2008 INFINITI FX35 wiring
[x] Cancel search: wiringPage 2875 of 3924

HOW TO USE THIS MANUALGI-13
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
DE
F
G H
I
J
K L
M B
GI
N
O P
How to Read Wiring DiagramINFOID:0000000001325669
CONNECTOR SYMBOLS
Most of connector symbols in wiring diagrams are shown from the terminal side.
SAIA1540E
3AA93ABC3ACD3AC03ACA3AC03AC63AC53A913A773A893A873A873A8E3A773A983AC73AC93AC03AC3
3A893A873A873A8F3A773A9D3AAF3A8A3A8C3A863A9D3AAF3A8B3A8C
Page 2876 of 3924
GI-14
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
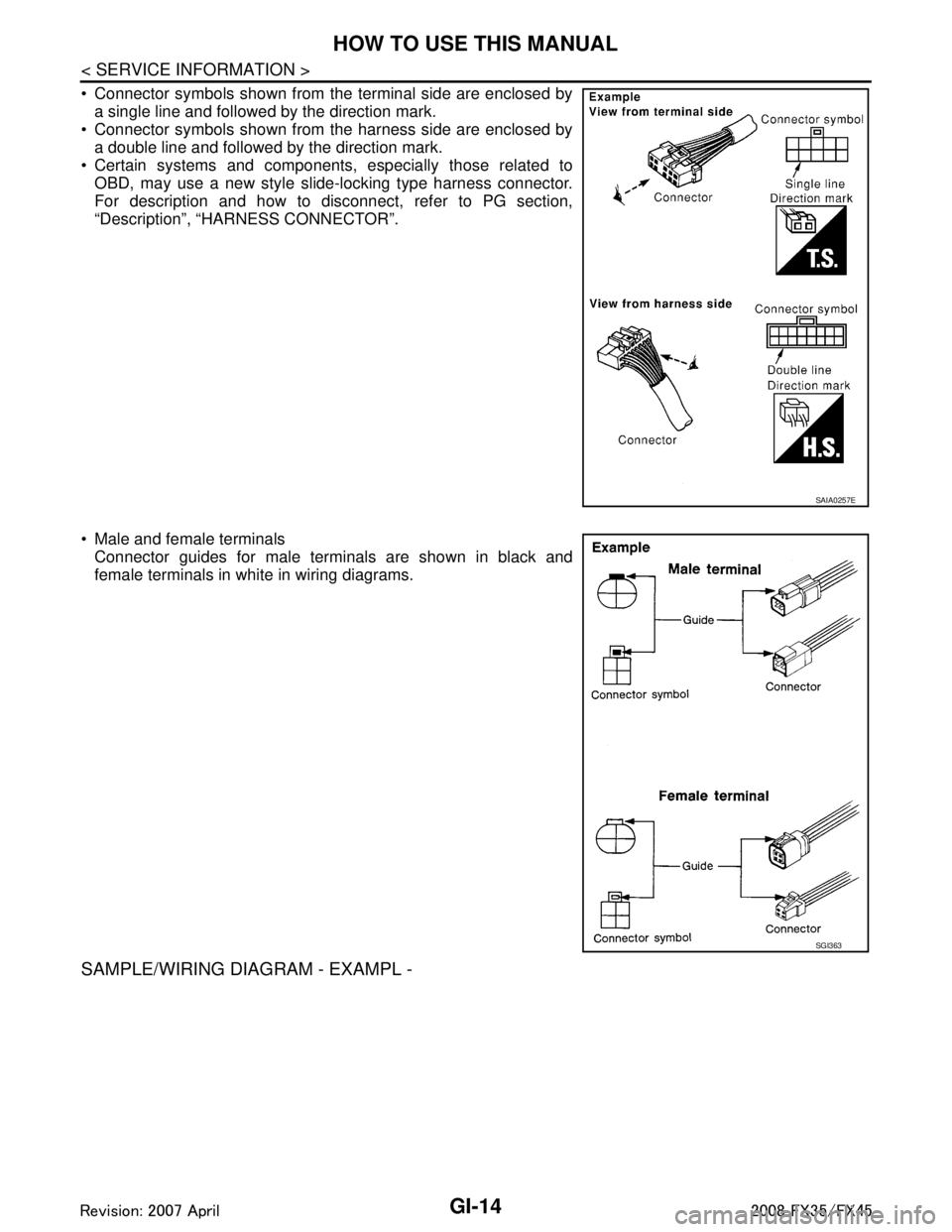
Connector symbols shown from the terminal side are enclosed bya single line and followed by the direction mark.
Connector symbols shown from the harness side are enclosed by
a double line and followed by the direction mark.
Certain systems and components, especially those related to OBD, may use a new style slide-locking type harness connector.
For description and how to disconnect, refer to PG section,
“Description”, “HARNESS CONNECTOR”.
Male and female terminals Connector guides for male terminals are shown in black and
female terminals in white in wiring diagrams.
SAMPLE/WIRING DIAGRAM - EXAMPL -
SAIA0257E
SGI363
3AA93ABC3ACD3AC03ACA3AC03AC63AC53A913A773A893A873A873A8E3A773A983AC73AC93AC03AC3
3A893A873A873A8F3A773A9D3AAF3A8A3A8C3A863A9D3AAF3A8B3A8C
Page 2879 of 3924

HOW TO USE THIS MANUALGI-17
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
DE
F
G H
I
J
K L
M B
GI
N
O P
Harness Indication
14 Wire color This shows a code for the color of the wire.
B = Black
W = White
R = Red
G = Green
L = Blue
Y = Yellow
LG = Light Green BR = Brown
OR or O = Orange
P = Pink
PU or V (Violet) = Purple
GY or GR = Gray
SB = Sky Blue
CH = Dark Brown
DG = Dark Green
When the wire color is striped, the base color is given first, followed by the stripe color as shown
below:
Example: L/W = Blue with White Stripe
15 Option description This shows a description of the option abbreviation used on the page.
16 Switch This shows that continuity exists between terminals 1 and 2 when the switch is in the A posi-
tion. Continuity exists between terminals 1 and 3 when the switch is in the B position.
17 Assembly parts Connector terminal in component shows that it is a harness incorporated assembly.
18 Cell code This identifies each page of the wiring diagram by section, system and wiring diagram page
number.
19 Current flow arrow Arrow indicates electric current flow, especially where the direction of standard flow (vertically
downward or horizontally from left to right) is difficult to follow.
A double arrow “ ” shows that current can flow in either direction depending on circuit operation.
20 System branch This shows that the system branches to another system identified by cell code (section and
system).
21 Page crossing This arrow shows that the circuit continues to another page identified by cell code.
The C will match with the C on another page within the system other than the next or preceding
pages.
22 Shielded line The line enclosed by broken line circle shows shield wire.
23 Component box in
wave line This shows that another part of the component is also shown on another page (indicated by
wave line) within the system.
24 Component name This shows the name of a component.
25 Connector number This shows the connector number.
The letter shows which harness the connector is located in.
Example:
M: main harness. For detail and to locate the connector, refer to PG section "Main
Harness", “Harness Layout”. A coordinate grid is included for complex harnesses to aid in lo-
cating connectors.
26 Ground (GND) The line spliced and grounded under wire color shows that ground line is spliced at the ground-
ed connector.
27 Ground (GND) This shows the ground connection. For detailed ground distribution information, refer to
"Ground Distribution" in PG section.
28 Connector views This area shows the connector faces of the components in the wiring diagram on the page.
29 Common component Connectors enclosed in broken line show that these connectors belong to the same compo-
nent.
30 Connector color This shows a code for the color of the connector. For code meaning, refer to wire color codes,
Number 14 of this chart.
31 Fusible link and fuse
box This shows the arrangement of fusible link(s) and fuse(s), used for connector views of "POW-
ER SUPPLY ROUTING" in PG section.
The open square shows current flow in, and the shaded square shows current flow out.
32 Reference area This shows that more information on the Super Multiple Junction (SMJ) and Joint Connectors
(J/C) exists on the PG section. Refer to "Reference Area" for details.
Num-
ber Item Description
3AA93ABC3ACD3AC03ACA3AC03AC63AC53A913A773A893A873A873A8E3A773A983AC73AC93AC03AC3
3A893A873A873A8F3A773A9D3AAF3A8A3A8C3A863A9D3AAF3A8B3A8C
Page 2880 of 3924
GI-18
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
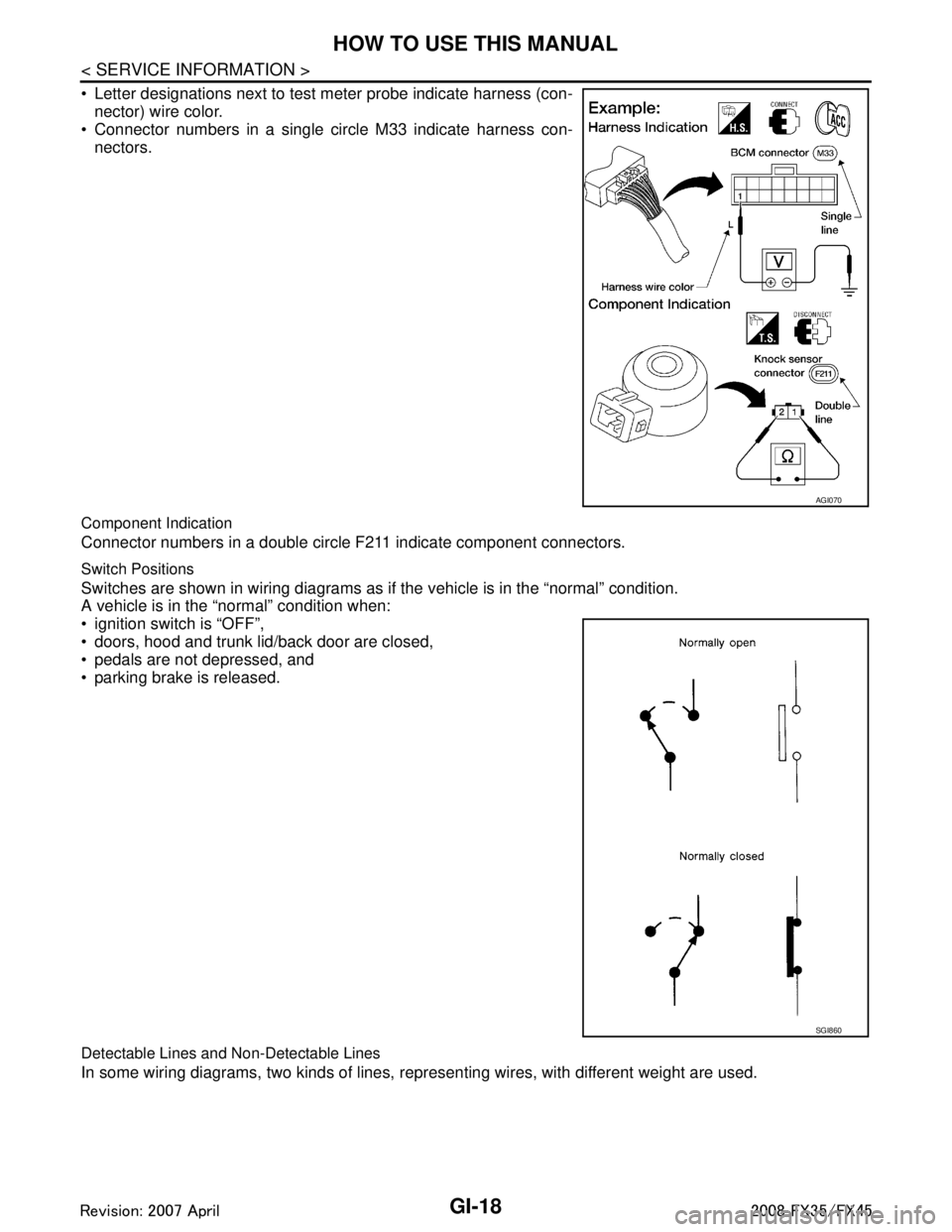
Letter designations next to test meter probe indicate harness (con-nector) wire color.
Connector numbers in a single circle M33 indicate harness con-
nectors.
Component Indication
Connector numbers in a double circle F211 indicate component connectors.
Switch Positions
Switches are shown in wiring diagrams as if the vehicle is in the “normal” condition.
A vehicle is in the “normal” condition when:
ignition switch is “OFF”,
doors, hood and trunk lid/back door are closed,
pedals are not depressed, and
parking brake is released.
Detectable Lines and Non-Detectable Lines
In some wiring diagrams, two kinds of lines, r epresenting wires, with different weight are used.
AGI070
SGI860
3AA93ABC3ACD3AC03ACA3AC03AC63AC53A913A773A893A873A873A8E3A773A983AC73AC93AC03AC3
3A893A873A873A8F3A773A9D3AAF3A8A3A8C3A863A9D3AAF3A8B3A8C
Page 2881 of 3924
HOW TO USE THIS MANUALGI-19
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
DE
F
G H
I
J
K L
M B
GI
N
O P
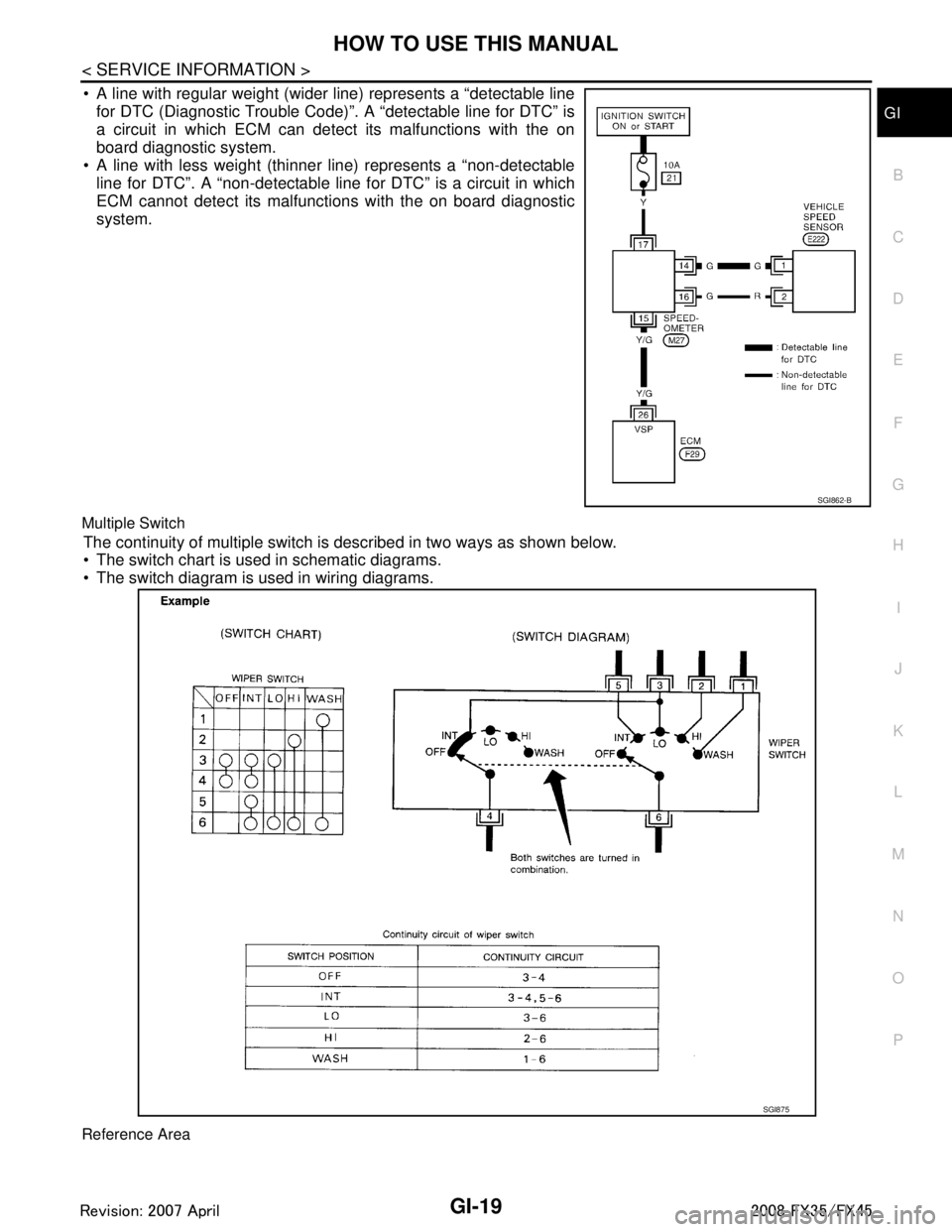
A line with regular weight (wider line) represents a “detectable line for DTC (Diagnostic Trouble Code)”. A “detectable line for DTC” is
a circuit in which ECM can detect its malfunctions with the on
board diagnostic system.
A line with less weight (thinner line) represents a “non-detectable line for DTC”. A “non-detectable line for DTC” is a circuit in which
ECM cannot detect its malfunctions with the on board diagnostic
system.
Multiple Switch
The continuity of multiple switch is described in two ways as shown below.
The switch chart is used in schematic diagrams.
The switch diagram is used in wiring diagrams.
Reference Area
SGI862-B
SGI875
3AA93ABC3ACD3AC03ACA3AC03AC63AC53A913A773A893A873A873A8E3A773A983AC73AC93AC03AC3
3A893A873A873A8F3A773A9D3AAF3A8A3A8C3A863A9D3AAF3A8B3A8C
Page 2882 of 3924
GI-20
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
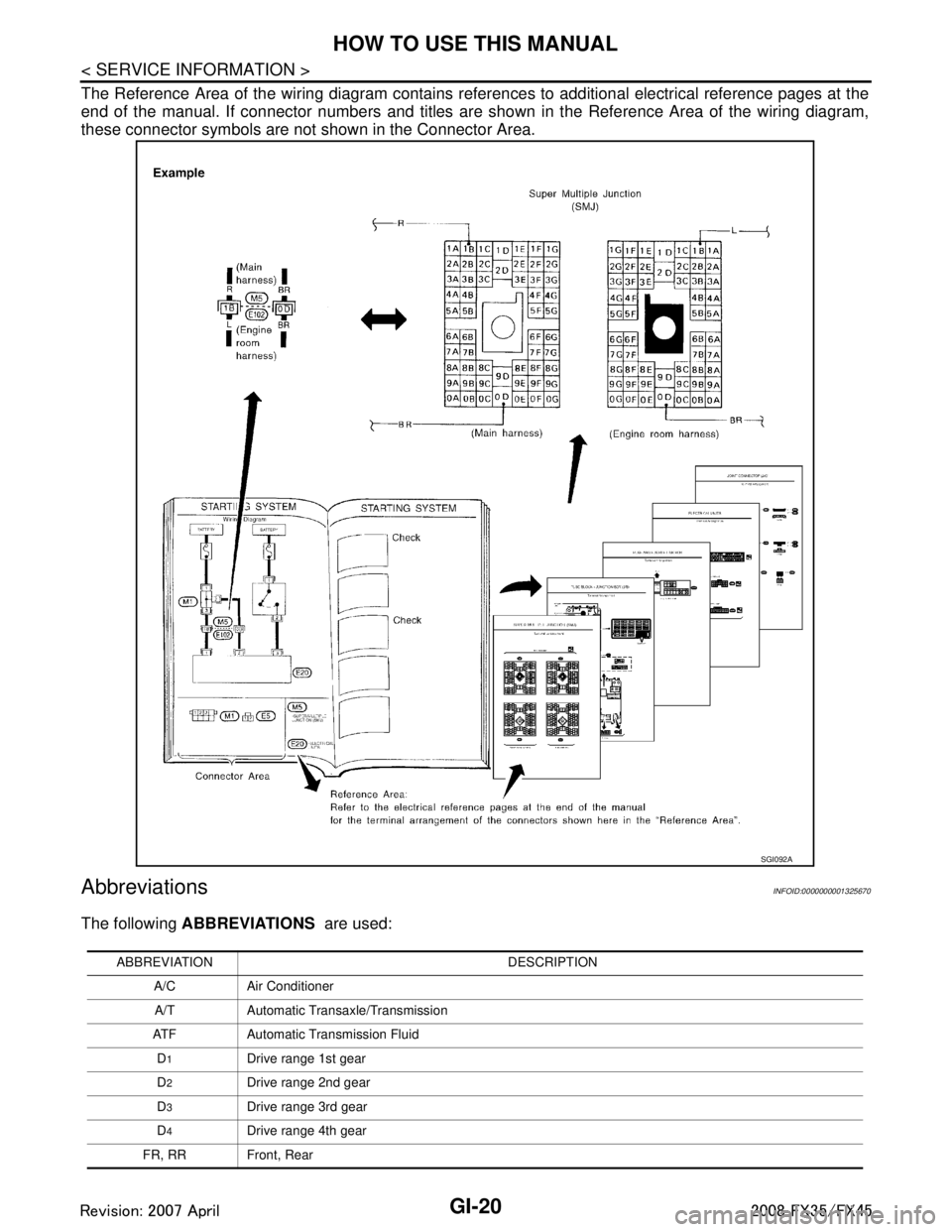
The Reference Area of the wiring diagram contains references to additional electrical reference pages at the
end of the manual. If connector numbers and titles are s hown in the Reference Area of the wiring diagram,
these connector symbols are not shown in the Connector Area.
AbbreviationsINFOID:0000000001325670
The following ABBREVIATIONS are used:
SGI092A
ABBREVIATION DESCRIPTION
A/C Air ConditionerA/T Automatic Transaxle/Transmission
ATF Automatic Transmission Fluid D
1Drive range 1st gear
D
2Drive range 2nd gear
D
3Drive range 3rd gear
D
4Drive range 4th gear
FR, RR Front, Rear
3AA93ABC3ACD3AC03ACA3AC03AC63AC53A913A773A893A873A873A8E3A773A983AC73AC93AC03AC3
3A893A873A873A8F3A773A9D3AAF3A8A3A8C3A863A9D3AAF3A8B3A8C
Page 2887 of 3924

SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENTGI-25
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
DE
F
G H
I
J
K L
M B
GI
N
O P
How to Perform Efficient Diagnos is for an Electrical IncidentINFOID:0000000001325672
WORK FLOW
INCIDENT SIMULATION TESTS
Introduction
Sometimes the symptom is not present when the vehicle is brought in for service. If possible, re-create the
conditions present at the time of the incident. Doi ng so may help avoid a No Trouble Found Diagnosis. The fol-
lowing section illustrates ways to simulate the c onditions/environment under which the owner experiences an
electrical incident.
The section is broken into the six following topics:
Vehicle vibration
Heat sensitive
Freezing
Water intrusion
Electrical load
SGI838
STEP DESCRIPTION
STEP 1 Get detailed information about the conditions and the environment when the incident occurred.
The following are key pieces of information required to make a good analysis:
WHAT
Vehicle Model, Engine, Transmission/Transaxle and the System (i.e. Radio).
WHEN Date, Time of Day, Weather Conditions, Frequency.
WHERE Road Conditions, Altitude and Traffic Situation.
HOW System Symptoms, Operating Conditions (Other Components Interaction).
Service History and if any After Market Accessories have been installed.
STEP 2 Operate the system, road test if necessary.
Verify the parameter of the incident.
If the problem cannot be duplicated, refer to “Incident Simulation Tests”.
STEP 3 Get the proper diagnosis materials together including:
Power Supply Routing
System Operation Descriptions
Applicable Service Manual Sections
Check for any Service Bulletins
Identify where to begin diagnosis based upon your knowledge of the system operation and the customer comments.
STEP 4 Inspect the system for mechanical binding, loose connectors or wiring damage.
Determine which circuits and components are involved and diagnose using the Power Supply Routing and Harness Lay-
outs.
STEP 5 Repair or replace the incident circuit or component.
STEP 6 Operate the system in all modes. Verify the system works properly under all conditions. Make sure you have not inad-
vertently created a new incident during your diagnosis or repair steps.
3AA93ABC3ACD3AC03ACA3AC03AC63AC53A913A773A893A873A873A8E3A773A983AC73AC93AC03AC3
3A893A873A873A8F3A773A9D3AAF3A8A3A8C3A863A9D3AAF3A8B3A8C
Page 2888 of 3924
GI-26
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Cold or hot start up
Get a thorough description of the incident from the customer. It is important for simulating the conditions of the
problem.
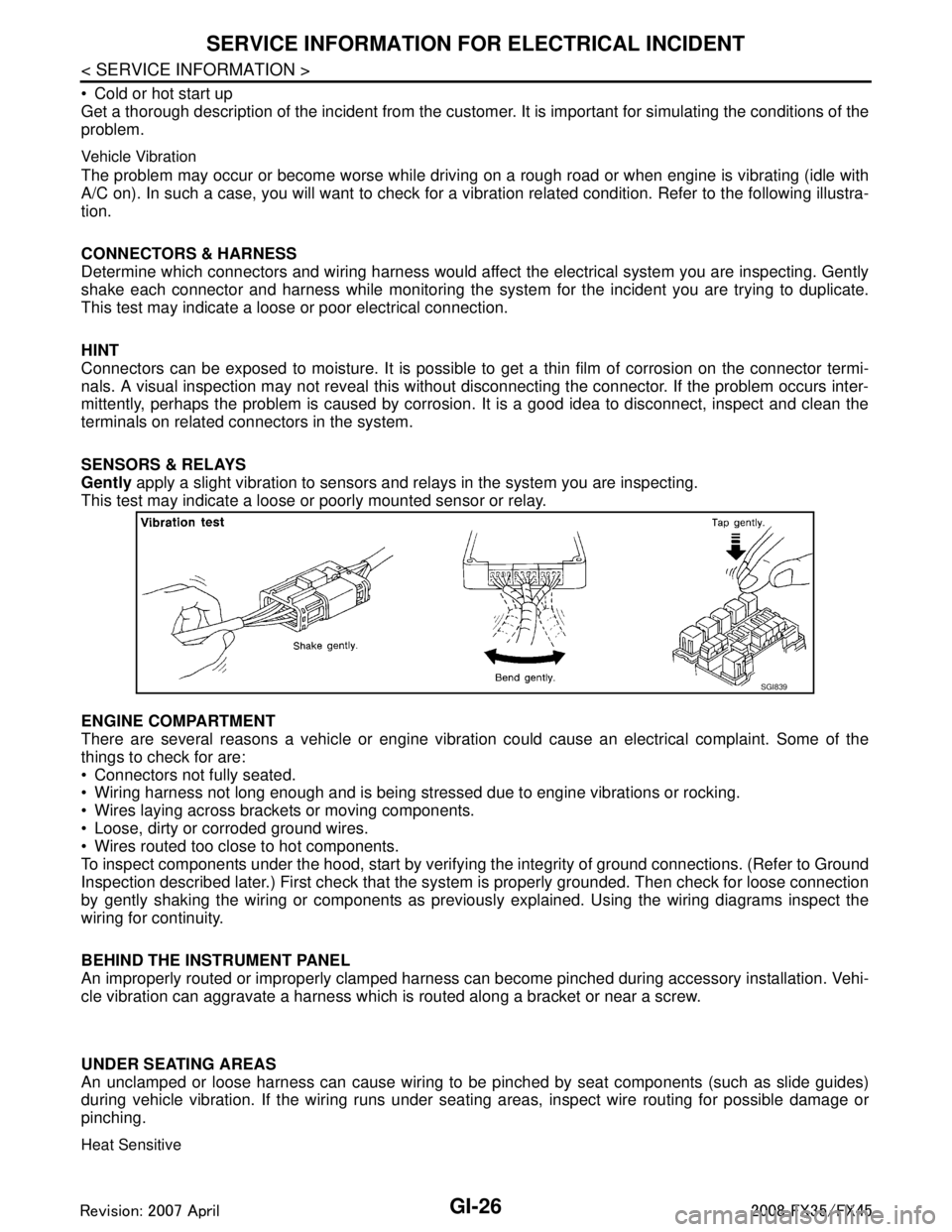
Vehicle Vibration
The problem may occur or become worse while drivi ng on a rough road or when engine is vibrating (idle with
A/C on). In such a case, you will want to check for a vi bration related condition. Refer to the following illustra-
tion.
CONNECTORS & HARNESS
Determine which connectors and wiring harness would affect the electrical system you are inspecting. Gently
shake each connector and harness while monitoring the sy stem for the incident you are trying to duplicate.
This test may indicate a loose or poor electrical connection.
HINT
Connectors can be exposed to moisture. It is possible to get a thin film of corrosion on the connector termi-
nals. A visual inspection may not reveal this without disconnecting the connector. If the problem occurs inter-
mittently, perhaps the problem is caused by corrosion. It is a good idea to disconnect, inspect and clean the
terminals on related connectors in the system.
SENSORS & RELAYS
Gently apply a slight vibration to sensors and relays in the system you are inspecting.
This test may indicate a loose or poorly mounted sensor or relay.
ENGINE COMPARTMENT
There are several reasons a vehicle or engine vibration could cause an e\
lectrical complaint. Some of the
things to check for are:
Connectors not fully seated.
Wiring harness not long enough and is being stressed due to engine vibrations or rocking.
Wires laying across brackets or moving components.
Loose, dirty or corroded ground wires.
Wires routed too close to hot components.
To inspect components under the hood, start by verifyi ng the integrity of ground connections. (Refer to Ground
Inspection described later.) First check that the system is properly grounded. Then check for loose connection
by gently shaking the wiring or components as previous ly explained. Using the wiring diagrams inspect the
wiring for continuity.
BEHIND THE INSTRUMENT PANEL
An improperly routed or improperly clamped harness can become pinched during accessory installation. Vehi-
cle vibration can aggravate a harness which is routed along a bracket or near a screw.
UNDER SEATING AREAS
An unclamped or loose harness can cause wiring to be pinched by seat components (such as slide guides)
during vehicle vibration. If the wiring runs under s eating areas, inspect wire routing for possible damage or
pinching.
Heat Sensitive
SGI839
3AA93ABC3ACD3AC03ACA3AC03AC63AC53A913A773A893A873A873A8E3A773A983AC73AC93AC03AC3
3A893A873A873A8F3A773A9D3AAF3A8A3A8C3A863A9D3AAF3A8B3A8C