Page 423 of 1449
ENGINE -Camshaft and Camshaft Oil Seal11A-17
2
3 45
67 8
9
1012
11
11±1 N·m
8.8±1.0 N·m3.5±0.5 N·m
5.0±1.0 N·m
13
3.0±0.5 N·m
1
11±1 N·m
Removal steps
1. Accelerator cable connection
2. Center cover
DIgnition coil
(Refer to Group 16 - Ignition System.)
3. Crank angle sensor connector
4. Oxygen sensor connector
5. Control wiring harness connection6. Camshaft position sensor connector
7. Breather hose
8. PCV hose
"KA9. Rocker cover
"JA10. Camshaft end seal
11. Spark plug hole gasket
"IA12. Rocker cover gasket
AA""HA13. Radiator upper hose connection
Page 435 of 1449
ENGINE -Cylinder Head Gasket11A-29
5.0±1.0 N·m
61
2
3 4
57
8
910
11 12
1314
13±1 N·m
15
16
17
5.0±1.0 N·m
1819
9.0±1.0 N·m
9.0±1.0 N·m
(Engine oil)
1
Removal steps
1. Ignition coil connector
2. Crank angle sensor connector
3. Oxygen sensor connector
4. Fuel pressure solenoid valve
connector
5. Detonation sensor connector
6. Purge control solenoid valve
connector
7. Throttle position sensor connector
8. Idle speed control servo connector
9. Injector connector
10. Camshaft position sensor connector
11. Engine coolant temperature gauge
unit connector12. Engine coolant temperature sensor
connector
DRocker cover (Refer to P.11A-17.)
13. EGR solenoid valve connector
14. Secondary air control solenoid valve
connector
15. Vacuum tank, solenoid valve, vacuum
pipe and hose assembly
16. Brake booster vacuum hose
connection
17. Oil level gauge and guide assembly
18. O-ring
19. Purge hose connection
Page 450 of 1449
ENGINE -Engine Assembly11A-44
1
2
3 4
5
67
8
910
11 12
13
14
26±5 N·m
14±3 N·m
1516
18
5.0±1.0 N·m
1
5.0±1.0 N·m
11±1 N·m
17
Removal steps
1. Ignition coil connector
2. Crank angle sensor connector
3. Oxygen sensor connector
4. Fuel pressure solenoid valve
connector
5. Detonation sensor connector
6. Purge control solenoid valve
connector
7. Throttle position sensor connector
8. Idle speed control servo connector
9. Injector connector
10. Camshaft position sensor connector11. Engine coolant temperature gauge
unit connector
12. Engine coolant temperature sensor
connector
13. Alternator connector
14. EGR solenoid valve connector
15. Secondary air control solenoid valve
connector
16. Engine oil pressure switch
connector
17. Waste gate actuator mounting bolt
AA"18. Drive belt
Page 455 of 1449
11B-1
ENGINE
OVERHAUL
CONTENTS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION 2...................
SPECIFICATIONS 3..........................
Service Specifications 3.........................
Machining Standards 5.........................
Tightening Torque 5............................
Sealants 8.....................................
Form-In-Place Gasket 8........................
SPECIAL TOOLS 9...........................
ALTERNATOR AND IGNITION SYSTEM 12....
TIMING BELT 13.............................
FUEL SYSTEM 26............................SECONDARY AIR SYSTEM AND INTAKE
MANIFOLD 28...............................
EXHAUST MANIFOLD 30.....................
WATER PUMP AND WATER HOSE 32........
ROCKER ARMS AND CAMSHAFT 34.........
CYLINDER HEAD AND VALVE 40.............
OIL PUMP AND OIL PAN 47.................
PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD 56..........
CRANKSHAFT AND CYLINDER BLOCK 64....
Page 456 of 1449
ENGINE OVERHAUL -General Description11B-2
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
LIST OF MODELS
Vehicle nameVehicle modelEngine modelDisplacement mLSpecifications
LANCER Evolution VIICT9A4G63 - 72000DOHC 16 valve T/C
SPECIFICATIONS
ItemsSpecifications
Bore×stroke mm85×88
Total displacement mL1,997
Combustion chamber shapePentroof type
Number of cylinders4
Valve mechanismTypeDOHC
Intake valve2
Exhaust valve2
Lash adjusterHydraulic type
Rocker armRoller follower type
Compression ratio8.8
Fuel injection deviceElectronic control MPI
Ignition device typeElectronic control type 2-coil
Alternator typeAlternating current type (IC regulator built in)
Starter motor typeDeceleration drive
Page 459 of 1449
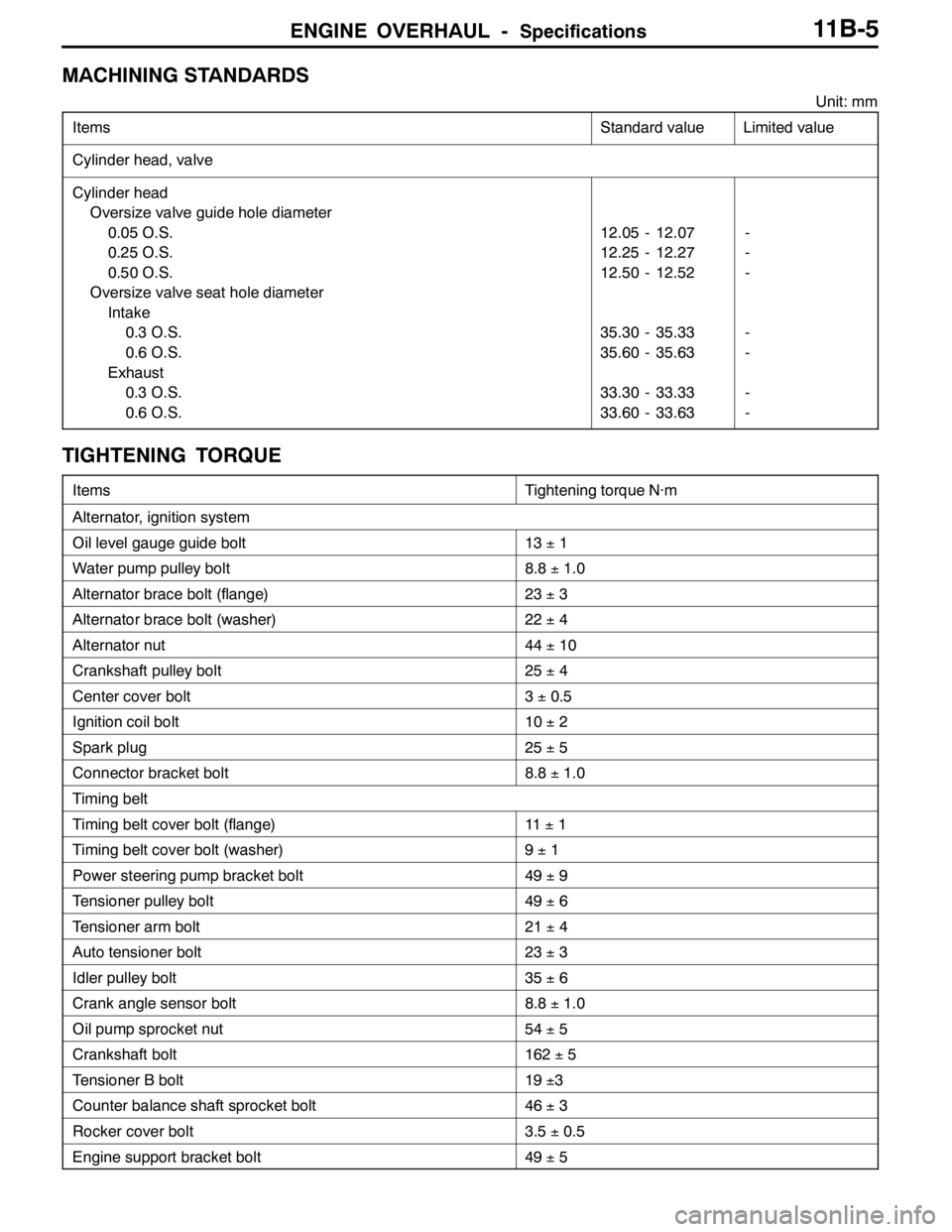
ENGINE OVERHAUL -Specifications11B-5
MACHINING STANDARDS
Unit: mm
Items
Standard valueLimited value
Cylinder head, valve
Cylinder head
Oversize valve guide hole diameter
0.05 O.S.
0.25 O.S.
0.50 O.S.
Oversize valve seat hole diameter
Intake
0.3 O.S.
0.6 O.S.
Exhaust
0.3 O.S.
0.6 O.S.
12.05 - 12.07
12.25 - 12.27
12.50 - 12.52
35.30 - 35.33
35.60 - 35.63
33.30 - 33.33
33.60 - 33.63-
-
-
-
-
-
-
TIGHTENING TORQUE
ItemsTightening torque N·m
Alternator, ignition system
Oil level gauge guide bolt13±1
Water pump pulley bolt8.8±1.0
Alternator brace bolt (flange)23±3
Alternator brace bolt (washer)22±4
Alternator nut44±10
Crankshaft pulley bolt25±4
Center cover bolt3±0.5
Ignition coil bolt10±2
Spark plug25±5
Connector bracket bolt8.8±1.0
Timing belt
Timing belt cover bolt (flange)11±1
Timing belt cover bolt (washer)9±1
Power steering pump bracket bolt49±9
Tensioner pulley bolt49±6
Tensioner arm bolt21±4
Auto tensioner bolt23±3
Idler pulley bolt35±6
Crank angle sensor bolt8.8±1.0
Oil pump sprocket nut54±5
Crankshaft bolt162±5
Tensioner B bolt19±3
Counter balance shaft sprocket bolt46±3
Rocker cover bolt3.5±0.5
Engine support bracket bolt49±5
Page 466 of 1449
ENGINE OVERHAUL -Alternator and Ignition System11B-12
ALTERNATOR AND IGNITION SYSTEM
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
1
13±1N•m
2
3
13
4
7
6
5
89
10
1211
22±4N•m8.8±1.0 N•m
25±5N•m 3±0.5 N•m
10±2N•m
8.8±1.0 N•m
23±3N•m
25±4N•m44±10 N•m
Removal steps
1. Oil level gauge
2. O-ring
3. Oil level gauge guide
4. O-ring
5. Water pump pulley
6. Alternator brace
7. Alternator8. Crankshaft pulley
9. Center cover
10. Spark plug cable
11. Ignition coil
12. Spark plug
13. Connector bracket
Page 535 of 1449

MPI -General Information13A-3
GENERAL INFORMATION
The Multipoint Fuel Injection System consists
of sensors which detect the engine conditions,
the engine-ECU which controls the system
based on signals from these sensors, and
actuators which operate under the control of
the engine-ECU. The engine-ECU carries outactivities such as fuel injection control, idle
speed control and ignition timing control. In
addition, the engine-ECU is equipped with
several diagnosis modes which simplify
troubleshooting when a problem develops.
FUEL INJECTION CONTROL
The injector drive times and injector timing are
controlled so that the optimum air/fuel mixture
is supplied to the engine to correspond to the
continually-changing engine operation condi-
tions.
A single injector is mounted at the intake port
of each cylinder. Fuel is sent under pressure
from the fuel tank by the fuel pump, with the
pressure being regulated by the fuel pressure
regulator. The fuel thus regulated is distributed
to each of the injectors.
Fuel injection is normally carried out once for
each cylinder for every two rotations of the
crankshaft. The firing order is 1-3-4-2. This iscalled sequential fuel injection. The
engine-ECU provides a richer air/fuel mixture
by carrying out “open-loop” control when the
engine is cold or operating under high load
conditions in order to maintain engine
performance. In addition, when the engine is
warm or operating under normal conditions,
the engine-ECU controls the air/fuel mixture
by using the oxygen sensor signal to carry out
“closed-loop” control in order to obtain the
theoretical air/fuel mixture ratio that provides
the maximum cleaning performance from the
three way catalyst.
IDLE AIR CONTROL
The idle speed is kept at the optimum speed
by controlling the amount of air that bypasses
the throttle valve in accordance with changes
in idling conditions and engine load during
idling. The engine-ECU drives the idle speed
control motor to keep the engine running at
the pre-set idle target speed in accordance
with the engine coolant temperature and airconditioner load. In addition, when the air
conditioner switch is turned off and on while
the engine is idling, the idle speed control motor
operates to adjust the throttle valve bypass
air amount in accordance with the engine load
conditions in order to avoid fluctuations in the
engine speed.
IGNITION TIMING CONTROL
The power transistor located in the ignition
primary circuit turns ON and OFF to control
the primary current flow to the ignition coil. This
controls the ignition timing in order to provide
the optimum ignition timing with respect to theengine operating conditions. The ignition timing
is determined by the engine-ECU from the
engine speed, intake air volume, engine coolant
temperature and barometric pressure.
SELF-DIAGNOSIS FUNCTION
DWhen an abnormality is detected in one
of the sensors or actuators related to
emission control, the engine warning lamp
(check engine lamp) illuminates as a
warning to the driver.
DWhen an abnormality is detected in one
of the sensors or actuators, a diagnosis
code corresponding to the abnormality is
output.DThe RAM data inside the engine-ECU that
is related to the sensors and actuators can
be read by means of the MUT-II. In addition,
the actuators can be force-driven under
certain circumstances.