2007 ISUZU KB P190 engine oil
[x] Cancel search: engine oilPage 3753 of 6020

Exhaust System – V6 Page 6F – 5
Service Notes
1. Vehicles fitted with catalytic converters should not be operated with leaded petrol. Lead will contaminate
the ceramic monolith.
2. Do not drop the catalytic converter as it will damage the ceramic monolith.
3. Replace the catalytic converter if it is damaged.
4. Do not allow water, oil or fuel to enter the converter as the ceramic monolith will be contaminated.
5. Do not use engine and/or fuel additives unless approved by General Motors. Many additives contain phosphorous that will contaminate the ceramic monolith.
6. The vehicle must not be started by pushing or towing, as unburned fuel could reach the catalytic converter and destroy the ceramic monolith. Always use jumper leads to start a vehicle that has a flat or
defective battery.
7. W hen carrying out a compression test, for V6 engines use Tech 2 to ensure the output control Engine Compression Test is set to enable, refer to 6A1 Engine Mechanical. This prevents fuel injection and
ignition during engine cranking.
8. Do not drive the vehicle with the engine misfiring or with any of the spark plug leads disconnected, as the catalytic converter will overheat.
9. Do not coast downhill with the engine misfiring or with any of the spark plug leads disconnected.
10. The catalytic converter is serviceable as part of the front exhaust assembly only. Refer to the service operations in this section for details of front exhaust pipe assembly removal and reinstallation.
11. The exhaust flange gaskets must be replaced whenever a new exhaust pipe, muffler or catalytic converter is installed.
1.3 WARNING, CAUTION and NOTES
This Section contains various W ARNINGS, CAUTIONS and NOTE statements that you must observe carefully to reduce
the risk of death or injury during service, repair procedures or vehicle operation. Incorrect service or repair procedures
may damage the vehicle or cause operational faults. W ARNINGS, CAUTION and NOTE statements are not exhaustive.
HOLDEN LTD can not possibly warn of all the potentially hazardous consequences of failure to follow these instructions.
1.1 Definition of WARNING, CAUTION and NOTE Statements
Diagnosis and repair procedures in this Section contain both general and specific W ARNING, CAUTION and NOTE
statements. HOLDEN LTD is dedicated to the presentation of service information that helps the technician to diagnose
and repair the systems necessary for proper operation of the vehicle. Certain procedures may present a hazard to the
technician if they are not followed in the recommended manner. W ARNING, CAUTION and NOTE statements are
designed to help prevent these hazards from occurring, but not all hazards can be foreseen.
WARNING defined
A W ARNING statement immediately precedes an operating procedure or maintenance practice which, if not correctly
followed, could result in death or injury. A W ARNING statement alerts you to take necessary action or not to take a
prohibited action. If a W ARNING statement is ignored, the following consequences may occur:
• Death or injury to the technician or other personnel working on the vehicle,
• Death or injury to other people in or near the workplace area, and / or
• Death or injury to the driver / or passenger(s) of the vehicle or other people, if the vehicle has been improperly
repaired.
CAUTION defined
A CAUTION statement immediately precedes an operating procedure or maintenance practice which, if not correctly
followed, could result in damage to or destruction of equipment, or corruption of data. If a CAUTION statement is
ignored, the following consequences may occur:
• Damage to the vehicle,
• Unnecessary vehicle repairs or component replacement,
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3764 of 6020

Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – General Information Page 7C1–4
1.2 7C1 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E –
General Information
This section provides general information about the automatic transmission, including:
• A glossary of terms,
• Transmission identification information,
• Electrical overview of the Transmission Control Module (TCM),
• Some notes that address safe workshop practices,
• Service notes relating to fasteners and consumable items used at various stages throughout this section,
• Special tools required to work on the transmission,
• Fastener torque specifications, and
• Transmission specifications.
For all information relating to the mechanical construction and function of the 4L60E automatic transmission, refer to the
General Motors Powertrain Group Electronically Controlled Automatic Transmission Technician’s Guide.
This guide includes such information as:
• Transmission Cutaway Views,
• Principles of Operation,
• Power Flow,
• Complete Hydraulic Circuits,
• Bushing and Bearing Locations,
• Seal Locations and
• Illustrated Parts List.
NOTE
Specifications quoted in this General Motors
Powertrain Group Electronically Controlled
Automatic Transmission Technician Guide may
not be for the vehicle you are working on. For
correct specifications refer to
7 Transmission Specifications.
Recommendations
When servicing the transmission, all parts should be cleaned and inspected. Individual units should be reassembled
before disassembly of other units to avoid confusion and interchanging of parts.
a Thoroughly clean the transmission exterior before removal of any component.
b Disassembly and reassembly must be made on a clean work bench. Cleanliness is of the utmost importance, the bench tools and parts must be kept clean at all times.
c Before installing screws and other fasteners into aluminium parts, dip screw threads into transmission fluid to prevent galling aluminium threads and to prevent screws from seizing.
d To prevent thread stripping, always use a torque wrench when installing screws or nuts.
e If threads in aluminium parts are stripped or damaged, the parts can be made serviceable by the use of commercially available thread inserts.
f Protective tools must be used when assembling seals to prevent damage. The slightest flaw in the sealing surface of the seal can cause an oil leak.
g Aluminium castings and valve parts are very susceptible to nicks, burrs, etc. and should be handled with care.
h Expand Internal snap rings and compress external snap rings if they are to be re-used to ensure proper seating when reinstalled.
i Do not re-use removed O-rings, gaskets and oil seals.
j Teflon oil seal rings should not be removed unless damaged.
k During assembly of each unit, all internal moving parts must be lubricated with transmission fluid.
Oil Cooler Pipes
Should any transmission fluid cooling pipe suffer accidental damage, a genuine replacement pipe must be fitted. Refer to
the current release of PartFinder™ to determine the correct part number for the particular engine and pipe involved.
Reworking of damaged pipes or hand made replacements are not permitted.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3765 of 6020

Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – General Information Page 7C1–5
Clean and Inspect
Do not use solvents on neoprene seals,
composition faced clutch plates or thrust
washers as damage to parts may occur.
After complete disassembly of a component, wash all metal parts in a clean solvent and dry with compressed air. Blow
oil passages out and check to make sure they are not obstructed, small passages should be checked with tag wire. All
parts should be inspected to determine if replacement is required.
Pay particular attention to the following:
• Inspect linkage and pivot points for excessive wear.
• Bearing and thrust surfaces of all parts should be checked for excessive wear and scoring.
• Check for broken seal rings, damaged ring lands and damaged threads.
• Inspect seals for damage.
• Mating surfaces of castings should be checked for burrs. Irregularities may be removed by lapping the surface with
emery paper laid on a flat surface, such as a piece of plate glass.
• Castings should be checked for cracks and porosity.
1.3 7C2 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E –
Electrical Diagnosis
For transmissions fitted to V6 engines, the electrical diagnosis is in this Section. A new electrical circuit and control
module has been introduced for automatic transmissions fitted to the V6 engines.
1.4 7C3 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Hydraulic and Mechanical Diagnosis
Information contained in 7C3 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Hydraulic and Mechanical Diagnosis will assist in the
diagnosis of the mechanical and hydraulic components in the 4L60E automatic transmission, while the transmission
remains installed on the vehicle.
Examples of the type of diagnostic information contained within this section are:
• transmission functional test,
• line pressure information,
• transmission fluid diagnosis,
• symptom diagnosis and
• shift speed charts.
1.5 7C4 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E –
On-vehicle Servicing
Information in 7C4 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – On-vehicle Servicing covers transmission fluid level checking, as
well as specific information for servicing some components while the transmission remains installed on the vehicle. This
Section also covers the transmission removal and reinstallation to the vehicle.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3768 of 6020

Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – General Information Page 7C1–8
2.4 System Protection Devices
Should 1st gear be selected and left in that range, the TCM will protect the engine from an over-speeding condition by
upshifting to 2nd gear at a pre-determined point. Similarly, the TCM provides high speed, downshift protection by
preventing a manual shift into 1st gear above pre-determined engine speeds.
Under severe operating conditions such as towing in high ambient temperatures, fluid temperatures can rise to a point
where lubrication breakdown can occur. In addition to having an oil cooler fitted to the vehicle, the 4L60E transmission is
also fitted with a transmission fluid temperature sensor located in the Transmission Range (TR) Pressure Switch
Assembly (PSA).
When fluid temperatures in excess of 135 °C are sensed, the torque converter clutch is applied as programmed, in 3rd or
4th gear. This action reduces further the fluid temperature during normal operation of the torque converter. While these
high fluid temperatures are sensed however, torque converter clutch apply is not available when the throttle opening is
above 50%.
Similarly, when the fluid temperature is below 29 °C, the TCM prevents torque converter clutch apply.
If a condition occurs, preventing electronic control of the transmission's functions, a 'Fail Safe' mode will default the
transmission to 3rd gear when either Drive or 3 is selected, applying also maximum line pressure. W hile in this mode, the
vehicle operator can still manually select 2, 1, Reverse, Park or Neutral, should the need arise.
2.5 Self Diagnosis
If any transmission operation controlled by the TCM begins to operate outside its pre-set parameters, the TCM has the
ability to store a range of diagnostic codes which can be accessed by the servicing technician, thereby localising the
problem.
2.6 TCM Sensors and Actuators
As indicated earlier, there are a number of sensors and switches providing input information for the TCM programming
that will allow the TCM to change the shift pattern, shift feel and torque converter clutch operation.
The TCM does this by comparing this input information with its predetermined values on shift pattern, fluid pressure
maps, shift duration parameters, extreme heat protection programming and adaptive controls.
In addition, each input signal and output actuator operation is also monitored and if outside its pre-set parameters, a
diagnostic code is logged for future reference by the servicing technician.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3772 of 6020
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – General Information Page 7C1–12
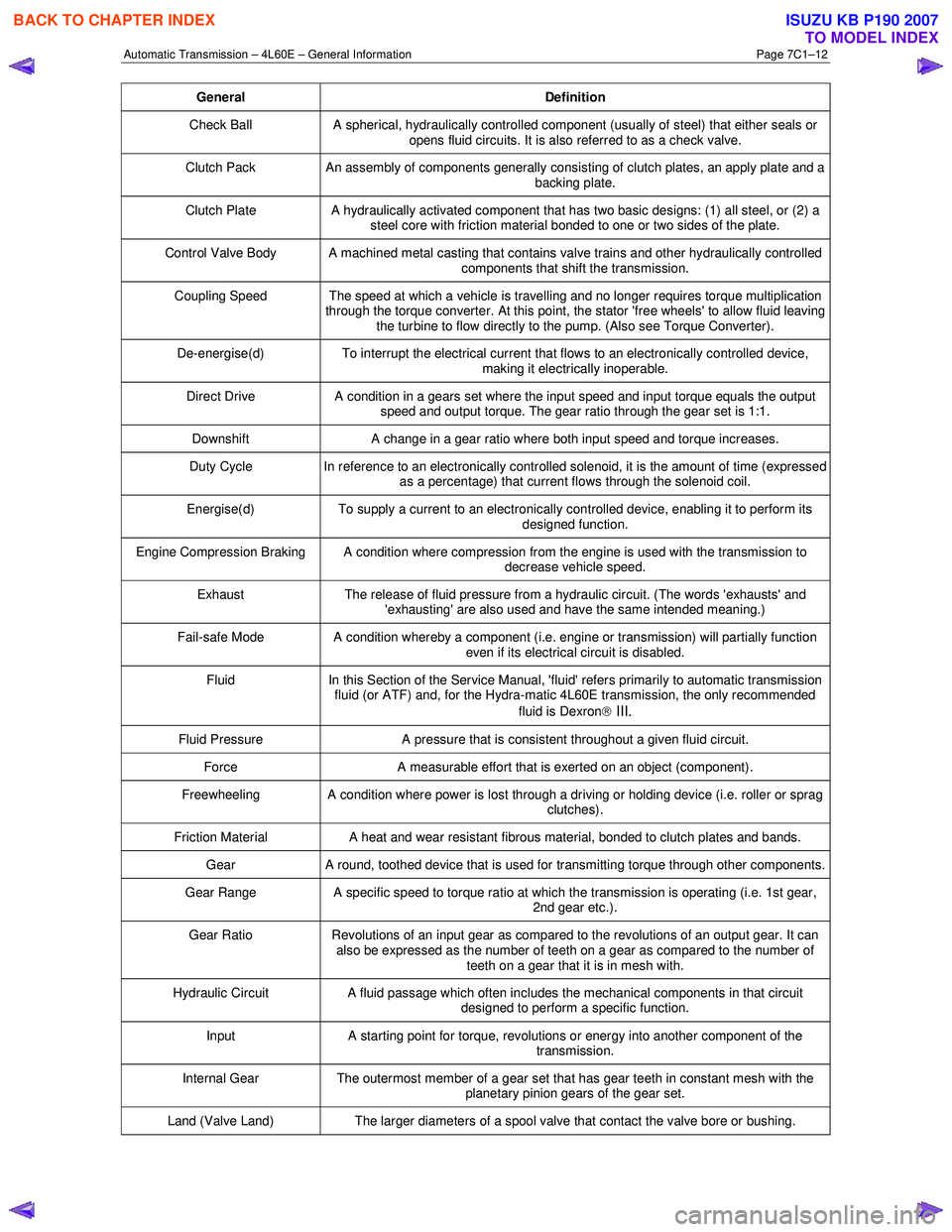
General Definition
Check Ball A spherical, hydraulically controlled component (usually of steel) that either seals or
opens fluid circuits. It is also referred to as a check valve.
Clutch Pack An assembly of components generally consisting of clutch plates, an apply plate and a
backing plate.
Clutch Plate A hydraulically activated component that has two basic designs: (1) all steel, or (2) a
steel core with friction material bonded to one or two sides of the plate.
Control Valve Body A machined metal casting that contains valve trains and other hydraulically controlled components that shift the transmission.
Coupling Speed The speed at which a vehicle is travelling and no longer requires torque multiplication through the torque converter. At this point, the stator 'free wheels' to allow fluid leaving
the turbine to flow directly to the pump. (Also see Torque Converter).
De-energise(d) To interrupt the electrical current that flows to an electronically controlled device,
making it electrically inoperable.
Direct Drive A condition in a gears set where the input speed and input torque equals the output
speed and output torque. The gear ratio through the gear set is 1:1.
Downshift A change in a gear ratio where both input speed and torque increases.
Duty Cycle In reference to an electronically controlled solenoid, it is the amount of time (expressed
as a percentage) that current flows through the solenoid coil.
Energise(d) To supply a current to an electronically controlled device, enabling it to perform its
designed function.
Engine Compression Braking A condition where compression from the engine is used with the transmission to decrease vehicle speed.
Exhaust The release of fluid pressure from a hydraulic circuit. (The words 'exhausts' and
'exhausting' are also used and have the same intended meaning.)
Fail-safe Mode A condition whereby a component (i.e. engine or transmission) will partially function even if its electrical circuit is disabled.
Fluid In this Section of the Service Manual, 'fluid' refers primarily to automatic transmission
fluid (or ATF) and, for the Hydra-matic 4L60E transmission, the only recommended
fluid is Dexron
III.
Fluid Pressure A pressure that is consistent throughout a given fluid circuit.
Force A measurable effort that is exerted on an object (component).
Freewheeling A condition where power is lost through a driving or holding device (i.e. roller or sprag
clutches).
Friction Material A heat and wear resistant fibrous material, bonded to clutch plates and bands.
Gear A round, toothed device that is used for transmitting torque through other components.
Gear Range A specific speed to torque ratio at which the transmission is operating (i.e. 1st gear,
2nd gear etc.).
Gear Ratio Revolutions of an input gear as compared to the revolutions of an output gear. It can
also be expressed as the number of teeth on a gear as compared to the number of
teeth on a gear that it is in mesh with.
Hydraulic Circuit A fluid passage which often includes the mechanical components in that circuit
designed to perform a specific function.
Input A starting point for torque, revolutions or energy into another component of the
transmission.
Internal Gear The outermost member of a gear set that has gear teeth in constant mesh with the
planetary pinion gears of the gear set.
Land (Valve Land) The larger diameters of a spool valve that contact the valve bore or bushing.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3777 of 6020

Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – General Information Page 7C1–17
7 Transmission Specifications
7.1 General
Type
Hydra-matic 4L60E
Special Features
Electronically controlled shift pattern, feel and torque
Converter clutch operation
Overdrive 4th speed range
Selector Location ..................................................................................Floor mounted console
Gear Ratios Park (P) ....................................................................................................................... ........... –
Reverse (R) .................................................................................................................... ... 2.29
Neutral (N) .............................................................................................................................. –
Drive (D – 4) .................................................................................................................. ...... 0.7
Drive (D – 3) .................................................................................................................. ...... 1.0
Second (2) ......................................................................................................................... 1.63
First (1) ...................................................................................................................... ........ 3.06
Shift Speeds Refer to 7C3 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Hydraulic and Mechanical Diagnosis
Oil Pressure
Refer to 7C3 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Hydraulic and Mechanical Diagnosis
Torque Converter
Number of Elements .................................................................. 3 plus torque converter clutch
Torque Converter Diameter and End Play
HFV6 ........................................................................................................................... 258 mm
End Play .............................................................................................................. 0.1 – 0.5 mm
Lubricant
Type recommended ................................................................................................ Dexron
® III
Capacity......................... Nominal only. Check when transmission is at operating temperature
Service Refill ............................................................................................................... 4. 8 litres
Total (Dry)................................................................................................................... 8 .8 litres
Fluid Cooling.....................................Transmission fluid to engine coolant in one radiator tank
Clutches and Band 2 – 4 Band:
Type........................................................................................... Composition lined, steel band
Operation: ..................................................................................................................... .. Servo
Adjustment: ................................................................................................ Selective Apply Pin
Pin Size and Identification.
65.82 – 66.12 mm ...................................................................................................... 1 Groove
67.23 – 67.53 mm ...................................................................................................... 2 Groove
68.64 – 68.94 mm ....................................................................................................No Groove
Reverse Input Clutch Type................................................................................................................Multiple we t disc
Backing plate ........................................................................................................ (1) Select ive
Clutch plate (numbers):
Steel ....................................................................................................................................... 4
Composition............................................................................................................................ 4
Belleville ..................................................................................................................... ............ 1
Backing Plate ........................................................................................................ 1 (Selecti ve)
Backing plate, identification and thickness:
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3785 of 6020
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – General Information Page 7C1–25
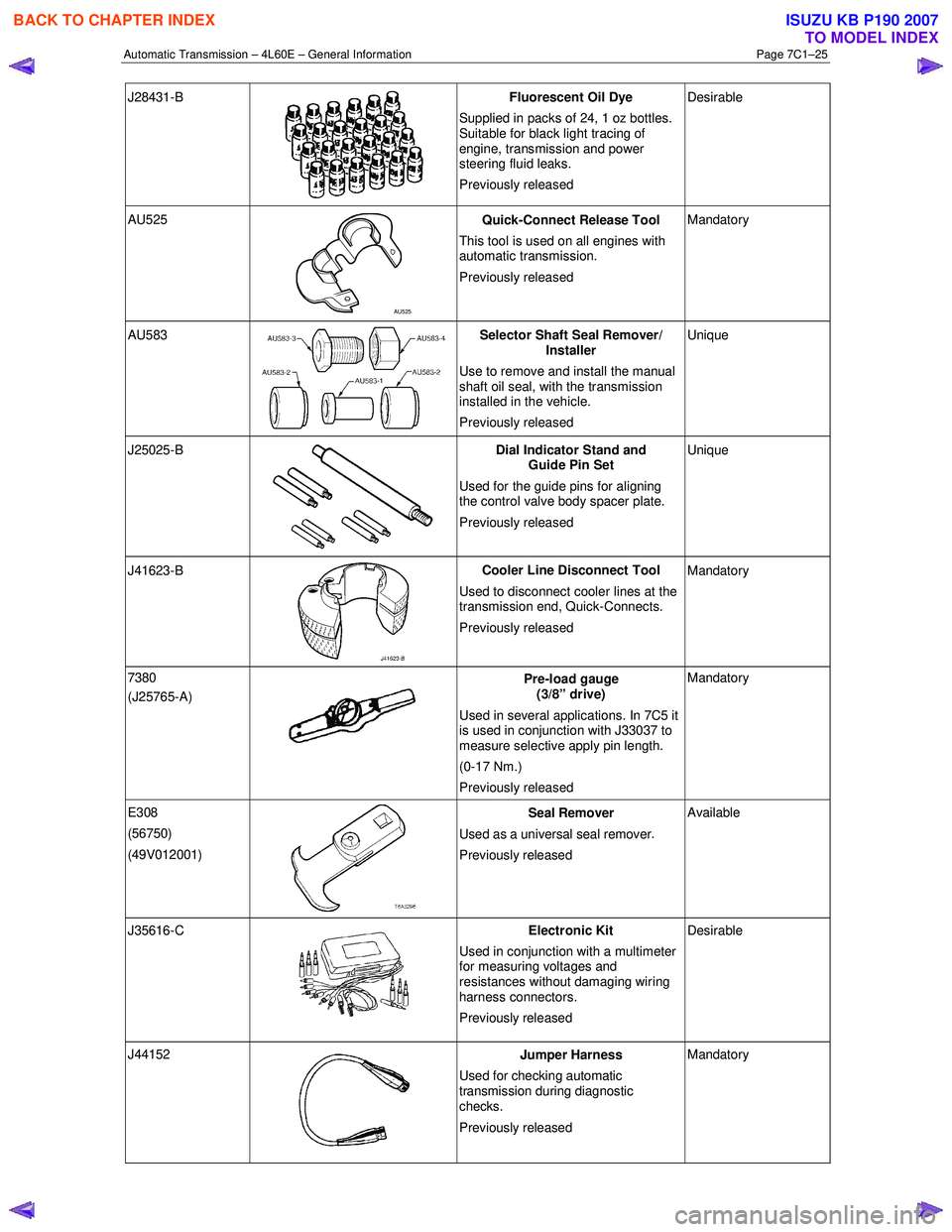
J28431-B
Fluorescent Oil Dye
Supplied in packs of 24, 1 oz bottles.
Suitable for black light tracing of
engine, transmission and power
steering fluid leaks.
Previously released Desirable
AU525
AU525 Quick-Connect Release Tool
This tool is used on all engines with
automatic transmission.
Previously released Mandatory
AU583 Selector Shaft Seal Remover/
Installer
Use to remove and install the manual
shaft oil seal, with the transmission
installed in the vehicle.
Previously released Unique
J25025-B
Dial Indicator Stand and
Guide Pin Set
Used for the guide pins for aligning
the control valve body spacer plate.
Previously released Unique
J41623-B
Cooler Line Disconnect Tool
Used to disconnect cooler lines at the
transmission end, Quick-Connects.
Previously released Mandatory
7380
(J25765-A)
Pre-load gauge
(3/8” drive)
Used in several applications. In 7C5 it
is used in conjunction with J33037 to
measure selective apply pin length.
(0-17 Nm.)
Previously released Mandatory
E308
(56750)
(49V012001)
Seal Remover
Used as a universal seal remover .
Previously released Available
J35616-C
Electronic Kit
Used in conjunction with a multimeter
for measuring voltages and
resistances without damaging wiring
harness connectors.
Previously released Desirable
J44152
Jumper Harness
Used for checking automatic
transmission during diagnostic
checks.
Previously released Mandatory
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3819 of 6020
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–33
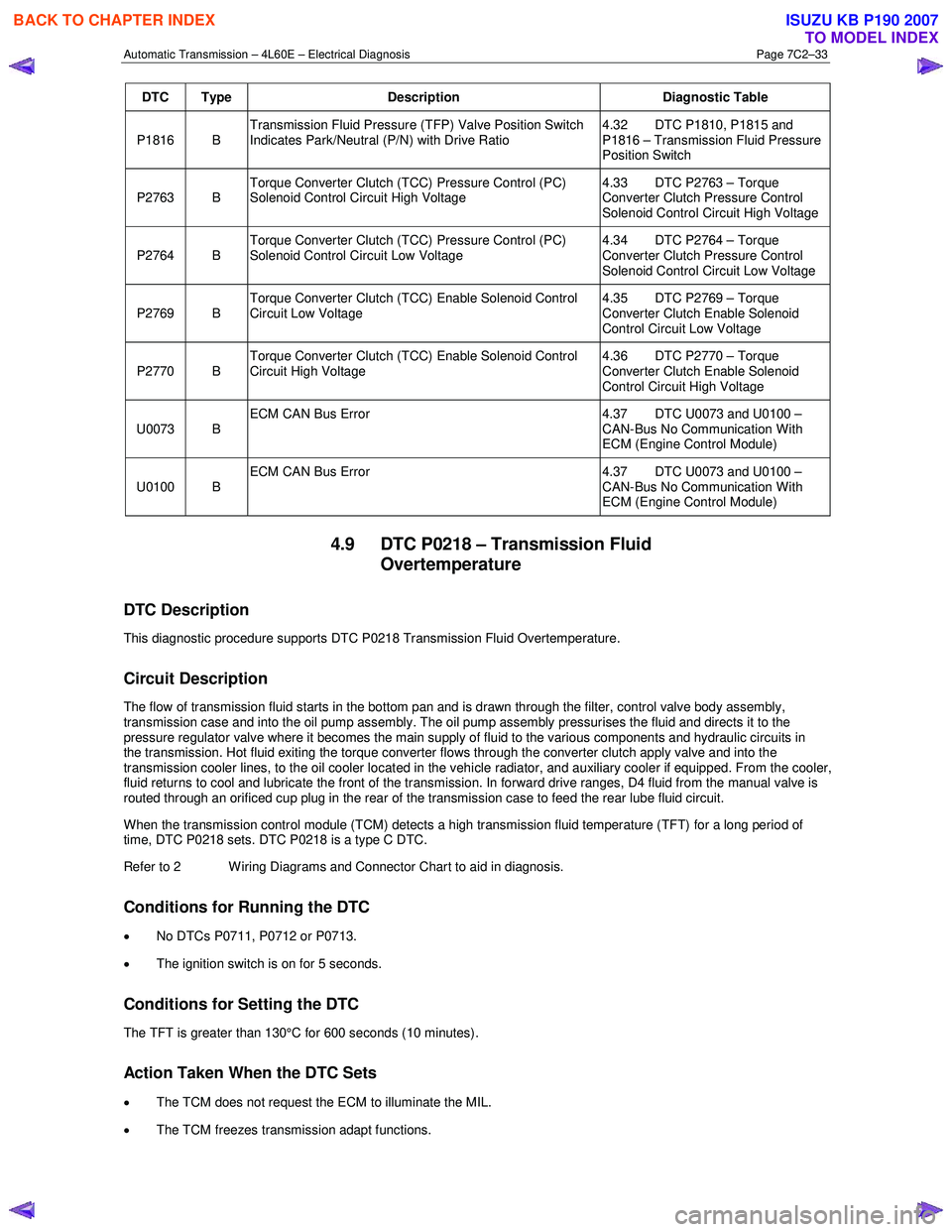
DTC Type Description Diagnostic Table
P1816 B Transmission Fluid Pressure (TFP) Valve Position Switch
Indicates Park/Neutral (P/N) with Drive Ratio 4.32 DTC P1810, P1815 and
P1816 – Transmission Fluid Pressure
Position Switch
P2763 B Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Pressure Control (PC)
Solenoid Control Circuit High Voltage 4.33 DTC P2763 – Torque
Converter Clutch Pressure Control
Solenoid Control Circuit High Voltage
P2764 B Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Pressure Control (PC)
Solenoid Control Circuit Low Voltage 4.34 DTC P2764 – Torque
Converter Clutch Pressure Control
Solenoid Control Circuit Low Voltage
P2769 B Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Enable Solenoid Control
Circuit Low Voltage 4.35 DTC P2769 – Torque
Converter Clutch Enable Solenoid
Control Circuit Low Voltage
P2770 B Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Enable Solenoid Control
Circuit High Voltage 4.36 DTC P2770 – Torque
Converter Clutch Enable Solenoid
Control Circuit High Voltage
U0073 B ECM CAN Bus Error
4.37 DTC U0073 and U0100 –
CAN-Bus No Communication With
ECM (Engine Control Module)
U0100 B ECM CAN Bus Error
4.37 DTC U0073 and U0100 –
CAN-Bus No Communication With
ECM (Engine Control Module)
4.9 DTC P0218 – Transmission Fluid Overtemperature
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports DTC P0218 Transmission Fluid Overtemperature.
Circuit Description
The flow of transmission fluid starts in the bottom pan and is drawn through the filter, control valve body assembly,
transmission case and into the oil pump assembly. The oil pump assembly pressurises the fluid and directs it to the
pressure regulator valve where it becomes the main supply of fluid to the various components and hydraulic circuits in
the transmission. Hot fluid exiting the torque converter flows through the converter clutch apply valve and into the
transmission cooler lines, to the oil cooler located in the vehicle radiator, and auxiliary cooler if equipped. From the cooler ,
fluid returns to cool and lubricate the front of the transmission. In forward drive ranges, D4 fluid from the manual valve is
routed through an orificed cup plug in the rear of the transmission case to feed the rear lube fluid circuit.
When the transmission control module (TCM) detects a high transmission fluid temperature (TFT) for a long period of
time, DTC P0218 sets. DTC P0218 is a type C DTC.
Refer to 2 W iring Diagrams and Connector Chart to aid in diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
• No DTCs P0711, P0712 or P0713.
• The ignition switch is on for 5 seconds.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The TFT is greater than 130°C for 600 seconds (10 minutes).
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
•
The TCM does not request the ECM to illuminate the MIL.
• The TCM freezes transmission adapt functions.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007