2010 JAGUAR XFR fuel
[x] Cancel search: fuelPage 2695 of 3039
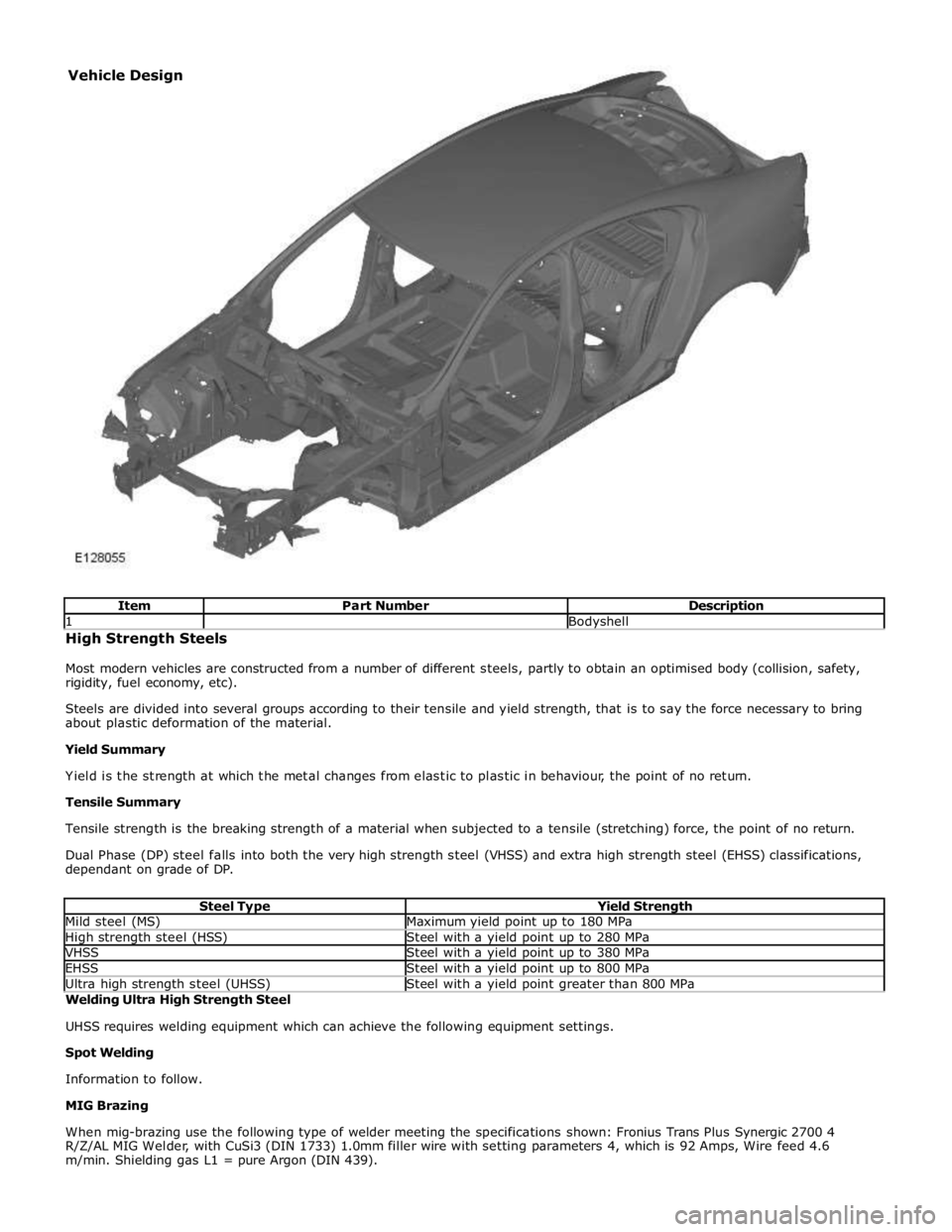
1 Bodyshell High Strength Steels
Most modern vehicles are constructed from a number of different steels, partly to obtain an optimised body (collision, safety,
rigidity, fuel economy, etc).
Steels are divided into several groups according to their tensile and yield strength, that is to say the force necessary to bring
about plastic deformation of the material.
Yield Summary
Yield is the strength at which the metal changes from elastic to plastic in behaviour, the point of no return.
Tensile Summary
Tensile strength is the breaking strength of a material when subjected to a tensile (stretching) force, the point of no return.
Dual Phase (DP) steel falls into both the very high strength steel (VHSS) and extra high strength steel (EHSS) classifications,
dependant on grade of DP.
Steel Type Yield Strength Mild steel (MS) Maximum yield point up to 180 MPa High strength steel (HSS) Steel with a yield point up to 280 MPa VHSS Steel with a yield point up to 380 MPa EHSS Steel with a yield point up to 800 MPa Ultra high strength steel (UHSS) Steel with a yield point greater than 800 MPa Welding Ultra High Strength Steel
UHSS requires welding equipment which can achieve the following equipment settings.
Spot Welding
Information to follow.
MIG Brazing
When mig-brazing use the following type of welder meeting the specifications shown: Fronius Trans Plus Synergic 2700 4
R/Z/AL MIG Welder, with CuSi3 (DIN 1733) 1.0mm filler wire with setting parameters 4, which is 92 Amps, Wire feed 4.6
m/min. Shielding gas L1 = pure Argon (DIN 439). Vehicle Design
Page 2714 of 3039

- Disadvantage: Scarring and hardening of the surface.
Flattening using a copper electrode.
- Small, sharp dents that face outwards can be worked on with a copper electrode.
Flattening using a flame and body files.
NOTE: When applied correctly, this method can be used with all the attached parts still in place (roof headlining,
wiring harnesses etc.).
- Small, soft dents (only slight stretching): Working at the edges of the dent in an inward spiral pattern, the dent
is heated with an oxyacetylene torch (torch size 1 - 2 mm, excess gas flame) to approx. 250° C.
- Working rapidly with a body file extracts heat from the edge area until the dent is flattened. Preferably alternate
between two files. This increases the amount of heat that can be extracted.
Safety measures
The electronic control modules (ECM) fitted to vehicles make it advisable to follow suitable precautions prior to carrying
out welding repair operations. Harsh conditions of heat and vibration may be generated during these operations which
could cause damage to the modules. In particular, it is essential to follow the appropriate precautions when
disconnecting or removing the airbag RCM.
Do not allow electronic modules or lines to come into contact with the ground connection or the welding electrode.
Seat belt anchorages are a safety critical. When making repairs in these areas, it is essential to follow design
specifications. Note that extra strength low alloy steel may be used for seat belt anchorages. Where possible, the
original production assembly should be used, complete with its seat belt anchorages, or the cut line should be so
arranged that the original seat belt anchorage is not disturbed.
All welds within 250mm (9.842) of seat belt anchorages must be carefully checked for weld quality, including spacing of
spot welds.
Remove the battery before carrying out welding work in its vicinity.
Utmost care must be taken when welding near the fuel tank or other components that contain fuel. If the tank filler
neck or a fuel line must be detached to allow access for welding work, then the fuel tank must be drained and removed.
Never weld, on components of a filled air conditioning system. The same applies if there is a risk of the air conditioning
system heating up.
Connect the ground connection of the electrical welder directly to the part that is to be welded. Make sure that there
are no electrically insulating parts between the ground connection and the welding point.
Adjacent vehicle parts and adjacent vehicles must be shielded against flying sparks and heat.
Pedestrian protection system
The pedestrian protection system is designed to mitigate injuries in a pedestrian collision with the vehicle. It does this by
utilizing a pair of pyrotechnic actuators to lift the hood away from the engine, creating a cushioned impact between the
pedestrian and the vehicle. It is essential that any repair or replacement operations do not affect the safe working of the
system.
For additional information, refer to: Pedestrian Protection System (501-20C Pedestrian Protection System, Description and Operation).
Resistance spot welding
Where resistance spot welds have been used in production, they must be reproduced with new spot welds in replacement
where possible. All such reproduction spot welds should be spaced 25 to 30mm apart.
Setting up the equipment and co-ordinating the welding parameters.
Equipment:
- Follow the equipment manufacturer's instructions for the equipment settings.
- Select the correct electrode arms (as short as possible).
- Align the electrode arms and tips exactly.
- Electrode tips should be convex (rough shaping with a file, fine shaping with a sanding block).
Body:
- Make sure that the flanges to be joined lie perfectly flat to one another.
- Prepare a bare metal joint surface (inside and outside).
Notes on technique/method:
- Carry out a test weld on a sample piece of the material coated in welding paste.
- If any metal parts are located between the electrode arms then there will be a loss of induction and therefore
power (adjust current setting).
- The power needs to be adjusted for high-strength low alloy steel.
- Repeated welding on old welding points often leads to poor quality welds.
- Keep the electrode tips as near as possible to an angle of 90° to the contact surface.
- Keep the pressure on the electrodes for a short period after finishing the weld.
- The electrodes work best if their shape is convex. Clean the contact surface of the electrodes regularly.
Resistance spot welding panels where the total thickness is 3 mm or more
For all repairs to modern Jaguar vehicles, spot-welding equipment should be suitable for reliable welding of zinc-plated,
high-strength and high-tensile steels in three or more layers, up to 5 mm total thickness. If these requirements are not
fulfilled, plug welding must be used for safety reasons. The electrical specifications (current, resistance, heat) of the
spot-welding equipment have different validity, depending upon the type of equipment. Therefore, it is essential that the
manufacturer's instructions are observed with regard to the actual welding performance.
www.JagDocs.com
Page 2726 of 3039

metal surfaces are bolted together always interpose a suitable interface material such as weldable zinc rich primer, extruded
strip, or zinc tape.
Steam Cleaning
Due to the high pressure/temperature generated by steam cleaning equipment, there is a risk that certain adhesives and
corrosion prevention material may become softened or liquified.
Take care not to allow the steam jet to dwell on one area, and keep the nozzle at least 300mm from the panel surface.
CAUTION: Do not remove wax or lacquer from underbody areas during repairs.
Inspection During Maintenance Servicing
It is a requirement of the corrosion warranty that the vehicle is inspected for corrosion by a Jaguar Authorised Repairer during a
routine service, to ensure that the factory-applied protection remains effective.
Rectify any bodywork damage or evidence of corrosion found during inspection as soon as is practicable, both to minimise the
extent of the damage and to ensure the long term effectiveness of the factory-applied corrosion prevention treatment.
Underbody Protection Repairs
Whenever body repairs have been carried out, ensure that full sealing and corrosion protection treatments are reinstated. This
applies both to the damaged areas and also to areas where protection has been indirectly impaired, as a result either of
accident damage or repair operations.
Remove corrosion protection from the damaged areas before straightening or panel beating. This applies in particular to panels
coated with wax, PVC underbody sealer, sound deadening pads etc.
CAUTION: Do not use oxy-acetylene to remove corrosion prevention material. Large volumes of fumes and gases are
liberated by these materials when they burn.
The most common method of removal is by means of a hot air blower with an integral scraper. High temperatures can be
generated with this equipment which may cause fumes. Take care during its use.
Structural Adhesive
CAUTION: When separating a joint with metal to metal adhesive, it is important to avoid distortion. Heat gradually until
the bond weakens sufficiently to permit panel separation - do not apply excessive heat.
NOTE: When spot welding through metal to metal adhesive, take particular care to adjust the equipment setting to
ensure a suitable weld.
Metal to metal adhesive is applied to critical joint areas during factory assembly. The material used is a high temperature,
heat cured, nitrile phenolic which serves to bond two metal surfaces and also to seal the joint against ingress of dust,
moisture and fumes. This material is not suitable for service use and, during repair, should be substituted by an approved
structural adhesive. For panel specific information and to identify the areas of structural adhesive application in repair, refer to
the relevant sheet metal removal and installation procedure.
Expanding Foam Acoustic Seals
Expanding foam acoustic seals are used in various closed-sections of the body to improve vehicle refinement. The seals are
installed during the vehicle body manufacture and expand during the paint process up to ten times original size, thus locking
them into position. They are located such that they prevent noise accentuation along a section and reflect air borne noise
away from the cabin.
The seals have spilt functionality depending on location. The seals located at the base of the body pillars have a primary
function of preventing water ingress when wading. Their secondary function is to prevent noise and dust ingress.
The seal around the fuel filler has a primary function of preventing both fuel and water ingress. With a secondary function of
preventing noise and dust ingress.
The remaining seals primary function is to prevent noise accentuation along a section and reflect air borne noise away from the
cabin.
Another advantage of the seals is that they marginally increase the overall stiffness of the body and its structural performance
in case of a crash.
The seals are manufactured from an expandible polymer.
Replacing Expanding Foam Acoustic Seals
As paint oven temperatures used in a repair workshop are significantly lower than those that are used during manufacture of
the vehicle, (the temperatures are not sufficient to expand the foam), a different process is required to replicate the foam in
repair.
Page 2730 of 3039
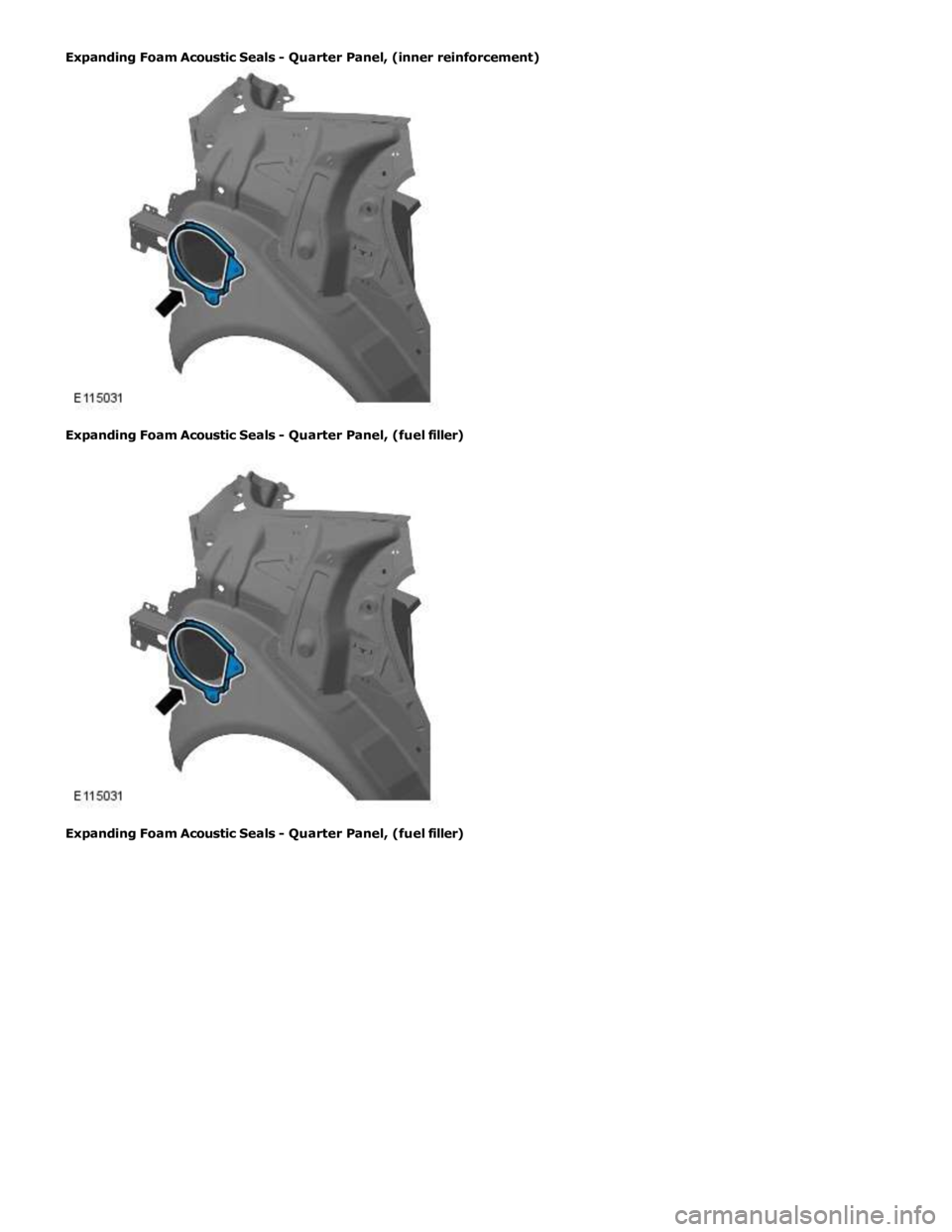
Expanding Foam Acoustic Seals - Quarter Panel, (inner reinforcement)
Expanding Foam Acoustic Seals - Quarter Panel, (fuel filler)
Expanding Foam Acoustic Seals - Quarter Panel, (fuel filler)
Page 2785 of 3039
Transmission (307-01A Automatic Transmission/Transaxle - V6 3.0L Petrol, Removal) /
Transmission - 4.2L (307-01, Removal) /
Transmission - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol (307-01B Automatic Transmission/Transaxle - TDV6 3.0L Diesel /V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L
Petrol, Removal) /
Front Shock Absorber (204-01 Front Suspension, Removal and Installation) /
Front Subframe - 2.7L Diesel (502-00, Removal and Installation) /
Front Subframe - V6 3.0L Petrol (502-00 Uni-Body, Subframe and Mounting System, Removal and Installation) /
Front Subframe - 4.2L, Vehicles Without: Supercharger (502-00, Removal
and Installation) /
Front Subframe - 4.2L, Vehicles With: Supercharger (502-00, Removal
and Installation).
8. Remove the pedestrian protection hood actuator.
For additional information, refer to: Pedestrian Protection Hood Actuator LH (501-20C Pedestrian Protection System, Removal and Installation) / Pedestrian Protection Hood Actuator RH (501-20C Pedestrian Protection System, Removal and Installation).
9. If the drivers side front side member and suspension top mount is to be
repaired, remove the brake master cylinder and reservoir.
For additional information, refer to: Brake Master Cylinder (206-06 Hydraulic Brake Actuation, Removal and Installation) /
Brake Fluid Reservoir (206-06 Hydraulic Brake Actuation, Removal and Installation).
10. If the left-hand front side member and suspension top mount assembly
is to be repaired, remove the fuel supply and return lines.
11. Release and position the front side member wiring harness to one side.
12. Remove any remaining miscellaneous components from the repair area.
13. NOTE: Retain the front fender support bracket
mounting if it is to be reused. If the front fender support
bracket mounting is to be renewed, it is not necessary to
remove or retain it.
Drill out the spot welds to remove the front fender support
bracket mounting.
Page 2798 of 3039

Actuation, Removal and Installation).
12. Remove the left-hand and right-hand front seats.
For additional information, refer to: Front Seat (501-10 Seating, Removal and Installation).
13. Remove the heater core and evaporator core housing.
For additional information, refer to: Heater Core and Evaporator Core Housing (412-01 Climate Control, Removal and Installation).
14. Remove the front safety belt retractor.
For additional information, refer to: Front Safety Belt Retractor (501-20A Safety Belt System, Removal and Installation).
15. Remove the B-pillar side impact sensor.
For additional information, refer to: B-Pillar Side Impact Sensor (501-20B Supplemental Restraint System, Removal and Installation).
16. Remove the left-hand and right-hand front floor covering.
17. Remove the rear floor covering.
18. If the left-hand front side member and suspension top mount assembly
is to be repaired, remove the left-hand rear foot well duct.
19. If the right-hand front side member and suspension top mount assembly
is to be repaired, remove the right-hand rear foot well duct.
20. If the drivers side front side member and suspension top mount is being
repaired, remove the pedal box.
21. Release and position the insulating material at the inner bulkhead to
one side.
22. Release and position the inner bulkhead and floor panel wiring harness
to one side.
23. Drain the fuel tank.
For additional information, refer to: Fuel Tank Draining (310-00 Fuel System - General Information, General Procedures).
24. If the left-hand front side member and suspension top mount assembly
is to be repaired, remove the left-hand under shield.
25. If the right-hand front side member and suspension top mount assembly
is to be repaired, remove the right-hand under shield.
26. If the left-hand front side member and suspension top mount assembly
is to be repaired, remove the fuel supply and return pipes.
27. For diesel engine vehicles only, if the left-hand front side member and
suspension top mount assembly is to be repaired, remove the fuel
cooler.
28. If the right-hand front side member and suspension top mount assembly
is to be repaired, release and position the underfloor wiring harness to
Page 2950 of 3039
Supplemental Restraint System, Removal and Installation).
23. Remove the rear window glass.
24. Remove the audio unit antenna amplifier.
For additional information, refer to: Audio Unit Antenna Amplifier (415-01A Information and Entertainment System, Removal and
Installation).
25. If the left-hand rear quarter panel is to be repaired, remove the diversity
antenna module.
26. Remove the C-Pillar side impact sensor.
For additional information, refer to: C-Pillar Side Impact Sensor (501-20B Supplemental Restraint System, Removal and Installation).
27. Remove the rear door striker.
28. Remove the luggage compartment lid.
29. If the right-hand rear quarter panel is to be repaired, drain the fuel tank.
For additional information, refer to: Fuel Tank Draining (310-00 Fuel System - General Information, General Procedures).
30. If the right-hand rear quarter panel is to be repaired, remove the fuel
filler door.
31. If the right-hand rear quarter panel is to be repaired, remove the fuel
tank filler pipe.
For additional information, refer to: Fuel Tank Filler Pipe (310-01 Fuel
Tank and Lines - 3.0L, Removal and Installation) /
Fuel Tank Filler Pipe (310-01 Fuel Tank and Lines - 4.2L, Removal and
Installation).
32. Remove the luggage compartment lid hinge.
Page 2980 of 3039
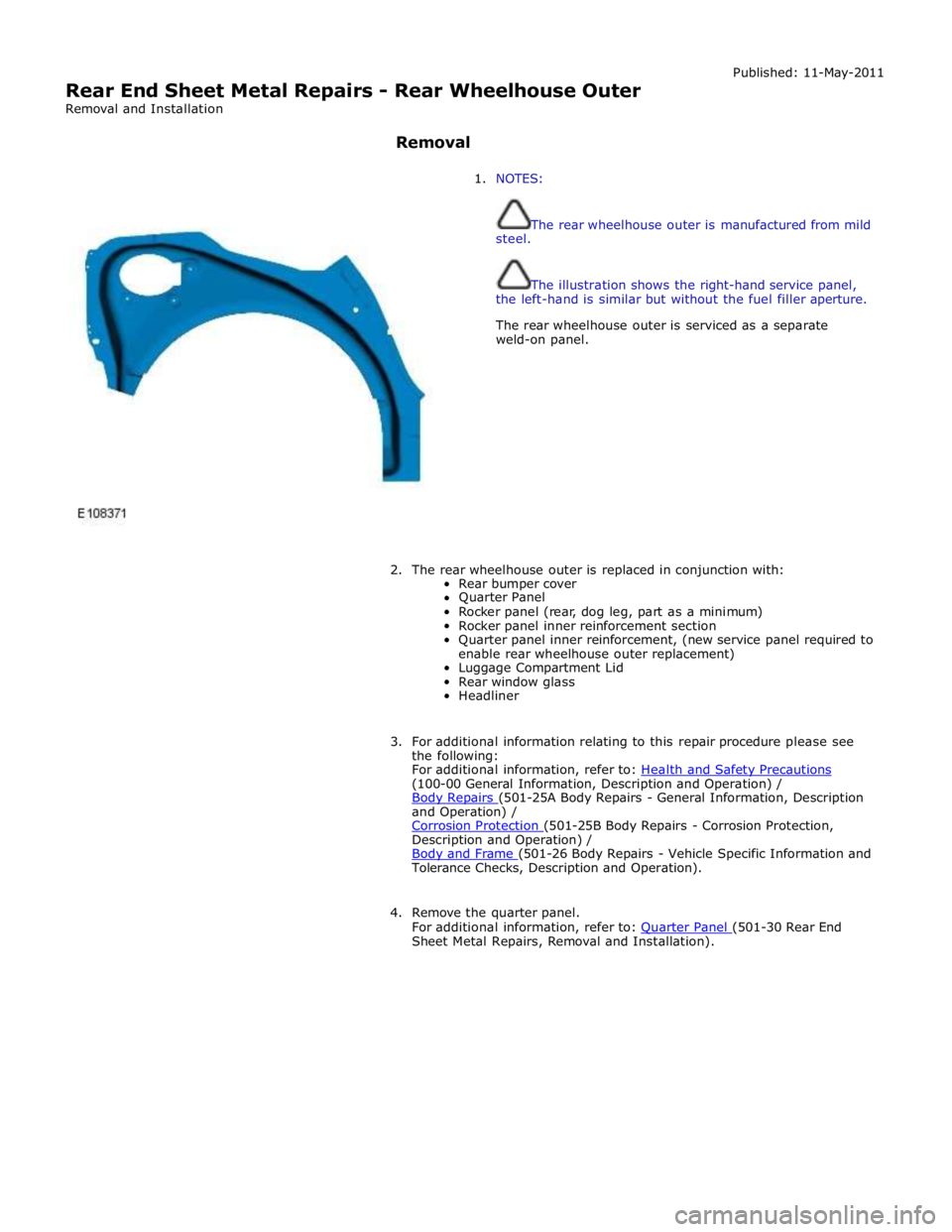
Rear End Sheet Metal Repairs - Rear Wheelhouse Outer
Removal and Installation
Removal Published: 11-May-2011
1. NOTES:
The rear wheelhouse outer is manufactured from mild
steel.
The illustration shows the right-hand service panel,
the left-hand is similar but without the fuel filler aperture.
The rear wheelhouse outer is serviced as a separate
weld-on panel.
2. The rear wheelhouse outer is replaced in conjunction with:
Rear bumper cover
Quarter Panel
Rocker panel (rear, dog leg, part as a minimum)
Rocker panel inner reinforcement section
Quarter panel inner reinforcement, (new service panel required to
enable rear wheelhouse outer replacement)
Luggage Compartment Lid
Rear window glass
Headliner
3. For additional information relating to this repair procedure please see
the following:
For additional information, refer to: Health and Safety Precautions (100-00 General Information, Description and Operation) /
Body Repairs (501-25A Body Repairs - General Information, Description and Operation) /
Corrosion Protection (501-25B Body Repairs - Corrosion Protection, Description and Operation) /
Body and Frame (501-26 Body Repairs - Vehicle Specific Information and Tolerance Checks, Description and Operation).
4. Remove the quarter panel.
For additional information, refer to: Quarter Panel (501-30 Rear End Sheet Metal Repairs, Removal and Installation).