2007 ISUZU KB P190 coolant temperature
[x] Cancel search: coolant temperaturePage 3386 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–108
Test One
The ECM performs the following:
1 Turns off the knock sensor signal circuits.
2 Applies different test signals to the ECM internal KS circuitry.
3 Verifies each test signal output response is within range.
4 If the ECM detects any of the tested signals are not within the normal range, DTC P0324 sets.
Test Two
The ECM performs the following:
1 Turns off the knock sensor signal circuits.
2 Tests for any output response when no test signals are applied.
3 If the ECM detects an output response, DTC P0324 sets.
Test Three
1 Turns off the knock sensor signal circuits.
2 Generates an internal test pulse then monitors the return signal.
3 If the return test pulse is less than a calibrated threshold, DTC P0324 sets.
DTC P0324 sets if the ECM detects an incorrect response to the ECM internal KS circuitry tests.
Conditions for Running the DTC
Condition One
Runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The ECM is controlling the ignition spark.
• The engine speed is less than 2,300 rpm and steady.
• The volumetric efficiency is steady.
Condition Two
Runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The ECM is controlling the ignition spark.
• The engine speed is 1,000 – 4,000 rpm
• The engine coolant temperature is greater than 60 ° C.
• The volumetric efficiency is steady.
Condition Three
Runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The ECM is controlling the ignition spark.
• The engine speed is less than 2,300 rpm and steady.
• The engine coolant temperature is greater than 40 ° C.
• The volumetric efficiency is steady.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The ECM detects an incorrect response to an internal ECM KS circuitry test.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3388 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–110
7.19 DTC P0327, P0328, P0332 or P0333
DTC Descriptor
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0327 – Knock Sensor Circuit Low Frequency (Bank 1)
• DTC P0328 – Knock Sensor Circuit High Frequency (Bank 1)
• DTC P0332 – Knock Sensor Circuit Low Frequency (Bank 2)
• DTC P0333 – Knock Sensor Circuit High Frequency (Bank 2)
Circuit Description
The ECM supplies the ground to the knock sensor (KS) low reference circuit. The KS produces a signal voltage, which is
proportional to the level of the engine vibration or spark knock.
W hen the ECM detects an excessive spark knock, it retards the ignition timing until the spark knock stops.
To differentiate between a normal engine vibration and the vibration created by a spark knock, the ECM samples the KS
signal under different engine speeds and load condition. The ECM uses this samples to determine maximum and
minimum KS signal voltage produced when the engine is running under normal conditions.
A knock sensor circuit DTC sets if the ECM detects the KS signal voltage is outside the normal range.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P0327 and P0332
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• DTCs P0324, P0335, P0342 and P0343 ran and passed.
• The ECM controls the ignition spark.
• Engine speed is greater than 2000 rpm and steady.
• The engine coolant temperature is greater than 60ºC.
• The volumetric efficiency is steady.
DTC P0328 or P0333
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The ECM controls the ignition spark.
• Engine speed is greater than 2,000 rpm and steady.
• The engine coolant temperature is greater than 60 °C.
• The volumetric efficiency is steady.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0327 and P0332
The ECM detects the KS signal voltage is less than the minimum KS signal normal range for at least 10 seconds.
DTC P0328 and P0333
The ECM detects the KS signal voltage is greater than the maximum KS signal normal range.
Conditions for Clearing DTC
The knock sensor circuit DTCs are Type B DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes in this Section, for action
taken when Type B DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type B DTCs.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3408 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–130
Step Action Yes No
8 Replace the ECM. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
W as the repair completed? Go to Step 9 —
9 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the cooling fan relay control circuit DTCs fail this ignition
cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 10
10 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs? Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table in this Section System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
7.27 DTC P0500
DTC Descriptor
This diagnostic procedure supports DTC P0500 – Vehicle Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction (Manual Transmission).
Circuit Description
Vehicle speed information is provided to the engine control module (ECM) by the vehicle speed sensor (VSS). The
ignition control relay applies ignition positive voltage to the VSS, and the ground circuit of the VSS is directly connected
to ground.
The VSS is a Hall effect switch. In conjunction with an 18 tooth reluctor wheel, the VSS provide a signal voltage to the
ECM. The ECM uses this signal voltage to determine vehicle speed.
If the ECM detects no vehicle speed, while other sensors indicate that the vehicle is moving, then DTC P0500 sets.
Conditions for Running the DTC
Runs once the following conditions are met:
• The engine coolant temperature is greater than 40º C,
• the ECM is in fuel shut-off mode, and
• the engine speed is between 1,520 and 3,520 rpm
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The ECM detects a speed of less than 0 km/h for 8 seconds continuously, or 50 seconds cumulative.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The vehicle speed sensor circuit malfunction DTC is a Type C DTC. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes in this
Section, for action taken when Type C DTCs set and conditions for clearing Type C DTCs.
Additional Information
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 5.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions in this Section.
• Refer to 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details on:
• VSS operation, and
• fuel shut-off mode.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3414 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–136
• To control the throttle opening, the ECM applies PW M voltage to the throttle actuator motor. The ECM increases
this PW M voltage duty cycle to increase the throttle opening.
• To decrease the throttle opening from the seven percent rest position, the ECM reverses the polarity of the throttle
actuator motor control circuit then applies a PW M voltage to the throttle actuator motor.
In addition, the ECM monitors the signal voltage applied to the throttle actuator motor control circuit. A TAC motor
control circuit DTC sets if the ECM detects a fault condition in the TAC circuits or motor performance.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P0506 and P0507
Runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• DTCs P0112, P0113, P0117, P0118, P0121, P0122, P0123, P0221, P0222, P0223, P0443, P0446, P0455, P0458
and P0459 are not set.
• The ignition is switched on.
• The vehicle speed is 0 km/h.
• The engine coolant temperature is greater than 60 °C.
• The intake air temperature is greater than -10.5 °C.
• The volumetric efficiency is less than 35 percent.
• The EVAP purge solenoid is off.
DTC P0638
Runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The ignition is switched on.
• The ignition voltage is greater than 7 V.
DTC P2100
Runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• DTC P2101 ran and passed.
• The ignition is switched on.
DTC P2101
Runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The battery voltage is greater than 7 V.
• The ignition is switched on.
DTC P1551, P2119 and P2176
Runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The ignition is switched on.
• The vehicle speed is 0 km/h.
• The engine speed is less than 40 rpm
• The engine coolant temperature is 5 – 60 °C.
• The intake air temperature is 5 – 60 °C.
• The ignition voltage is greater than 10 V.
• The APP is less than 15 percent.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3458 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–180
Step Action Yes
No
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
7.49 DTC P2107
DTC Descriptor
This diagnostic procedure supports DTC P2107 – Throttle Control Malfunction.
Circuit Description
The ECM applies 5 V to the throttle position (TP) sensor 1 through the 5 V reference circuit 2701 and the ground
through the low reference circuit 2752. TP sensor 1 and TP sensor 2 share a common 5 V reference circuit and a
common low reference circuit.
The TP sensor 1 and TP sensor 2 have individual signal circuits with opposite functionality. These signal circuits provide
the ECM with a signal voltage that is proportional to the throttle plate movement.
• The TP sensor 1 signal voltage is less than 1 V when the throttle plate is in closed position, which increases to
greater than 4 V when the throttle plate is moved to wide-open throttle.
• The TP sensor 2 signal voltage is greater than 4 V when the throttle plate is in closed position, which decreases to
less than 1 V when the throttle plate is moved to wide-open throttle.
The ECM monitors and evaluates the accelerator pedal position (APP) sensors signal voltage along with other sensor
inputs to determine the desired throttle opening. To control the throttle plate movement, the ECM applies a pulse width
modulated (PW M) signal voltage to the throttle actuator motor through the throttle actuator motor control circuits.
• At engine idle speed or when no current is flowing into the throttle actuator control (TAC) motor, a constant force
return spring holds the throttle plate at a constant seven percent throttle opening position.
• To control the throttle opening, the ECM applies PW M voltage to the TAC motor. The ECM increases this PW M
voltage duty cycle to increase the throttle opening.
To decrease the throttle opening from the seven percent rest position, the ECM reverses the polarity of the TAC motor
control circuit then applies a PW M voltage to the TAC motor.
If the ECM detects the TP sensor 1 amplification output does not correlate with the TP sensor 1 signal voltage during a
predetermined sets of conditions, DTC P2107 sets.
Conditions for Running the DTC
DTC P2107 runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The vehicle speed is 0 km/h.
• The engine speed is less than 40 rpm
• The engine coolant temperature is 5 – 60 ° C.
• The intake air temperature is 5 – 60 ° C.
• The ignition voltage is greater than 10 V.
• The APP is less than 15 percent.
• The ECM is performing the closed throttle test with the ignition switched on and the engine not running.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The ECM detects that its internal TP sensor 1 amplification output does not correlate with the TP sensor 1 signal voltage.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
DTC P2107 – Throttle Actuator Control Module Internal Circuit is a Type ‘C’ DTC. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble
Codes in this Section, for action taken when a Type ‘C’ DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type ‘C’ DTC.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3462 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–184
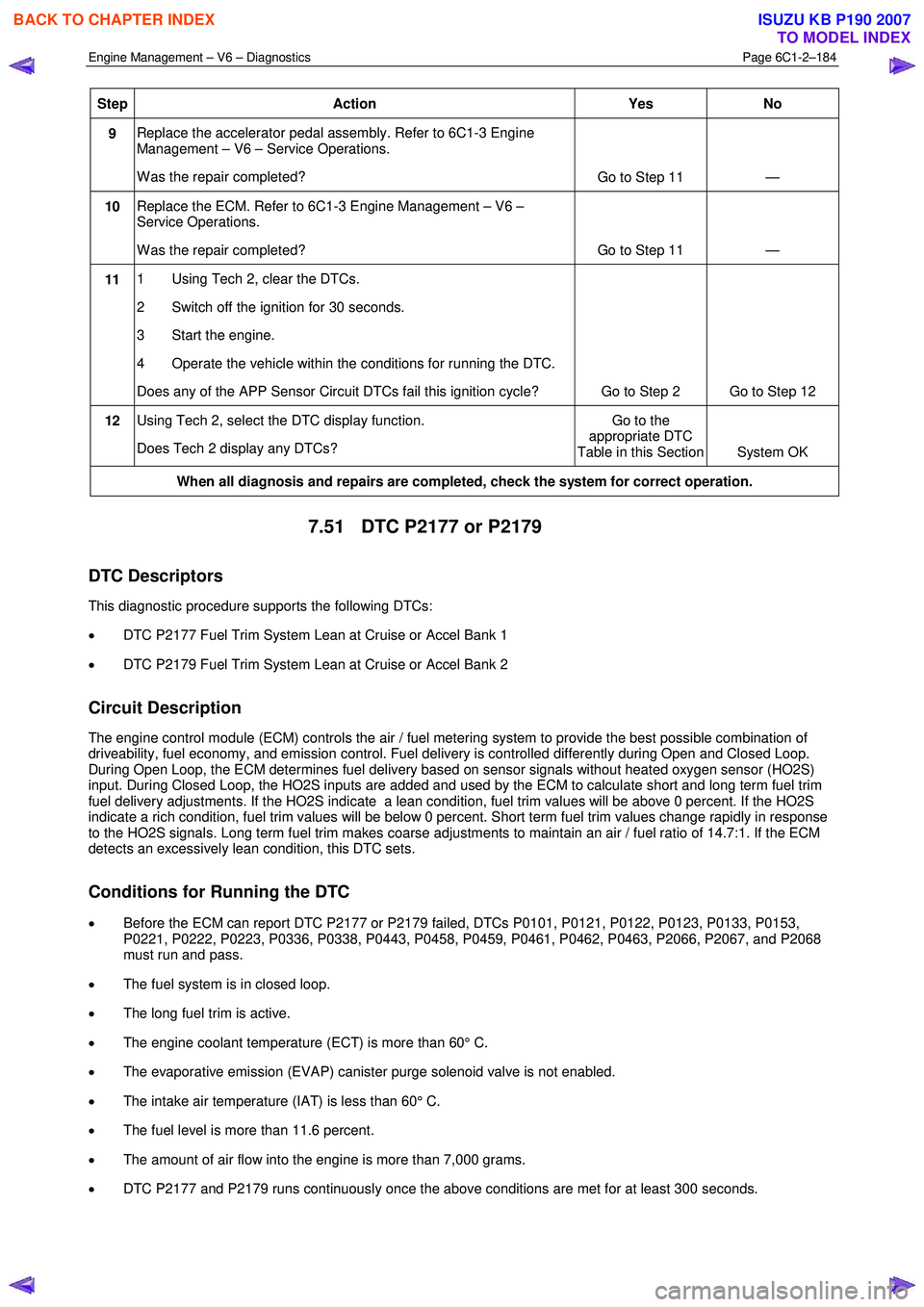
Step Action Yes No
9 Replace the accelerator pedal assembly. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
W as the repair completed? Go to Step 11 —
10 Replace the ECM. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
W as the repair completed? Go to Step 11 —
11 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the APP Sensor Circuit DTCs fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 12
12 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs? Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table in this Section System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
7.51 DTC P2177 or P2179
DTC Descriptors
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P2177 Fuel Trim System Lean at Cruise or Accel Bank 1
• DTC P2179 Fuel Trim System Lean at Cruise or Accel Bank 2
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) controls the air / fuel metering system to provide the best possible combination of
driveability, fuel economy, and emission control. Fuel delivery is controlled differently during Open and Closed Loop.
During Open Loop, the ECM determines fuel delivery based on sensor signals without heated oxygen sensor (HO2S)
input. During Closed Loop, the HO2S inputs are added and used by the ECM to calculate short and long term fuel trim
fuel delivery adjustments. If the HO2S indicate a lean condition, fuel trim values will be above 0 percent. If the HO2S
indicate a rich condition, fuel trim values will be below 0 percent. Short term fuel trim values change rapidly in response
to the HO2S signals. Long term fuel trim makes coarse adjustments to maintain an air / fuel ratio of 14.7:1. If the ECM
detects an excessively lean condition, this DTC sets.
Conditions for Running the DTC
• Before the ECM can report DTC P2177 or P2179 failed, DTCs P0101, P0121, P0122, P0123, P0133, P0153,
P0221, P0222, P0223, P0336, P0338, P0443, P0458, P0459, P0461, P0462, P0463, P2066, P2067, and P2068
must run and pass.
• The fuel system is in closed loop.
• The long fuel trim is active.
• The engine coolant temperature (ECT) is more than 60° C.
• The evaporative emission (EVAP) canister purge solenoid valve is not enabled.
• The intake air temperature (IAT) is less than 60° C.
• The fuel level is more than 11.6 percent.
• The amount of air flow into the engine is more than 7,000 grams.
• DTC P2177 and P2179 runs continuously once the above conditions are met for at least 300 seconds.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3466 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–188
7.52 DTC P2178 or P2180
DTC Descriptors
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P2178 Fuel Trim System Rich at Cruise or Accel Bank 1
• DTC P2180 Fuel Trim System Rich at Cruise or Accel Bank 2
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) controls the air / fuel metering system to provide the best possible combination of
driveability, fuel economy, and emission control. Fuel delivery is controlled differently during Open and Closed Loop.
During Open Loop, the ECM determines fuel delivery based on sensor signals without heated oxygen sensor (HO2S)
input. During Closed Loop, the HO2S inputs are added and used by the ECM to calculate short and long term fuel trim
fuel delivery adjustments. If the HO2S indicates a lean condition, fuel trim values will be above 0 percent. If the HO2S
indicates a rich condition, fuel trim values will be below 0 percent. Short term fuel trim values change rapidly in response
to the HO2S signals. Long term fuel trim makes coarse adjustments to maintain an air / fuel ratio of 14.7:1. If the ECM
detects an excessively rich condition, this DTC sets.
Conditions for Running the DTC
• Before the ECM can report DTC P2178 or P2180 failed, DTCs P0101, P0121, P0122, P0123, P0133, P0153,
P0221, P0222, P0223, P0336, P0338, P0443, P0458, P0459, P0461, P0462, P0463, P2066, P2067, and P2068
must run and pass.
• The fuel system is in closed loop.
• The long fuel trim is active.
• The engine coolant temperature (ECT) is more than 60° C.
• The evaporative emission (EVAP) canister purge solenoid valve is not enabled.
• The intake air temperature (IAT) is less than 60° C.
• The fuel level is more than 11.6 percent.
• The amount of air flow into the engine is more than 7,000 grams.
• DTC P2178 and P2180 run continuously once the above conditions are met for at least 300 seconds.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
• The Total Fuel Trim Avg. is less than –22 percent.
• The condition exists for 4 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
• The control module illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that
the diagnostic runs and fails.
• The control module records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic
fails, the control module stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the
second consecutive ignition cycle, the control module records the operating conditions at the time of the failure.
The control module writes the operating conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
• The Fuel Trim System circuit DTCs are Type ‘B’ DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes in this Section,
for action taken when a Type ‘B’ DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type ‘B’ DTCs.
• Use Tech 2 to clear the MIL and the DTC.
Additional Information
• A fuel delivery condition causes this DTC to set. Thoroughly inspect all items that could cause a rich condition.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3469 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–191
7.53 DTC P2187 or P2189
DTC Descriptors
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P2187 Fuel Trim System Lean at Idle Bank 1
• DTC P2189 Fuel Trim System Lean at Idle Bank 2
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) controls the air / fuel metering system to provide the best possible combination of
driveability, fuel economy, and emission control. Fuel delivery is controlled differently during Open and Closed Loop.
During Open Loop, the ECM determines fuel delivery based on sensor signals without heated oxygen sensor (HO2S)
input. During Closed Loop, the HO2S inputs are added and used by the ECM to calculate short and long term fuel trim
fuel delivery adjustments. If the HO2S indicate a lean condition, fuel trim values will be above 0 percent. If the O2S
indicate a rich condition, fuel trim values will be below 0 percent. Short term fuel trim values change rapidly in response
to the HO2S signals. Long term fuel trim makes coarse adjustments to maintain an air / fuel ratio of 14.7:1. If the ECM
detects an excessively lean condition, this DTC sets.
Conditions for Running the DTC
• Before the ECM can report DTC P2187 or P2189 failed, DTCs P0101, P0121, P0122, P0123, P0133, P0153,
P0221, P0222, P0223, P0336, P0338, P0443, P0458, P0459, P0461, P0462, P0463, P2066, P2067, and P2068
must run and pass.
• The fuel system is in closed loop.
• The long fuel trim is active.
• The engine coolant temperature (ECT) is more than 60° C.
• The evaporative emission (EVAP) canister purge solenoid valve is not enabled.
• The intake air temperature (IAT) is less than 60° C.
• The fuel level is more than 11.6 percent.
• The amount of air flow into the engine is more than 7000 grams.
• DTC P2187 and P2189 runs continuously once the above conditions are met for at least 300 seconds.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
• The Total Fuel Trim Avg. is more than 40 percent.
• The LT FT Idle / Decel is more than seven percent.
• The condition exists for four seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The control module illuminates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the
diagnostic runs and fails.
The control module records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails,
the control module stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second
consecutive ignition cycle, the control module records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The control
module writes the operating conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
• The Fuel Trim System circuit DTCs are Type ‘B’ DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes in this Section,
for action taken when a Type ‘B’ DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type ‘B’ DTCs.
• Use Tech 2 to clear the MIL and the DTC.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007