2010 JAGUAR XFR ABS
[x] Cancel search: ABSPage 2562 of 3039

Roof opening panel System Operation
Operation of the roof opening panel is controlled by the roof opening panel control module, which is integral with the motor.
The control module receives inputs from the CJB, which provides an 'open' or 'close' signal for remote handset operation, and
an 'enable' signal when the vehicle enters power mode 6.
The control module also receives a vehicle speed signal from the ABS module. The vehicle speed signal is used by the control
module to calibrate the anti-trap feature.
If the battery is disconnected, or the power supply is interrupted while the roof opening panel is in a partially open position,
the motor and control module will need to be calibrated to restore full functionality. To recalibrate:
1. Switch ignition on.
2. Press the front of the switch, so the roof opening panel is the tilt position, and then release the switch.
3. Press the front of the switch and hold for thirty seconds.
4. After thirty seconds the roof opening panel will begin to move. Keep the front of the switch pressed until the roof
opening panel has fully opened and then closed.
5. Once the open/close cycle has completed and the roof opening panel has stopped moving, release the switch.
6. The roof opening panel can now be operated as normal.
Drain hoses are connected to the front and rear corners of the roof opening panel frame. The drain hoses are located inside of
the cabin on the 'A' and 'D' post pillars to allow water, which has collected in the frame, to escape. One-way valves fitted to
the end of each drain hose, prevent the ingress of dirt and moisture.
Rear window sunblind
The powered rear window sunblind is operated through a switch in the roof console. Power to the sunblind motor is provided by
a pair of relays located in the CJB when the vehicle enters power mode 4. The sunblind motor is located beneath the rear parcel
shelf and is supplied as a sealed unit with the sunblind mechanism.
If the battery is disconnected or a replacement sunblind is fitted, the motor will require re-calibrating. To re-calibrate the
motor the sunblind should be powered through two-full cycles of movement.
Roof opening panel, motor Component Description
The roof opening panel motor has a worm drive which drives a gear in the cast housing attached to the end of the motor. The
gear has a small pinion gear attached to the outer part of its spindle. The pinion engages with two cables to form a rack and
pinion drive. Rotation of the motor turns the pinion which in turn drives the cables in the required direction.
The two cables are attached either side of the pinion. One end of each cable is attached to the guide; the opposite end of
each cable is held in position on the pinion by a metal insert in the frame. The cables run in channels, in the panel frame to
the guides. As the panel is closed the cables are pushed through channels in the front of the frame. The displaced cable is
guided into a further two channels in the frame, which protect the cable and prevent it from snagging. The cables
manufactured from rigid spring steel can pull as well as push the panel along the guides.
The motor contains a micro-switch and Hall effect sensor. Signals received from these components enable the control module
to calculate the exact position of the roof opening panel. The Hall effect sensor is also responsible for the operation of the
anti-trap function.
If the anti-trap feature is activated while the roof opening panel is closing, the panel is reversed for 200mm or as far as
possible. The Hall effect sensor, located in the motor, monitors the speed of the motor and if the speed decreases below a set
threshold, indicating an obstruction, the power feed to the motor is reversed so the panel goes back. In an emergency the
anti-trap function can be overridden by holding the switch in the closed position.
Roof opening panel, control module
The roof opening panel control module is integrated within the motor. The control module receives inputs from the CJB, which
provides an 'open' or 'close' signal for remote handset operation, and an 'enable' signal when the vehicle enters power mode 6.
The control module also contains the algorithm for the anti-trap system and receives a vehicle speed signal from the ABS
module. The vehicle speed signal is used by the control module to calibrate the anti-trap feature.
Page 2694 of 3039

Part N-umber
Body Repairs - General Information - Body Repairs
Description and Operation
General Information
Introduction Published: 11-May-2011
The body plays a significant role in the increasing trend of ever more rapidly changing model variants. The different customer
groups are strongly influenced by the design and shape of the body. At the same time the stability of the body plays the most
important part in ensuring passenger and driver safety. Lightweight construction, alternative materials, composite materials,
plastics and appropriate joining processes are all design features that characterise modern Jaguar vehicle bodies.
In terms of manufacturing technology, modern safety cell bodies can be produced almost without any problems. Jaguar
guarantee high quality standards by ensuring that mechanical strength properties are tried and tested in numerous computer
simulations, crash tests, by testing materials and by employing sophisticated manufacturing technologies. In the event of
repairs it is vital that the production quality standards are upheld. This requires a well-equipped workshop, and places
particular emphasis on the qualifications of the workshop technicians. Up-to-date knowledge of current manufacturing
technologies and continuous training on new repair methods and techniques are vital for high-quality body repairs. The model-
specific repair manuals and the general repair techniques provide valuable support when undertaking body repairs.
Always follow the repair instructions published in this manual. Failure to observe this instruction can result in serious
impairment of vehicle safety. All specified safety requirements must be met after the work has been carried out.
Vehicle design
The body
The XF adopts the latest generation steels, especially in the upper body – including high carbon steels, dual-phase,
hot-formed boron steels, and bake-hardened steels to form a vertical safety ‘ring’ around the occupant cell. As well as
combining strength with lightness, these steels improve corrosion resistance, by making best use of zinc and improving e-coat
paint flow – and new thinking means that in spite of their strength, the XF’s A and B-pillars are impressively slim, to the
benefit of both visibility and accessibility. Similarly, the lower sills are the first component on any Jaguar to use incredibly
strong, dual-phase DP600 steel.
The safety of the driver and the passengers is paramount for every body design. There are two key safety aspects in the body:
Safety passenger cell
Crumple zones
Safety passenger cell
Stable pillars, rocker panel and door profiles.
Side impact protection in the doors.
Doors are designed to open even in the event of extreme deformation.
Crumple zone
Dynamic absorption of deforming forces.
Protection of the passenger cell. www.JagDocs.com
Page 2707 of 3039
For instance, the crumple zones absorb the bulk of the impact energy. If any unprofessional repair techniques or
methods are used in these areas then this can pose a fundamental threat to vehicle safety.
Hidden damage
As well as looking at external indicators like flaked off paint, it is vital to check for hidden body damage or deformation
that is not visible from the outside. Large attached parts like bumpers and inner fenders often need to be removed to
allow accurate assessment of damage to underlying body parts.
Gap dimensions
Gap dimensions offer another alternative for diagnosis by visual inspection. If any changes or misaligned edges are apparent,
then this usually indicates that the dimensions of the affected part are incorrect.
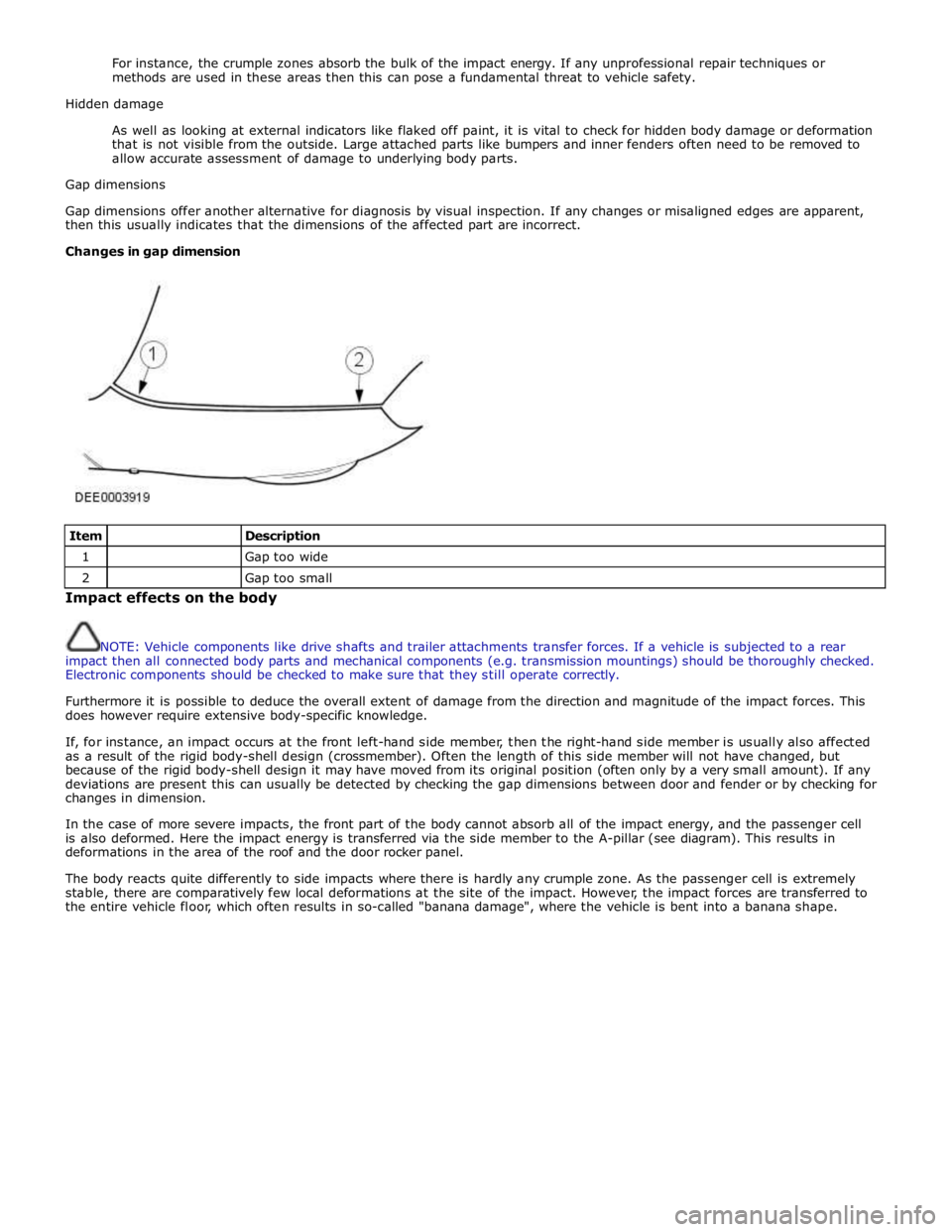
Changes in gap dimension
Item
Description 1
Gap too wide 2
Gap too small Impact effects on the body
NOTE: Vehicle components like drive shafts and trailer attachments transfer forces. If a vehicle is subjected to a rear
impact then all connected body parts and mechanical components (e.g. transmission mountings) should be thoroughly checked.
Electronic components should be checked to make sure that they still operate correctly.
Furthermore it is possible to deduce the overall extent of damage from the direction and magnitude of the impact forces. This
does however require extensive body-specific knowledge.
If, for instance, an impact occurs at the front left-hand side member, then the right-hand side member is usually also affected
as a result of the rigid body-shell design (crossmember). Often the length of this side member will not have changed, but
because of the rigid body-shell design it may have moved from its original position (often only by a very small amount). If any
deviations are present this can usually be detected by checking the gap dimensions between door and fender or by checking for
changes in dimension.
In the case of more severe impacts, the front part of the body cannot absorb all of the impact energy, and the passenger cell
is also deformed. Here the impact energy is transferred via the side member to the A-pillar (see diagram). This results in
deformations in the area of the roof and the door rocker panel.
The body reacts quite differently to side impacts where there is hardly any crumple zone. As the passenger cell is extremely
stable, there are comparatively few local deformations at the site of the impact. However, the impact forces are transferred to
the entire vehicle floor, which often results in so-called "banana damage", where the vehicle is bent into a banana shape.
Page 2732 of 3039

Part N-umber
Body Repairs - Water Leaks - Water Leaks
Description and Operation
General Published: 11-May-2011
If water leaks occur after bodywork repairs, the cause can be established using the checks described below. A
systematic and logical procedure is required to locate water leaks. Before beginning extensive checks, a thorough visual
inspection must be carried out.
Visual Inspection
- The following characteristics may indicate existing leaks:
- Check the clearance and accurate fit of ancillary components such as the hood, tailgate, liftgate, doors, and so
on.
- Check for correct fit and possible damage to sealing elements such as blanking plugs, rubber door seals, and so
on.
- Check water drain holes for unhindered flow.
Various tests can be used to provide further information on possible leaks:
- Water test
- Washer test
- Road test
- Chalk (powder) test
Practical execution of tests and checks
Water test
NOTE: Never aim a jet of water directly at a rubber seal.
Carry out the water test with a second person present (in the passenger compartment).
Use variable washer nozzles (concentrated water jet to fine spray mist).
Start in the lower section and spray the whole area, working upwards in stages.
Washer test
Further tests can be carried out in the washer system.
Some leaks originate here, or only occur here.
The relevant passenger compartment should be checked using a torch during the wash procedure.
Road test
If no leaks are located during the tests above, road tests should be carried out on wet roads.
Road tests under various conditions:
- At various speeds.
- On various road surfaces (asphalt to cobbles).
- With loaded or unloaded vehicle.
- Driving through puddles (splash water).
Chalk test (powder test)
In this test, the clamping load and the bearing surface of the seal are checked.
Performing the test:
- Dust the door seal with powder or coat with chalk.
- Coat the bearing surface of the seal with a thin film of Vaseline.
- Slowly close the door and open it again.
- Check the width and continuity of the imprint on the door seal.
Other test equipment
Other equipment such as stethoscopes, UV lamps, special mirrors or ultrasound measuring instruments can be used to
locate leaks.
Rectifying the leak using recommended tools, auxiliary equipment and materials
Tools and auxiliary equipment:
- Dry, absorbent cloths
- Variable washer nozzle
- Torch, fluorescent tube
- Mirror
- Compressed air
- Seal lip installer
- Wet/dry vacuum cleaner
- Sealing compound compressor
- Remover for interior trim
- Cutter blade or pocket knife
- Wedge (wood or plastic)
- Hot air blower
- Special mirror for concealed leaks
Page 2785 of 3039
Transmission (307-01A Automatic Transmission/Transaxle - V6 3.0L Petrol, Removal) /
Transmission - 4.2L (307-01, Removal) /
Transmission - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol (307-01B Automatic Transmission/Transaxle - TDV6 3.0L Diesel /V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L
Petrol, Removal) /
Front Shock Absorber (204-01 Front Suspension, Removal and Installation) /
Front Subframe - 2.7L Diesel (502-00, Removal and Installation) /
Front Subframe - V6 3.0L Petrol (502-00 Uni-Body, Subframe and Mounting System, Removal and Installation) /
Front Subframe - 4.2L, Vehicles Without: Supercharger (502-00, Removal
and Installation) /
Front Subframe - 4.2L, Vehicles With: Supercharger (502-00, Removal
and Installation).
8. Remove the pedestrian protection hood actuator.
For additional information, refer to: Pedestrian Protection Hood Actuator LH (501-20C Pedestrian Protection System, Removal and Installation) / Pedestrian Protection Hood Actuator RH (501-20C Pedestrian Protection System, Removal and Installation).
9. If the drivers side front side member and suspension top mount is to be
repaired, remove the brake master cylinder and reservoir.
For additional information, refer to: Brake Master Cylinder (206-06 Hydraulic Brake Actuation, Removal and Installation) /
Brake Fluid Reservoir (206-06 Hydraulic Brake Actuation, Removal and Installation).
10. If the left-hand front side member and suspension top mount assembly
is to be repaired, remove the fuel supply and return lines.
11. Release and position the front side member wiring harness to one side.
12. Remove any remaining miscellaneous components from the repair area.
13. NOTE: Retain the front fender support bracket
mounting if it is to be reused. If the front fender support
bracket mounting is to be renewed, it is not necessary to
remove or retain it.
Drill out the spot welds to remove the front fender support
bracket mounting.
Page 2797 of 3039

(100-00 General Information, Description and Operation) /
Body Repairs (501-25A Body Repairs - General Information, Description and Operation) /
Corrosion Protection (501-25B Body Repairs - Corrosion Protection, Description and Operation) /
Body and Frame (501-26 Body Repairs - Vehicle Specific Information and Tolerance Checks, Description and Operation).
5. Remove the fender apron panel front extension.
For additional information, refer to: Fender Apron Panel Front Extension (501-27 Front End Sheet Metal Repairs, Removal and Installation).
6. Remove the front fender support bracket.
For additional information, refer to: Front Fender Support Bracket (501-27 Front End Sheet Metal Repairs, Removal and Installation).
7. Remove the fender apron panel.
For additional information, refer to: Fender Apron Panel (501-27 Front End Sheet Metal Repairs, Removal and Installation).
8. Remove the engine, transmission / transaxle, front subframe and front
suspension, as an assembly.
For additional information, refer to: Engine (303-01A, Removal) /
Engine (303-01B Engine - V6 3.0L Petrol, Removal) / Engine (303-01D, Removal) /
Engine (303-01E, Removal) /
Transmission - 2.7L Diesel (307-01, Removal) /
Transmission - TDV6 3.0L Diesel (307-01B Automatic Transmission/Transaxle - TDV6 3.0L Diesel /V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L
Petrol, Removal) /
Transmission (307-01A Automatic Transmission/Transaxle - V6 3.0L Petrol, Removal) /
Transmission - 4.2L (307-01, Removal) /
Transmission - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol (307-01B Automatic Transmission/Transaxle - TDV6 3.0L Diesel /V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L
Petrol, Removal) /
Front Shock Absorber (204-01 Front Suspension, Removal and Installation) /
Front Subframe - 2.7L Diesel (502-00, Removal and Installation) /
Front Subframe - V6 3.0L Petrol (502-00 Uni-Body, Subframe and Mounting System, Removal and Installation) /
Front Subframe - 4.2L, Vehicles Without: Supercharger (502-00, Removal
and Installation) /
Front Subframe - 4.2L, Vehicles With: Supercharger (502-00, Removal
and Installation).
9. Remove the pedestrian protection hood actuator.
For additional information, refer to: Pedestrian Protection Hood Actuator LH (501-20C Pedestrian Protection System, Removal and Installation) / Pedestrian Protection Hood Actuator RH (501-20C Pedestrian Protection System, Removal and Installation).
10. If the drivers side front side member and suspension top mount is to be
repaired, remove the brake master cylinder and reservoir.
For additional information, refer to: Brake Master Cylinder (206-06 Hydraulic Brake Actuation, Removal and Installation) /
Brake Fluid Reservoir (206-06 Hydraulic Brake Actuation, Removal and Installation).
11. If the drivers side front side member and suspension top mount is to be
repaired, remove the brake booster.
Page 3013 of 3039

Front lower arm to front subframe retaining nut and bolt 175 129 - Rear lower arm to front subframe retaining nut and bolt 175 129 - Engine mount lower retaining nut 63 46 - Steering gear retaining bolts 100 74 - Front Shock absorber and spring assembly retaining bolt 175 129 - Front subframe to body front retaining bolt Stage 1 100 73 - Stage 2 270° 270° - Front subframe to body rear retaining bolt Stage 1 80 59 - Stage 2 240° 240° - Front Stabilizer bar link retaining nuts 43 31 - Front Stabilizer bar link retaining bolts 55 41 - Rear Shock absorber and spring assembly retaining bolt 133 98 - Rear subframe reinforcement plate retaining bolts 47 35 - Rear subframe to body retaining bolts Stage 1 80 59 - Stage 2 240° 240° -