2007 ISUZU KB P190 service
[x] Cancel search: servicePage 1070 of 6020
6E-36 Engine Control System (4JH1)
Scan Tool Data List
The scan tool Data List contains all engine related
parameters that are available on the scan tool. Use the
scan tool Data List only after the following is
determined: • The Diagnostic System Check - Engine Controls is
completed.
• No diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) are present.
• On-board diagnostics are functioning properly.
The scan tool values from a properly running engine
may be used for comparison with the engine you are
diagnosing. The scan tool Data List represents values
that would be seen on a normal running engine.
Important:
A scan tool that displays faulty data should not be used.
The scan tool problem should be reported to the
manufacturer. Use of a faulty scan tool can result in
misdiagnosis and unnecessary parts replacement. Onl
y
the parameters listed below are referenced in this
service manual for use in diagnosis.
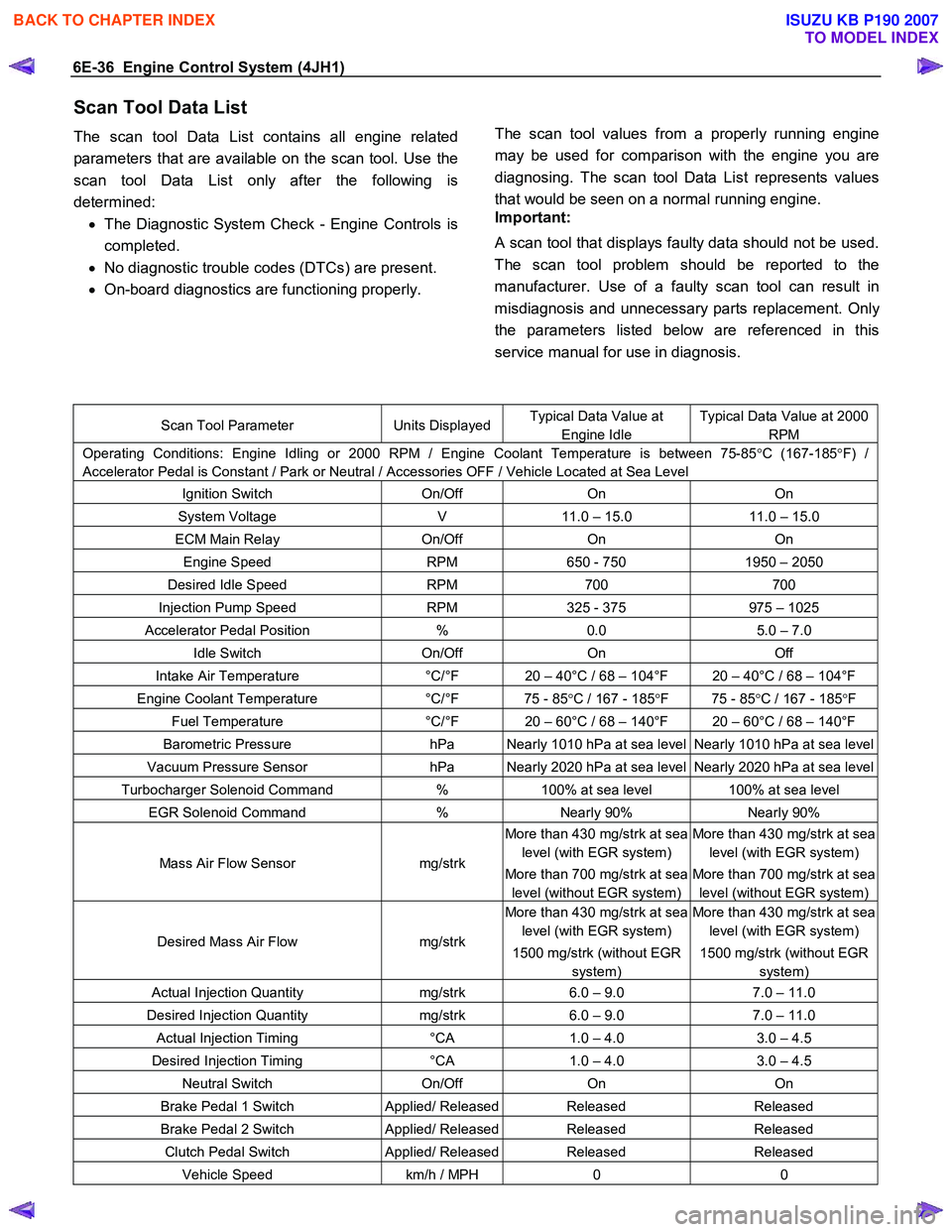
Scan Tool Parameter Units DisplayedTypical Data Value at
Engine Idle
Typical Data Value at 2000
RPM
Operating Conditions: Engine Idling or 2000 RPM / Engine Coolant Temperature is between 75-85 °C (167-185 °F) /
Accelerator Pedal is Constant / Park or Neutral / Accessories OFF / Vehicle Located at Sea Level
Ignition Switch On/Off On On
System Voltage V 11.0 – 15.0 11.0 – 15.0
ECM Main Relay On/Off On On
Engine Speed RPM 650 - 750 1950 – 2050
Desired Idle Speed RPM 700 700
Injection Pump Speed RPM 325 - 375 975 – 1025
Accelerator Pedal Position % 0.0 5.0 – 7.0
Idle Switch On/Off On Off
Intake Air Temperature °C/°F 20 – 40°C / 68 – 104°F 20 – 40°C / 68 – 104°F
Engine Coolant Temperature °C/°F 75 - 85 °C / 167 - 185 °F 75 - 85 °C / 167 - 185 °F
Fuel Temperature °C/°F 20 – 60°C / 68 – 140°F 20 – 60°C / 68 – 140°F
Barometric Pressure hPa Nearly 1010 hPa at sea level Nearly 1010 hPa at sea level
Vacuum Pressure Sensor hPa Nearly 2020 hPa at sea level Nearly 2020 hPa at sea level
Turbocharger Solenoid Command % 100% at sea level 100% at sea level
EGR Solenoid Command % Nearly 90% Nearly 90%
Mass Air Flow Sensor mg/strk
More than 430 mg/strk at sea
level (with EGR system)
More than 700 mg/strk at sea
level (without EGR system)
More than 430 mg/strk at sea
level (with EGR system)
More than 700 mg/strk at sea
level (without EGR system)
Desired Mass Air Flow mg/strk
More than 430 mg/strk at sea
level (with EGR system)
1500 mg/strk (without EGR
system)
More than 430 mg/strk at sea
level (with EGR system)
1500 mg/strk (without EGR
system)
Actual Injection Quantity mg/strk 6.0 – 9.0 7.0 – 11.0
Desired Injection Quantity mg/strk 6.0 – 9.0 7.0 – 11.0
Actual Injection Timing °CA 1.0 – 4.0 3.0 – 4.5
Desired Injection Timing °CA 1.0 – 4.0 3.0 – 4.5
Neutral Switch On/Off On On
Brake Pedal 1 Switch Applied/ ReleasedReleased Released
Brake Pedal 2 Switch Applied/ ReleasedReleased Released
Clutch Pedal Switch Applied/ ReleasedReleased Released
Vehicle Speed km/h / MPH 0 0
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1081 of 6020
Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-47
Engine Cranks but Does Not Run
Description
The Engine Cranks but Does Not Run diagnostic table
is an organized approach to identifying a condition that
causes an engine to not start. The diagnostic table
directs the service technician to the appropriate system
diagnosis. The diagnostic table assumes the following
conditions are met:
• The battery is completely charged and terminals
are cleaned and tight.
• The engine cranking speed is normal.
• There is adequate fuel in the fuel tank.
• There is no fuel leak in the fuel line.
• There is no air in the fuel line.
• Filters (Air, Fuel) are clean.
• Fuse and slow blow fuse are normal.
Diagnostic Aids
• If an intermittent condition is suspected, refer to
Intermittent Conditions in this section.
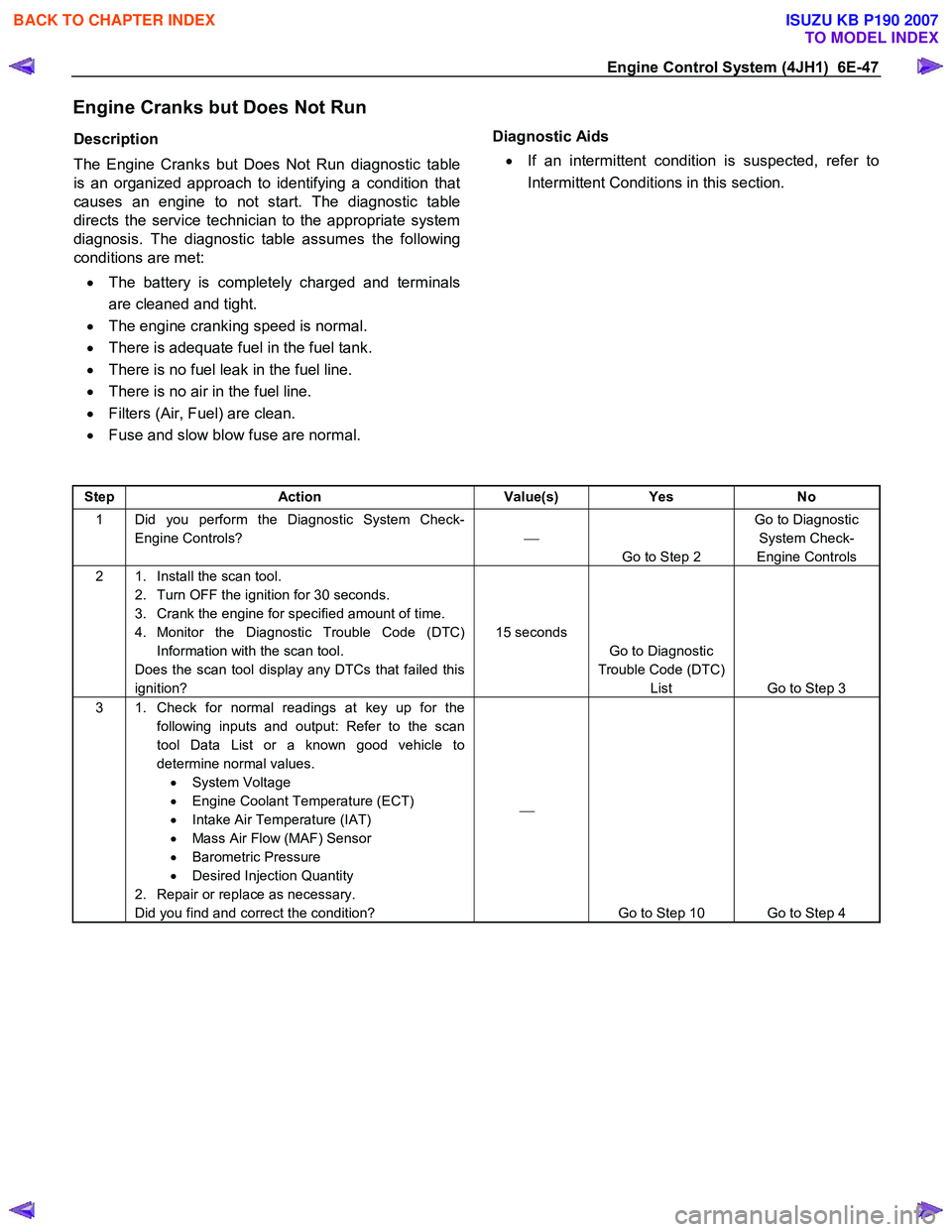
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1 Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check-
Engine Controls?
Go to Step 2 Go to Diagnostic
System Check-
Engine Controls
2 1. Install the scan tool. 2. Turn OFF the ignition for 30 seconds.
3. Crank the engine for specified amount of time.
4. Monitor the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Information with the scan tool.
Does the scan tool display any DTCs that failed this
ignition? 15 seconds
Go to Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) List Go to Step 3
3 1. Check for normal readings at key up for the
following inputs and output: Refer to the scan
tool Data List or a known good vehicle to
determine normal values. • System Voltage
• Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT)
• Intake Air Temperature (IAT)
• Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor
• Barometric Pressure
• Desired Injection Quantity
2. Repair or replace as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition?
Go to Step 10 Go to Step 4
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1208 of 6020
6E-174 Engine Control System (4JH1)
DTC P0602
Description
The engine control module (ECM) has the ability to set
a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) if it detects that there is
no vehicle identification (VIN) programmed.
Diagnostic Aids
Notice:
• Production and service ECM does not require
software programming when it is replaced except
calibration software update. This DTC indicates
that a production or service ECM does not
program VIN.
DTC P0602
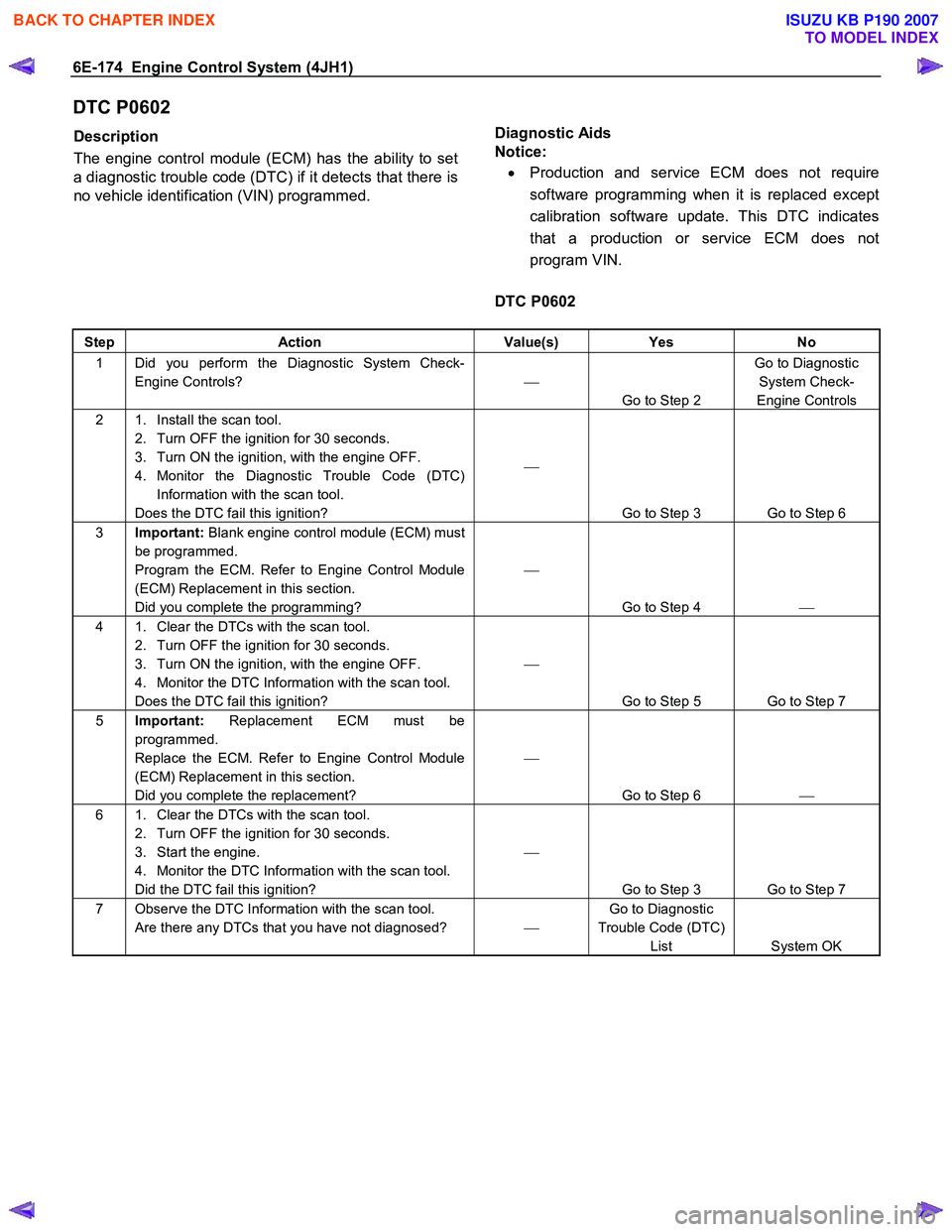
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1 Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check-
Engine Controls?
Go to Step 2 Go to Diagnostic
System Check-
Engine Controls
2 1. Install the scan tool. 2. Turn OFF the ignition for 30 seconds.
3. Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
4. Monitor the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Information with the scan tool.
Does the DTC fail this ignition?
Go to Step 3 Go to Step 6
3 Important: Blank engine control module (ECM) must
be programmed.
Program the ECM. Refer to Engine Control Module
(ECM) Replacement in this section.
Did you complete the programming?
Go to Step 4
4 1. Clear the DTCs with the scan tool.
2. Turn OFF the ignition for 30 seconds.
3. Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
4. Monitor the DTC Information with the scan tool.
Does the DTC fail this ignition?
Go to Step 5 Go to Step 7
5 Important: Replacement ECM must be
programmed.
Replace the ECM. Refer to Engine Control Module
(ECM) Replacement in this section.
Did you complete the replacement?
Go to Step 6
6 1. Clear the DTCs with the scan tool.
2. Turn OFF the ignition for 30 seconds.
3. Start the engine.
4. Monitor the DTC Information with the scan tool.
Did the DTC fail this ignition?
Go to Step 3 Go to Step 7
7 Observe the DTC Information with the scan tool. Are there any DTCs that you have not diagnosed? Go to Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) List System OK
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1268 of 6020

6E-234 Engine Control System (4JH1)
DTC P1690 (Symptom Code 4) (Flash Code 77)
Circuit Description
The malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) is located on the
instrument panel cluster (IPC). The battery voltage is
supplied to the MIL. The engine control module (ECM)
turns the MIL ON by grounding the MIL control circuit.
After a fixed time passes, the ECM turns OFF the MIL
with the ignition ON and the engine OFF. The MIL has
the following functions:
• The MIL informs the driver that a malfunction has
occurred and the vehicle should be taken in fo
r
service as soon as possible.
• The MIL illuminates during a bulb test and a
system test.
•
A DTC will be stored if a MIL is requested by the
ECM.
If the ECM detects an open circuit or short circuit on the
MIL control circuit, this DTC will set.
Condition for Running the DTC • The ignition switch is ON.
Condition for Setting the DTC
• The ECM detects a low voltage condition on the
MIL control circuit for longer than 3 seconds when
the MIL is commanded OFF.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets • The ECM does not illuminates the MIL when the
diagnostic runs and fails.
Condition for Clearing the DTC • A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive driving
cycles without a fault. Or clear with the scan tool.
Diagnostic Aids
• If an intermittent condition is suspected, refer to
Intermittent Conditions in this section.
DTC P1690 (Symptom Code 4) (Flash Code 77)
Schematic Reference: Engine Controls Schematics
Connector End View Reference: Engine Controls
Connector End Views or Engine Control Module (ECM)
Connector End Views
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1 Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check-
Engine Controls?
Go to Step 2 Go to Diagnostic
System Check-
Engine Controls
2 1. Install the scan tool. 2. Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
3. Perform the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) test with the scan tool.
4. Command the MIL ON with the scan tool.
Does the MIL turn ON when commanded ON with
the scan tool?
Go to Step 3 Go to Step 4
3 Command the MIL OFF with the scan tool. Does the MIL OFF?
Go to Step 17 Go to Step 10
4 1. Turn OFF the ignition.
2. Inspect the Meter (15A) fuse (C-14) in the cabin fuse block.
Is the Meter (15A) fuse (C-14) open?
Go to Step 5 Go to Step 6
5 Replace the Meter (15A) fuse (C-14). If the fuse continues to open, repair the short to ground on one
of the circuits that fed by the Meter (15A) fuse (C-14)
or replace the shorted attached component fed by
the Meter (15A) fuse (C-14).
Did you complete the repair?
Go to Step 19
6 1. Turn OFF the ignition.
2. Disconnect the engine control module (ECM) harness connector.
3. Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
4. Connect a 3-amp fused jumper wire between the MIL control circuit of the ECM harness connector
(pin 42 of C-56 connector) and a known good
ground.
Does the MIL illuminate?
Go to Step 11 Go to Step 7
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1271 of 6020
Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-237
DTC P1690 (Symptom Code 8) (Flash Code 77)
Circuit Description
The malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) is located on the
instrument panel cluster (IPC). The battery voltage is
supplied to the MIL. The engine control module (ECM)
turns the MIL ON by grounding the MIL control circuit.
After a fixed time passes, the ECM turns OFF the MIL
with the ignition ON and the engine OFF. The MIL has
the following functions:
• The MIL informs the driver that a malfunction has
occurred and the vehicle should be taken in fo
r
service as soon as possible.
• The MIL illuminates during a bulb test and a
system test.
•
A DTC will be stored if a MIL is requested by the
ECM.
If the ECM detects a short to battery or ignition voltage
on the MIL control circuit, this DTC will set.
Condition for Running the DTC • The ignition switch is ON.
Condition for Setting the DTC
• The ECM detects a high voltage condition on the
MIL control circuit for longer than 1 second when
the MIL is commanded ON.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
• The ECM does not illuminates the MIL when the
diagnostic runs and fails.
Condition for Clearing the DTC
• A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive driving
cycles without a fault. Or clear with the scan tool.
Diagnostic Aids
• If an intermittent condition is suspected, refer to
Intermittent Conditions in this section.
Test Description
The number below refers to the step number on the
diagnostic table.
3. If the control circuit of the MIL between the ECM and
the IPC is normal, the control circuit voltage low DTC
P1690 (Symptom Code 4) will set.
4. If the control circuit of the MIL between the ECM and
the IPC is normal, the control circuit voltage low DTC
P1690 (Symptom Code 4) will set.
DTC P1690 (Symptom Code 8) (Flash Code 77)
Schematic Reference: Engine Controls Schematics
Connector End View Reference: Engine Controls
Connector End Views or Engine Control Module (ECM)
Connector End Views
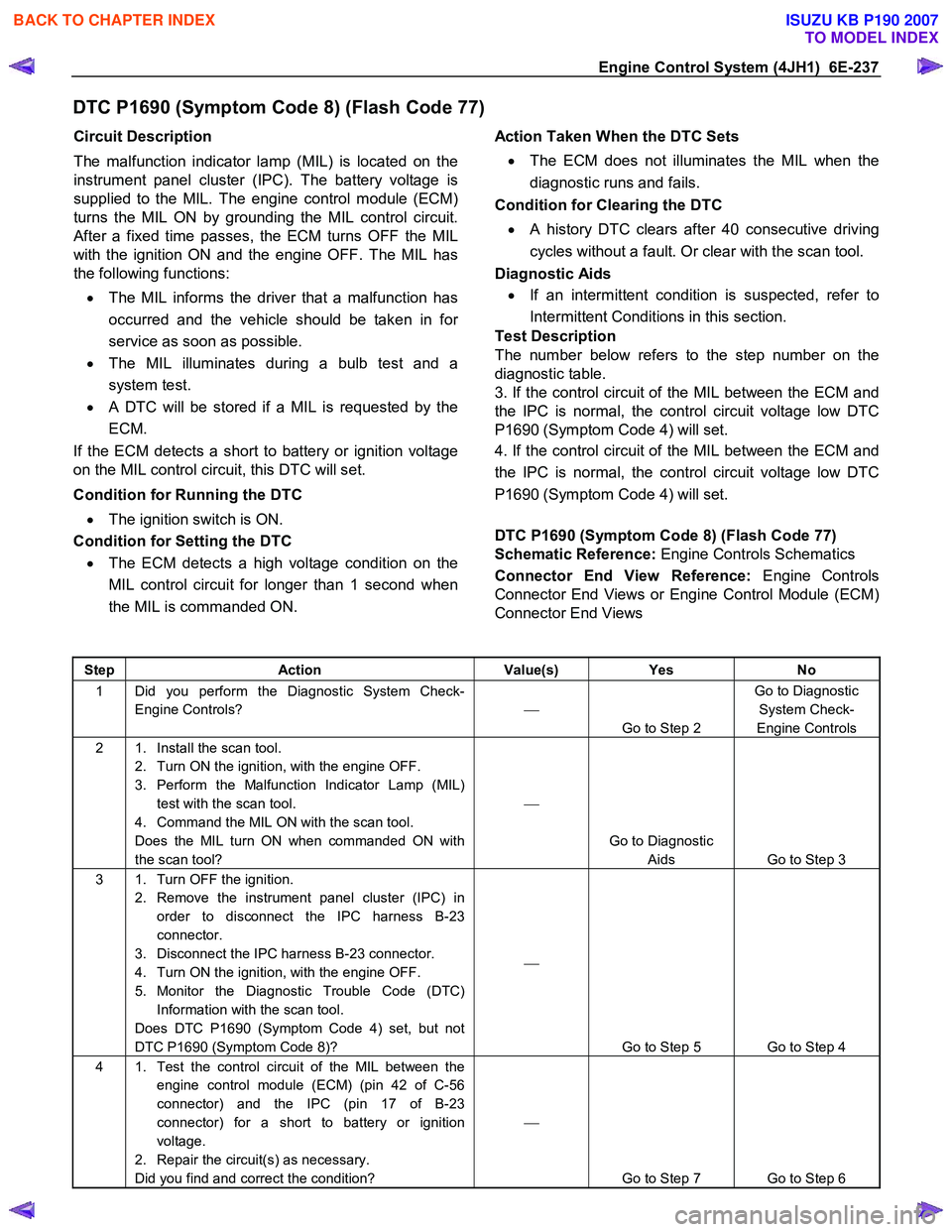
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1 Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check-
Engine Controls?
Go to Step 2 Go to Diagnostic
System Check-
Engine Controls
2 1. Install the scan tool. 2. Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
3. Perform the Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) test with the scan tool.
4. Command the MIL ON with the scan tool.
Does the MIL turn ON when commanded ON with
the scan tool?
Go to Diagnostic Aids Go to Step 3
3 1. Turn OFF the ignition. 2. Remove the instrument panel cluster (IPC) in order to disconnect the IPC harness B-23
connector.
3. Disconnect the IPC harness B-23 connector.
4. Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
5. Monitor the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Information with the scan tool.
Does DTC P1690 (Symptom Code 4) set, but not
DTC P1690 (Symptom Code 8)?
Go to Step 5 Go to Step 4
4 1. Test the control circuit of the MIL between the engine control module (ECM) (pin 42 of C-56
connector) and the IPC (pin 17 of B-23
connector) for a short to battery or ignition
voltage.
2. Repair the circuit(s) as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition?
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 6
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1292 of 6020
6E-258 Engine Control System (4JH1)
Checks Action
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
and Electrical Noise Some electrical components/circuits are sensitive to EMI or other types of electrical
noise. Inspect for the following conditions:
• A misrouted harness that is too close to high voltage/high current devices such as
injection components, motors, generator etc. These components may induce
electrical noise on a circuit that could interfere with normal circuit operation.
• Electrical system interference caused by a malfunctioning relay, or the engine control
module (ECM) driven solenoid or switch. These conditions can cause a sharp
electrical surge. Normally, the problem will occur when the malfunctioning
component is operating.
• Improper installation of non-factory or aftermarket add on accessories such as lights,
2-way radios, amplifiers, electric motors, remote starters, alarm systems, cell
phones, etc. These accessories may lead to an emission related failure while in use,
but do not fail when the accessories are not in use.
• Test for an open diode across the A/C compressor clutch and for other open diodes.
Some relays may contain a clamping diode.
• Test the generator for a bad rectifier bridge that may be allowing AC noise into the
electrical system.
Incorrect ECM Programming • There are only a few situations where reprogramming a ECM is appropriate:
Important:
DO NOT reprogram the ECM with the SAME software/calibration files that are already
present in the ECM. This is not an effective repair for any type of driveability problem. - A ECM from another vehicle is installed.
- Revised software/calibration files have been released for this vehicle.
• Verify that the ECM contains the correct software/calibration. If incorrect
programming is found, reprogram the ECM with the most current
software/calibration.
Duplicating Failure Conditions • If none of the previous tests are successful, attempt to duplicate and/or capture the
failure conditions.
• An alternate method is to drive the vehicle with the DMM connected to a suspected
circuit. An abnormal reading on the DMM when the problem occurs, may help you
locate the problem.
scan tool Snapshot The scan tool can be set up to take a Snapshot of the parameters available via serial
data. The Snapshot function records live data over a period of time. The recorded data
can be played back and analyzed. The scan tool can also graph parameters singly or
in combinations of parameters for comparison. The Snapshot can be triggered
manually at the time the symptom is noticed, or set up in advance to trigger when a
DTC sets.
An abnormal value captured in the recorded data may point to a system or component
that needs to be investigated further.
Refer to the scan tool user instructions for more information on the Snapshot function.
Hard Start
Checks Action
DEFINITION:The engine cranks OK, but does not start for a long time. The engine does eventually run, or may start but
immediately dies.
Preliminary Checks •
Diagnostic System Check - Engine Controls.
• Ensure the driver is using the correct starting procedure.
• Inspect the engine control module (ECM) and fuel injection pump control unit (PCU)
grounds for being clean, tight, and in their proper locations.
• Inspect that the harness connectors are correctly connected.
• Inspect the fuel type and quality.
• Inspect the scan tool Data List in this section.
• Inspect the Service Bulletins for ECM software updates.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1294 of 6020
6E-260 Engine Control System (4JH1)
Checks Action
Engine Mechanical Checks Inspect the engine mechanical for the following conditions. Refer to the Engine
Mechanical section.
• Inspect for poor cylinder compression. Proper compression is more than 2100 kPa
(309 psi).
• Improper mechanical timing (timing gear)
• Improper valve gap
• Broken or weak valve springs
• W orn camshaft lobes
Electrical System Checks Inspect the engine electrical for the following conditions. Refer to the Engine Electrical
section.
• Inspect the glow plug control (preheating) system operation.
• Inspect for slow cranking speed.
• Inspect for weakened batteries.
Rough, Unstable, or Incorrect Idle And Stalling
Checks Action
DEFINITION:Engine runs unevenly at idle. If severe, the engine or vehicle may shake. Engine idle speed may vary in RPM.
Either condition may be severe enough to stall the engine.
Preliminary Checks • Diagnostic System Check - Engine Controls.
• Remove the air cleaner and check for dirt, or for air ducts being plugged or restricted.
Replace as necessary.
• Inspect the Engine Control Module (ECM) and fuel injection pump control unit (PCU)
grounds for being clean, tight, and in their proper locations.
• Inspect that the harness connectors are correctly connected.
• Inspect the fuel type and quality.
• Inspect the scan tool Data List in this section.
• Inspect the Service Bulletins for ECM software updates.
Sensor Checks Inspect the engine control sensors for the following conditions. Refer to the scan tool Data
List in this section.
• Use the scan tool to compare the Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) with the Intake Air
Temperature (IAT) and Fuel Temperature (FT) on a cold engine condition. If the
difference among temperature reading is more than 5°C (9°F) on a cold engine, check for
high resistance on the low reference circuit and signal circuit or for a skewed sensor.
Notice: The mass air flow (MAF) sensor is heated and as a result the IAT sensor may
indicate a higher than normal intake air temperature if the ignition switch is being ON. FT
sensor is internal to the PCU and it is part of the fuel injection pump assembly.
• Use the scan tool to compare the MAF Sensor parameter with the Desired MAF
parameter. Start the engine and warm up (allow engine coolant temperature to reach at
least 60°C [140°F]). The MAF Sensor parameter must follow the Desired MAF parameter
within 100 mg/strk. If not, inspect the air intake system, EGR system components and
contaminated, skewed or slow MAF sensor.
• Inspect the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor is tight and the flywheel circumference is
not damaged.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1296 of 6020
6E-262 Engine Control System (4JH1)
Checks Action
Additional Checks •
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) on the reference circuit can cause an engine miss
condition. The scan tool can usually detect EMI by monitoring the engine speed. A
sudden increase in speed with little change in actual engine speed change indicates that
EMI is present. If a problem exists, check routing of high voltage components, such as
fuel injection solenoid valve wiring, near the sensor circuits.
• Inspect for faulty engine mounts.
• Inspect faulty crank pulley.
• Inspect faulty generator & A/C compressor.
• Inspect the generator output voltage. Repair if less than 9 volts or more than 16 volts.
• Inspect the EGR system operating correctly.
• Inspect the A/C operation.
Cut Out, Misses
Checks Action
DEFINITION:A constant jerking that follows the engine speed, usually more pronounced as the engine load increase. The
exhaust has a steady spitting sound at idle, low speed, or hard acceleration for the fuel starvation that can cause the engine to
cut-out.
Preliminary Check • Diagnostic System Check - Engine Controls.
• Inspect that the harness connectors are correctly connected.
• Inspect the engine control module (ECM) and fuel injection pump control unit (PCU)
grounds for being clean, tight, and in their proper locations.
• Inspect the scan tool Data List in this section.
• Inspect the Service Bulletins for ECM software updates.
Sensor Checks Inspect the engine control sensors for the following conditions. Refer to the scan tool
Data List in this section.
• Use the scan tool to observe the Accelerator Pedal Position. Accelerator Pedal
Position indicating angle parameter should change linearly from 0% to 100%
according to the accelerator pedal operation.
• Inspect the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor is tight and the flywheel circumference
is not damaged.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007