2008 NISSAN LATIO ignition
[x] Cancel search: ignitionPage 1861 of 2771

GI-10
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
3.Refer to Component Parts and Harness Connector Location for the Systems described in each
section for identification/location of components and harness connectors.
4.Refer to the Circuit Diagram for quick pinpoint check.
If you need to check circuit continuity between harness connectors in more detail, such as when a
sub-harness is used, refer to Wiring Diagram in each individual section and Harness Layout in PG
section for identification of harness connectors.
5.When checking circuit continuity, ignition switch should be OFF.
6.Before checking voltage at connectors, check battery voltage.
7.After accomplishing the Diagnostic Procedures and Electrical Components Inspection, make sure
that all harness connectors are reconnected as they were.
HOW TO FOLLOW TEST GROUPS IN TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
1.Work and diagnostic procedure
Start to diagnose a problem using procedures indicated in enclosed test groups.
2.Questions and required results
Questions and required results are indicated in bold type in test group.
The meaning of are as follows:
3.Symbol used in illustration
Symbols included in illustrations refer to measurements or procedures. Before diagnosing a problem,
familiarize yourself with each symbol. Refer to "Connector Symbols" in GI Section and "KEY TO SYM-
BOLS SIGNIFYING MEASUREMENTS OR PROCEDURES" below.
4.Action items
Next action for each test group is indicated based on result of each question. Test group number is shown
in the left upper portion of each test group.
HARNESS WIRE COLOR AND CONNECTOR NUMBER INDICATION
There are two types of harness wire color and connector number indication.
TYPE 1: Harness Wire Color and Connector Number are Shown in Illustration
SAIA0256E
a. Battery voltage → 11 - 14V or approximately 12V
b. Voltage : Approximately 0V → Less than 1V
Page 1869 of 2771
GI-18
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
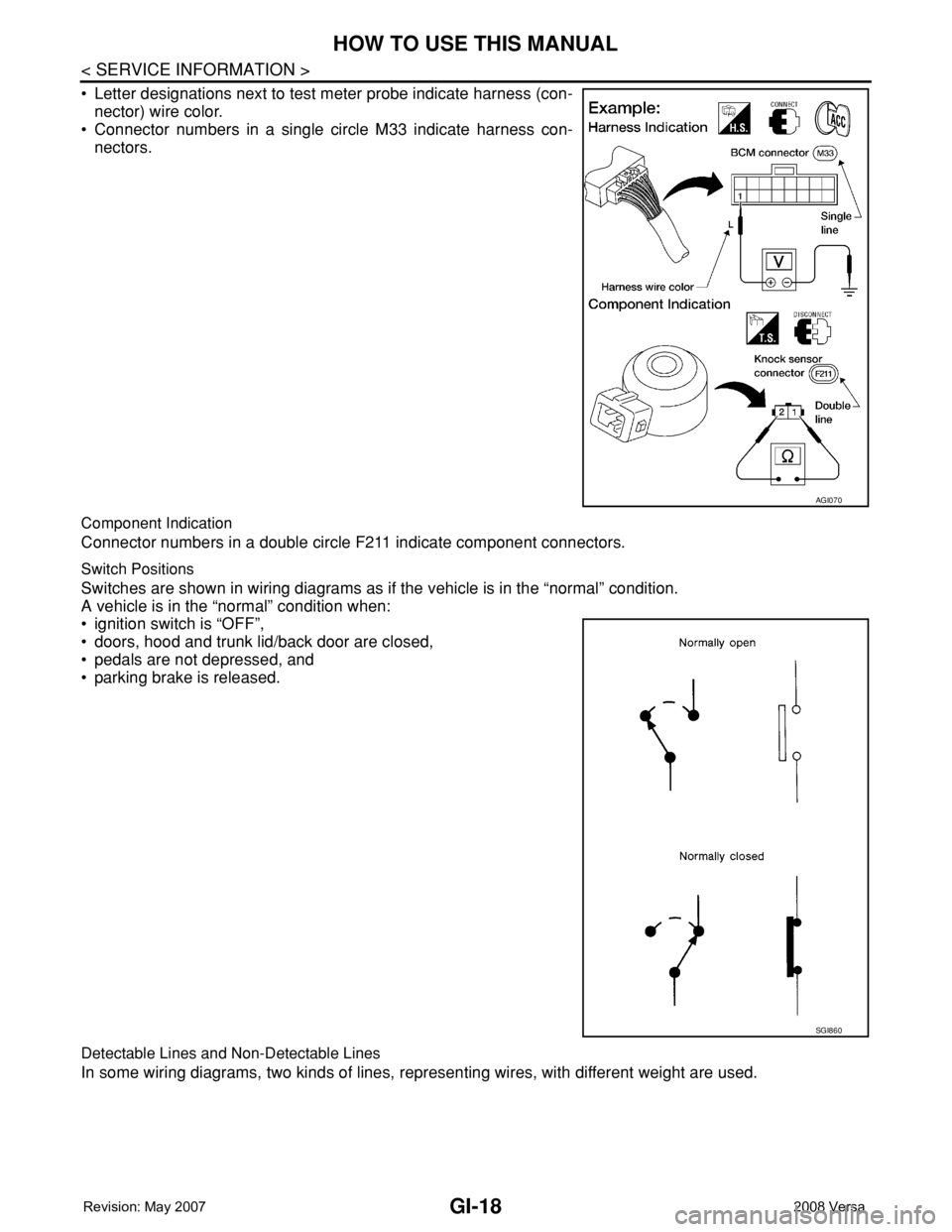
• Letter designations next to test meter probe indicate harness (con-
nector) wire color.
• Connector numbers in a single circle M33 indicate harness con-
nectors.
Component Indication
Connector numbers in a double circle F211 indicate component connectors.
Switch Positions
Switches are shown in wiring diagrams as if the vehicle is in the “normal” condition.
A vehicle is in the “normal” condition when:
• ignition switch is “OFF”,
• doors, hood and trunk lid/back door are closed,
• pedals are not depressed, and
• parking brake is released.
Detectable Lines and Non-Detectable Lines
In some wiring diagrams, two kinds of lines, representing wires, with different weight are used.
AGI070
SGI860
Page 1880 of 2771
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
GI-29
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
N
O
P
• Close the relay and probe at the solenoid.
voltage; open is further down the circuit than the solenoid.
no voltage; open is between relay and solenoid (point C).
Any powered circuit can be diagnosed using the approach in the previous example.
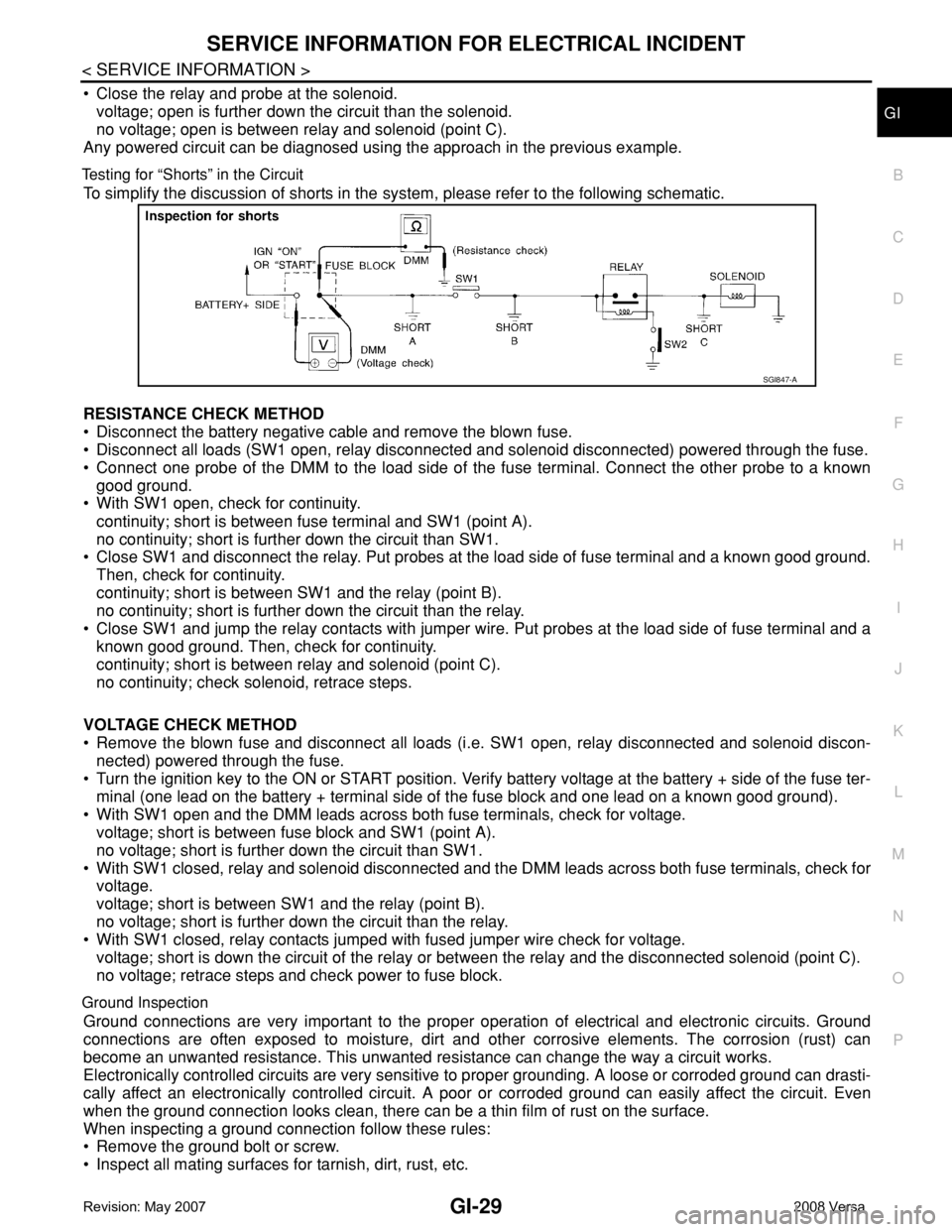
Testing for “Shorts” in the Circuit
To simplify the discussion of shorts in the system, please refer to the following schematic.
RESISTANCE CHECK METHOD
• Disconnect the battery negative cable and remove the blown fuse.
• Disconnect all loads (SW1 open, relay disconnected and solenoid disconnected) powered through the fuse.
• Connect one probe of the DMM to the load side of the fuse terminal. Connect the other probe to a known
good ground.
• With SW1 open, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between fuse terminal and SW1 (point A).
no continuity; short is further down the circuit than SW1.
• Close SW1 and disconnect the relay. Put probes at the load side of fuse terminal and a known good ground.
Then, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between SW1 and the relay (point B).
no continuity; short is further down the circuit than the relay.
• Close SW1 and jump the relay contacts with jumper wire. Put probes at the load side of fuse terminal and a
known good ground. Then, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between relay and solenoid (point C).
no continuity; check solenoid, retrace steps.
VOLTAGE CHECK METHOD
• Remove the blown fuse and disconnect all loads (i.e. SW1 open, relay disconnected and solenoid discon-
nected) powered through the fuse.
• Turn the ignition key to the ON or START position. Verify battery voltage at the battery + side of the fuse ter-
minal (one lead on the battery + terminal side of the fuse block and one lead on a known good ground).
• With SW1 open and the DMM leads across both fuse terminals, check for voltage.
voltage; short is between fuse block and SW1 (point A).
no voltage; short is further down the circuit than SW1.
• With SW1 closed, relay and solenoid disconnected and the DMM leads across both fuse terminals, check for
voltage.
voltage; short is between SW1 and the relay (point B).
no voltage; short is further down the circuit than the relay.
• With SW1 closed, relay contacts jumped with fused jumper wire check for voltage.
voltage; short is down the circuit of the relay or between the relay and the disconnected solenoid (point C).
no voltage; retrace steps and check power to fuse block.
Ground Inspection
Ground connections are very important to the proper operation of electrical and electronic circuits. Ground
connections are often exposed to moisture, dirt and other corrosive elements. The corrosion (rust) can
become an unwanted resistance. This unwanted resistance can change the way a circuit works.
Electronically controlled circuits are very sensitive to proper grounding. A loose or corroded ground can drasti-
cally affect an electronically controlled circuit. A poor or corroded ground can easily affect the circuit. Even
when the ground connection looks clean, there can be a thin film of rust on the surface.
When inspecting a ground connection follow these rules:
• Remove the ground bolt or screw.
• Inspect all mating surfaces for tarnish, dirt, rust, etc.
SGI847-A
Page 1886 of 2771

CONSULT-III CHECKING SYSTEM
GI-35
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
N
O
PCONSULT-III CHECKING SYSTEM
DescriptionINFOID:0000000001806209
• CONSULT-III is a hand-held type tester. When it is connected with a diagnostic connector equipped on the
vehicle side, it will communicate with the control unit equipped in the vehicle and then enable various kinds
of diagnostic tests.
• Refer to CONSULT-III Operator's Manual for more information.
Function and System ApplicationINFOID:0000000001806219
x: Applicable.
*1: If equipped.
*2: This option is shown on vehicles equipped with continuously variable transmission (CVT).
*3: NVIS (NATS) [NISSAN Vehicle Immobilizer System (Nissan Anti-theft System)]. Diagnostic test mode Function
ENGINE
ABS*
1
AIR BAG
EPS
IPDM E/R
BCM
METER/M&A
INTELLIGENT KEY*
1
A/T*
1
TRANSMISSION*
2
NVIS (NATS)*
3
NVIS (NATS BCM OR S/ENT)*
3
NATS I-KEY
*3,5
Work supportThis mode enables a technician to adjust some devices faster
and more accurately by following indications on CONSULT-III.x----x-xxx--x
Self-diagnostic results Self-diagnostic results can be read and erased quickly. xxxxxxxxxxx - x
Trouble diagnostic
recordCurrent self-diagnostic results and all trouble diagnostic records
previously stored can be read.--x----------
Data monitor Input/Output data in the ECU can be read. xx - xx - xxxx - - -
CAN diagnostic support
monitorThe communication condition of CAN communication line can
be read.xx - xxxxxxx - - -
Calibration data*
2Shows unit calibration IDs, offsets and gains. This data is stored
in the ECU memory.---------x---
Active testDiagnostic Test Mode in which CONSULT-III drives actuators
apart from ECU shifting some parameters in a specified range.xx--x--x-----
Function testThis mode can show results of self-diagnosis of ECU with either
"OK" or "NG". For engines, more practical tests regarding sen-
sors/switches and/or actuators are available.xxx-----xx---
DTC & SRT confirmationThe results of SRT (System Readiness Test) and the self-diag-
nosis status/result can be confirmed.x------------
DTC work supportThe operating condition to confirm Diagnosis Trouble Codes
can be selected.x-------x----
ECM/ECU part number ECM/ECU part number can be read. x x - x - x - x x x - - -
ECU discriminated No.Classification number of a replacement ECU can be read to pre-
vent an incorrect ECU from being installed.--x----------
Passenger airbag Displays the STATUS (readiness) of front passenger air bag. --x----------
Configuration Sets control module parameters to match vehicle options. -----x-------
Steering lock release
*4,5Condition of steering lock release solenoid. -----------x-
Control unit initializa-
tion
*4,6All registered ignition key IDs in NATS components can be ini-
tialized and new IDs can be registered.----------x--
PIN Read
*4This mode enables technician to get BCM-specific 5-digit code.-----------x-
Page 1898 of 2771

TERMINOLOGY
GI-47
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
N
O
PTERMINOLOGY
SAE J1930 Terminology ListINFOID:0000000001702459
All emission related terms used in this publication in accordance with SAE J1930 are listed. Accordingly, new
terms, new acronyms/abbreviations and old terms are listed in the following chart.
NEW TERMNEW ACRONYM /
ABBREVIATIONOLD TERM
Air cleaner ACL Air cleaner
Barometric pressure BARO ***
Barometric pressure sensor-BCDD BAROS-BCDD BCDD
Camshaft position CMP ***
Camshaft position sensor CMPS Crank angle sensor
Canister *** Canister
Carburetor CARB Carburetor
Charge air cooler CAC Intercooler
Closed loop CL Closed loop
Closed throttle position switch CTP switch Idle switch
Clutch pedal position switch CPP switch Clutch switch
Continuous fuel injection system CFI system ***
Continuous trap oxidizer system CTOX system ***
Crankshaft position CKP ***
Crankshaft position sensor CKPS ***
Data link connector DLC ***
Data link connector for CONSULT-III DLC for CONSULT-III Diagnostic connector for CONSULT-III
Diagnostic test mode DTM Diagnostic mode
Diagnostic test mode selector DTM selector Diagnostic mode selector
Diagnostic test mode I DTM I Mode I
Diagnostic test mode II DTM II Mode II
Diagnostic trouble code DTC Malfunction code
Direct fuel injection system DFI system ***
Distributor ignition system DI system Ignition timing control
Early fuel evaporation-mixture heater EFE-mixture heater Mixture heater
Early fuel evaporation system EFE system Mixture heater control
Electrically erasable programmable read
only memoryEEPROM ***
Electronic ignition system EI system Ignition timing control
Engine control EC ***
Engine control module ECM ECCS control unit
Engine coolant temperature ECT Engine temperature
Engine coolant temperature sensor ECTS Engine temperature sensor
Engine modification EM ***
Engine speed RPM Engine speed
Erasable programmable read only memory EPROM ***
Evaporative emission canister EVAP canister Canister
Evaporative emission system EVAP system Canister control solenoid valve
Exhaust gas recirculation valve EGR valve EGR valve
Page 1899 of 2771
GI-48
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
TERMINOLOGY
Exhaust gas recirculation control-BPT
valveEGRC-BPT valve BPT valve
Exhaust gas recirculation control-solenoid
valveEGRC-solenoid valve EGR control solenoid valve
Exhaust gas recirculation temperature sen-
sor
EGRT sensor Exhaust gas temperature sensor
EGR temperature sensor
Flash electrically erasable programmable
read only memoryFEEPROM ***
Flash erasable programmable read only
memoryFEPROM ***
Flexible fuel sensor FFS ***
Flexible fuel system FF system ***
Fuel pressure regulator *** Pressure regulator
Fuel pressure regulator control solenoid
valve*** PRVR control solenoid valve
Fuel trim FT ***
Heated Oxygen sensor HO2S Exhaust gas sensor
Idle air control system IAC system Idle speed control
Idle air control valve-air regulator IACV-air regulator Air regulator
Idle air control valve-auxiliary air control
valveIACV-AAC valve Auxiliary air control (AAC) valve
Idle air control valve-FICD solenoid valve IACV-FICD solenoid valve FICD solenoid valve
Idle air control valve-idle up control sole-
noid valveIACV-idle up control solenoid valve Idle up control solenoid valve
Idle speed control-FI pot ISC-FI pot FI pot
Idle speed control system ISC system ***
Ignition control IC ***
Ignition control module ICM ***
Indirect fuel injection system IFI system ***
Intake air IA Air
Intake air temperature sensor IAT sensor Air temperature sensor
Knock *** Detonation
Knock sensor KS Detonation sensor
Malfunction indicator lamp MIL Check engine light
Manifold absolute pressure MAP ***
Manifold absolute pressure sensor MAPS ***
Manifold differential pressure MDP ***
Manifold differential pressure sensor MDPS ***
Manifold surface temperature MST ***
Manifold surface temperature sensor MSTS ***
Manifold vacuum zone MVZ ***
Manifold vacuum zone sensor MVZS ***
Mass air flow sensor MAFS Air flow meter
Mixture control solenoid valve MC solenoid valve Air-fuel ratio control solenoid valve
Multiport fuel injection System MFI system Fuel injection controlNEW TERMNEW ACRONYM /
ABBREVIATIONOLD TERM
Page 1919 of 2771
GW-18
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
POWER WINDOW SYSTEM
POWER WINDOW SYSTEM
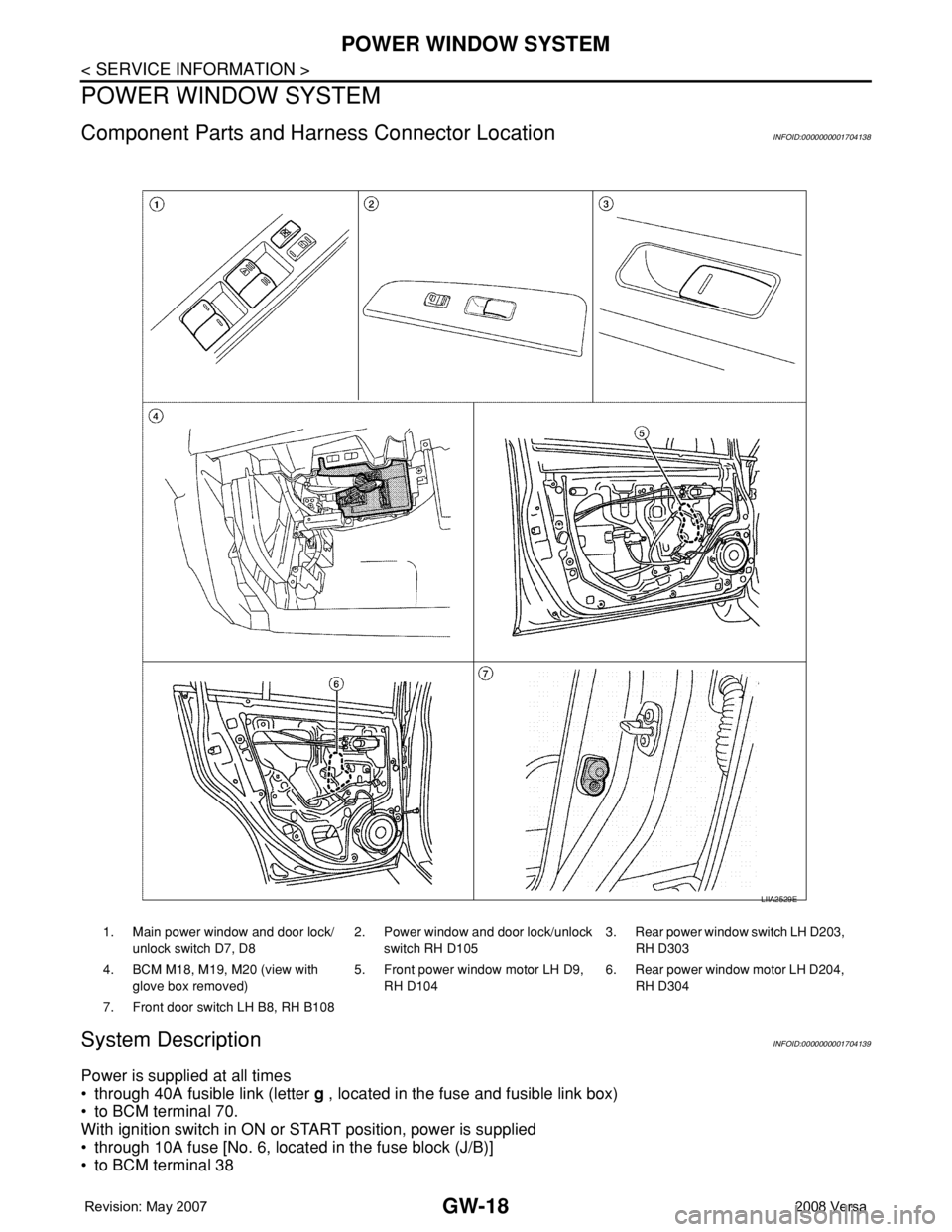
Component Parts and Harness Connector LocationINFOID:0000000001704138
System DescriptionINFOID:0000000001704139
Power is supplied at all times
• through 40A fusible link (letter g , located in the fuse and fusible link box)
• to BCM terminal 70.
With ignition switch in ON or START position, power is supplied
• through 10A fuse [No. 6, located in the fuse block (J/B)]
• to BCM terminal 38
1. Main power window and door lock/
unlock switch D7, D82. Power window and door lock/unlock
switch RH D1053. Rear power window switch LH D203,
RH D303
4. BCM M18, M19, M20 (view with
glove box removed)5. Front power window motor LH D9,
RH D1046. Rear power window motor LH D204,
RH D304
7. Front door switch LH B8, RH B108
LIIA2529E
Page 1920 of 2771

POWER WINDOW SYSTEM
GW-19
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
MA
B
GW
N
O
P
• through BCM terminal 68
• to main power window and door lock/unlock switch terminal 10
• to power window and door lock/unlock switch RH terminal 8 and
• to rear power window switches LH and RH terminal 1.
Ground is supplied
• to BCM terminal 67
• to main power window and door lock/unlock switch terminal 17 and
• to power window and door lock/unlock switch RH terminal 3
• through body grounds M57 and M61.
With ignition switch in ACC or ON position, power is supplied
• through 10A fuse [No. 20, located in the fuse block (J/B)]
• to BCM terminal 11.
MANUAL OPERATION
Front Door LH
WINDOW UP
When the front LH switch in the main power window and door lock/unlock switch is pulled in the up position,
power is supplied
• through main power window and door lock/unlock switch terminal 8
• to front power window motor LH terminal 2.
Ground is supplied
• through main power window and door lock/unlock switch terminal 11
• to front power window motor LH terminal 3.
Then, the motor raises the window until the switch is released.
WINDOW DOWN
When the front LH switch in the main power window and door lock/unlock switch is pressed in the down posi-
tion, power is supplied
• through main power window and door lock/unlock switch terminal 11
• to front power window motor LH terminal 3.
Ground is supplied
• through main power window and door lock/unlock switch terminal 8
• to front power window motor LH terminal 2.
Then, the motor lowers the window until the switch is released.
Front Door RH
POWER WINDOW AND DOOR LOCK/UNLOCK SWITCH RH OPERATION
WINDOW UP
When the power window and door lock/unlock switch RH is pulled in the up position, power is supplied
• through power window and door lock/unlock switch RH terminal 7
• to front power window motor RH terminal 2.
Ground is supplied
• through power window and door lock/unlock switch RH terminal 6
• to front power window motor RH terminal 1.
Then, the motor raises the window until the switch is released.
WINDOW DOWN
When the power window and door lock/unlock switch RH is pressed in the down position, power is supplied
• through power window and door lock/unlock switch RH terminal 6
• to front power window motor RH terminal 1.
Ground is supplied
• through power window and door lock/unlock switch RH terminal 7
• to front power window motor RH terminal 2.
Then, the motor lowers the window until the switch is released.
MAIN POWER WINDOW AND DOOR LOCK/UNLOCK SWITCH OPERATION
WINDOW UP
When the main power window and door lock/unlock switch (front RH) is pulled in the up position, power is sup-
plied
• through main power window and door lock/unlock switch terminal 16
• to power window and door lock/unlock switch RH terminal 12
• through power window and door lock/unlock switch RH terminal 7
• to front power window motor RH terminal 2.
Ground is supplied