2010 BUICK LACROSSE fuel
[x] Cancel search: fuelPage 335 of 414
Vehicle Care 9-53
Tire Pressure
Tires need the correct amount of
air pressure to operate
effectively.
Notice:Do not let anyone tell
you that under-inflation or
over-inflation is all right. It is
not. If your tires do not have
enough air (under-inflation),
you can get the following:
.Too much flexing
.Too much heat
.Tire overloading
.Premature or
irregular wear
.Poor handling
.Reduced fuel economy If your tires have too much air
(over-inflation), you can get
the following:
.Unusual wear
.Poor handling
.Rough ride
.Needless damage from
road hazards
A vehicle specific Tire and
Loading Information label is
attached to your vehicle. This
label shows your vehicle's
original equipment tires and the
correct inflation pressures for
your tires when they are cold.
The recommended cold tire
inflation pressure, shown on the
label, is the minimum amount of
air pressure needed to support
your vehicle's maximum load
carrying capacity. For additional information
regarding how much weight your
vehicle can carry, and an
example of the Tire and Loading
Information label, see
Vehicle
Load Limits
on page 8‑12. How
you load your vehicle affects
vehicle handling and ride
comfort. Never load your vehicle
with more weight than it was
designed to carry.
When to Check
Check your tires once a month
or more. Do not forget to check
the compact spare tire, if the
vehicle has one. The compact
spare should be at 60 psi
(420 kPa). For additional
information regarding the
compact spare tire, see
Compact Spare Tire
on
page 9‑74
.
Page 336 of 414

9-54 Vehicle Care
How to Check
Use a good quality pocket-type
gage to check tire pressure. You
cannot tell if your tires are
properly inflated simply by
looking at them. Radial tires may
look properly inflated even when
they are under-inflated. Check
the tire's inflation pressure when
the tires are cold. Cold means
your vehicle has been sitting for
at least three hours or driven no
more than 1.6 km (1 mile).
Remove the valve cap from the
tire valve stem. Press the tire
gage firmly onto the valve to get
a pressure measurement. If the
cold tire inflation pressure
matches the recommended
pressure on the Tire and
Loading Information label, no
further adjustment is necessary.
If the inflation pressure is low,
add air until you reach the
recommended amount.If you overfill the tire, release air
by pushing on the metal stem in
the center of the tire valve.
Re-check the tire pressure with
the tire gage.
Be sure to put the valve caps
back on the valve stems. They
help prevent leaks by keeping
out dirt and moisture.
Tire Pressure Monitor
System
The Tire Pressure Monitor System
(TPMS) uses radio and sensor
technology to check tire pressure
levels. The TPMS sensors monitor
the air pressure in your vehicle's
tires and transmit tire pressure
readings to a receiver located in the
vehicle.
Each tire, including the spare
(if provided), should be checked
monthly when cold and inflated to
the inflation pressure recommended
by the vehicle manufacturer on the
vehicle placard or tire inflation pressure label. (If your vehicle has
tires of a different size than the size
indicated on the vehicle placard or
tire inflation pressure label, you
should determine the proper tire
inflation pressure for those tires.)
As an added safety feature, your
vehicle has been equipped with a
tire pressure monitoring system
(TPMS) that illuminates a low tire
pressure telltale when one or more
of your tires is significantly
under-inflated.
Accordingly, when the low tire
pressure telltale illuminates, you
should stop and check your tires as
soon as possible, and inflate them
to the proper pressure. Driving on a
significantly under-inflated tire
causes the tire to overheat and can
lead to tire failure. Under-inflation
also reduces fuel efficiency and tire
tread life, and may affect the
vehicle's handling and stopping
ability.
Page 362 of 414
9-80 Vehicle Care
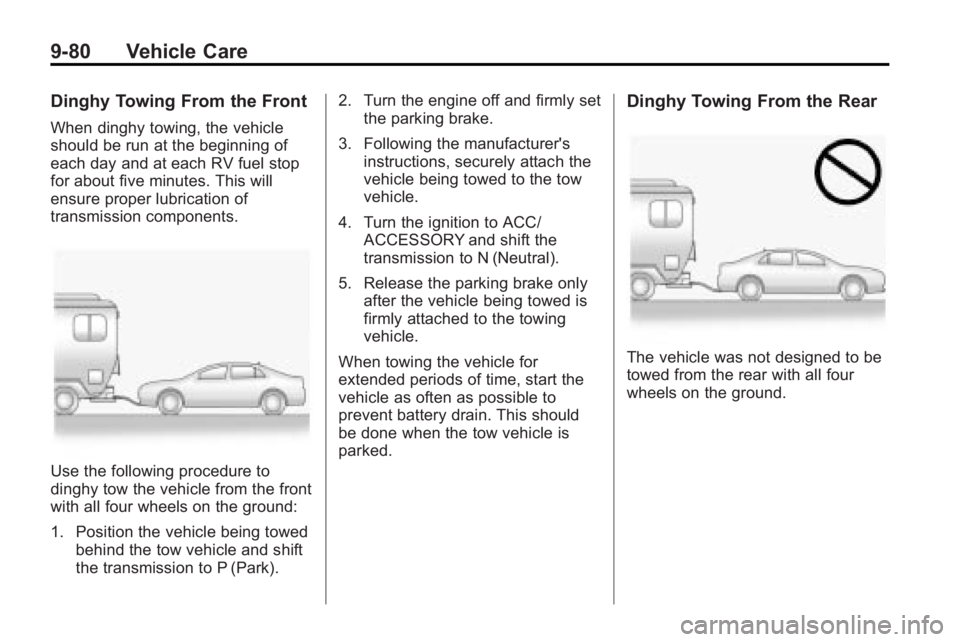
Dinghy Towing From the Front
When dinghy towing, the vehicle
should be run at the beginning of
each day and at each RV fuel stop
for about five minutes. This will
ensure proper lubrication of
transmission components.
Use the following procedure to
dinghy tow the vehicle from the front
with all four wheels on the ground:
1. Position the vehicle being towedbehind the tow vehicle and shift
the transmission to P (Park). 2. Turn the engine off and firmly set
the parking brake.
3. Following the manufacturer's instructions, securely attach the
vehicle being towed to the tow
vehicle.
4. Turn the ignition to ACC/ ACCESSORY and shift the
transmission to N (Neutral).
5. Release the parking brake only after the vehicle being towed is
firmly attached to the towing
vehicle.
When towing the vehicle for
extended periods of time, start the
vehicle as often as possible to
prevent battery drain. This should
be done when the tow vehicle is
parked.
Dinghy Towing From the Rear
The vehicle was not designed to be
towed from the rear with all four
wheels on the ground.
Page 367 of 414
Vehicle Care 9-85
Wipers can be damaged by:
.Extreme dusty conditions
.Sand and salt
.Heat and sun
.Snow and ice, without proper
removal
Tires
Use a stiff brush with tire cleaner to
clean the tires.
Notice:Using petroleum-based
tire dressing products on the
vehicle may damage the paint
finish and/or tires. When applying
a tire dressing, always wipe off
any overspray from all painted
surfaces on the vehicle.
Sheet Metal Damage
If the vehicle is damaged and
requires sheet metal repair or
replacement, make sure the body
repair shop applies anti-corrosion
material to parts repaired or
replaced to restore corrosion
protection. Original manufacturer replacement
parts will provide the corrosion
protection while maintaining the
vehicle warranty.
Finish Damage
Any stone chips, fractures or deep
scratches in the finish should be
repaired right away. Bare metal will
corrode quickly and may develop
into major repair expense.
Minor chips and scratches can be
repaired with touch-up materials
available from your dealer/retailer.
Larger areas of finish damage can
be corrected in your dealer's/
retailer's body and paint shop.
Underbody Maintenance
Chemicals used for ice and snow
removal and dust control can collect
on the underbody. If these are not
removed, corrosion and rust can
develop on the underbody parts
such as fuel lines, frame, floor pan,
and exhaust system even though
they have corrosion protection.
At least every spring, flush these
materials from the underbody with
plain water. Clean any areas where
mud and debris can collect. Dirt
packed in close areas of the frame
should be loosened before being
flushed. Your dealer/retailer or an
underbody car washing system can
do this.
Chemical Paint Spotting
Some weather and atmospheric
conditions can create a chemical
fallout. Airborne pollutants can fall
upon and attack painted surfaces on
the vehicle. This damage can take
two forms: blotchy, ring-shaped
discolorations, and small, irregular
dark spots etched into the paint
surface.
Page 371 of 414

Service and Maintenance 10-1
Service and
Maintenance
General Information
General Information . . . . . . . . . . 10-1
Scheduled Maintenance
Scheduled Maintenance . . . . . 10-2
Recommended Fluids,
Lubricants, and Parts
Recommended Fluids andLubricants . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-7
Maintenance Replacement Parts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-9
Maintenance Records
Maintenance Records . . . . . . 10-10
General Information
Notice: Maintenance intervals,
checks, inspections,
recommended fluids, and
lubricants are necessary to keep
this vehicle in good working
condition. Damage caused by
failure to follow scheduled
maintenance might not be
covered by the vehicle warranty.
Proper vehicle maintenance helps to
keep the vehicle in good working
condition, improves fuel economy,
and reduces vehicle emissions for
better air quality.
Because of all the different ways
people use vehicles, maintenance
needs vary. The vehicle might need
more frequent checks and services. Please read the information under
Scheduled Maintenance. To keep
the vehicle in good condition, see
your dealer/retailer.
The maintenance schedule is for
vehicles that:
.carry passengers and cargo
within recommended limits on
the Tire and Loading Information
label. See
Vehicle Load Limits
on page 8‑12.
.are driven on reasonable road
surfaces within legal driving
limits.
.use the recommended fuel.
SeeRecommended Fuelon
page 8‑50.
Page 374 of 414

10-4 Service and Maintenance
.Windshield wiper blade
inspection for wear, cracking,
or contamination and windshield
and wiper blade cleaning,
if contaminated. SeeExterior
Care
on page 9‑82. Worn or
damaged wiper blade
replacement. See Wiper Blade
Replacement on page 9‑29.
.Body hinges and latches, key
lock cylinders, folding seat
hardware, and sunroof
(if equipped) lubrication.
See Recommended Fluids and
Lubricants
on page 10‑7.
More frequent lubrication may
be required when vehicle is
exposed to a corrosive
environment. Applying silicone
grease on weatherstrips with a
clean cloth makes them last
longer, seal better, and not stick
or squeak.
.Restraint system component
check. See Safety System
Check on page 2‑23.
.Automatic transmission fluid
level check and adding fluid,
if needed. See Automatic
Transmission Fluid
on
page 9‑15.
.Engine air cleaner filter
inspection. See Engine Air
Cleaner/Filter on page 9‑15.
.Passenger compartment air
filter replacement (or every
12 months, whichever occurs
first). More frequent replacement
may be required if vehicle is
driven regularly under dusty
conditions.
Additional Required Services
At Each Fuel Stop
.Engine oil level check. See
Engine Oil on page 9‑11.
.Engine coolant level check. See
Engine Coolant on page 9‑18.
.Windshield washer fluid level
check. See Washer Fluidon
page 9‑23.
Once a Month
.Tire inflation check. See Tire
Pressure on page 9‑53.
.Tire wear inspection. See Tire
Inspection on page 9‑59.
Once a Year
.See Starter Switch Checkon
page 9‑27.
.See Automatic Transmission
Shift Lock Control System
Check on page 9‑27.
Page 375 of 414

Service and Maintenance 10-5
.SeeIgnition Transmission Lock
Check on page 9‑28.
.See Park Brake and P (Park)
Mechanism Checkon
page 9‑28.
.Engine cooling system and
pressure cap pressure check.
Radiator and air conditioning
condenser outside cleaning.
See Cooling System
on
page 9‑17.
.Exhaust system and nearby heat
shields inspection for loose or
damaged components.
.Accelerator pedal check for
damage, high effort, or binding.
Replace if needed.
First Engine Oil Change After
Every 40 000 km/25,000 Miles
.Fuel system inspection for
damage or leaks. First Engine Oil Change After
Every 80 000 km/50,000 Miles
.Engine air cleaner filter
replacement. See
Engine Air
Cleaner/Filter on page 9‑15.
.Automatic transmission fluid
change (severe service) for
vehicles mainly driven in heavy
city traffic in hot weather,
in hilly or mountainous terrain,
when frequently towing a
trailer, or used for taxi,
police, or delivery service.
See Automatic Transmission
Fluid on page 9‑15.
First Engine Oil Change After
Every 160 000 km/100,000 Miles
.Automatic transmission fluid
change (normal service).
See Automatic Transmission
Fluid on page 9‑15.
.Spark plug replacement and
spark plug wires inspection.
An Emission Control Service. First Engine Oil Change After
Every 240 000 km/150,000 Miles
.Engine cooling system drain,
flush, and refill, cooling system
and cap pressure check, and
cleaning of outside of radiator
and air conditioning condenser
(or every 5 years, whichever
occurs first). See
Cooling
System
on page 9‑17.
An Emission Control Service.
.Engine accessory drive belt
inspection for fraying, excessive
cracks, or obvious damage
and replacement, if needed.
An Emission Control Service.
Page 385 of 414

Technical Data 11-3
ApplicationCapacities
Metric English
Fuel Tank
AWD 74.0 L 19.5 gal
FWD 70.5 L 18.6 gal
Transmission Fluid* (Drain and Refill)
2.4L L4 Engine, 6–Speed Automatic 8.0 L 8.5 qt
3.0L V6 Engine, All Wheel Drive, 6–Speed Automatic 9.0 L 9.5 qt
3.0L V6 Engine, Front Wheel Drive, 6–Speed Automatic 9.0 L 9.5 qt
3.6L V6 Engine, 6–Speed Automatic 9.0 L 9.5 qt
Wheel Nut Torque 150 Y110 ft lb
*See Automatic Transmission Fluid
on page 9‑15for information on checking fluid level.
All capacities are approximate. When adding, be sure to fill to the approximate level, as recommended in this
manual. Recheck fluid level after filling.