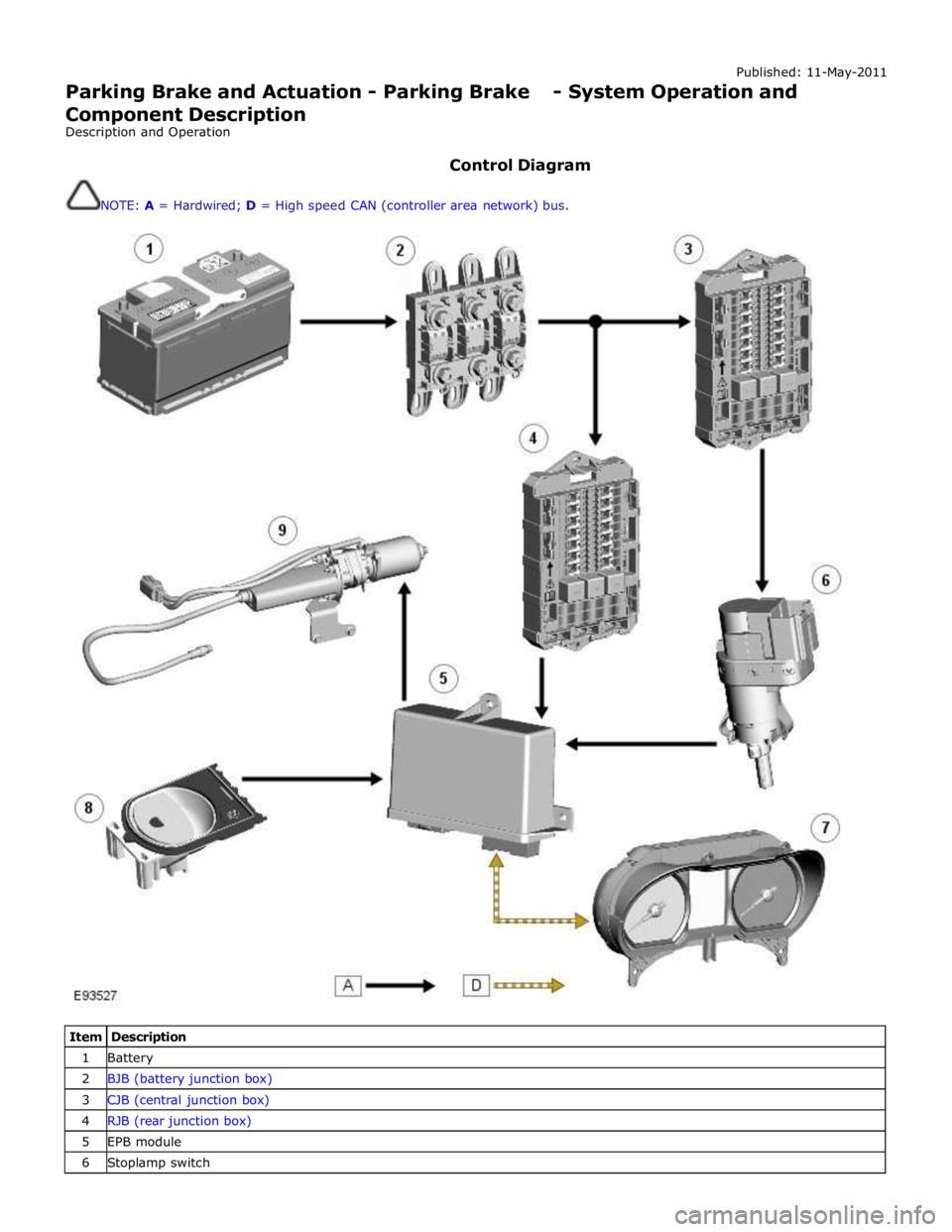
Published: 11-May-2011
Parking Brake and Actuation - Parking Brake - System Operation and
Component Description
Description and Operation
Control Diagram
NOTE: A = Hardwired; D = High speed CAN (controller area network) bus.
Item Description 1 Battery 2 BJB (battery junction box) 3 CJB (central junction box) 4 RJB (rear junction box) 5 EPB module 6 Stoplamp switch
Page 648 of 3039

7 Instrument cluster 8 Parking brake switch 9 Parking brake actuator
Static Apply System Operation
The EPB module receives a vehicle speed signal from the ABS (anti-lock brake system) module on the high speed CAN bus. If the parking brake switch is pulled to the 'Apply' position and vehicle speed is less than 2 mph (3 km/h), the EPB module will
instigate its 'Static Apply' mode and drive the actuator to apply full parking brake force to the rear wheels.
The EPB module monitors the current drawn by the actuator and compares this to information held within its configuration
software to determine when full braking force has been applied.
Dynamic Apply
There are two 'Dynamic Apply' modes; low speed dynamic and high speed dynamic. The low speed dynamic mode operates at
speeds between 2 mph (3 km/h) and 20 mph (32 km/h). The high speed dynamic mode operates at speeds above 20 mph (32
km/h).
If the parking brake switch is pulled up to the 'Apply' position and vehicle speed is within the low speed dynamic range, the
EPB module drives the actuator to apply full parking brake force to the rear wheels.
If the parking brake switch is pulled up to the 'Apply' position and vehicle speed is within the high speed dynamic range, the
EPB module will apply braking force to the rear wheels at a slower rate until full braking load is reached or the switch is
released. The rate with which braking force is applied is controlled by the EPB module, which monitors both current drawn by
the actuator and positional information from the actuator hall sensor and compares this to information held within its
configuration software.
Drive Away Release
The EPB module will initiate its 'Drive Away Release' function and automatically release the parking brake if the following
conditions are detected:
The engine is running.
Drive , or reverse is selected.
Positive throttle movement is detected.
The EPB module receives messages of gear selector position and throttle angle over the high speed CAN bus from the TCM (transmission control module) and the ECM (engine control module) respectively.
Release from Park
The EPB module will initiate its 'Release from Park' function and automatically release the parking brake if the gear selector is
moved from Park to any position except Neutral.
Repairs
Before carrying out any work on the parking brake system, the Jaguar approved diagnostic system must be connected and the
'parking brake unjam' routine run. The routine can be found in the 'Vehicle Configuration' area, under the 'Set-up and
Configuration' menu. After any work has been carried out on the parking brake, the system will require resetting.
CAUTION: Do not use the 'Emergency Release' tool to allow work to be carried out on the parking brake. Work can only be
carried out on the parking brake system after the 'parking brake unjam' routine has been run.
Resetting
If the electrical supply is disconnected from the EPB module, the actuator will loose its position memory. On battery
re-connection and ignition on, 'APPLY FOOT AND PARK BRAKE' will be displayed in the instrument cluster message center
indicating the parking brake requires resetting.
Refer to: Parking Brake (206-05, Diagnosis and Testing).
Operating Voltages
The EPB module will only operate the actuator if the power supply from the battery is between 9 V and 16 V. At any voltage
within this range, the actuator is able to fully tighten and release the brake cables. If the power supply falls outside of the
range, a fault code is stored in the EPB module and can be retrieved using the Jaguar approved diagnostic system.
Page 651 of 3039

Stoplamp Switch
The stoplamp switch is mounted on the brake pedal box. One of the prerequisites for releasing the parking brake is that the
foot brake is applied. The EPB module is able to determine the position of the footbrake by monitoring the status of the
stoplamp switch via a hardwired electrical connection.
The stoplamp switch also forms part of:
The ABS. Refer to: Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist (206-09 Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist, Description and Operation). The speed control system. For additional information, refer to:
Speed Control (310-03A, Description and Operation),
Speed Control (310-03B, Description and Operation),
Speed Control (310-03C, Description and Operation).
Page 653 of 3039

Parking Brake and Actuation - Parking Brake
Diagnosis and Testing
Principle of Operation Published: 12-May-2014
For a detailed description of the Parking Brake operation, refer to the relevant Description and Operation section of the
workshop manual. REFER to: (206-05 Parking Brake and Actuation)
Parking Brake (Description and Operation), Parking Brake (Description and Operation), Parking Brake (Description and Operation).
Parking Brake Calibration
The parking brake system must be calibrated whenever the battery has been disconnected or has been in a state of discharge,
or repairs have been carried out to the rear service or parking brake system.
NOTE: If new rear brake pads have been installed, pressure must be applied to the brake pedal a minimum of five times
prior to calibration of the parking brake system.
To calibrate the parking brake system:
1. Place gear selector lever in 'P' Park position.
2. Release parking brake cable tension to service position.
REFER to: Parking Brake Cable Tension Release (206-05 Parking Brake and Actuation, General Procedures).
3. Set the ignition status to 'ON'.
4. Apply and hold the footbrake then pull up the parking brake switch.
5. To release the parking brake, apply and hold the footbrake then release and press down the parking brake switch.
Inspection and Verification
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle.
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of damage and system integrity.
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical
Parking brake cable
Parking brake actuator
Brake caliper
Brake pads
Stabilizer bar drop link caps
Fuse(s)
Wiring harness/electrical connectors
Check for bent/corroded pins
Parking brake switch
Parking brake module
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step.
4. If the cause is not visually evident check the system for any logged Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and proceed to
the DTC Index , alternatively, verify the customer concern and refer to the Symptom Chart.
Symptom Chart
Symptom Possible Cause Action The parking brake will not
engage or release (with no
parking brake warning
message)
Cables fouled, trapped or damaged
Cables incorrectly routed or installed
Rear lining wear
Service brake incorrectly adjusted following
lining change
Caliper malfunction
Check the rear and primary
cables for correct installation
and damage
Inspect the rear brake linings for
wear
Re-calibrate the parking brake,
refer to the calibration procedure
Check the rear service brake for
correct installation and operation