2010 JAGUAR XFR ABS
[x] Cancel search: ABSPage 1398 of 3039
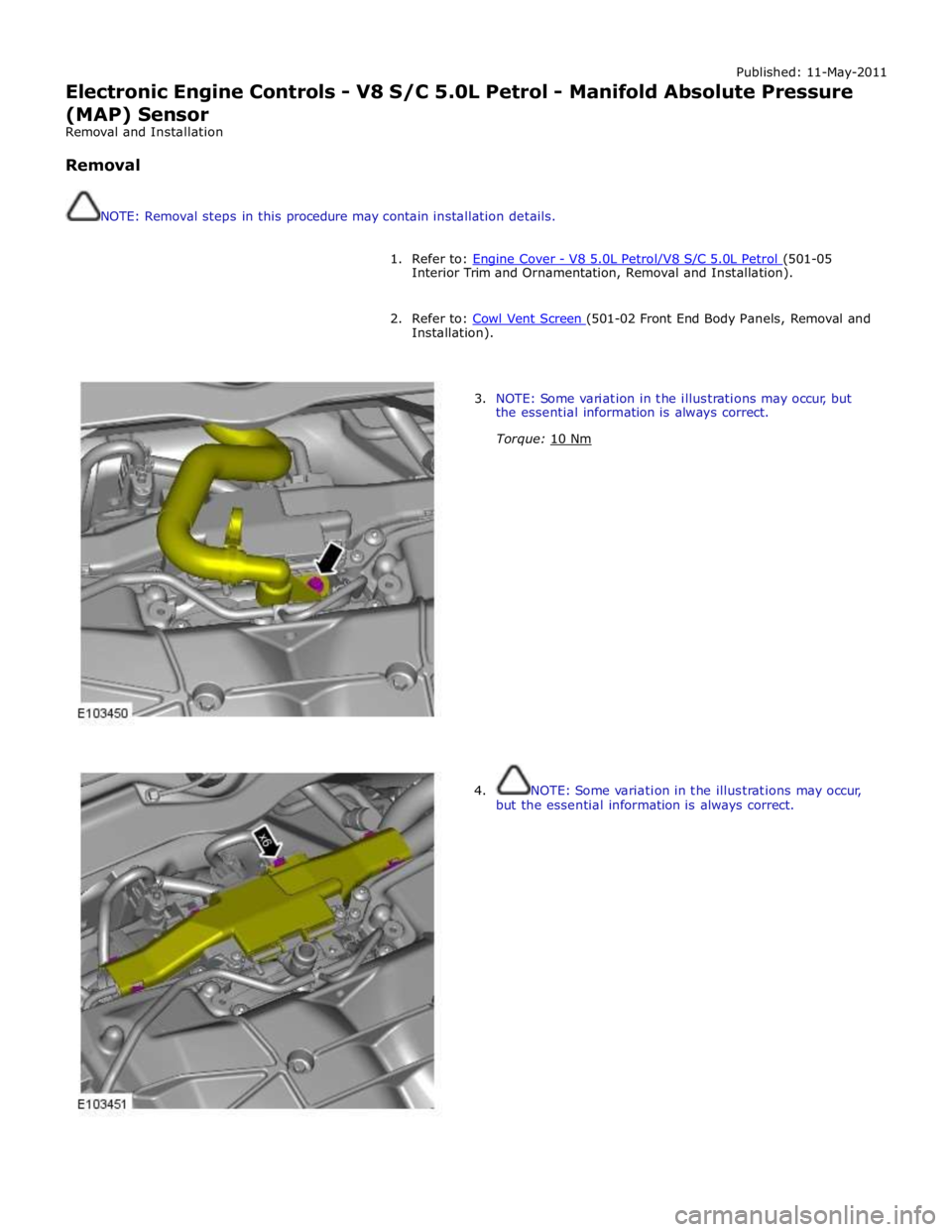
Published: 11-May-2011
Electronic Engine Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Manifold Absolute Pressure
(MAP) Sensor
Removal and Installation
Removal
NOTE: Removal steps in this procedure may contain installation details.
1. Refer to: Engine Cover - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol (501-05 Interior Trim and Ornamentation, Removal and Installation).
2. Refer to: Cowl Vent Screen (501-02 Front End Body Panels, Removal and Installation).
3. NOTE: Some variation in the illustrations may occur, but
the essential information is always correct.
Torque: 10 Nm
4. NOTE: Some variation in the illustrations may occur,
but the essential information is always correct.
Page 1422 of 3039
1 Transmission selected gear status 2 MIL (malfunction indicator lamp) 3 Message center The instrument cluster is connected to the TCM via the high speed CAN bus. Transmission status is transmitted by the TCM and displayed to the driver in one of two displays in the instrument cluster. For additional information, refer to 413-01
Instrument Cluster.
Malfunction Indicator Lamp
The MIL (malfunction indicator lamp) is located in the tachometer in the instrument cluster. Transmission related faults which
may affect the vehicle emissions output will illuminate the MIL.
The MIL is illuminated by the ECM (engine control module) on receipt of a relevant fault message from the TCM on the high speed CAN. The nature of the fault can be diagnosed using a Jaguar approved diagnostic system which reads the fault codes stored in the TCM memory.
Transmission Status Display
The transmission status display is located in a LCD (liquid crystal display) at the top of the instrument cluster, between the
speedometer and the tachometer. The LCD shows the JaguarDrive selector position or the selected gear when in manual 'Jaguar Sequential Shift' mode.
The following table shows the displays and their descriptions.
Symbol Description P Park selected R Reverse selected N Neutral selected D Drive selected S Sport mode selected 1 1st gear selected (manual Jaguar sequential shift mode) 2 2nd gear selected (manual Jaguar sequential shift mode) 3 3rd gear selected (manual Jaguar sequential shift mode) 4 4th gear selected (manual Jaguar sequential shift mode) 5 5th gear selected (manual Jaguar sequential shift mode) 6 6th gear selected (manual Jaguar sequential shift mode) The message center is located in the lower center of the instrument cluster. The message center is a LCD to relay vehicle status and operating information to the driver and can display messages relating to a number of the vehicle systems. If a
transmission fault occurs, the message center will display the message 'GEARBOX FAULT'.
TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE
The TCM outputs signals to control the shift control solenoid valve and the EPRS (electronic pressure regulating solenoid) to control the hydraulic operation of the transmission.
The TCM processes signals from the transmission speed and temperature sensors, the ECM and other vehicle systems. From the received signal inputs and pre-programmed data, the module calculates the correct gear, torque converter clutch setting
and optimum pressure settings for gear shift and lock-up clutch control.
The ECM supplies the engine management data over the high speed CAN bus. The TCM requires engine data to efficiently control the transmission operation, for example; flywheel torque, engine speed, accelerator pedal angle, engine temperature.
The steering angle sensor and the ABS (anti-lock brake system) module also supply data to the TCM on the high speed CAN bus. The TCM uses data from these systems to suspend gear changes when the vehicle is cornering and/or the ABS module is controlling braking or traction control.
Using the signal inputs and the memorized data, the TCM control program computes the correct gear and torque converter lock-up clutch setting and the optimum pressure settings for gear shift and lock-up clutch control. Special output-side modules
(power output stages, current regulator circuits), allow the TCM to control the solenoid valves and pressure regulators and consequently precisely control the hydraulics of the automatic transmission. In addition, the amount and duration of engine
interventions are supplied to the engine management by way of the CAN bus.
The transmission has a fully electronic JaguarDrive selector with no Bowden cable connection to the transmission. The
transmission selections are made using a rotary JaguarDrive selector which rises from the floor console once the engine is
running. Rotation of the JaguarDrive selector to any of the five positions is sensed by the TCM via the high speed CAN bus. The TCM then reacts according to the selected position. The 'S' (sport) position selection allows the TCM to operate the transmission using the semi-automatic 'Jaguar Sequential Shift'.
Gear selections are sensed by the TCM when the driver operates the steering wheel paddle switches. Once the JaguarDrive selector position is confirmed, the TCM outputs appropriate information on the high speed CAN bus.
If the JaguarDrive selector is in 'D', 'Jaguar Sequential Shift' is temporary and will cancel after a time period or can be cancelled
by pressing and holding the + paddle for approximately 2 seconds.
If the JaguarDrive selector is in 'S', 'Jaguar Sequential Shift' is permanent and can only be cancelled by pressing and holding
the + paddle for approximately 2 seconds or by moving the JaguarDrive selector to the 'D' position.
www.JagDocs.com
Page 1431 of 3039

transmission functions. The Mechatronic valve block comprises the following components:
TCM
Pressure regulator solenoids
Shift control solenoid
Damper
Hydraulic spool valves
Selector valve
Temperature sensor
Turbine speed sensor
Output shaft speed sensor.
Sensors
Speed Sensors
The turbine speed sensor and the output shaft speed sensor are Hall effect type sensors located in the Mechatronic valve block
and are not serviceable items. The TCM monitors the signals from each sensor to determine the input (turbine) speed and the output shaft speed.
The turbine speed is monitored by the TCM to calculate the slip of the torque converter clutch and internal clutch slip. This signal allows the TCM to accurately control the slip timing during shifts and adjust clutch application or release pressure for overlap shift control.
The output shaft speed is monitored by the TCM and compared to engine speed signals received on the CAN bus from the ECM. Using a comparison of the two signals the TCM calculates the transmission slip ratio for plausibility and maintains adaptive pressure control.
Temperature Sensor
The temperature sensor is also located in the Mechatronic valve block. The TCM uses the temperature sensor signals to determine the temperature of the transmission fluid. These signals are used by the TCM to control the transmission operation to promote faster warm-up in cold conditions or to assist with fluid cooling by controlling the transmission operation when high
fluid temperatures are experienced. If the sensor fails, the TCM will use a default value and a fault code will be stored in the TCM.
Damper
There is one damper located in the valve housing. The damper is used to regulate and dampen the regulated pressure supplied
via EPRS. The damper is load dependent through modulation of the damper against return spring pressure.
The damper comprises a piston, a housing bore and a spring. The piston is subject to the pressure applied by the spring. The
bore has a connecting port to the function to which it applies. Fluid pressure applied to the applicable component (i.e. a
clutch) is also subjected to the full area of the piston, which moves against the opposing force applied by the spring. The
movement of the piston creates an action similar to a shock absorber, momentarily delaying the build up of pressure in the
circuit. This results in a more gradual application of clutches improving shift quality.
Spool Valves
The valve block spool valves control various functions of the transmission. The spool valves are of conventional design and are
operated by fluid pressure.
Each spool valve is located in its spool bore and held in a default (unpressurized) position by a spring. The spool bore has a
number of ports which allow fluid to flow to other valves and clutches to enable transmission operation. Each spool has a
piston which is waisted to allow fluid to be diverted into the applicable ports when the valve is operated.
When fluid pressure moves a spool, one or more ports in the spool bore are covered or uncovered. Fluid is prevented from
flowing or is allowed to flow around the applicable waisted area of the spool and into another uncovered port. The fluid is
either passed through galleries to actuate another spool, operate a clutch or is returned to the fluid pan.
Page 1547 of 3039

Published: 28-Apr-2014
Exhaust System - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Exhaust System - System Operation and Component Description
Description and Operation
CATALYTIC CONVERTERS System Operation
In the catalytic converters, the exhaust gases are passed through honeycombed ceramic elements coated with a special
surface treatment called 'washcoat'. The washcoat increases the surface area of the ceramic elements by a factor of
approximately 7000. On top of the washcoat is a coating containing palladium and rhodium, which are the active constituents
for converting harmful emissions into inert by-products. The palladium and rhodium add oxygen to the carbon monoxide and
the hydrocarbons in the exhaust gases, to convert them into carbon dioxide and water respectively.
SEMI-ACTIVE MUFFLER VALVE (5.0L SUPERCHARGER VEHICLES ONLY)
The semi-active muffler valve is operated by the pressure in the exhaust system. At low engine speeds the valve head is
closed or partially closed to provide a more refined noise quality. At higher engine speeds the increased pressure within the
exhaust system opens the valve head to provide a more sporting noise. This is achieved by the valve, which once open, allows
the exhaust gasses to by-pass the baffle tubes and plates in the rear silencer.
Component Description
FRONT SECTION - 4.2L NATURALLY ASPIRATED (NAS ONLY) - From 2010MY
The front section comprises two separate pipes, each incorporating a catalytic converter. Each catalytic converter has a welded
inlet pipe with a flange. The inlet pipe is flared into a cone which mates with the exhaust manifold. The flange has two holes
which locate on studs in the exhaust manifold and is secured with flanged nuts. Each catalytic converter is fitted with a pre
and post catalyst HO2S (heated oxygen sensor).
Each catalytic converter has a curved outlet pipe which mates with the respective inlet pipe for the applicable resonator on the
center section. The joint on each pipe is secured with a clamp.
FRONT SECTION - 5.0L NATURALLY ASPIRATED AND SUPERCHARGER - From 2010MY
The front section is common to both the naturally aspirated and supercharger vehicles. The front section comprises two
separate pipes each incorporating a catalytic converter. Each catalytic converter has a welded pipe with a flange, which is
flared into a cone which mates with the exhaust manifold. Each flange has two holes which locate on studs in the exhaust
manifold and are secured with nuts. Each catalytic converter is fitted with a mid catalyst HO2S. The mid catalyst HO2S is located in the catalytic converter.
NOTE: The pre catalyst HO2S is located in the exhaust manifold.
On vehicles from 2013MY, a post catalyst HO2S is located in the curved pipe from each catalytic converter.
A curved pipe from each catalytic converter locates into the resonator inlet pipes of the center section. The LH (left-hand) pipe
is fitted with a mass damper which absorbs resonance from the system.
REAR SECTION - 4.2L NATURALLY ASPIRATED (NAS ONLY) - From 2010MY
The 2 inlet pipes each connect into a separate resonator silencer. Each resonator silencer is cylindrical in shape and houses 2
perforated tubes separated by 2 baffle plates. Exhaust gasses exit each resonator silencer via an outlet pipe. The 2 outlet
pipes are joined together behind the resonators with a cross over pipe. Each pipe also has a welded hanger bracket which
allow the rear section to be supported on mounting rubbers. A further bracket is welded to each pipe which braces the 2 pipes
together.
The 2 rear silencers each have a welded inlet pipe which mate with the outlet pipes from the resonator silencers and are each
secured with a clamp. The inlet pipes each have a welded hanger bracket which support each rear silencer at the rear of the
vehicle on mounting rubbers. The fabricated rear silencers have 2 perforated tubes which are supported on 2 perforated baffle
plates. The exhaust gasses are expelled from the rear silencer via a single outlet pipe. The outlet pipe from each silencer has
a welded hanger bar which support the rear silencer on mounting rubbers. The outlet pipe is fitted with a welded outlet which
is covered with a polished stainless steel finisher which is part welded to the silencer.
REAR SECTION - 5.0L NATURALLY ASPIRATED - From 2010MY
The 2 pipes from the front section each connect into 2 short pipes on the center resonator box and are secured with clamps.
Two pipes from the resonator box split the system into 2 sections which each connect into another resonator. Each resonator
silencer houses perforated tubes separated by baffle plates. Exhaust gasses exit each resonator silencer via an outlet pipe.
The 2 outlet pipes are joined together behind the resonators with a cross over pipe. Each pipe also has a welded hanger
bracket which allow the rear section to be supported on mounting rubbers. A further bracket is welded to each pipe which
braces the 2 pipes together.
The 2 rear silencers each have a welded inlet pipe which mate with the outlet pipes from the cylindrical resonator silencers and
www.JagDocs.com
Page 1595 of 3039

Published: 28-Jul-2014
Fuel Tank and Lines - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Fuel Tank and
Lines
Diagnosis and Testing
Principle of Operation
For a detailed description of the fuel tank and lines system and operation, refer to the relevant Description and Operation
section of the workshop manual. REFER to: (310-01C Fuel Tank and Lines - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol)
Fuel Tank and Lines (Description and Operation), Fuel Tank and Lines (Description and Operation), Fuel Tank and Lines (Description and Operation).
Inspection and Verification
WARNINGS:
Eye protection must be worn at all times when working on or near any fuel related components. Failure to follow this
instruction may result in personal injury.
This procedure involves fuel handling. Be prepared for fuel spillage at all times and always observe fuel handling
precautions. Failure to follow this instruction may result in personal injury.
After carrying out repairs, the fuel system must be checked visually for leaks. This should be done after the engine has
been run, but with the engine switched OFF. Failure to follow this instruction may result in personal injury.
If taken internally, DO NOT induce vomiting. Seek immediate medical attention. Failure to follow this instruction may
result in personal injury.
If fuel contacts the eyes, flush the eyes with cold water or eyewash solution and seek medical attention. Failure to follow
this instruction may result in personal injury.
Wash hands thoroughly after handling, as prolonged contact may cause irritation. Should irritation develop, seek medical
attention. Failure to follow this instruction may result in personal injury.
CAUTIONS:
Before disconnecting any part of the system, it is imperative that all dust, dirt and debris is removed from around
components to prevent ingress of foreign matter into the fuel system. Failure to follow this instruction may result in damage to
the vehicle.
It is essential that absolute cleanliness is observed when working with these components. Always install blanking plugs
to any open orifices or lines. Failure to follow this instruction may result in damage to the vehicle.
Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not guarantee
confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle.
NOTES:
Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests.
When measuring fuel sender resistance values with a multimeter, it is critical to use the correct multimeter setting. The
multimeter should not be on the 'Auto' setting and must be set to 'Manual'. This will help prevent incorrect diagnosis and
unnecessary replacement of fuel senders. If the multimeter range is set at 'Auto' then, during a sweep of the sender from 50
Ohms to 998 Ohms, the multimeter has to change its measurement range. For approximately 1 second, during the range switch
over point, the multimeter display indicates an open circuit. This can lead to a mis-diagnosis of a fuel sender fault.
1. Verify the customer concern
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of damage and system integrity
Page 1638 of 3039

10 Electric throttle actuator 11 ABS (anti-lock brake system) module www.JagDocs.com
Page 1639 of 3039

Published: 11-May-2011
Speed Control - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Speed Control - Overview
Description and Operation
OVERVIEW
Speed Control
The speed control system is integrated with the engine management system and uses fueling intervention to automatically
maintain a set vehicle speed. Once engaged, the system can also be used to accelerate the vehicle without using the
accelerator pedal.
The speed control system comprises the following components:
On/Off/Suspend switch
'+' and '-' (set/accelerate and decelerate) steering wheel switches
Resume switch
Clock spring
Speed control warning indicator.
Adaptive Speed Control
The adaptive speed control system uses a forward looking radar sensor to scan the road ahead, looking for objects that are
moving at a different rate to itself. When a target is identified the adaptive speed control system will monitor the time gap
between it and the target vehicle. When that gap falls below a set driver selected level the adaptive speed control system will
intervene slowing the vehicle by backing off the throttle and/ or applying the brakes, until the correct gap is attained.
The adaptive speed control system comprises the following components:
Adaptive speed control sensor
Adaptive speed control module
Steering wheel control switches
ECM (engine control module)
Electric throttle actuator
ABS (anti-lock brake system) module and pump
Adaptive speed control warning indicator (in the instrument cluster).
Page 1640 of 3039
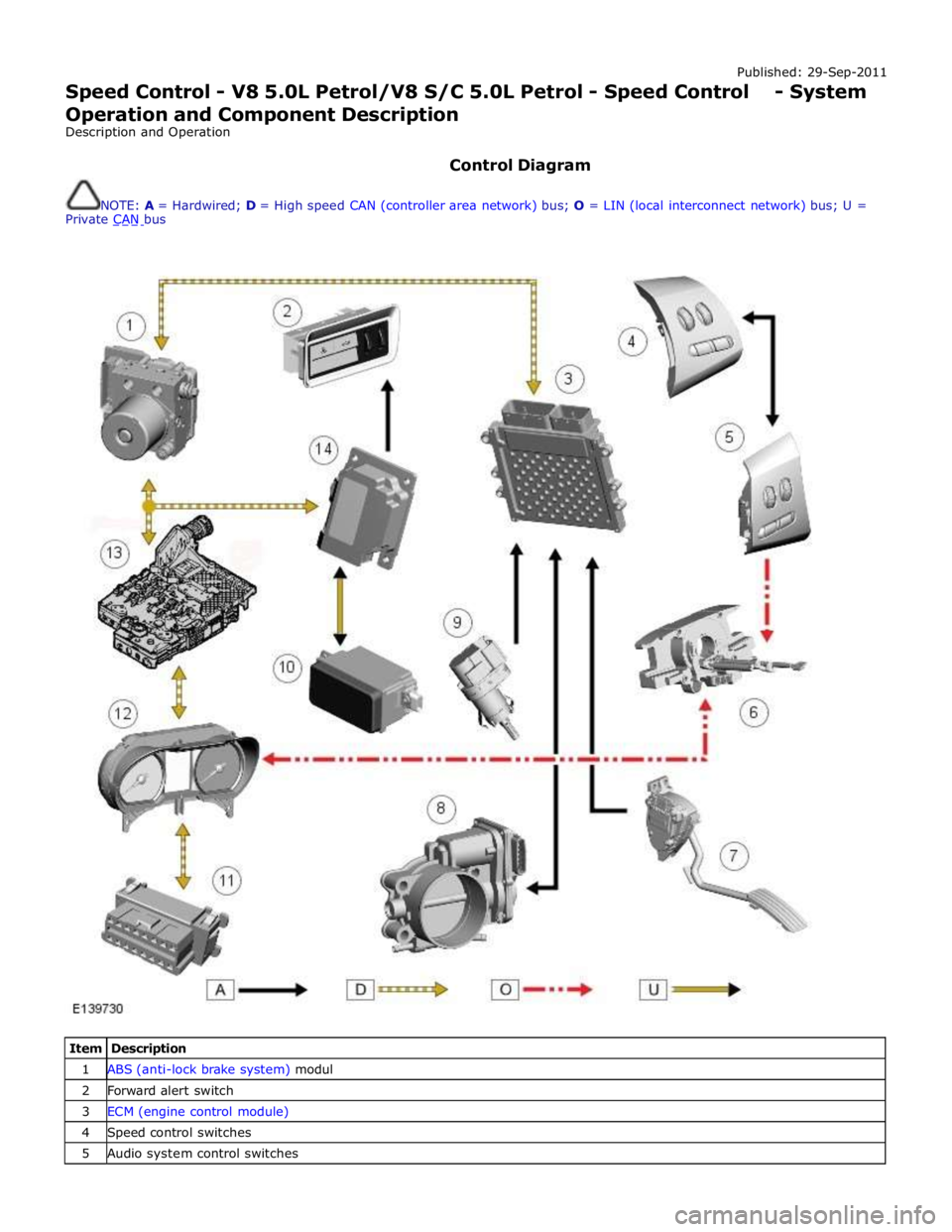
Published: 29-Sep-2011
Speed Control - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Speed Control - System
Operation and Component Description
Description and Operation
Control Diagram
NOTE: A = Hardwired; D = High speed CAN (controller area network) bus; O = LIN (local interconnect network) bus; U =
Private CAN bus
Item Description 1 ABS (anti-lock brake system) modul 2 Forward alert switch 3 ECM (engine control module) 4 Speed control switches 5 Audio system control switches