2008 NISSAN TIIDA Eps
[x] Cancel search: EpsPage 1759 of 2771
EM-82
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
CYLINDER BLOCK
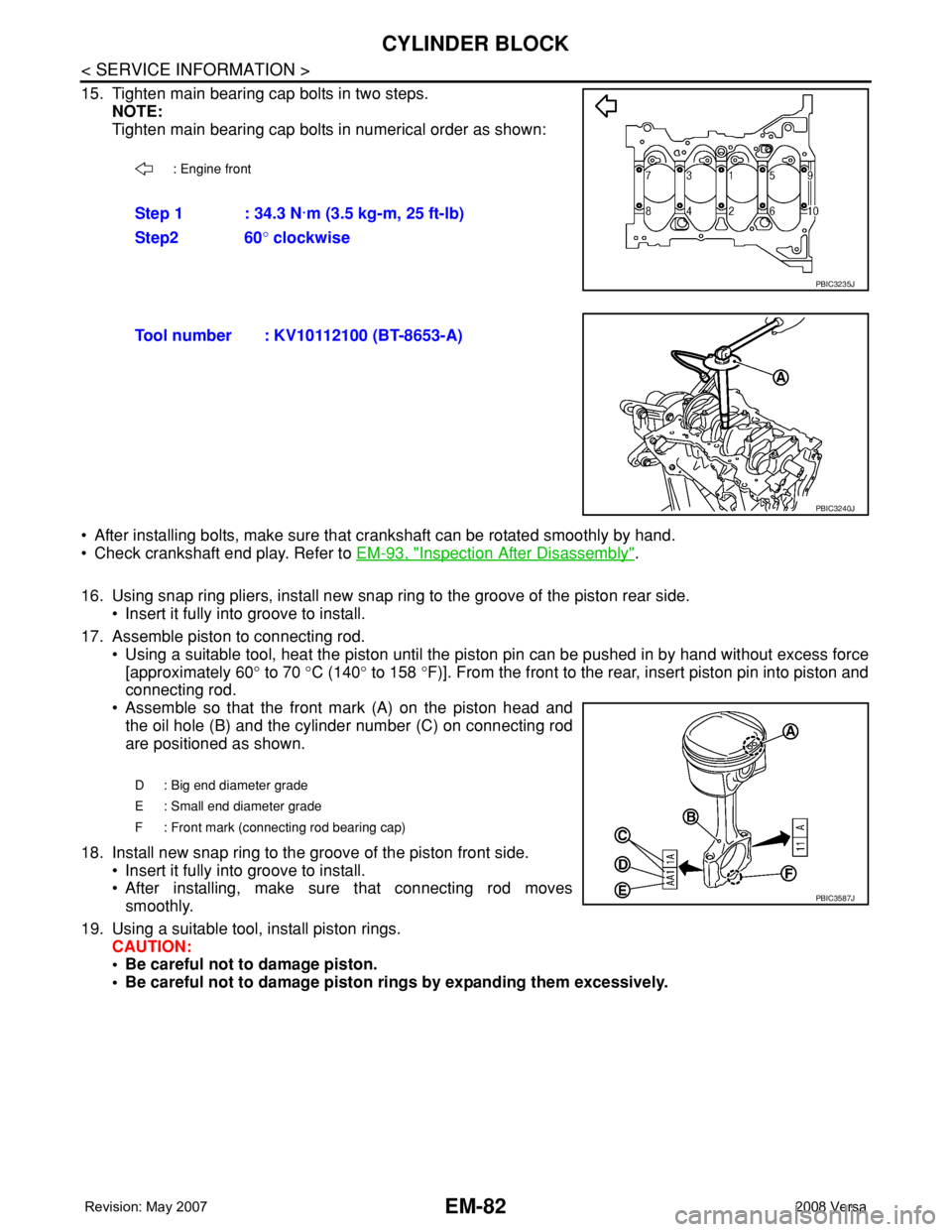
15. Tighten main bearing cap bolts in two steps.
NOTE:
Tighten main bearing cap bolts in numerical order as shown:
• After installing bolts, make sure that crankshaft can be rotated smoothly by hand.
• Check crankshaft end play. Refer to EM-93, "
Inspection After Disassembly".
16. Using snap ring pliers, install new snap ring to the groove of the piston rear side.
• Insert it fully into groove to install.
17. Assemble piston to connecting rod.
• Using a suitable tool, heat the piston until the piston pin can be pushed in by hand without excess force
[approximately 60° to 70 °C (140° to 158 °F)]. From the front to the rear, insert piston pin into piston and
connecting rod.
• Assemble so that the front mark (A) on the piston head and
the oil hole (B) and the cylinder number (C) on connecting rod
are positioned as shown.
18. Install new snap ring to the groove of the piston front side.
• Insert it fully into groove to install.
• After installing, make sure that connecting rod moves
smoothly.
19. Using a suitable tool, install piston rings.
CAUTION:
• Be careful not to damage piston.
• Be careful not to damage piston rings by expanding them excessively.
: Engine front
Step 1 : 34.3 N·m (3.5 kg-m, 25 ft-lb)
Step2 60° clockwise
PBIC3235J
Tool number : KV10112100 (BT-8653-A)
PBIC3240J
D : Big end diameter grade
E : Small end diameter grade
F : Front mark (connecting rod bearing cap)
PBIC3587J
Page 1761 of 2771
![NISSAN TIIDA 2008 Service Repair Manual EM-84
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
CYLINDER BLOCK
• Using a piston ring compressor [SST: EM03470000 (J-8037)]
(A) or suitable tool, install piston with the front mark on the pis-
ton head facing the fron NISSAN TIIDA 2008 Service Repair Manual EM-84
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
CYLINDER BLOCK
• Using a piston ring compressor [SST: EM03470000 (J-8037)]
(A) or suitable tool, install piston with the front mark on the pis-
ton head facing the fron](/manual-img/5/57399/w960_57399-1760.png)
EM-84
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
CYLINDER BLOCK
• Using a piston ring compressor [SST: EM03470000 (J-8037)]
(A) or suitable tool, install piston with the front mark on the pis-
ton head facing the front of the engine.
CAUTION:
Be careful not to damage the cylinder wall and crankshaft
pin, resulting from an interference of the connecting rod
big end.
22. Install connecting rod cap.
• Match the stamped cylinder number marks (C) on connecting
rod with those on connecting rod cap to install.
23. Tighten connecting rod bolt with the following procedure:
CAUTION:
• Make sure that there is no gap in the thrust surface (A) of
the joint between connecting rod (1) and connecting rod
bearing cap (2) and that these parts are in the correct
position. And then, tighten the connecting rod bolts.
• If the connecting rod bolts are reused, measure the outer
diameter. Refer to EM-93, "
Inspection After Disassembly".
24. Apply new engine oil to the threads and seats of connecting rod
bolts.
25. Tighten bolts in three steps
• After tightening connecting rod bolt, make sure that crankshaft rotates smoothly.
• Check the connecting rod side clearance. Refer to EM-93, "
Inspection After Disassembly".
26. Install oil pan (upper). Refer to EM-24
.
NOTE:
Install the rear oil seal after installing the oil pan (upper).
27. Install rear oil seal. Refer to EM-24
.
28. Install flywheel (M/T models) or drive plate (1) (A/T or CVT mod-
els).
• Secure crankshaft using Tool. (A), and tighten bolts crosswise
over several times.
NOTE:
A/T model shown CVT and M/T similar.
PBIC3244J
A : Front mark (piston)
B : Oil hole
D : Big end diameter grade
E : Small end diameter grade
F : Front mark (connecting rod bearing cap)
PBIC3587J
Step 1 : 27.4 N·m (2.8 kg-m, 20 ft-lb)
Step 2 : 0 N·m (0 kg-m, 0 ft-lb)
Step 3 : 19.6 N·m (2.0 kg-m, 14 ft-lb)
Tool number : KV11105210 (J-44716)PBIC3510J
PBIC3998E
Page 1824 of 2771
FL-4
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
FUEL SYSTEM
FUEL SYSTEM
Checking Fuel LineINFOID:0000000001703097
Inspect fuel lines, fuel filler cap and fuel tank for improper attach-
ment, leaks, cracks, damage, loose connections, chafing or deterio-
ration.
If necessary, repair or replace damaged parts.
General PrecautionINFOID:0000000001703098
WARNING:
When replacing fuel line parts, be sure to observe the following.
• Put a “CAUTION: FLAMMABLE” sign in the work area.
• Be sure to work in a well ventilated area and have a CO
2 fire extinguisher.
• Do not smoke while working on the fuel system. Keep open flames and sparks away from the work
area.
• Put drained fuel in an explosion-proof container and put the lid on securely. Keep the container in
safe area.
CAUTION:
• Use gasoline required by the regulations for octane number. Refer to GI-4, "
Precaution for Fuel
(Unleaded Regular Gasoline Recommended)".
• Before removing fuel line parts, perform the following procedures:
- Release fuel pressure from the fuel lines. Refer to EC-78, "
Fuel Pressure Check".
- Disconnect the battery ground cable.
• Always replace O-rings and clamps with new ones.
• Do not kink or twist tubes when they are being installed.
• Perform work on level surface.
• Do not tighten hose clamps excessively to avoid damaging hoses.
• After connecting fuel tube quick connectors, make sure quick connectors are secure.
Ensure that connector and resin tube do not contact any adjacent parts.
• After installing tubes, make sure there is no fuel leakage at connections in the following steps.
- Apply fuel pressure to fuel lines by turning ignition switch ON (without starting the engine). Then
check for fuel leaks at the fuel tube connections.
- Start engine and rev it up and check for fuel leaks at connections.
• Use only a genuine NISSAN fuel filler cap as a replacement. If an incorrect fuel filler cap is used, the
MIL may come on.
• For servicing “Evaporative Emission System” parts, refer to EC-31
.
• For servicing "On Board Refueling Vapor Recovery (ORVR)" parts, refer to EC-38
.
SMA803A
Page 1858 of 2771

HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
GI-7
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
N
O
PHOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
DescriptionINFOID:0000000001702431
This volume explains “Removal, Disassembly, Installation, Inspection and Adjustment” and “Trouble Diag-
noses”.
Te r m sINFOID:0000000001702432
• The captions WARNING and CAUTION warn you of steps that must be followed to prevent personal injury
and/or damage to some part of the vehicle.
WARNING indicates the possibility of personal injury if instructions are not followed.
CAUTION indicates the possibility of component damage if instructions are not followed.
BOLD TYPED STATEMENTS except WARNING and CAUTION give you helpful information.
Standard value:Tolerance at inspection and adjustment.
Limit value:The maximum or minimum limit value that should not be exceeded at inspection and adjustment.
UnitsINFOID:0000000001702433
• The UNITS given in this manual are primarily expressed as the SI UNIT (International System of Unit), and
alternatively expressed in the metric system and in the yard/pound system.
Also with regard to tightening torque of bolts and nuts, there are descriptions both about range and about the
standard tightening torque.
“Example”
Range
Standard
ContentsINFOID:0000000001702434
•ALPHABETICAL INDEX is provided at the end of this manual so that you can rapidly find the item and page
you are searching for.
•A QUICK REFERENCE INDEX, a black tab (e.g. ) is provided on the first page. You can quickly find the
first page of each section by matching it to the section's black tab.
•THE CONTENTS are listed on the first page of each section.
•THE TITLE is indicated on the upper portion of each page and shows the part or system.
•THE PAGE NUMBER of each section consists of two or three letters which designate the particular section
and a number (e.g. “BR-5”).
•THE SMALL ILLUSTRATIONS show the important steps such as inspection, use of special tools, knacks of
work and hidden or tricky steps which are not shown in the previous large illustrations.
Assembly, inspection and adjustment procedures for the complicated units such as the automatic transaxle
or transmission, etc. are presented in a step-by-step format where necessary. Outer Socket Lock Nut : 59 - 78 N·m (6.0 - 8.0 kg-m, 43 - 58 ft-lb)
Drive Shaft Installation Bolt: 44.3 N·m (4.5 kg-m, 33 ft-lb)
Page 1876 of 2771

SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
GI-25
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
N
O
P
How to Perform Efficient Diagnosis for an Electrical IncidentINFOID:0000000001702441
WORK FLOW
INCIDENT SIMULATION TESTS
Introduction
Sometimes the symptom is not present when the vehicle is brought in for service. If possible, re-create the
conditions present at the time of the incident. Doing so may help avoid a No Trouble Found Diagnosis. The fol-
lowing section illustrates ways to simulate the conditions/environment under which the owner experiences an
electrical incident.
The section is broken into the six following topics:
• Vehicle vibration
• Heat sensitive
• Freezing
• Water intrusion
• Electrical load
SGI838
STEP DESCRIPTION
STEP 1Get detailed information about the conditions and the environment when the incident occurred.
The following are key pieces of information required to make a good analysis:
WHATVehicle Model, Engine, Transmission/Transaxle and the System (i.e. Radio).
WHENDate, Time of Day, Weather Conditions, Frequency.
WHERERoad Conditions, Altitude and Traffic Situation.
HOWSystem Symptoms, Operating Conditions (Other Components Interaction).
Service History and if any After Market Accessories have been installed.
STEP 2Operate the system, road test if necessary.
Verify the parameter of the incident.
If the problem cannot be duplicated, refer to “Incident Simulation Tests”.
STEP 3Get the proper diagnosis materials together including:
• Power Supply Routing
• System Operation Descriptions
• Applicable Service Manual Sections
• Check for any Service Bulletins
Identify where to begin diagnosis based upon your knowledge of the system operation and the customer comments.
STEP 4Inspect the system for mechanical binding, loose connectors or wiring damage.
Determine which circuits and components are involved and diagnose using the Power Supply Routing and Harness Lay-
outs.
STEP 5 Repair or replace the incident circuit or component.
STEP 6Operate the system in all modes. Verify the system works properly under all conditions. Make sure you have not inad-
vertently created a new incident during your diagnosis or repair steps.
Page 1880 of 2771
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
GI-29
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
N
O
P
• Close the relay and probe at the solenoid.
voltage; open is further down the circuit than the solenoid.
no voltage; open is between relay and solenoid (point C).
Any powered circuit can be diagnosed using the approach in the previous example.
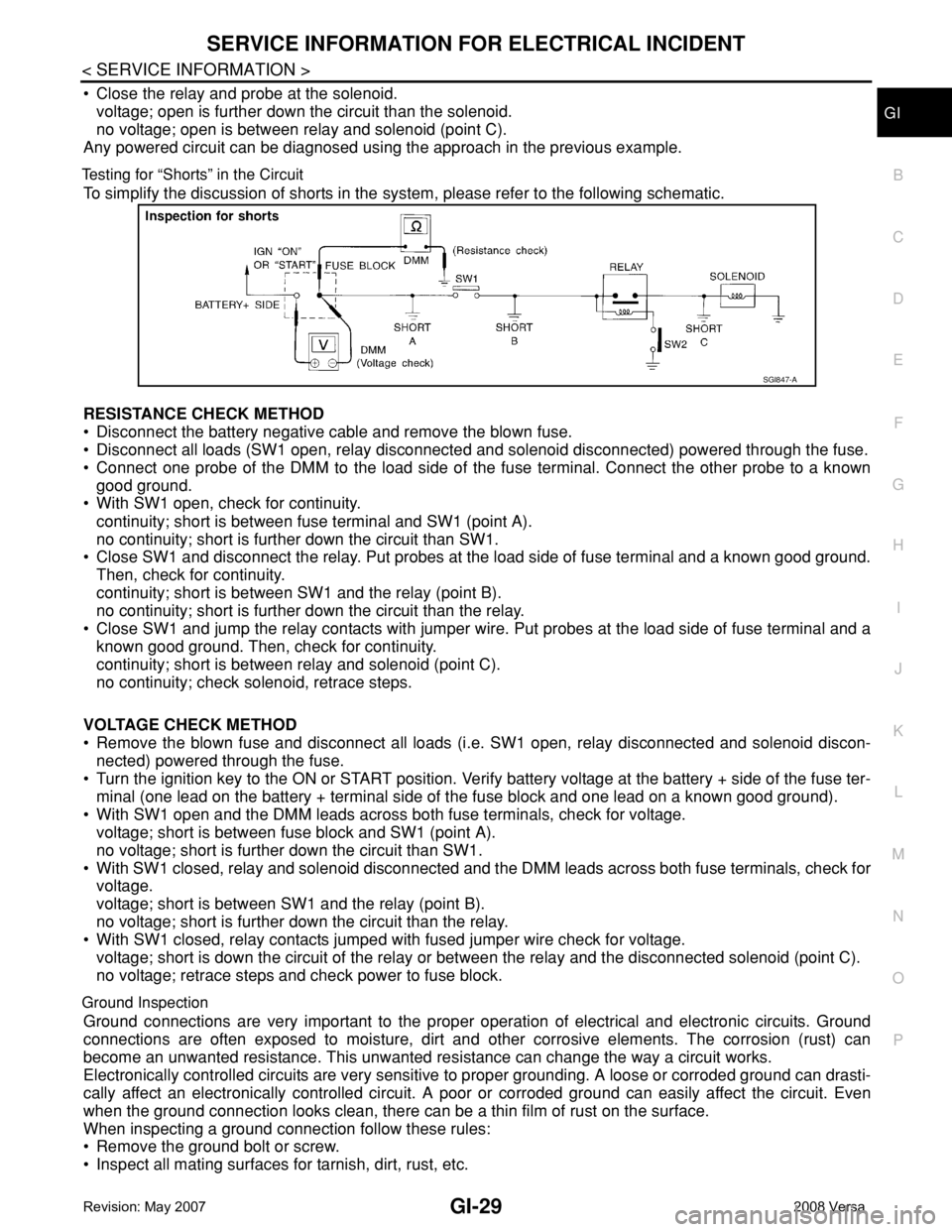
Testing for “Shorts” in the Circuit
To simplify the discussion of shorts in the system, please refer to the following schematic.
RESISTANCE CHECK METHOD
• Disconnect the battery negative cable and remove the blown fuse.
• Disconnect all loads (SW1 open, relay disconnected and solenoid disconnected) powered through the fuse.
• Connect one probe of the DMM to the load side of the fuse terminal. Connect the other probe to a known
good ground.
• With SW1 open, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between fuse terminal and SW1 (point A).
no continuity; short is further down the circuit than SW1.
• Close SW1 and disconnect the relay. Put probes at the load side of fuse terminal and a known good ground.
Then, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between SW1 and the relay (point B).
no continuity; short is further down the circuit than the relay.
• Close SW1 and jump the relay contacts with jumper wire. Put probes at the load side of fuse terminal and a
known good ground. Then, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between relay and solenoid (point C).
no continuity; check solenoid, retrace steps.
VOLTAGE CHECK METHOD
• Remove the blown fuse and disconnect all loads (i.e. SW1 open, relay disconnected and solenoid discon-
nected) powered through the fuse.
• Turn the ignition key to the ON or START position. Verify battery voltage at the battery + side of the fuse ter-
minal (one lead on the battery + terminal side of the fuse block and one lead on a known good ground).
• With SW1 open and the DMM leads across both fuse terminals, check for voltage.
voltage; short is between fuse block and SW1 (point A).
no voltage; short is further down the circuit than SW1.
• With SW1 closed, relay and solenoid disconnected and the DMM leads across both fuse terminals, check for
voltage.
voltage; short is between SW1 and the relay (point B).
no voltage; short is further down the circuit than the relay.
• With SW1 closed, relay contacts jumped with fused jumper wire check for voltage.
voltage; short is down the circuit of the relay or between the relay and the disconnected solenoid (point C).
no voltage; retrace steps and check power to fuse block.
Ground Inspection
Ground connections are very important to the proper operation of electrical and electronic circuits. Ground
connections are often exposed to moisture, dirt and other corrosive elements. The corrosion (rust) can
become an unwanted resistance. This unwanted resistance can change the way a circuit works.
Electronically controlled circuits are very sensitive to proper grounding. A loose or corroded ground can drasti-
cally affect an electronically controlled circuit. A poor or corroded ground can easily affect the circuit. Even
when the ground connection looks clean, there can be a thin film of rust on the surface.
When inspecting a ground connection follow these rules:
• Remove the ground bolt or screw.
• Inspect all mating surfaces for tarnish, dirt, rust, etc.
SGI847-A
Page 1886 of 2771

CONSULT-III CHECKING SYSTEM
GI-35
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
N
O
PCONSULT-III CHECKING SYSTEM
DescriptionINFOID:0000000001806209
• CONSULT-III is a hand-held type tester. When it is connected with a diagnostic connector equipped on the
vehicle side, it will communicate with the control unit equipped in the vehicle and then enable various kinds
of diagnostic tests.
• Refer to CONSULT-III Operator's Manual for more information.
Function and System ApplicationINFOID:0000000001806219
x: Applicable.
*1: If equipped.
*2: This option is shown on vehicles equipped with continuously variable transmission (CVT).
*3: NVIS (NATS) [NISSAN Vehicle Immobilizer System (Nissan Anti-theft System)]. Diagnostic test mode Function
ENGINE
ABS*
1
AIR BAG
EPS
IPDM E/R
BCM
METER/M&A
INTELLIGENT KEY*
1
A/T*
1
TRANSMISSION*
2
NVIS (NATS)*
3
NVIS (NATS BCM OR S/ENT)*
3
NATS I-KEY
*3,5
Work supportThis mode enables a technician to adjust some devices faster
and more accurately by following indications on CONSULT-III.x----x-xxx--x
Self-diagnostic results Self-diagnostic results can be read and erased quickly. xxxxxxxxxxx - x
Trouble diagnostic
recordCurrent self-diagnostic results and all trouble diagnostic records
previously stored can be read.--x----------
Data monitor Input/Output data in the ECU can be read. xx - xx - xxxx - - -
CAN diagnostic support
monitorThe communication condition of CAN communication line can
be read.xx - xxxxxxx - - -
Calibration data*
2Shows unit calibration IDs, offsets and gains. This data is stored
in the ECU memory.---------x---
Active testDiagnostic Test Mode in which CONSULT-III drives actuators
apart from ECU shifting some parameters in a specified range.xx--x--x-----
Function testThis mode can show results of self-diagnosis of ECU with either
"OK" or "NG". For engines, more practical tests regarding sen-
sors/switches and/or actuators are available.xxx-----xx---
DTC & SRT confirmationThe results of SRT (System Readiness Test) and the self-diag-
nosis status/result can be confirmed.x------------
DTC work supportThe operating condition to confirm Diagnosis Trouble Codes
can be selected.x-------x----
ECM/ECU part number ECM/ECU part number can be read. x x - x - x - x x x - - -
ECU discriminated No.Classification number of a replacement ECU can be read to pre-
vent an incorrect ECU from being installed.--x----------
Passenger airbag Displays the STATUS (readiness) of front passenger air bag. --x----------
Configuration Sets control module parameters to match vehicle options. -----x-------
Steering lock release
*4,5Condition of steering lock release solenoid. -----------x-
Control unit initializa-
tion
*4,6All registered ignition key IDs in NATS components can be ini-
tialized and new IDs can be registered.----------x--
PIN Read
*4This mode enables technician to get BCM-specific 5-digit code.-----------x-
Page 1930 of 2771
POWER WINDOW SYSTEM
GW-29
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
MA
B
GW
N
O
P
WORK SUPPORT
DATA MONITOR
Power Window Auto Operation InitializationINFOID:0000000001871741
1. Turn the ignition switch ON.
2. Open the window—all the way DOWN.
3. Pull all the way UP on the switch and hold (close the window).
• Continue holding the switch all the way UP for 4 seconds after the window is closed.
4. Confirm the window is now operating correctly.
NOTE:
• If the window is still not operating correctly, refer to GW-29, "
Trouble Diagnosis Symptom Chart".
• The above initialization procedure must be performed if any of the following occur:
- Battery cable is disconnected
- Power window switch connector is disconnected
- Power window regulator is replaced
- Power window motor is replaced
- Window glass is removed
- Window glass run rubber is replaced
- Power window fuse is blown
- Window is partly opened and/or closed many times without being fully closed.
Trouble Diagnosis Symptom ChartINFOID:0000000001704148
Check that other systems using the signal of the following systems operate normally.
Work item Description
RETAINED PWRRAP signal’s power supply period can be changed by mode setting. Selects RAP signal’s power
supply period between three steps
• MODE1 (45 sec.)/MODE2 (OFF)/MODE3 (2 min.).
Work item Description
IGN ON SW Indicates (ON/OFF) condition of ignition switch
DOOR SW-DR Indicates (ON/OFF) condition of front door switch LH
DOOR SW-AS Indicates (ON/OFF) condition of front door switch RH
Symptom Repair order Refer to page
None of the power windows can be operated using any switch1. BCM power supply and ground circuit checkBCS-15
2. Main power window and door lock/unlock
power supply and ground circuit checkGW-30
3. Replace main power window and door lock/
unlock switchEI-32
Front power window LH alone does not operate1. Front power window motor LH circuit checkGW-312. Replace main power window and door lock/
unlock switchEI-32
Front power window RH does not operate from power window and
door lock/unlock switch RH only1. Front power window RH circuit check (power
window and door lock/unlock switch RH opera-
tion)GW-32
Front power window RH does not operate from main power window
and door lock/unlock switch only1. Replace main power window and door lock/
unlock switchEI-32
Front power window RH does not operate from any switch 1. Front power window motor RH circuit checkGW-32