2007 ISUZU KB P190 fuel cap
[x] Cancel search: fuel capPage 2282 of 6020
6E–112 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
22 1. Command the fuel pump ON with the Scan Tool.2. Using suitable pliers which will not damage thefuel hose, gradually apply pressure with the pliers
to pinch the flexible fuel return hose closed. 376 kPa
(55 psi)
Does the fuel pressure indicated by the fuel pressure
gauge rise above the first specified value?
Caution: Do not let the fuel pressure exceed the
second specified value. 414 kPa
(60 psi) Go to Step 11Go to Step 7
23 1. Command the fuel pump ON with the Scan Tool. 2. Remove the fuel filler cap and listen for the soundof the fuel pump running.
3. Turn the pump off.
Was the fuel pump running? — Go to Step 7Go to
Fuel
System
Electrical Test Chart
Step
Action Value(s) Yes No
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2381 of 6020
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–211
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1167 FUEL SUPPLY SYSTEM RICH DURING DECELERATION FUEL CUT OFF
Condition for setting the DTC and action taken when the DTC sets
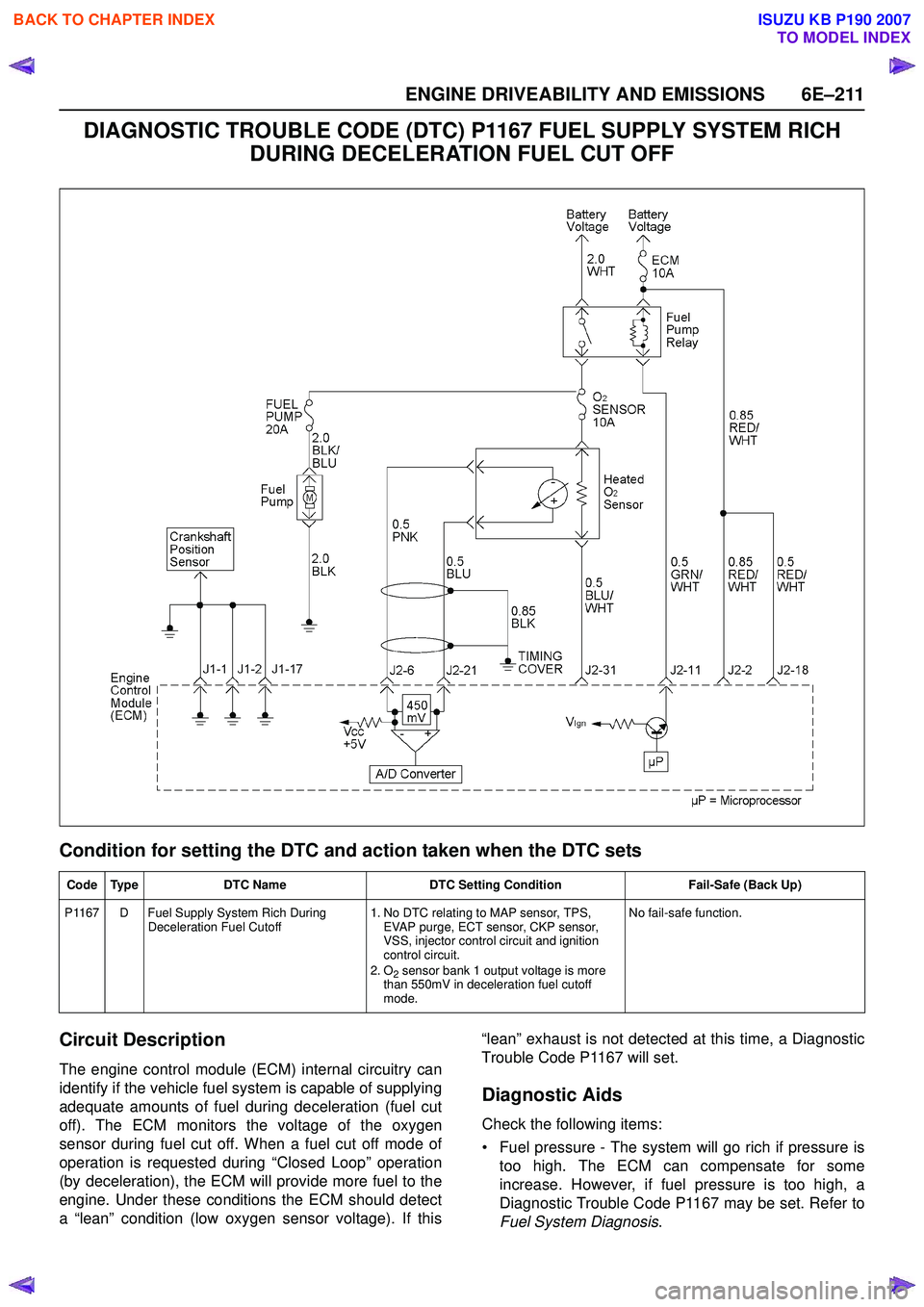
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) internal circuitry can
identify if the vehicle fuel system is capable of supplying
adequate amounts of fuel during deceleration (fuel cut
off). The ECM monitors the voltage of the oxygen
sensor during fuel cut off. When a fuel cut off mode of
operation is requested during “Closed Loop” operation
(by deceleration), the ECM will provide more fuel to the
engine. Under these conditions the ECM should detect
a “lean” condition (low oxygen sensor voltage). If this “lean” exhaust is not detected at this time, a Diagnostic
Trouble Code P1167 will set.
Diagnostic Aids
Check the following items:
• Fuel pressure - The system will go rich if pressure is too high. The ECM can compensate for some
increase. However, if fuel pressure is too high, a
Diagnostic Trouble Code P1167 may be set. Refer to
Fuel System Diagnosis .
Code Type DTC Name DTC Setting Condition Fail-Safe (Back Up)
P1167 D Fuel Supply System Rich During Deceleration Fuel Cutoff 1. No DTC relating to MAP sensor, TPS,
EVAP purge, ECT sensor, CKP sensor,
VSS, injector control circuit and ignition
control circuit.
2. O
2 sensor bank 1 output voltage is more
than 550mV in deceleration fuel cutoff
mode. No fail-safe function.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2384 of 6020
6E–214 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1171 FUEL SUPPLY SYSTEM LEAN DURING POWER ENRICHMENT
Condition for setting the DTC and action taken when the DTC sets
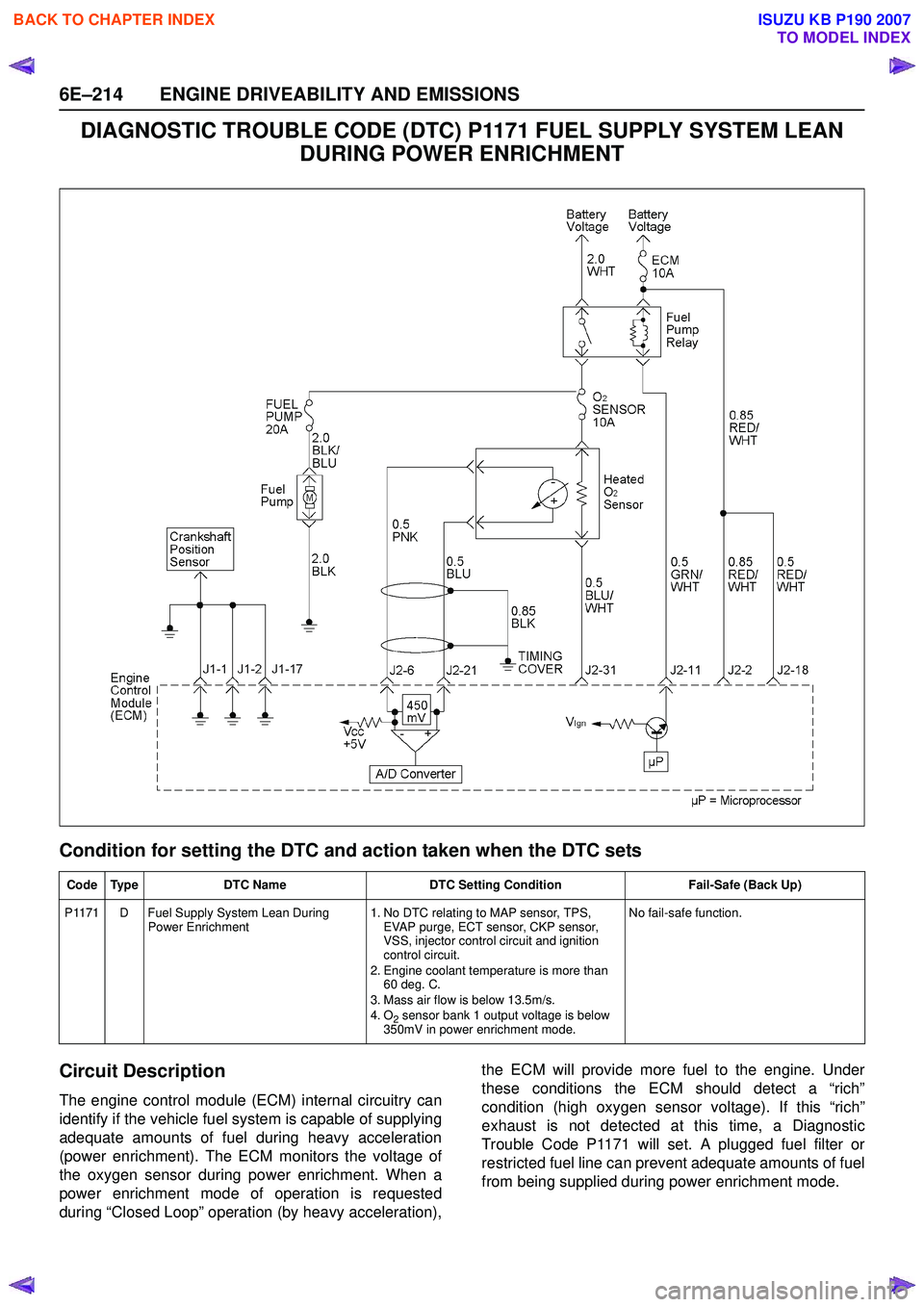
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) internal circuitry can
identify if the vehicle fuel system is capable of supplying
adequate amounts of fuel during heavy acceleration
(power enrichment). The ECM monitors the voltage of
the oxygen sensor during power enrichment. When a
power enrichment mode of operation is requested
during “Closed Loop” operation (by heavy acceleration), the ECM will provide more fuel to the engine. Under
these conditions the ECM should detect a “rich”
condition (high oxygen sensor voltage). If this “rich”
exhaust is not detected at this time, a Diagnostic
Trouble Code P1171 will set. A plugged fuel filter or
restricted fuel line can prevent adequate amounts of fuel
from being supplied during power enrichment mode.
Code Type DTC Name DTC Setting Condition Fail-Safe (Back Up)
P1171 D Fuel Supply System Lean During Power Enrichment 1. No DTC relating to MAP sensor, TPS,
EVAP purge, ECT sensor, CKP sensor,
VSS, injector control circuit and ignition
control circuit.
2. Engine coolant temperature is more than 60 deg. C.
3. Mass air flow is below 13.5m/s.
4. O
2 sensor bank 1 output voltage is below
350mV in power enrichment mode. No fail-safe function.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2428 of 6020
6E–258 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
EXCESSIVE EXHAUST EMISSIONS OR ODORS SYMPTOM
DEFINITIONS: Vehicle fails an emission test. There is excessive “rotten egg” smell. (Excessive odors do not
necessarily indicate excessive emissions.)
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1 Was the “ On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check ”
performed? — Go to Step 2Go to
OBD
System Check
2 1. Perform a bulletin search. 2. If a bulletin that addresses the symptom is found,correct the condition as instructed in the bulletin.
Was a bulletin found that addresses the symptom? — Verify repair Go to Step 3
3 Was a visual/physical check performed? —Go to Step 4Go to
Visual /
physical Check .
4 Does the customer continual accelerate On/Off during cold condition? — System OK Go to Step 5
5 Is the customer using the incorrect fuel type? —Replace with
unleaded fuel Go to Step 6
6 Check for vacuum leaks (vacuum lines, intake manifold, throttle body, etc.)
Were any vacuum leaks found? — Go to Step 17Go to Step 7
7 1. Check fuel cap for proper installation. 2. Secure the fuel cap if necessary.
Was a problem found? — Go to Step 17Go to Step 8
8 Check the fuel pressure. Refer to 6E-108 page “Fuel
System Diagnosis” .
Was a problem found? — Go to Step 17Go to Step 9
9 1. Check for faulty, plugged or incorrectly installed PCV valve.
2. Verify that the PCV system is not plugged.
Was a problem found? — Go to Step 17Go to Step 10
10 Check the injector connectors, if any of the injectors are connected to an incorrect cylinder, correct as
necessary.
Was a problem found? — Go to Step 17Go to Step 11
11 Perform the “Injector Coil/Balance Test
” (Refer to 6E-
98 page).
Was a problem found. — Go to Step 17Go to Step 12
12 Check for a problem with the engine cooling system. Was a problem found? — Go to Step 17Go to Step 13
13 Check EVAP canister for fuel loading. Refer to Evaporative Emission Control System.
Was a problem found? — Go to Step 17Go to Step 14
14 Check the EVAP purge solenoid valve operation. Is the valve operated normally? — Go to Step 17Verify repair &
Go to Step 15
15 Check the exhaust system for a possible restriction: • Damaged or collapsed pipes
• Internal catalytic converter failure
Was a problem found? —Verify repair &
Go to Step 16 Go to Step 17
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2440 of 6020

6E–270 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
FUEL PRESSURE RELIEF
Caution: To reduce the risk of fire and personal
injury, it is necessary to relieve the fuel system
pressure before servicing the fuel system
components.
Caution: After relieving the fuel system pressure, a
small amount of fuel may be released when
servicing fuel lines or connections. Reduce the
chance of personal injury by covering the fuel line
fitting with a short towel before disconnecting the
fittings. The towel will absorb any fuel that may leak
out. When the disconnect is completed, place the
towel in an approved container.
1. Remove the fuel filler cap.
2. Remove the fuel pump relay from the underhood relay box.
3. Start the engine and allow it to stall.
4. Crank the engine for about 30 seconds.
5. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
FUEL RAIL ASSEMBLY
Removal Procedure
NOTE:
• Use care when removing the fuel rail assembly in order to prevent damage to the injector al connector
terminal and the injector spray tips.
• Fitting should be capped and holes plugged during servicing to prevent dirt and other contaminants from
entering open lines and passage.
Important: An eight-digit identification number is
stamped on side of the fuel injector. Refer to this
number when you service the fuel rail or when a
replacement part is required.
1. Disconnect 4 injector connectors.
2. Lift side-clip up on the fuel rail.
3. Disconnect fuel pressure regulator hose.
4. Disconnect wiring harness from the bands on the fuel rail.
5. Remove the intake pipe.
6. Loosen flare nut.
A. Lift up the injectors carefully to separate them from intake manifold.
B. Lift up the fuel rail with injectors as assembly. Do not separate the fuel injectors from fuel rail.
C. If an injector become separated from fuel rail, injector backup O-ring and injector retainer clip
must be replaced.
D. Drain residual fuel from fuel rail into an approved container.
7. If removal of fuel pressure regulator is necessary, Refer to Fuel Pressure Regulator Removal
Procedure .
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2490 of 6020

Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–11
Figure 6A1 – 3
Legend
1 PCV Hose
2 PCV Hose O-Ring Outer (larger)
3 PCV Hose O-Ring Inner (smaller)
4 Upper Intake Manifold
5 Lower Intake Manifold
6 Upper Intake Manifold Bolt – Long
7 Upper Intake Manifold Bolt – Short
8 Lower Intake Manifold to Upper Intake Manifold Guide Pin
9 Upper Intake Manifold to Lower Intake Manifold Gasket
10 Lower Intake Manifold to Cylinder Head Gasket
11 Lower Intake Manifold Bolt
12 Fuel Rail Bolt
13 Fuel Rail
14 Fuel Injector
15 Fuel Injector Retainer
16 Fuel Injector Upper O-ring 17 Fuel Injector Lower O-ring
18 Fuel Pressure Service Valve Cap
19 Fuel Pressure Service Valve
20 Ball Stud
21 Fuel Injector Wiring Harness
22 Throttle Body
23 Throttle Body Bolt
24 Throttle Body Gasket
25 Throttle Body Engine Wiring Harness Clip
26 EVAP Purge Solenoid
27 EVAP Purge Solenoid Bolt
28 EVAP Purge Solenoid Tube
29 EVAP Purge Solenoid Bracket
30 BARO Sensor Bolt
31 BARO Sensor
32 BARO Sensor O-Ring
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2514 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–35
2.11 Engine Noise Under Load
NOTE
A cold piston knock which disappears in
approximately 1.5 minutes from start up, should
be considered acceptable. A cold engine knock
usually disappears when the specific cylinder’s
secondary ignition circuit is grounded out during
diagnosis.
A light rattle/tapping noise may indicate a valve train/upper engine concern, while a low rumble/knocking may indicate a
crankshaft, piston or lower engine concern.
Cause Correction
Low oil pressure. 1 Perform an oil pressure test, refer to 2.19
Engine Oil Pressure Diagnosis.
2 Repair or replace the engine oil pump as required, refer to 3.17 Oil Pump Assembly.
Detonation or spark knock. Confirm the correct operation of the ignition system, refer to
6C1-2 Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics.
Loose torque converter bolts. Inspect and tighten the torque converter bolts to the correct
torque specification, refer to 7C1 Automatic – 4L60E –
General Information – 4L60E – General Information.
Cracked flexplate. Replace the flywheel/flex-plate as required, refer to 4.3
Flexplate Assembly.
Excessive connecting rod bearing clearance. Inspect the connecting rod, crankshaft and bearings and
repair/replace components as required, refer to 4.5
Pistons, Pins, Rings, Connecting Rods and Big-
end Bearings and 4.6 Crankshaft and Main Bearings.
Excessive crankshaft bearing clearance Inspect the crankshaft, cylinder block journals, main
bearings and main bearing caps and repair/replace
components as required, refer to 4.6 Crankshaft
and Main Bearings and 4.7Cylinder Block.
2.12 Engine Will Not Crank – Crankshaft Will Not Rotate
Cause Correction
Seized accessory drive system component. 1 Remove the accessory drive belt, refer to 3.5
Accessory Drive Belt.
2 Rotate the crankshaft by hand at the balancer pulley or flywheel.
3 Repair or replace accessory drive system components as required.
Hydraulically locked cylinder caused by:
• coolant in cylinder,
• oil in cylinder, or
• fuel in cylinder. 1 Remove the spark plugs and check for fluid, refer to
6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service
Operations.
2 Inspect for broken head gasket/s.
3 Inspect for cracked engine block or cylinder head.
4 Inspect for sticking fuel injector.
5 Repair or replace components as required.
Seized torque converter. 1 Remove the torque converter bolts, refer to 7C1
Automatic – 4L60E – General Information – 4L60E –
General Information.
2 Rotate the crankshaft by hand at the balancer pulley or flywheel.
3 Repair or replace torque converter as required.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2771 of 6020

Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–292
6 Torque Wrench Specifications
ATTENTION
�„
�„�„
�„
Fasteners must be replaced after loosening.
Fasteners either have micro encapsulated sealant applied or incorporate a mechanical thread lock and
should only be re-used once. If in doubt, replacement is recommended.
Oil Pan Drain Plug ................................................................................ 25.0 Nm
Oil Filter Adaptor Attaching Bolt ................................................ 20.0 – 26.0 Nm
Oil Level Indicator Tube Attaching Bolt........................................ 8.0 – 12.0 Nm
Accessory Drive Belt Idler Pulley Attaching Bolt................................... 50.0 Nm
Accessory Drive Belt Tensioner Attaching Bolt .................................... 50.0 Nm
Power Steering Reservoir Bracket Attaching Screw.............................. 9.0 Nm
Power Steering Pump Bracket Attaching Bolt ........................... 49.0 – 67.0 Nm
Upper Intake Manifold to Lower Intake Manifold Attaching Bolt ........... 23.0 Nm
Upper Intake Manifold to Cylinder Head Attaching Bolt........................ 23.0 Nm
Lower Intake Manifold to Cylinder Head Attaching Bolt........................ 23.0 Nm
Fuel Injector Wiring Harness Bracket Attaching bolt .............................. 9.0 Nm
Exhaust Manifold to Cylinder Head Attaching Bolt ..................... 17.0 - 23.0 Nm
Exhaust Manifold Heat Shield Attaching Bolt ............................... 8.0 - 12.0 Nm
Battery Harness Ground Terminal Attaching Nut ................................. 13.0 Nm
Camshaft Cover Attaching Bolt ................................................... 8.0 – 12.0 Nm
Engine Ground Connector Bolt............................................................. 10.0 Nm
Engine Wiring Harness Former Attaching Bolt .......................... 12.0 – 16.0 Nm
�„ Crankshaft Balancer Assembly Attaching Bolt:
Stage 1 ..................................................................................... 90.0 –110.0 Nm
Stage 2 ....................................................................................................... 150 °
Engine Front Cover Assembly Attaching Bolt ............................ 20.0 – 26.0 Nm
Camshaft Intermediate Driveshaft Sprocket Attaching Bolt ....... 58.0 – 72.0 Nm
Secondary Timing Chain Guide Attaching Bolt.......................... 20.0 – 26.0 Nm
Secondary Timing Chain Shoe Attaching Bolt ........................... 20.0 – 26.0 Nm
Secondary Timing Chain Tensioner Attaching Bolt ................... 20.0 – 26.0 Nm
Primary Timing Chain Upper Guide Attaching Bolt.................... 20.0 – 26.0 Nm
Primary Timing Chain Tensioner Attaching Bolt ........................ 20.0 – 26.0 Nm
Oil Pump Assembly Attaching Bolt ............................................ 20.0 – 26.0 Nm
Camshaft Sprocket Attaching Bolt ............................................. 49.0 – 67.0 Nm
Exhaust Camshaft Sprocket Attaching Bolt ............................... 49.0 – 67.0 Nm
Camshaft Bearing Cap Attaching Bolt ......................................... 8.0 – 12.0 Nm
Cylinder Head Threaded Plug .............................................................. 31.0 Nm
�„ Cylinder Head M11 Attaching Bolt:
Stage 1 ...................................................................................... 40.0 – 50.0 Nm
Stage 2 ....................................................................................................... 120 °
�„ Cylinder Head M8 Attaching Bolt:
Stage 1 ...................................................................................... 12.0 – 18.0 Nm
Stage 2 ......................................................................................................... 60 °
Engine Mount Bracket to Cylinder Block Attaching Bolt ............ 43.0 – 57.0 Nm
Engine Mount to Bracket Attaching Nut ..................................... 70.0 – 90.0 Nm
Engine Mount to Frame Attaching Nut....................................... 44.0 – 60.0 Nm
Engine Lift Bracket Attaching Bolt .......................................... 58.0 – 72.0.0 Nm
Knock Sensor Attaching Nut................................................................. 23.0 Nm
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007