2010 HUMMER H3 spare wheel
[x] Cancel search: spare wheelPage 191 of 410

Driving and Operating 9-7
Off-Road Driving
The airbag system is designed to
work properly under a wide range of
conditions, including off‐road usage.
Always wear your safety belt and
observe safe driving speeds,
especially on rough terrain.
Drinking and driving can be very
dangerous on any road and this is
certainly true for off-road driving.
At the very time you need special
alertness and driving skills, your
reflexes, perceptions, and judgment
can be affected by even a small
amount of alcohol. You could have a
serious—or even fatal —accident
if you drink and drive or ride with a
driver who has been drinking. Off-roading can be great fun but has
some definite hazards. The greatest
of these is the terrain itself. When
off-road driving, traffic lanes are not
marked, curves are not banked, and
there are no road signs. Surfaces
can be slippery, rough, uphill,
or downhill.
Avoid sharp turns and abrupt
maneuvers. Failure to operate the
vehicle correctly off‐road could
result in loss of vehicle control or
vehicle rollover.
Off-roading involves some new
skills. That is why it is very
important that you read these
driving tips and suggestions to
help make off-road driving safer
and more enjoyable.
Before You Go Off-Roading
.Have all necessary maintenance
and service work done.
.Make sure there is enough fuel,
that fluid levels are where they
should be, and that the spare
tire is fully inflated.
.Be sure to read all the
information about
four-wheel-drive vehicles
in this manual.
.Make sure all underbody
shields, if the vehicle has them,
are properly attached.
.Know the local laws that apply
to off-roading where you will
be driving or check with law
enforcement people in the area.
.Be sure to get the necessary
permission if you will be on
private land.
Page 268 of 410

10-2 Vehicle Care
Wheels and Tires
Tires . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-44
Tire Sidewall Labeling . . . . . . 10-44
Tire Designations . . . . . . . . . . . 10-46
Tire Terminology andDefinitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-48
Tire Pressure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-51
Tire Pressure Monitor System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-52
Tire Pressure Monitor Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-53
Tire Inspection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-57
Tire Rotation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-57
When It Is Time for New Tires . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-58
Buying New Tires . . . . . . . . . . . 10-59
Different Size Tires and Wheels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-60
Uniform Tire Quality Grading . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-61 Wheel Alignment and Tire
Balance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-62
Wheel Replacement . . . . . . . . 10-63
Tire Chains . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-64
If a Tire Goes Flat . . . . . . . . . . 10-64
Tire Changing (H3T) . . . . . . . . 10-66
Tire Changing (H3) . . . . . . . . . 10-75
Secondary Latch System . . . 10-84
Full-Size Spare Tire . . . . . . . . 10-85
Jump Starting
Jump Starting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-86
Towing
Towing the Vehicle . . . . . . . . . 10-90
Recreational Vehicle Towing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-90
Appearance Care
Exterior Care . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-92
Interior Care . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-96
General Information
For service and parts needs, visit
your dealer/retailer. You will receive
genuine parts and trained and
supported service people.
California Proposition 65
Warning
Most motor vehicles, including this
one, contain and/or emit chemicals
known to the State of California to
cause cancer and birth defects or
other reproductive harm. Engine
exhaust, many parts and systems,
many fluids, and some component
wear by-products contain and/or
emit these chemicals.
Page 319 of 410

Vehicle Care 10-53
Please note that the TPMS is
not a substitute for proper tire
maintenance, and it is the driver's
responsibility to maintain correct tire
pressure, even if under‐inflation
has not reached the level to trigger
illumination of the TPMS low tire
pressure telltale.
Your vehicle has also been
equipped with a TPMS malfunction
indicator to indicate when the
system is not operating properly.
The TPMS malfunction indicator is
combined with the low tire pressure
telltale. When the system detects a
malfunction, the telltale will flash for
approximately one minute and then
remain continuously illuminated.
This sequence will continue upon
subsequent vehicle start‐ups as
long as the malfunction exists.
When the malfunction indicator
is illuminated, the system may
not be able to detect or signal
low tire pressure as intended.TPMS malfunctions may occur for
a variety of reasons, including the
installation of replacement or
alternate tires or wheels on the
vehicle that prevent the TPMS
from functioning properly. Always
check the TPMS malfunction
telltale after replacing one or more
tires or wheels on your vehicle to
ensure that the replacement or
alternate tires and wheels allow
the TPMS to continue to function
properly.
See
Tire Pressure Monitor
Operation
on page 10‑53for
additional information.
Federal Communications
Commission (FCC) and
Industry Canada
See Radio Frequency Statementon
page 13‑16for information
regarding Part 15 of the Federal
Communications Commission (FCC)
Rules and RSS-210/211 of Industry
Canada.
Tire Pressure Monitor
Operation
This vehicle may have a Tire
Pressure Monitor System (TPMS).
The TPMS is designed to warn the
driver when a low tire pressure
condition exists. TPMS sensors are
mounted onto each tire and wheel
assembly on the vehicle, excluding
the spare tire. The TPMS sensors
monitor the air pressure in the
vehicle's tires and transmit the tire
pressure readings to a receiver
located in the vehicle.
When a low tire pressure
condition is detected, the TPMS
illuminates the low tire pressure
warning light located on the
instrument panel cluster.
Page 323 of 410
Vehicle Care 10-57
10. Set all four tires to therecommended air pressure
level as indicated on the Tire
and Loading Information label.
11. Put the valve caps back on the valve stems.
Tire Inspection
We recommend that you
regularly inspect your vehicle's
tires, including the spare tire,
if the vehicle has one, for
signs of wear or damage. See
When It Is Time for New Tires
on
page 10‑58
for more information.
Tire Rotation
Tires should be rotated every
5,000 to 8,000 miles (8 000 to
13 000 km). See Scheduled
Maintenance
on page 11‑2. The purpose of a regular tire
rotation is to achieve a uniform
wear for all tires on the vehicle.
This will ensure that the vehicle
continues to perform most like it
did when the tires were new.
The first rotation is the most
important. See
Scheduled
Maintenance
on page 11‑2.
Any time you notice unusual
wear, rotate the tires as soon
as possible and check wheel
alignment. Also check for
damaged tires or wheels.
See When It Is Time for New
Tires
on page 10‑58and Wheel
Replacement
on page 10‑63.
Make sure the spare tire is
stored securely. Push, pull and
then try to rotate or turn the tire.
If it moves, use the wheel
wrench/hoist shaft to tighten the
cable. See If a Tire Goes Flat
on
page 10‑64
.
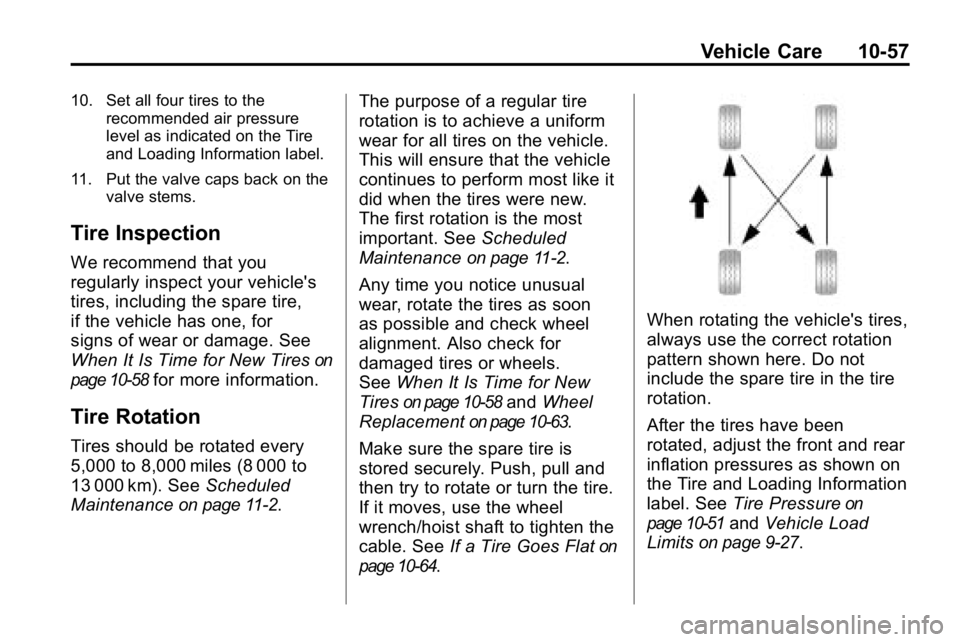
When rotating the vehicle's tires,
always use the correct rotation
pattern shown here. Do not
include the spare tire in the tire
rotation.
After the tires have been
rotated, adjust the front and rear
inflation pressures as shown on
the Tire and Loading Information
label. See Tire Pressure
on
page 10‑51
and Vehicle Load
Limits
on page 9‑27.
Page 327 of 410

Vehicle Care 10-61
Additionally, if your vehicle has
electronic systems such as anti‐lock
brakes, rollover airbags, traction
control, and electronic stability
control, the performance of these
systems can be affected.
{WARNING
If you add different sized
wheels, your vehicle may not
provide an acceptable level of
performance and safety if tires not
recommended for those wheels
are selected. You may increase
the chance that you will crash and
suffer serious injury. Only use
Hummer specific wheel and tire
systems developed for your
vehicle, and have them properly
installed by a GM certified
technician.
See Buying New Tires
on
page 10‑59and Accessories and
Modificationson page 10‑3for
additional information.
Uniform Tire Quality
Grading
Quality grades can be found
where applicable on the tire
sidewall between tread shoulder
and maximum section width. For
example:
Treadwear 200 Traction AA
Temperature A
The following information relates
to the system developed by the
United States National Highway
Traffic Safety Administration
(NHTSA), which grades tires
by treadwear, traction, and
temperature performance. This
applies only to vehicles sold in
the United States. The grades
are molded on the sidewalls
of most passenger car tires.
The Uniform Tire Quality
Grading (UTQG) system
does not apply to deep
tread, winter-type snow tires, space-saver, or temporary use
spare tires, tires with nominal
rim diameters of 10 to 12 inches
(25 to 30 cm), or to some
limited-production tires.
While the tires available on
Hummer light trucks may vary
with respect to these grades,
they must also conform to
federal safety requirements and
additional General Motors Tire
Performance Criteria (TPC)
standards.
All Passenger Car Tires Must
Conform to Federal Safety
Requirements In Addition To
These Grades.
Treadwear
The treadwear grade is a
comparative rating based
on the wear rate of the tire
when tested under controlled
conditions on a specified
government test course.
Page 332 of 410

10-66 Vehicle Care
SeeTire Changing (H3T)on
page 10‑66or Tire Changing (H3)on page 10‑75for more information.
To use the wheel blocks, lift the
wheel block and lock it into place.
Use the following example as a
guide to assist in the placement of
the wheel blocks (A) when the
vehicle has a flat tire (B).
A. Wheel Block
B. Flat Tire
The following information explains
how to use the jack and change
a tire.
Tire Changing (H3T)
Removing the Spare Tire and
Tools
To access the jack and tools located
under the rear seat:
1. Turn the wing nut (A)
counterclockwise to release the
jack and tools.
2. Remove the jack and tool kit from the bracket.
3. Release the straps (B) that secure the tool bag to the jack.
Page 333 of 410
Vehicle Care 10-67
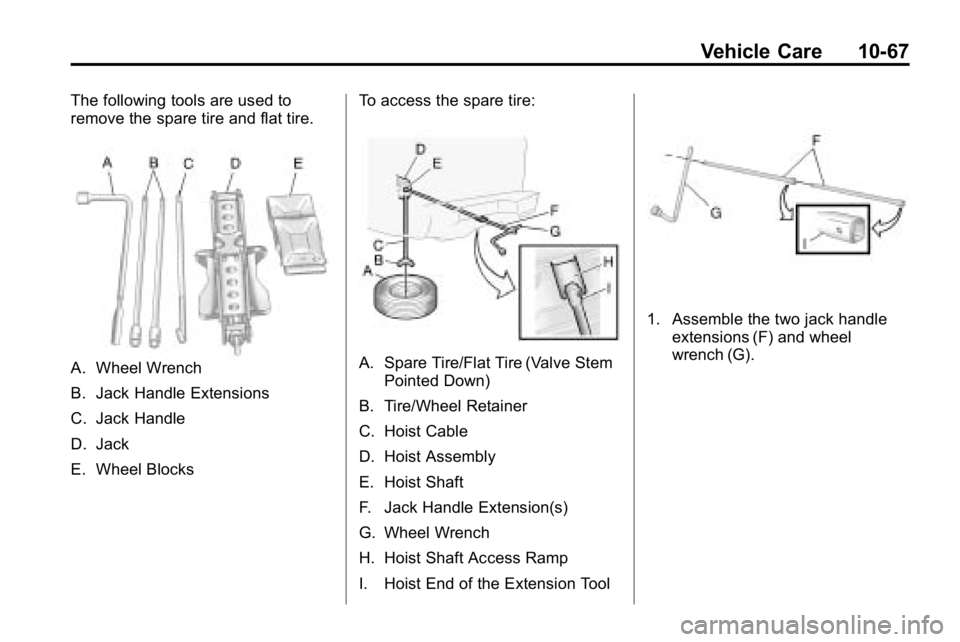
The following tools are used to
remove the spare tire and flat tire.
A. Wheel Wrench
B. Jack Handle Extensions
C. Jack Handle
D. Jack
E. Wheel BlocksTo access the spare tire:A. Spare Tire/Flat Tire (Valve Stem
Pointed Down)
B. Tire/Wheel Retainer
C. Hoist Cable
D. Hoist Assembly
E. Hoist Shaft
F. Jack Handle Extension(s)
G. Wheel Wrench
H. Hoist Shaft Access Ramp
I. Hoist End of the Extension Tool
1. Assemble the two jack handle extensions (F) and wheel
wrench (G).
Page 334 of 410

10-68 Vehicle Care
2. Insert the hoist end of theextension tool (I) through the
hoist shaft access ramp (H). 3. The hoist end of the extension
tool (I) must connect to the hoist
shaft (E). The hoist end of the
extension tool is used to lower
the spare tire.
Do not use the chiseled end of
the wheel wrench.
4. Turn the wheel wrench (G) counterclockwise to lower the
spare tire (A) to the ground.
Continue to turn the wheel
wrench (G) until the spare tire (A)
can be pulled from under the
vehicle.
If the spare tire does not lower to
the ground, the secondary latch
is engaged. See Secondary
Latch System on page 10‑84.
5. Pull the spare tire towards you.6. Tilt the tire, with slack in the cable, to access the tire/wheel
retainer (B).