2007 ISUZU KB P190 coolant temperature
[x] Cancel search: coolant temperaturePage 1305 of 6020
Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-271
Checks Action
Engine Mechanical Checks Inspect the engine mechanical for the following conditions. Refer to the Engine
Mechanical section.
• Inspect for poor cylinder compression. Proper compression is more than 2100 kPa
(309 psi).
• Inspect for incorrect basic engine parts such as camshaft, cylinder head, pistons,
etc.
• Inspect for any excessive oil entering combustion chamber.
Additional Checks •
Inspect the EGR system operating correctly.
• Inspect other possible causes that can make similar noise such as loose component
parts, bracket, mount and weak clutch damper spring.
Poor Fuel Economy
Checks Action
DEFINITION:Fuel economy, as measured by actual road tests and several tanks of fuel, is noticeably lower than expected.
Also, the economy is noticeably lower than it was on this vehicle at one time, as previously shown by actual road tests.
Preliminary Checks • Remove the air cleaner and check for dirt, or for air ducts being plugged or
restricted. Replace as necessary.
• Inspect the driving habits of the owner.
• Is the A/C ON full time, defroster mode ON?
• Are the tires at the correct pressure?
• Are the tire sizes changed?
• Are excessively heavy loads being carried?
• Is the acceleration too much, too often?
• Inspect for clutch slip.
• Inspect brake drag.
• Inspect dive belt tension.
• Inspect for a proper transmission shift pattern and down shift operation (A/T only).
• Inspect the fuel quality (cetane index).
• Inspect the engine oil level and quality.
• Suggest to the owner to fill the fuel tank and recheck the fuel economy.
• Suggest to the driver to read the Important Facts on Fuel Economy in the Owner
Manual.
• Inspect the odometer is correctly operated.
• Inspect the Service Bulletins for ECM software updates.
Sensor Checks Inspect the engine control sensors for the following conditions. Refer to the scan tool
Data List in this section.
• Use the scan tool to compare the Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) with the Intake
Air Temperature (IAT) and Fuel Temperature (FT) on a cold engine condition. If the
difference among temperature reading is more than 5°C (9°F) on a cold engine,
check for high resistance on the low reference circuit and signal circuit or for a
skewed sensor.
Notice: The mass air flow (MAF) sensor is heated and as a result the IAT sensor may
indicate a higher than normal intake air temperature if the ignition switch is being ON.
FT sensor is internal to the PCU and it is part of the fuel injection pump assembly.
Fuel System Checks Inspect the fuel system for the following conditions. Refer to the Fuel System section.
• Inspect the fuel type and quality.
• Check fuel leak.
Cooling System Checks Inspect the cooling system for the following conditions. Refer to the Cooling System
Section.
• Inspect the engine coolant level.
• Inspect the engine thermostat for always being open or for the wrong heat range.
• Inspect the engine cooling fan for always being ON.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1306 of 6020
6E-272 Engine Control System (4JH1)
Checks Action
Air Intake System Checks Inspect the air intake system for the following conditions.
• Inspect the air cleaner and air intake ducts for a restriction, holes, or leaks.
• Inspect for a restriction or leak in the intercooler.
• Inspect for a restriction in the turbocharger inlet duct.
• Inspect for a restriction or deposit in the intake throttle bore.
• Inspect for a restriction or leak in the intake manifold.
• Inspect for a restriction or damage at MAF sensor.
Exhaust System Checks Inspect the exhaust system for a possible restriction. Refer to the Exhaust System
section.
• Inspect for a restriction in the catalytic converter or exhaust pipes.
Engine Mechanical Checks Inspect the engine mechanical for the following conditions. Refer to the Engine
Mechanical section.
• Inspect for poor cylinder compression. Proper compression is more than 2100 kPa
(309 psi).
Excessive Smoke (Black Smoke)
Checks Action
DEFINITION:Black smoke under load, idle or start up hot or cold.
Preliminary Check •
Ensure the vehicle has an actual problem.
• Inspect the engine control module (ECM) and fuel injection pump control unit (PCU)
grounds for being clean, tight, and in their proper locations.
• Remove the air cleaner and check for dirt, or for air ducts being plugged or
restricted. Replace as necessary.
• Inspect the fuel quality (cetane index).
• Inspect the engine oil level and quality.
• Inspect the Service Bulletins for ECM software updates.
Sensor Checks Inspect the engine control sensors for the following conditions. Refer to the scan tool
Data List in this section.
• Use the scan tool to compare the Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) with the Intake
Air Temperature (IAT) and Fuel Temperature (FT) on a cold engine condition. If the
difference among temperature reading is more than 5°C (9°F) on a cold engine,
check for high resistance on the low reference circuit and signal circuit or for a
skewed sensor.
Notice: The mass air flow (MAF) sensor is heated and as a result the IAT sensor may
indicate a higher than normal intake air temperature if the ignition switch is being ON.
FT sensor is internal to the PCU and it is part of the fuel injection pump assembly.
• Use the scan tool to compare the MAF Sensor parameter with the Desired MAF
parameter. Start the engine and warm up (allow engine coolant temperature to reach
at least 60°C [140°F]). The MAF Sensor parameter must follow the Desired MAF
parameter within 100 mg/strk. If not, inspect the air intake system, EGR system
components and contaminated, skewed or slow MAF sensor.
• Use the scan tool to observe the Accelerator Pedal Position Accelerator Pedal
Position. Accelerator Pedal Position indicating angle parameter should change
linearly from 0% to 100% according to the accelerator pedal operation.
Fuel System Checks Inspect the fuel system for the following conditions. Refer to the Fuel System section.
• Inspect the fuel injection nozzle(s) for proper splay condition or operating pressure.
Notice: Only first stage of operating pressure can be checked.
• Inspect the timing device operating correctly. Observe the Actual Injection Timing
parameter with the scan tool while running the engine. The Actual Injection Timing
parameter must follow the Desired Injection Timing within 2°CA on each engine
speed. Engine idle > around 2000 RPM> around 3000 RPM. If not, inspect the fuel
system restriction, air in the fuel or fuel injection pump operation.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1307 of 6020
Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-273
Checks Action
Air Intake System Checks Inspect the air intake system for the following conditions.
• Inspect the air cleaner and air intake ducts for a restriction, holes, or leaks.
• Inspect for a restriction or leak in the intercooler.
• Inspect for a restriction in the turbocharger inlet duct.
• Inspect for a restriction or deposit in the intake throttle bore.
• Inspect for a restriction or leak in the intake manifold.
• Inspect for a restriction or damage at MAF sensor.
• Inspect for a worn or damaged turbocharger turbine wheel, shaft or compressor
wheel. Refer to turbocharger inspection in the Engine Mechanical section.
Exhaust System Checks Inspect the exhaust system for a possible restriction. Refer to the Exhaust System
section.
• Inspect for a restriction in the catalytic converter or exhaust pipes.
Engine Mechanical Check Inspect the engine mechanical for the following conditions. Refer to the Engine
Mechanical section.
• Inspect for poor cylinder compression. Proper compression is more than 2100 kPa
(309 psi).
• Inspect for incorrect basic engine parts such as camshaft, cylinder head, pistons,
etc.
• Inspect for any excessive oil entering combustion chamber.
• Improper mechanical timing
• Improper valve gap
• Broken or weak valve springs
• W orn camshaft lobes
Additional Checks •
Inspect the EGR system operating correctly.
• Inspect the excessive blow-by gasses.
• Inspect the scan tool Data List in this section.
Excessive Smoke (White Smoke)
Checks Action
DIFINITION:W hite smoke under load, idle or start up hot or cold.
Preliminary Check •
Ensure the vehicle has an actual problem.
• Inspect the engine control module (ECM) and fuel injection pump control unit (PCU)
grounds for being clean, tight, and in their proper locations.
• Inspect the fuel quality (cetane index).
• Inspect the Service Bulletins for ECM software updates.
Sensor Check Inspect the engine control sensors for the following conditions. Refer to the scan tool
Data List in this section.
• Use the scan tool to compare the Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) with the Intake
Air Temperature (IAT) and Fuel Temperature (FT) on a cold engine condition. If the
difference among temperature reading is more than 5°C (9°F) on a cold engine,
check for high resistance on the low reference circuit and signal circuit or for a
skewed sensor.
Notice: The mass air flow (MAF) sensor is heated and as a result the IAT sensor may
indicate a higher than normal intake air temperature if the ignition switch is being ON.
FT sensor is internal to the PCU and it is part of the fuel injection pump assembly.
• Inspect the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor is tight and the flywheel circumference
is not damaged.
Fuel System Checks Inspect the fuel system for the following conditions. Refer to the Fuel System section.
• Inspect the fuel injection nozzle(s) for proper splay condition or operating pressure.
Notice: Only first stage of operating pressure can be checked.
• Inspect the timing device operating correctly. Observe the Actual Injection Timing
parameter with the scan tool while running the engine. The Actual Injection Timing
parameter must follow the Desired Injection Timing within 2°CA on each engine
speed. Engine idle > around 2000 RPM> around 3000 RPM. If not, inspect the fuel
system restriction, air in the fuel or fuel injection pump operation.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1314 of 6020
6E-280 Engine Control System (4JH1)
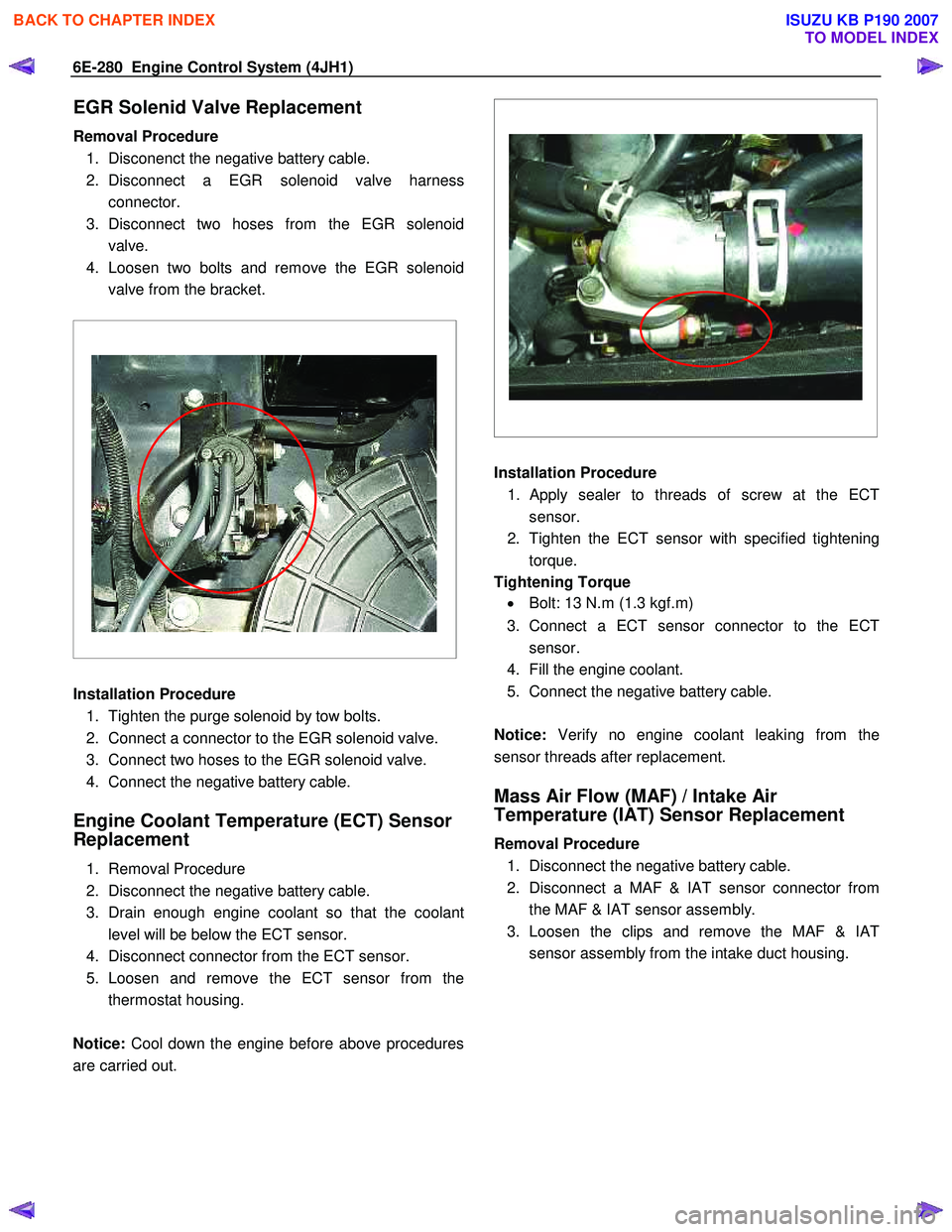
EGR Solenid Valve Replacement
Removal Procedure 1. Disconenct the negative battery cable.
2. Disconnect a EGR solenoid valve harness connector.
3. Disconnect two hoses from the EGR solenoid valve.
4. Loosen two bolts and remove the EGR solenoid valve from the bracket.
Installation Procedure
1. Tighten the purge solenoid by tow bolts.
2. Connect a connector to the EGR solenoid valve.
3. Connect two hoses to the EGR solenoid valve.
4. Connect the negative battery cable.
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
Replacement
1. Removal Procedure
2. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
3. Drain enough engine coolant so that the coolant level will be below the ECT sensor.
4. Disconnect connector from the ECT sensor.
5. Loosen and remove the ECT sensor from the thermostat housing.
Notice: Cool down the engine before above procedures
are carried out.
Installation Procedure
1.
Apply sealer to threads of screw at the ECT
sensor.
2. Tighten the ECT sensor with specified tightening torque.
Tightening Torque • Bolt: 13 N.m (1.3 kgf.m)
3. Connect a ECT sensor connector to the ECT sensor.
4. Fill the engine coolant.
5. Connect the negative battery cable.
Notice: Verify no engine coolant leaking from the
sensor threads after replacement.
Mass Air Flow (MAF) / Intake Air
Temperature (IAT) Sensor Replacement
Removal Procedure
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Disconnect a MAF & IAT sensor connector from the MAF & IAT sensor assembly.
3. Loosen the clips and remove the MAF & IAT sensor assembly from the intake duct housing.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1319 of 6020
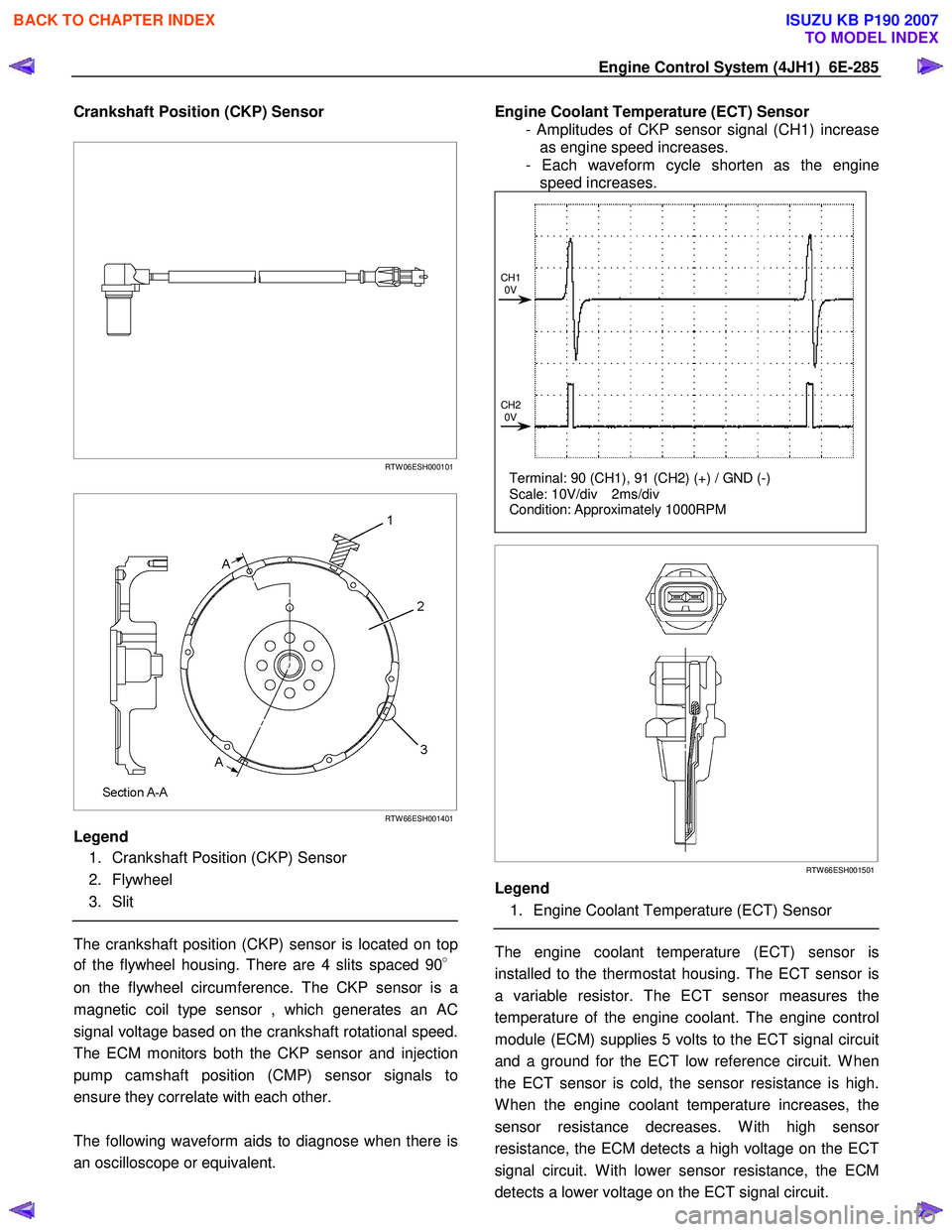
Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-285
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
RTW 06ESH000101
RTW 66ESH001401
Legend
1. Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
2. Flywheel
3. Slit
The crankshaft position (CKP) sensor is located on top
of the flywheel housing. There are 4 slits spaced 90 °
on the flywheel circumference. The CKP sensor is a
magnetic coil type sensor , which generates an AC
signal voltage based on the crankshaft rotational speed.
The ECM monitors both the CKP sensor and injection
pump camshaft position (CMP) sensor signals to
ensure they correlate with each other.
The following waveform aids to diagnose when there is
an oscilloscope or equivalent.
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
- Amplitudes of CKP sensor signal (CH1) increase as engine speed increases.
- Each waveform cycle shorten as the engine speed increases.
Terminal: 90 (CH1), 91 (CH2) (+) / GND (-)
Scale: 10V/div 2ms/div
Condition: Approximately 1000RPM
CH1
0V
CH2 0V
RTW 66ESH001501
Legend
1. Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
The engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor is
installed to the thermostat housing. The ECT sensor is
a variable resistor. The ECT sensor measures the
temperature of the engine coolant. The engine control
module (ECM) supplies 5 volts to the ECT signal circuit
and a ground for the ECT low reference circuit. W hen
the ECT sensor is cold, the sensor resistance is high.
W hen the engine coolant temperature increases, the
sensor resistance decreases. W ith high senso
r
resistance, the ECM detects a high voltage on the ECT
signal circuit. W ith lower sensor resistance, the ECM
detects a lower voltage on the ECT signal circuit.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1320 of 6020
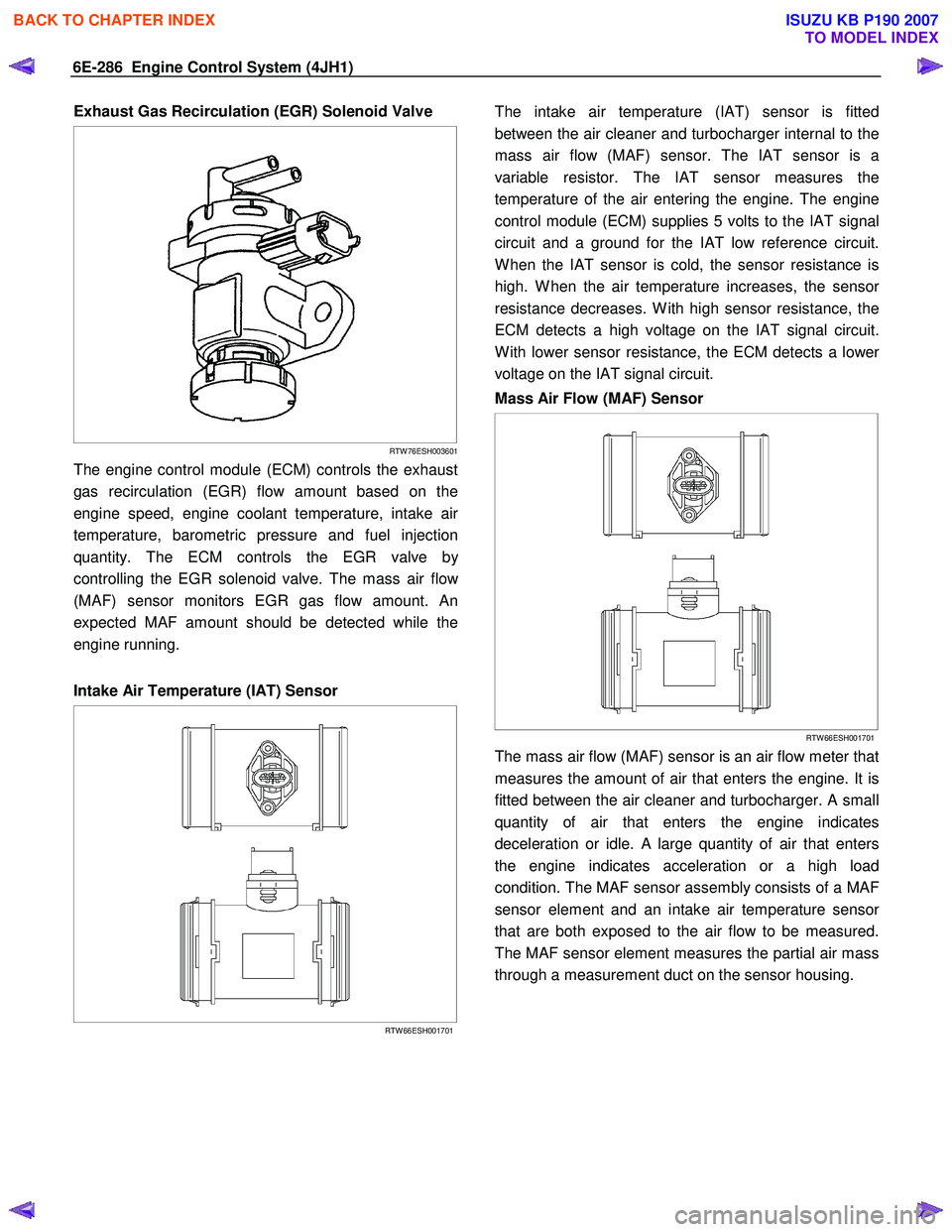
6E-286 Engine Control System (4JH1)
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Solenoid Valve
RTW 76ESH003601
The engine control module (ECM) controls the exhaust
gas recirculation (EGR) flow amount based on the
engine speed, engine coolant temperature, intake ai
r
temperature, barometric pressure and fuel injection
quantity. The ECM controls the EGR valve b
y
controlling the EGR solenoid valve. The mass air flo
w
(MAF) sensor monitors EGR gas flow amount. An
expected MAF amount should be detected while the
engine running.
Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
RTW 66ESH001701
The intake air temperature (IAT) sensor is fitted
between the air cleaner and turbocharger internal to the
mass air flow (MAF) sensor. The IAT sensor is a
variable resistor. The IAT sensor measures the
temperature of the air entering the engine. The engine
control module (ECM) supplies 5 volts to the IAT signal
circuit and a ground for the IAT low reference circuit.
W hen the IAT sensor is cold, the sensor resistance is
high. W hen the air temperature increases, the senso
r
resistance decreases. W ith high sensor resistance, the
ECM detects a high voltage on the IAT signal circuit.
W ith lower sensor resistance, the ECM detects a lowe
r
voltage on the IAT signal circuit.
Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor
RTW 66ESH001701
The mass air flow (MAF) sensor is an air flow meter that
measures the amount of air that enters the engine. It is
fitted between the air cleaner and turbocharger. A small
quantity of air that enters the engine indicates
deceleration or idle. A large quantity of air that enters
the engine indicates acceleration or a high load
condition. The MAF sensor assembly consists of a MAF
sensor element and an intake air temperature senso
r
that are both exposed to the air flow to be measured.
The MAF sensor element measures the partial air mass
through a measurement duct on the sensor housing.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1328 of 6020
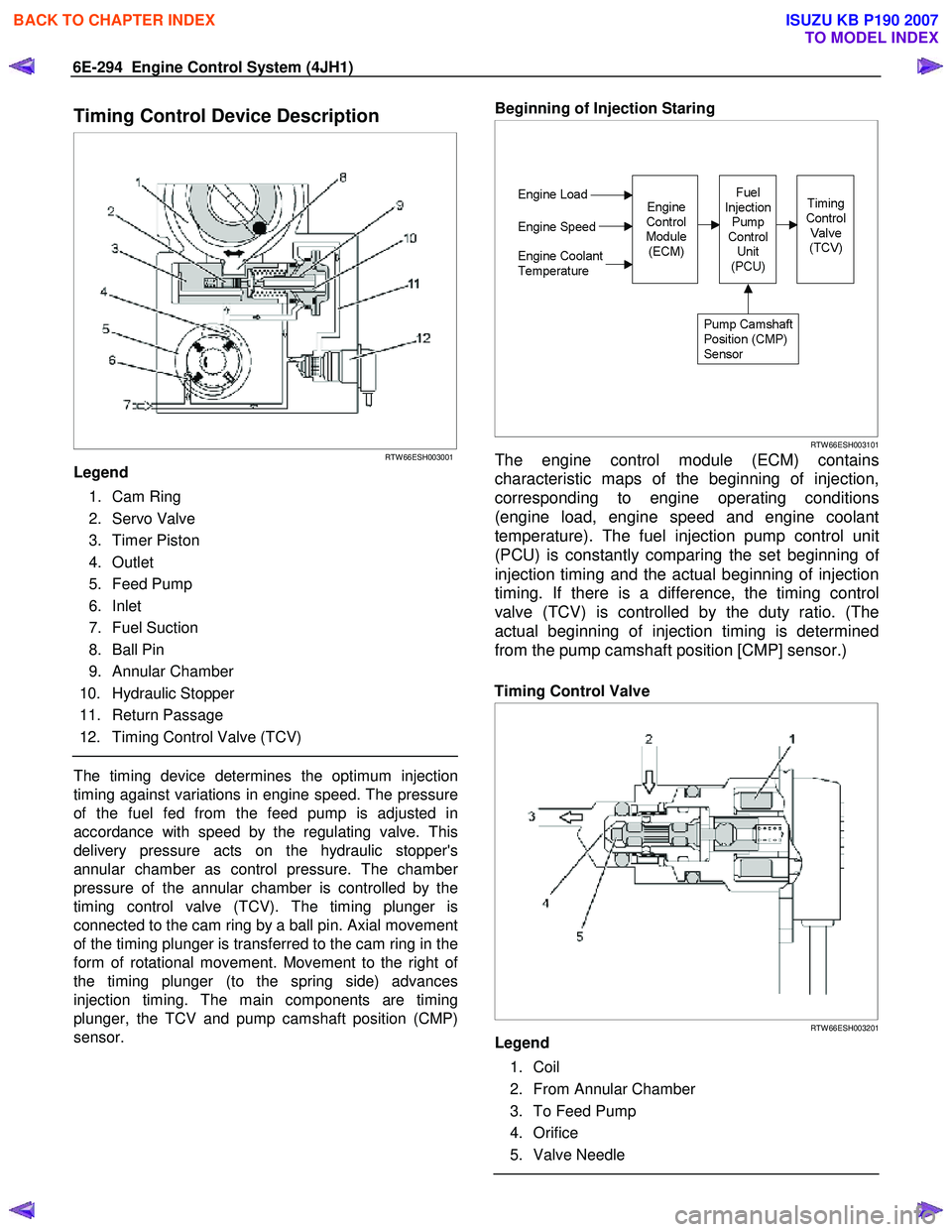
6E-294 Engine Control System (4JH1)
Timing Control Device Description
RTW 66ESH003001
Legend
1. Cam Ring
2. Servo Valve
3. Timer Piston
4. Outlet
5. Feed Pump
6. Inlet
7. Fuel Suction
8. Ball Pin
9. Annular Chamber
10. Hydraulic Stopper
11. Return Passage
12. Timing Control Valve (TCV)
The timing device determines the optimum injection
timing against variations in engine speed. The pressure
of the fuel fed from the feed pump is adjusted in
accordance with speed by the regulating valve. This
delivery pressure acts on the hydraulic stopper's
annular chamber as control pressure. The chambe
r
pressure of the annular chamber is controlled by the
timing control valve (TCV). The timing plunger is
connected to the cam ring by a ball pin. Axial movement
of the timing plunger is transferred to the cam ring in the
form of rotational movement. Movement to the right o
f
the timing plunger (to the spring side) advances
injection timing. The main components are timing
plunger, the TCV and pump camshaft position (CMP)
sensor.
Beginning of Injection Staring
RTW 66ESH003101
The engine control module (ECM) contains
characteristic maps of the beginning of injection,
corresponding to engine operating conditions
(engine load, engine speed and engine coolant
temperature). The fuel injection pump control unit
(PCU) is constantly comparing the set beginning o
f
injection timing and the actual beginning of injection
timing. If there is a difference, the timing control
valve (TCV) is controlled by the duty ratio. (The
actual beginning of injection timing is determined
from the pump camshaft position [CMP] sensor.)
Timing Control Valve
RTW 66ESH003201
Legend
1. Coil
2. From Annular Chamber
3. To Feed Pump
4. Orifice
5. Valve Needle
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1331 of 6020
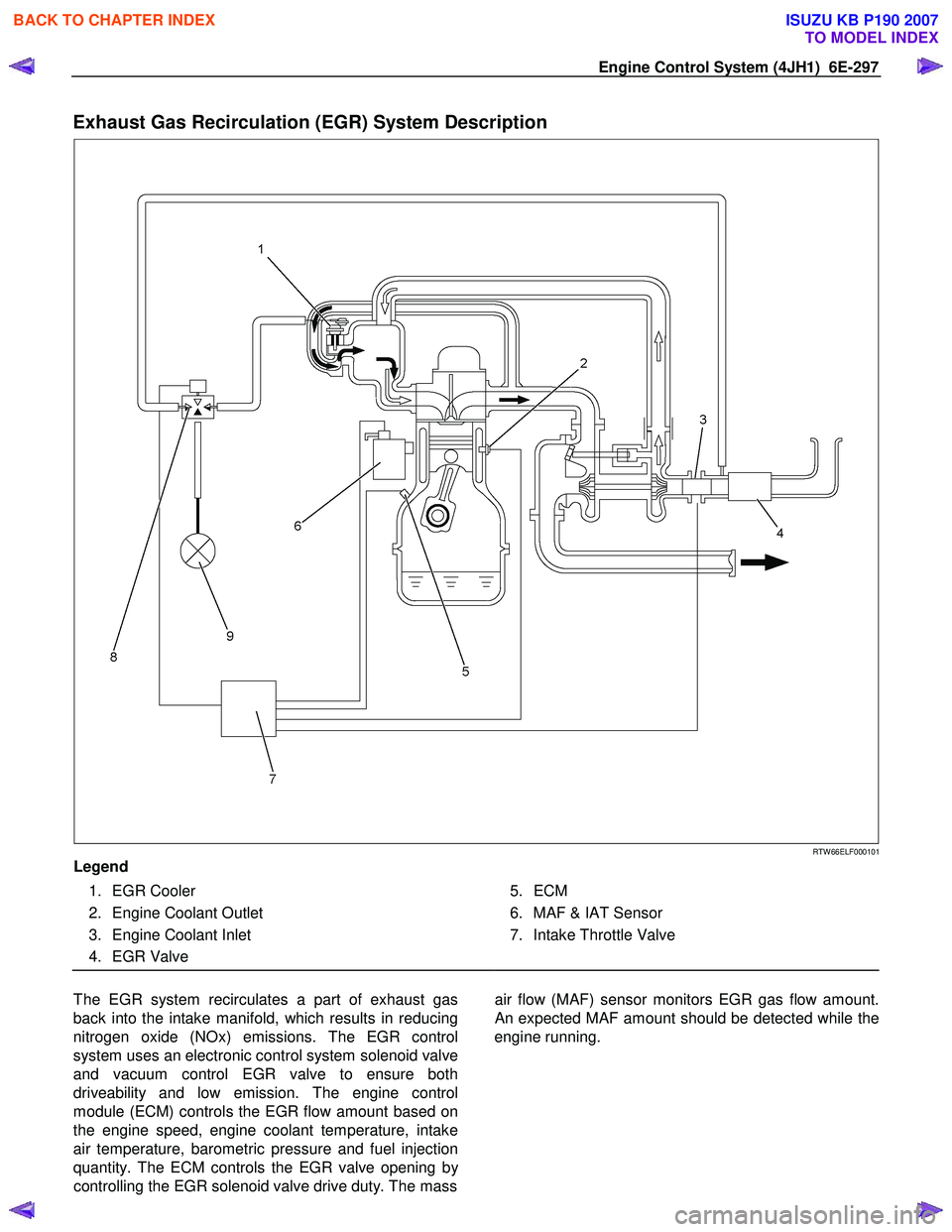
Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-297
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System Description
RTW 66ELF000101
Legend
1. EGR Cooler
2. Engine Coolant Outlet
3. Engine Coolant Inlet
4. EGR Valve
5. ECM
6. MAF & IAT Sensor
7. Intake Throttle Valve
The EGR system recirculates a part of exhaust gas
back into the intake manifold, which results in reducing
nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions. The EGR control
system uses an electronic control system solenoid valve
and vacuum control EGR valve to ensure both
driveability and low emission. The engine control
module (ECM) controls the EGR flow amount based on
the engine speed, engine coolant temperature, intake
air temperature, barometric pressure and fuel injection
quantity. The ECM controls the EGR valve opening b
y
controlling the EGR solenoid valve drive duty. The mass
air flow (MAF) sensor monitors EGR gas flow amount.
An expected MAF amount should be detected while the
engine running.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007