Page 8 of 228
8
In brief
Seat inclination Pull lever, adjust inclination by
shifting body weight. Release lever
and audibly engage seat in position.
Seats 3 46, Seat position 3 46. Head restraint adjustment
Press release button, adjust height,
engage.
Head restraints
3 44. Seat belt
Pull out the seat belt and engage in
belt
buckle. The seat belt must not be
twisted and must fit close against the
body. The backrest must not be tilted
back too far (maximum approx. 25 °).
To release belt, press red button on
belt buckle.
Seat belts 3 54, Airbag system
3 57, Seat position 3 46.
Page 47 of 228
Seats, restraints
47
Pull handle, slide seat, release
handle.
Seat backrests Turn handwheel. Do not lean on seat
when adjusting. Seat height
Lever pumping motion
up = higher
down = lower Seat inclination
Pull lever, adjust inclination by
shifting body weight. Release lever
and audibly engage seat in position.
Page 62 of 228
62
Seats, restraints
Child restraints
Child restraint systems
Follow the usage instructions for the
child restraint system.
Always comply with local or national
regulations. In some countries, the
use of child restraint systems is
forbidden on certain seats.
Selecting the right system
Your child should travel facing
backwards in the vehicle, until as old
as possible. A child has a very weak
cervical spinal column and in the
event of an accident is less likely to
suffer injury in a rearward-facing,
semi-lying position than if seated
upright.
Children
under 12 years or under 150
cm tall should only travel in an
appropriate child safety seat.
When transporting children, use the
child restraint systems suitable for the
child's weight. Note
Do not stick anything on the child
restraint systems and do not cover
them with any other materials.
A child restraint system which has
been subjected to stress in an
accident must be replaced.
Page 63 of 228
Seats, restraints
63
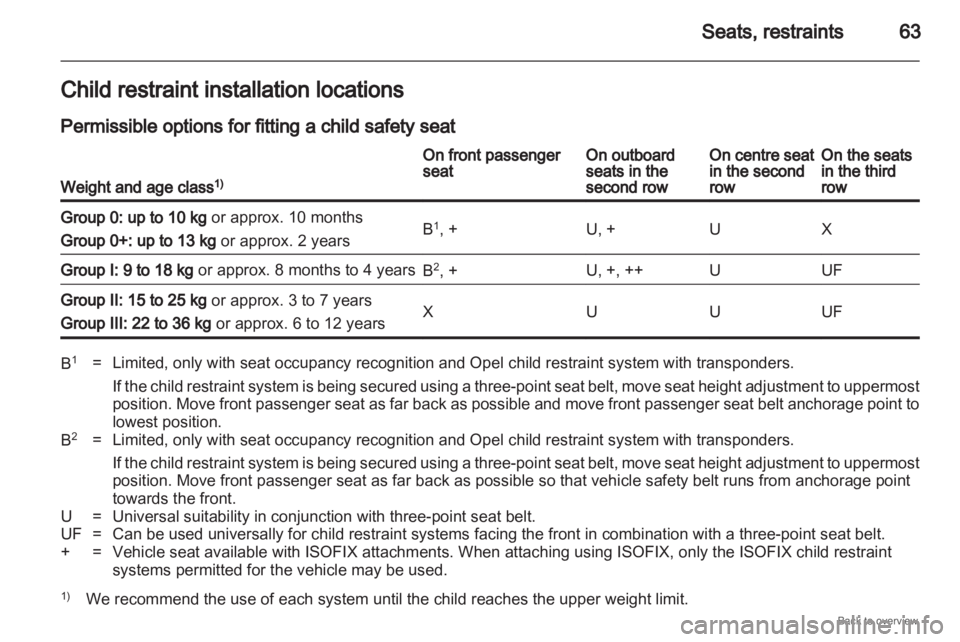
Child restraint installation locations
Permissible options for fitting a child safety seat
Weight and age class 1) On front passenger
seat On outboard
seats in the
second row On centre seat
in the second
row On the seats
in the third
row
Group 0: up to 10 kg or approx. 10 months
Group 0+: up to 13 kg or approx. 2 years
B
1
, + U, + U X
Group I: 9 to 18 kg or approx. 8 months to 4 years
B
2
, + U, +, ++ U UF
Group II: 15 to 25 kg or approx. 3 to 7 years
Group III: 22 to 36 kg or approx. 6 to 12 years
X U U UF
B
1
= Limited, only with seat occupancy recognition and Opel child restraint system with transponders.
If the child restraint system is being secured using a three-point seat belt, move seat height adjustment to uppermost
position. Move front passenger seat as far back as possible and move front passenger seat belt anchorage point to
lowest position.
B 2
= Limited, only with seat occupancy recognition and Opel child restraint system with transponders.
If
the child restraint system is being secured using a three-point seat belt, move seat height adjustment to uppermost
position. Move front passenger seat as far back as possible so that vehicle safety belt runs from anchorage point
towards the front.
U = Universal suitability in conjunction with three-point seat belt.
UF = Can be used universally for child restraint systems facing the front in combination with a three-point seat belt.
+ = Vehicle seat available with ISOFIX attachments. When attaching using ISOFIX, only the ISOFIX child restraint systems permitted for the vehicle may be used.
1) We recommend the use of each system until the child reaches the upper weight limit.
Page 64 of 228
64
Seats, restraints
++ = Vehicle seat available with ISOFIX attachments. When attaching using ISOFIX and Top-tether, universally permitted
ISOFIX child restraint systems may be used.
X = No child restraint system permitted in this weight class.
Page 75 of 228
Storage
75
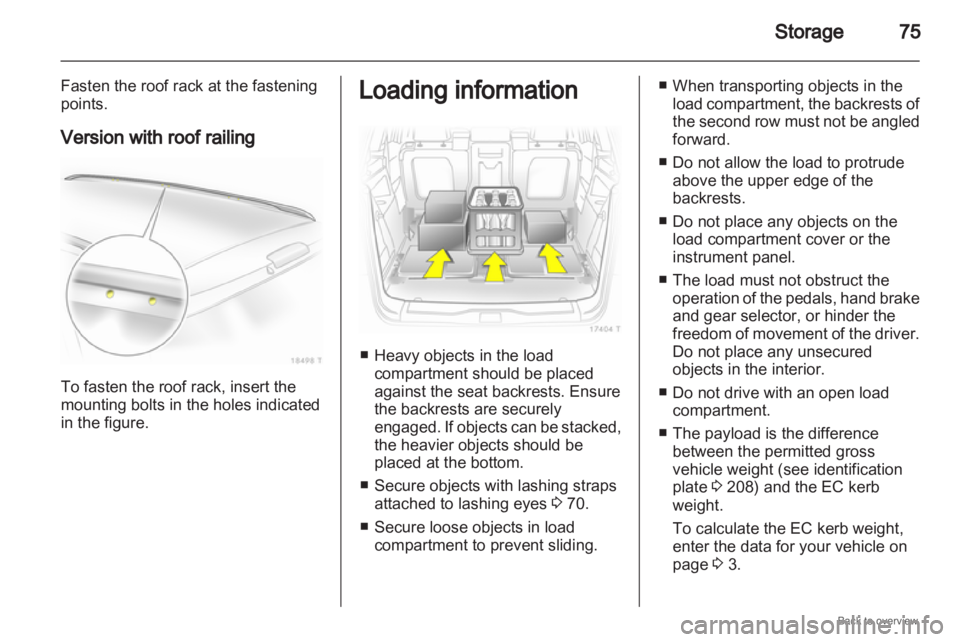
Fasten the roof rack at the fastening
points.
Version with roof railing To fasten the roof rack, insert the
mounting bolts in the holes indicated
in the figure. Loading information
■ Heavy objects in the load
compartment should be placed
against the seat backrests. Ensure
the backrests are securely
engaged.
If objects can be stacked,
the heavier objects should be
placed at the bottom.
■ Secure objects with lashing straps attached to lashing eyes 3 70.
■ Secure loose objects in load compartment to prevent sliding. ■ When transporting objects in the
load
compartment, the backrests of
the second row must not be angled
forward.
■ Do not allow the load to protrude above the upper edge of the
backrests.
■ Do not place any objects on the load compartment cover or the
instrument panel.
■ The load must not obstruct the operation of the pedals, hand brake
and gear selector, or hinder the
freedom of movement of the driver.
Do not place any unsecured
objects in the interior.
■ Do not drive with an open load compartment.
■ The payload is the difference between the permitted gross
vehicle weight (see identification
plate 3 208) and the EC kerb
weight.
To calculate the EC kerb weight,
enter the data for your vehicle on
page 3 3.
Page 76 of 228
76
Storage
The EC kerb weight includes
weights for the driver (68 kg),
luggage (7 kg) and all fluids (tank
90% full).
Optional equipment and
accessories increase the kerb
weight.
■
Driving with a roof load increases the sensitivity of the vehicle to
cross-winds and has a detrimental
effect on vehicle handling due to
the vehicle’s higher centre of
gravity. Distribute the load evenly
and secure it properly with retaining
straps. Adjust the tyre pressure and
vehicle speed according to the load
conditions. Check and retighten the
straps frequently.
The permissible roof load is 75 kg
and 100 kg for vehicles with roof
railing. The roof load is the
combined weight of the roof rack
and the load.
Page 149 of 228
Driving and operating
149
driving with approx. 2
/3 . Cold starts
and acceleration phases are also
taken into consideration.
The specification of CO 2 emission is
also a constituent of the directive.
The figures given must not be taken
as a guarantee for the actual fuel
consumption of a particular vehicle.
Furthermore, fuel consumption is
dependent on personal driving style
as
well as road and traffic conditions.
All values are based on the EU base
model with standard equipment.
The calculation of fuel consumption
takes account of the vehicle’s kerb
weight, ascertained in accordance
with the regulations. Options may
result in slightly higher fuel
consumption and CO 2 emission
levels and a lower top speed.
Fuel consumption, CO 2 emissions
3 213. Natural gas
The fuel consumption information
was obtained using reference fuel
G20 (methane proportion 99 - 100
mol%) under prescribed driving
conditions. When using natural gas
with a lower proportion of methane,
the fuel consumption can differ from
the specified values.
Towing
General information
Only use towing equipment that has
been approved for your vehicle.
Entrust retrofitting of towing
equipment to a workshop. It may be
necessary to make changes that
affect the cooling system, heat
shields or other equipment.
Installation dimensions of factory-
fitted towing equipment
3 223.
Driving characteristics and
towing tips
Before attaching a trailer, lubricate
the
coupling ball. However, do not do
so if a stabiliser, which acts on the
coupling ball, is being used to reduce
snaking movements.
For trailers with low driving stability
and trailers with a permitted gross
vehicle weight of more than 1300 kg
a speed of 80 km/h must not be
exceeded; the use of a stabiliser is
recommended.