2007 MITSUBISHI LANCER EVOLUTION Engine oil pump
[x] Cancel search: Engine oil pumpPage 505 of 1449

ENGINE OVERHAUL -Oil Pump and Oil Pan11B-51
4. Align and insert the special tool into the guide pin, and
tap in the counter balance shaft front bearing.
"DAOIL PUMP OIL SEAL INSTALLATION
Install the oil pump oil seal using an appropriate socket wrench.
"EACOUNTER BALANCE SHAFT OIL SEAL
INSTALLATION
Install the counter balance shaft oil seal using an appropriate
socket wrench.
"FACRANKSHAFT FRONT OIL SEAL INSTALLATION
Install the crankshaft front oil seal using the special tool.
MD998705
Guide pin
Socket wrench
Oil pump case Oil seal
Socket wrench
Oil pump case
Oil seal
MD998375
Oil pump case Oil seal
Page 506 of 1449

ENGINE OVERHAUL -Oil Pump and Oil Pan11B-52
"GAOIL PUMP DRIVE GEAR/OIL PUMP DRIVEN
GEAR INSTALLATION
Apply sufficient engine oil onto the gears, align the match
marks, and assemble.
"HAOIL PUMP CASE INSTALLATION
1. Install the special tool onto the front end of the crankshaft,
and apply a light coat of engine oil onto the periphery
of the guide. If an oil seal is installed on the oil pump
case, always use a guide.
2. Install the oil pump case through the new oil pump case
gasket, and temporarily tighten the bolts other than the
oil filter bracket tightening bolt.
3. Install the oil filter bracket through the oil filter bracket
gasket, and temporarily tighten with the bolt.
4. Tighten the oil pump case at the specified torque 23
±3N•m, and the oil filter bracket at the specified torque
19±3N•m.
"IAFLANGE BOLT INSTALLATION
1. Insert a Phillips driver (shaft diameter 8 mm) by 60 mm
or more into the hole on the left side of the cylinder block
to stop the rotation of the counter balance shaft left.
2. Tighten the flange bolt at the specified torque 36±3
N•m.
Match marks
MD998285
Counter balance
shaft left
Counter balance
shaft right
MD998285
Phillips driver
Page 507 of 1449
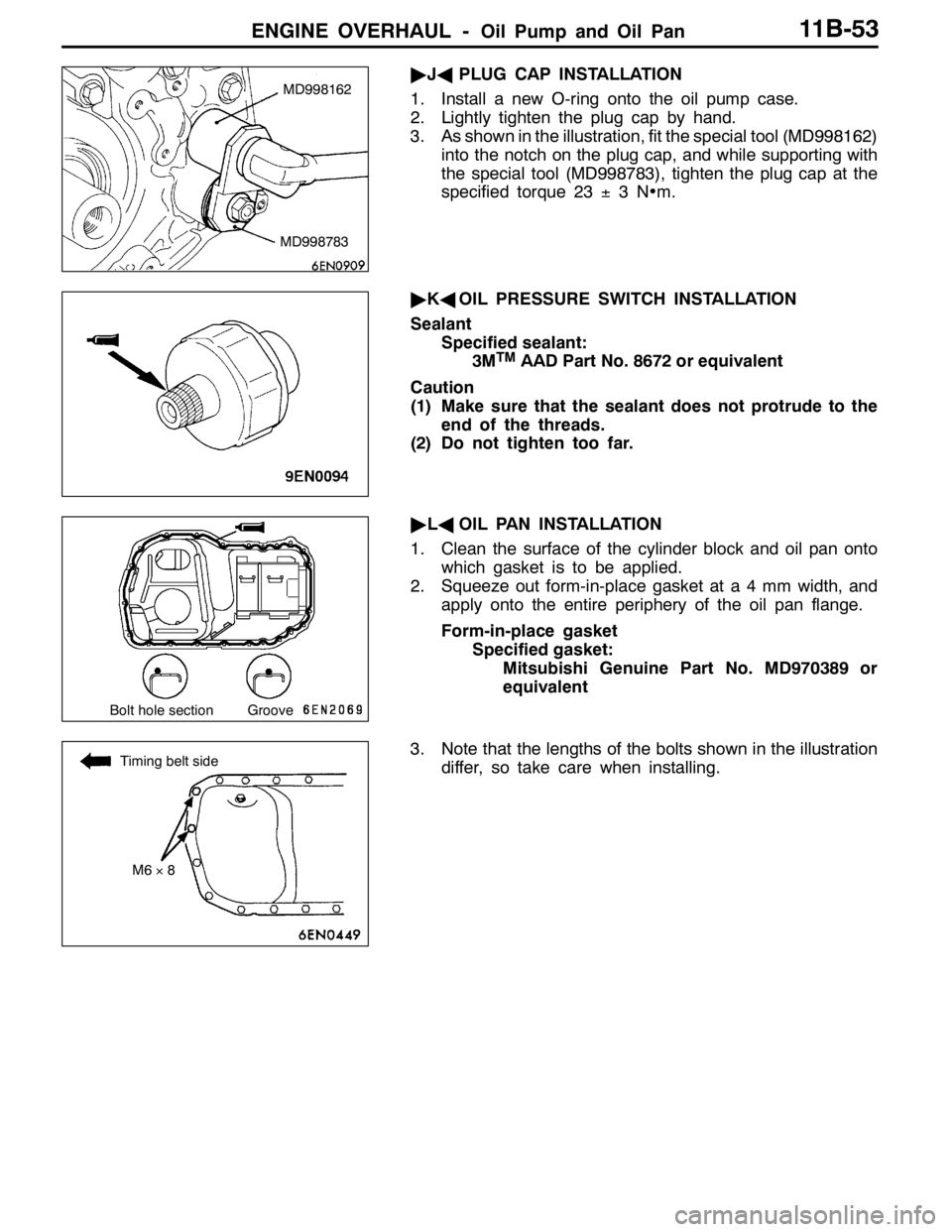
ENGINE OVERHAUL -Oil Pump and Oil Pan11B-53
"JAPLUG CAP INSTALLATION
1. Install a new O-ring onto the oil pump case.
2. Lightly tighten the plug cap by hand.
3. As shown in the illustration, fit the special tool (MD998162)
into the notch on the plug cap, and while supporting with
the special tool (MD998783), tighten the plug cap at the
specified torque 23±3N•m.
"KAOIL PRESSURE SWITCH INSTALLATION
Sealant
Specified sealant:
3M
TMAAD Part No. 8672 or equivalent
Caution
(1) Make sure that the sealant does not protrude to the
end of the threads.
(2) Do not tighten too far.
"LAOIL PAN INSTALLATION
1. Clean the surface of the cylinder block and oil pan onto
which gasket is to be applied.
2. Squeeze out form-in-place gasket at a 4 mm width, and
apply onto the entire periphery of the oil pan flange.
Form-in-place gasket
Specified gasket:
Mitsubishi Genuine Part No. MD970389 or
equivalent
3. Note that the lengths of the bolts shown in the illustration
differ, so take care when installing.
MD998162
MD998783
Bolt hole section Groove
Timing belt side
M6×8
Page 508 of 1449
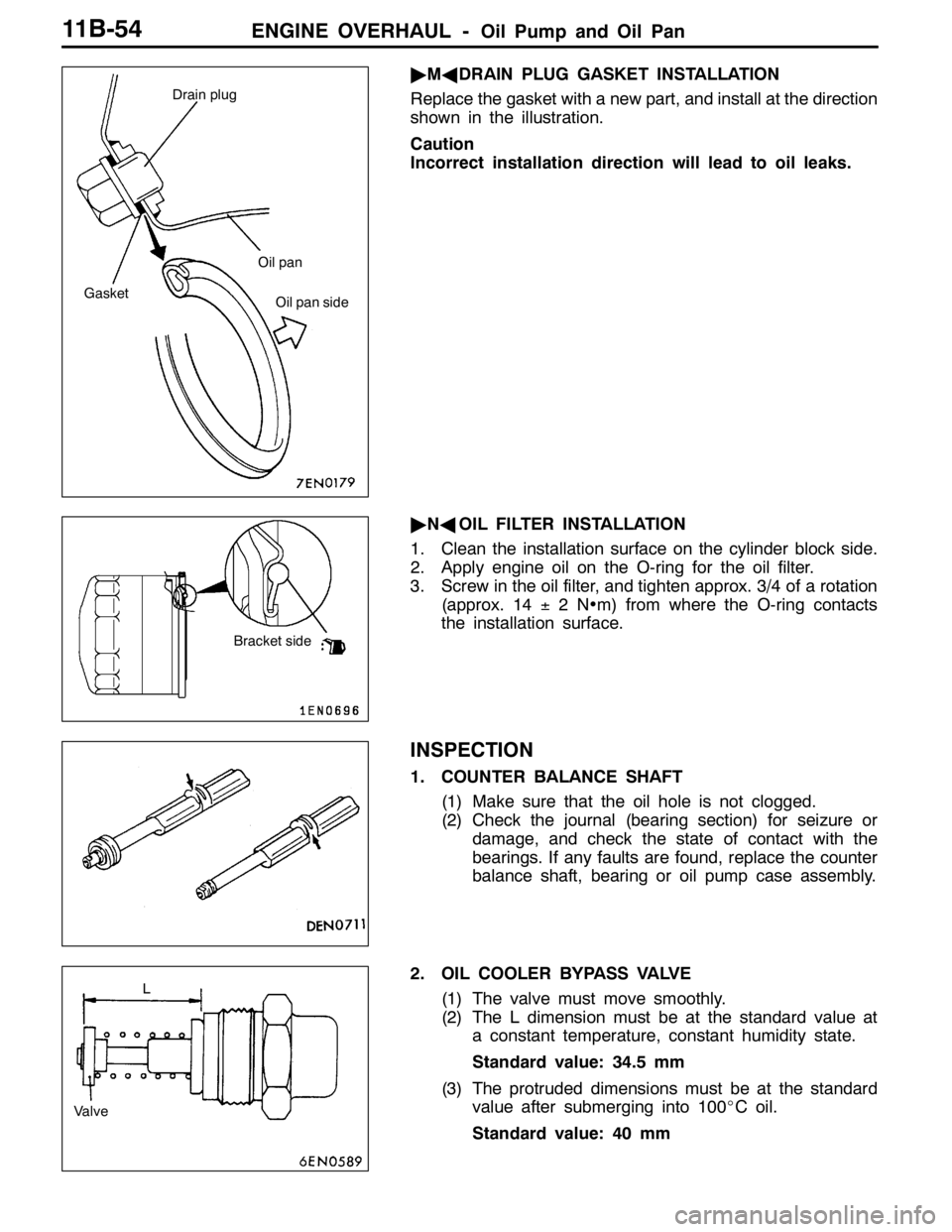
ENGINE OVERHAUL -Oil Pump and Oil Pan11B-54
"MADRAIN PLUG GASKET INSTALLATION
Replace the gasket with a new part, and install at the direction
shown in the illustration.
Caution
Incorrect installation direction will lead to oil leaks.
"NAOIL FILTER INSTALLATION
1. Clean the installation surface on the cylinder block side.
2. Apply engine oil on the O-ring for the oil filter.
3. Screw in the oil filter, and tighten approx. 3/4 of a rotation
(approx. 14±2N•m) from where the O-ring contacts
the installation surface.
INSPECTION
1. COUNTER BALANCE SHAFT
(1) Make sure that the oil hole is not clogged.
(2) Check the journal (bearing section) for seizure or
damage, and check the state of contact with the
bearings. If any faults are found, replace the counter
balance shaft, bearing or oil pump case assembly.
2. OIL COOLER BYPASS VALVE
(1) The valve must move smoothly.
(2) The L dimension must be at the standard value at
a constant temperature, constant humidity state.
Standard value: 34.5 mm
(3) The protruded dimensions must be at the standard
value after submerging into 100_C oil.
Standard value: 40 mm
Drain plug
Oil pan
Oil pan side Gasket
Bracket side
L
Valve
Page 509 of 1449

ENGINE OVERHAUL -Oil Pump and Oil Pan11B-55
3. OIL PUMP
(1) Assemble the drive gear and driven gear into the
oil pump case.
(2) Inspect the side clearance with a thickness gauge.
Standard value:
Drive gear 0.08 - 0.14 mm
Driven gear 0.06 - 0.12 mm
Page 526 of 1449

ENGINE LUBRICATION -General Information12-2
GENERAL INFORMATION
The lubrication method is a fully force-fed, full-flow
filtration type. The oil pump is a gear type which
is driven by the crankshaft via the timing belt.
ENGINE OILS
Health Warning
Prolonged and repeated contact with mineral oil
will result in the removal of natural fats from the
skin, leading to dryness, irritation and dermatitis.
In addition, used engine oil contains potentiallyharmful contaminants which may cause skin cancer.
Adequate means of skin protection and washing
facilities must be provided.
Recommended Precautions
The most effective precaution is to adapt working
practices which prevent, as far as practicable, the
risk of skin contact with mineral oils, for example
by using enclosed systems for handling used engine
oil and by degreasing components, where
practicable, before handling them.
Other precautions:
DAvoid prolonged and repeated contact with oils,
particularly used engine oils.
DWear protective clothing, including impervious
gloves where practicable.
DAvoid contaminating clothes, particularly
underpants, with oil.
DDo not put oily rags in pockets, the use of
overalls without pockets will avoid this.
DDo not wear heavily soiled clothing and
oil - impregnated foot - wear. Overalls must be
cleaned regularly and kept separate from
personal clothing.DWhere there is a risk of eye contact, eye
protection should be worn, for example,
chemical goggles or face shields; in addition
an eye wash facility should be provided.
DObtain First Aid treatment immediately for open
cuts and wounds.
DWash regularly with soap and water to ensure
all oil is removed, especially before meals (skin
cleansers and nail brushes will help). After
cleaning, the application of preparations
containing lanolin to replace the natural skin
oils is advised.
DDo not use petrol, kerosine, diesel fuel, gas
oil, thinners or solvents for cleaning skin.
DUse barrier creams, applying them before each
work period, to help the removal of oil from
the skin after work.
DIf skin disorders develop, obtain medical advice
without delay.
Page 535 of 1449

MPI -General Information13A-3
GENERAL INFORMATION
The Multipoint Fuel Injection System consists
of sensors which detect the engine conditions,
the engine-ECU which controls the system
based on signals from these sensors, and
actuators which operate under the control of
the engine-ECU. The engine-ECU carries outactivities such as fuel injection control, idle
speed control and ignition timing control. In
addition, the engine-ECU is equipped with
several diagnosis modes which simplify
troubleshooting when a problem develops.
FUEL INJECTION CONTROL
The injector drive times and injector timing are
controlled so that the optimum air/fuel mixture
is supplied to the engine to correspond to the
continually-changing engine operation condi-
tions.
A single injector is mounted at the intake port
of each cylinder. Fuel is sent under pressure
from the fuel tank by the fuel pump, with the
pressure being regulated by the fuel pressure
regulator. The fuel thus regulated is distributed
to each of the injectors.
Fuel injection is normally carried out once for
each cylinder for every two rotations of the
crankshaft. The firing order is 1-3-4-2. This iscalled sequential fuel injection. The
engine-ECU provides a richer air/fuel mixture
by carrying out “open-loop” control when the
engine is cold or operating under high load
conditions in order to maintain engine
performance. In addition, when the engine is
warm or operating under normal conditions,
the engine-ECU controls the air/fuel mixture
by using the oxygen sensor signal to carry out
“closed-loop” control in order to obtain the
theoretical air/fuel mixture ratio that provides
the maximum cleaning performance from the
three way catalyst.
IDLE AIR CONTROL
The idle speed is kept at the optimum speed
by controlling the amount of air that bypasses
the throttle valve in accordance with changes
in idling conditions and engine load during
idling. The engine-ECU drives the idle speed
control motor to keep the engine running at
the pre-set idle target speed in accordance
with the engine coolant temperature and airconditioner load. In addition, when the air
conditioner switch is turned off and on while
the engine is idling, the idle speed control motor
operates to adjust the throttle valve bypass
air amount in accordance with the engine load
conditions in order to avoid fluctuations in the
engine speed.
IGNITION TIMING CONTROL
The power transistor located in the ignition
primary circuit turns ON and OFF to control
the primary current flow to the ignition coil. This
controls the ignition timing in order to provide
the optimum ignition timing with respect to theengine operating conditions. The ignition timing
is determined by the engine-ECU from the
engine speed, intake air volume, engine coolant
temperature and barometric pressure.
SELF-DIAGNOSIS FUNCTION
DWhen an abnormality is detected in one
of the sensors or actuators related to
emission control, the engine warning lamp
(check engine lamp) illuminates as a
warning to the driver.
DWhen an abnormality is detected in one
of the sensors or actuators, a diagnosis
code corresponding to the abnormality is
output.DThe RAM data inside the engine-ECU that
is related to the sensors and actuators can
be read by means of the MUT-II. In addition,
the actuators can be force-driven under
certain circumstances.
Page 537 of 1449

MPI -General Information13A-5
MULTI-POINT FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM DIAGRAM
L1 Oxygen sensor (front)
L2 Oxygen sensor (rear)
L3 Air flow sensor
L4 Intake air temperature sensor
L5 Throttle position sensor
L6 Camshaft position sensor
L7 Crank angle sensor
L8 Barometric pressure sensor
L9 Engine coolant temperature sensor
L10 Detonation sensor
Engine-ECU
l1 Injector
l2 Idle speed control servo
l3 Fuel pressure control solenoid valve
l4 Waste gate solenoid valve
l5 EGR control solenoid valve
l6 Purge control solenoid valve
l7 Secondary air control solenoid valve
DPower supply
DIgnition switch IG
DIgnition switch ST
DVehicle speed sensor
DA/C switch
DA/C load signal
DTachometer
DPower steering fluid pressure switch
DAlternator FR terminal
DDiagnosis control terminal
DIntercooler water spray switch (automatic)
DIntercooler water spray switch (manual)DEngine control relay
DFuel pump relay 2, 3
DA/C relay
DIgnition coil
DFan controller
DCondenser fan relay (HI)
DCondenser fan relay (LOW)
DEngine warning lamp
DDiagnosis output
DAlternator G terminal
DIntercooler water spray relay
DIntercooler water spray lamp
L1 Oxygen
sensor
(front)
L4 Intake air
temperature
sensorL5 Throttle
position
sensor
L6 Camshaft
position sensorl1 Injector l2 Idle
speed
control
servo
l6 Purge
control
solenoid
valve
Three-way
catalytic converter Canister
Air
inletVacuum
tank
Fuel
pressure
reguratorFrom
fuel tank
To fuel tank
PCV valveFrom
fuel pump
Waste gate
actuatorL2 Oxygen sensor (rear) Check
valveBy-pass
valve
l5 EGR control
solenoid valve
l4 Waste gate
solenoid valve L8 Barometric
pressure
sensor
L3 Air flow
sensorl7 Secondary
air control
solenoid
valve
Secondary
air valvel3 Fuel pressure
control
solenoid valve
EGR
valve
L9 Engine coolant
temperature sensor
L7 Crank angle sensor
L10 Detonation sensor