2007 ISUZU KB P190 lights
[x] Cancel search: lightsPage 1967 of 6020

6E-350 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1)
• The hardware key is plugged into the computerport.
• Vehicle system voltage: - There are no charging system concerns. Allcharging system concerns must be repaired
before programming the ECM.
- The battery voltage is greater than 12 volts but less than 16 volts. The battery must be fully
charged before programming the ECM.
- A battery charger is NOT connected to the vehicles battery. Incorrect system voltage or
voltage fluctuations from a battery charger may
cause programming failure or ECM damage.
- Turn OFF or disable any system that may put a load on the vehicles battery. Turn OFF or
disable systems such as:
◊ Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning
(HVAC) systems
◊ Headlights
◊ Room lights
◊ Accessory equipment
• The ignition switch is in the proper position. The scan tool prompts you to turn ON the ignition, with
the engine OFF. DO NOT change the position of
the ignition switch during the programming
procedure unless instructed to do so.
• All tool connections are secure: - The RS-232 cable
- The connection at the DLC
- The voltage supply circuits
• DO NOT disturb the tool harnesses while programming. If an interruption occurs during the
programming procedure, programming failure or
ECM damage may occur.
• If you are performing the Pass-Thru programming procedure using a notebook computer without the
power cord, ensure that the internal battery is fully
charged.
Service Programming System (SPS)
(Remote Procedure)
Notice: Some module will not accept SPS remote
procedure using 10MB PCMCIA card. In such case,
use 32MB PCMCIA card or SPS pass-thru procedure.
The Remote SPS method is a three-step process that
involves the following procedures:
1. Connecting the scan tool to the vehicle and obtaining the information from the ECM.
2. Connecting the scan tool to the terminal and downloading a new calibration file from the
terminal into the scan tool memory.
3. Reconnecting the scan tool to the vehicle and uploading the new calibration file into the ECM. Performing the Remote Procedure
1. Connect a scan tool to the vehicle and obtain the ECM information using the following procedure:
Notice: Ensure the ECM is installed in the vehicle and
the battery is fully charged before programming.
a. Install a scan tool.
b. Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
c. Select Service Programming System (SPS) > Request Info.
d. If there is already stored in the scan tool, the existing data is displayed on the screen. The
scan tool asks user to keep existing data "Keep
Data" or "Continue" to request new vehicle
information from the ECM. If there is no data in
the scan tool, it will immediately start vehicle
identification.
e. Select the vehicle description by following the on-screen instructions based on stamped VIN
or affixed VIN plate on the vehicle.
f. During obtaining information, the scan tool is receiving information from all modules at the
same time. But only ECM information is
displayed on the screen.
g. Turn OFF all accessories and press "Okay".
h. Verify that the correct VIN is displayed on the scan tool. If the VIN is incorrect or no VIN,
record the correct VIN.
2. Turn OFF the ignition.
3. Turn OFF the scan tool and disconnect from the vehicle.
4. Transfer the data from the terminal to the scan tool using the following procedure:
Notice: The TIS supports service programming with
the Tech 2 scan tool only.
a. Connect the scan tool to the terminal.
b. Launch the TIS application.
c. Select the Service Programming System at the main screen.
d. Highlight the following information on the Select Diagnostic Tool and Programming Process
screen, then click "Next".
• Select Diagnostic Tool - Tech 2
• Select Programming Process - Identify whether an existing ECM is being
reprogrammed or an ECM is being replaced
with a new one
• Select ECU Location - Vehicle
e. Verify the connections on the Preparing for Communication screen, then click "Next".
f. Verify the VIN on the Validate Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) screen, then click
"Next".
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2002 of 6020
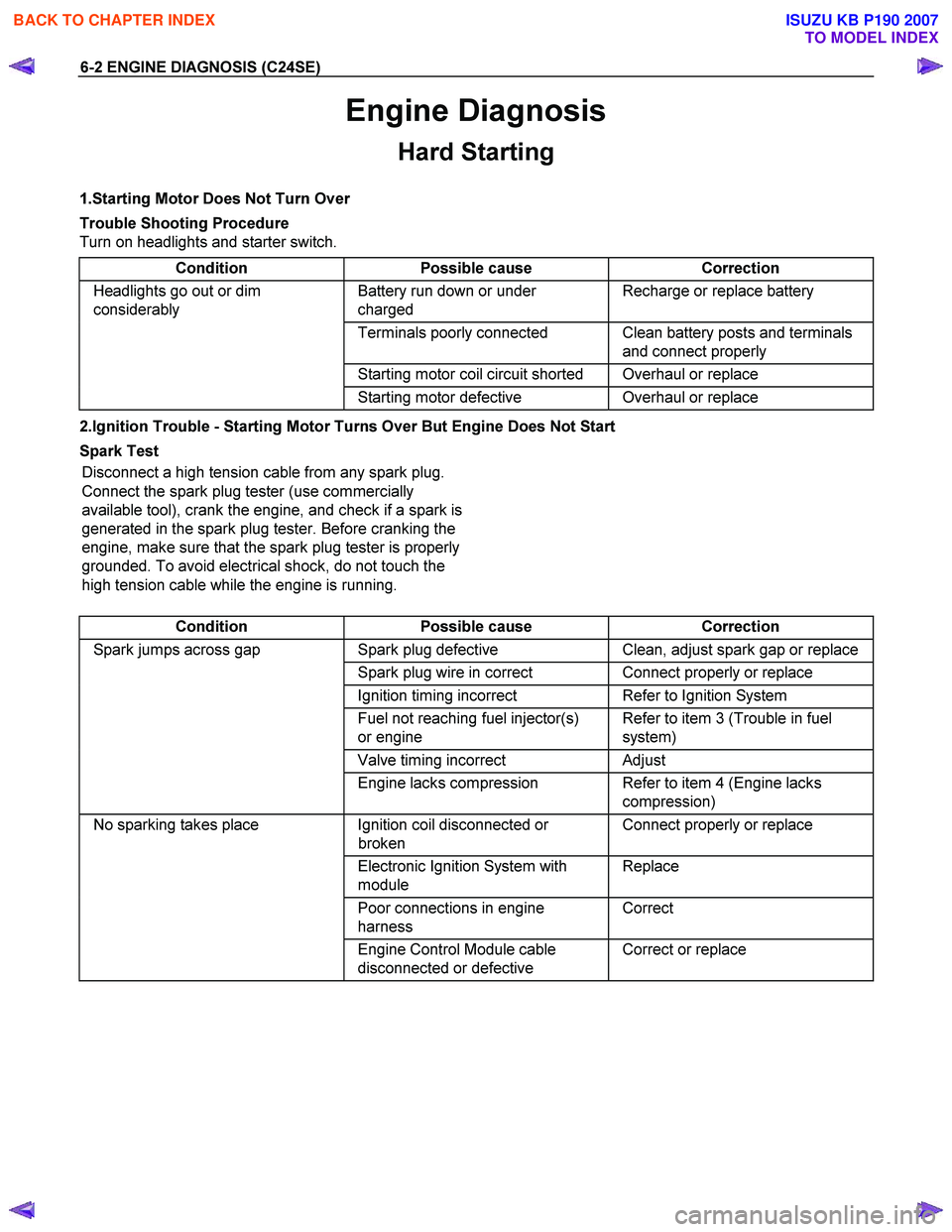
6-2 ENGINE DIAGNOSIS (C24SE)
Engine Diagnosis
Hard Starting
1.Starting Motor Does Not Turn Over
Trouble Shooting Procedure
Turn on headlights and starter switch.
Condition Possible cause Correction
Headlights go out or dim
considerably Battery run down or under
charged Recharge or replace battery
Terminals poorly connected Clean battery posts and terminals
and connect properly
Starting motor coil circuit shorted Overhaul or replace
Starting motor defective Overhaul or replace
2.Ignition Trouble - Starting Motor Turns Over But Engine Does Not Start
Spark Test Disconnect a high tension cable from any spark plug.
Connect the spark plug tester (use commercially
available tool), crank the engine, and check if a spark is
generated in the spark plug tester. Before cranking the
engine, make sure that the spark plug tester is properly
grounded. To avoid electrical shock, do not touch the
high tension cable while the engine is running.
Condition Possible cause Correction
Spark jumps across gap Spark plug defective Clean, adjust spark gap or replace
Spark plug wire in correct Connect properly or replace
Ignition timing incorrect Refer to Ignition System
Fuel not reaching fuel injector(s)
or engine Refer to item 3 (Trouble in fuel
system)
Valve timing incorrect Adjust
Engine lacks compression Refer to item 4 (Engine lacks
compression)
No sparking takes place Ignition coil disconnected or
broken Connect properly or replace
Electronic Ignition System with
module Replace
Poor connections in engine
harness Correct
Engine Control Module cable
disconnected or defective Correct or replace
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2142 of 6020

ENGINE ELECTRICAL 6D1-5
Battery fluid is a highly corrosive acid.
Should battery fluid come in contact with your eyes, skin,
fabric, or a painted surface, immediately and thoroughly rinse
the affected area with clean tap water.
Never allow metal tools or jumper cables to come in contact
with the positive battery terminal, or any other metal surface of
the vahicle. This will protect against a short circuit.
Always keep batteries out of reach of young children.
Jump Starting Procedure
1. Set the vehicle parking brake and place the shift lever in the
"NEUTRAL" position.
Turn "OFF" the ignition.
Turn "OFF" all lights and any other accessory requiring electrical power.
2. Look at the built-in hydrometer.
If the indication area of the built-in hydrometer is completel
y
clear, do not try to jump start.
3.
Attach the end of one jumper cable to the positive terminal
of the booster battery.
Attach the other end of the same cable to the positive
terminal of the discharged battery.
Do not allow the vehicles to touch each other. This will cause a ground connection, effectively neutralizing the
charging procedure.
Be sure that the booster battery has a 12 volt rating.
4.
Attach one end of the remaining cable to the negative
terminal of the booster battery.
Attach the other end of the same cable to a solid engine ground (such as the air conditioning compressor bracket o
r
the generator mounting bracket) of the vehicle with the
discharged battery.
The ground connection must be at least 450 mm (18 in.) from the battery of the vehicle whose battery is being
charged.
WARNING: NEVER ATTACH THE END OF THE JUMPER
CABLE DIRECTLY TO THE NEGATIVE TERMINAL OF THE
DEAD BATTERY.
5. Start the engine of the vehicle with the good battery.
Make sure that all unnecessary electrical accessories have been turned "OFF".
6. Start the engine of the vehicle with the dead battery.
7. To remove the jumper cables, follow the above directions in reverse order.
Be sure to first disconnect the negative cable from the vehicle with the discharged battery.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2161 of 6020

STARTING AND CHARGING SYSTEM 6D3-13
5. During current output tests please make sure that the
ammeter is securely connceted into the charge circuit.
6. Some battery powered timing lights can produce high transient voltages when connected or disconnected. Onl
y
disconnect or connect timing lights when the engine is
switched off.
7. Make sure the warning lamp circuit is functioning normall
y
before commencing tests.
8. Battery isolation switches must only be operated when the engine is stopped.
9. To protect the charging system when using 240 volt chargers it is recommeneded that the battery is
disconnected whilst charging.
10. Due to the very low resistance value of the stator winding it may not be possible to obtain accurate readings without
special equipment.
11. 12 volts must never be connected to the "L" terminal of the regulator as this will damage the lamp driver circuit.
12. No loads apart from the warning lamp can be connected to the "L" termainal. The "W " terminal is provided for this
purpose.
Disassembly
1. Mark the relative positions of the end housings in relation to the stator assembly to aid reassembly. Use a permanent
marking pen do not use centre punched as this can cause
misalignmnet of the housings.
2. Remove the EP regulator from the slipring end housing b
y
removing the two screws. Tilt the regulator slightly from the
plug connection until the regulator clears the housing, then
lift clear.
3. Remove the four through bolts.
4. Carefully remove the stator assembly along with the slipring end housing taking care not to put strain on the stator wires.
5. To disconnect the stator from the rectifier assembly, grasp the stator wires close to the wire loop with a pair of long
nosed pliers, heat the joint with a soldering iron, when the
point becomes plastic apply a slight twisting motion to the
wires, then pull upwards to release the wires. Remove the
stator.
This procedure opens the wire loop to release the stato
r
connections easily.
6. To remove the rectifier remove the three retaining scre
w
and the B+ terminal nut and washers.
Note: the B+ bolt and the positive heatsink retaining screw are
fitted with mica insulating washers.
These must be discarded and replaced with new washers and
heatsink compound.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2201 of 6020
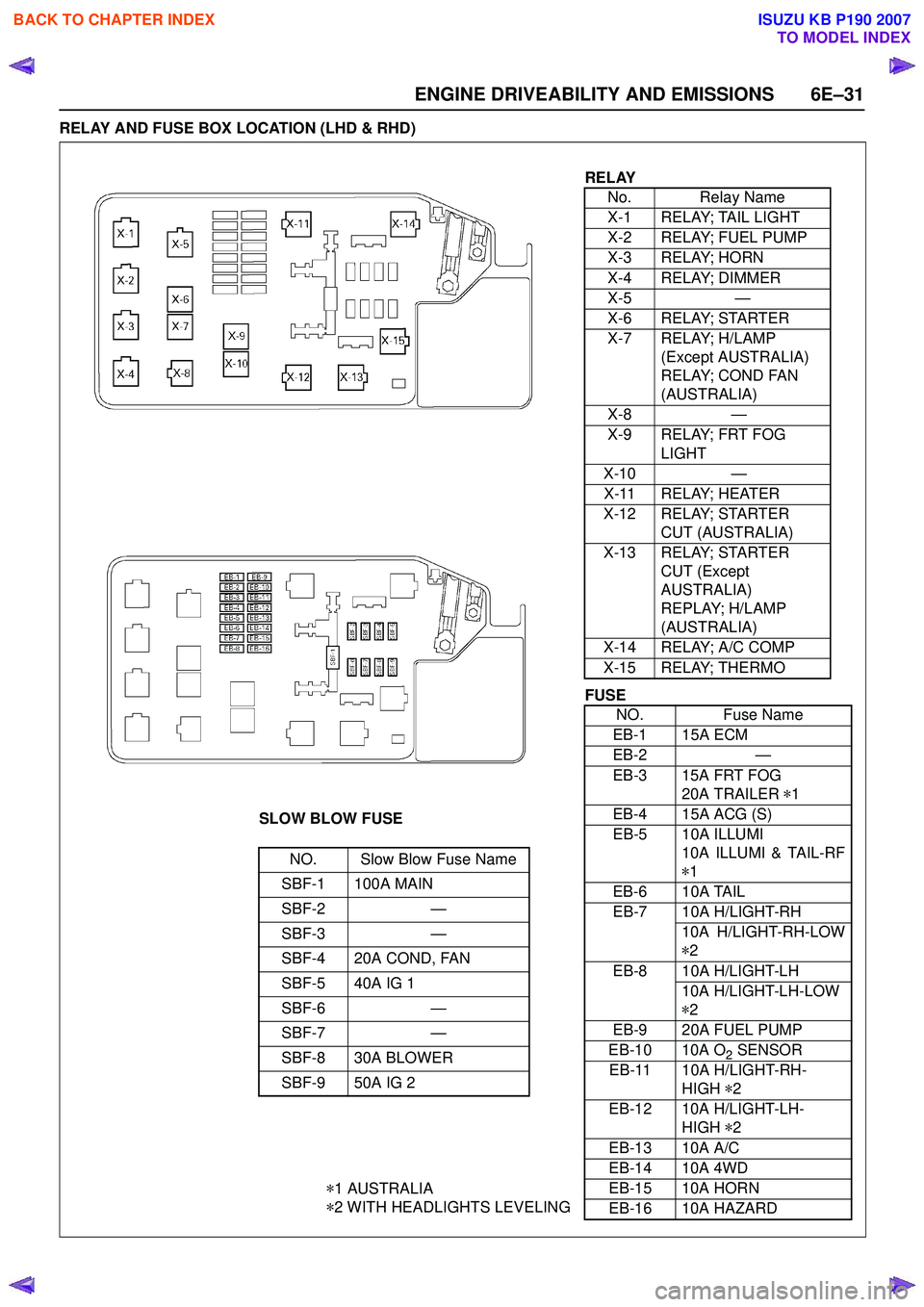
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–31
RELAY AND FUSE BOX LOCATION (LHD & RHD)
RELAYNo. Relay Name
X-1 RELAY; TAIL LIGHT
X-2 RELAY; FUEL PUMP
X-3 RELAY; HORN
X-4 RELAY; DIMMER
X-5 —
X-6 RELAY; STARTER
X-7 RELAY; H/LAMP (Except AUSTRALIA)
RELAY; COND FAN
(AUSTRALIA)
X-8 —
X-9 RELAY; FRT FOG LIGHT
X-10 —
X-11 RELAY; HEATER
X-12 RELAY; STARTER CUT (AUSTRALIA)
X-13 RELAY; STARTER CUT (Except
AUSTRALIA)
REPLAY; H/LAMP
(AUSTRALIA)
X-14 RELAY; A/C COMP
X-15 RELAY; THERMO
SLOW BLOW FUSE
NO. Slow Blow Fuse Name
SBF-1 100A MAIN
SBF-2 —
SBF-3 —
SBF-4 20A COND, FAN
SBF-5 40A IG 1
SBF-6 —
SBF-7 —
SBF-8 30A BLOWER
SBF-9 50A IG 2
* 1 AUSTRALIA
* 2 WITH HEADLIGHTS LEVELING
FUSE
NO. Fuse Name
EB-1 15A ECM
EB-2 —
EB-3 15A FRT FOG 20A TRAILER *1
EB-4 15A ACG (S)
EB-5 10A ILLUMI 10A ILLUMI & TAIL-RF
* 1
EB-6 10A TAIL
EB-7 10A H/LIGHT-RH 10A H/LIGHT-RH-LOW
* 2
EB-8 10A H/LIGHT-LH 10A H/LIGHT-LH-LOW
* 2
EB-9 20A FUEL PUMP
EB-10 10A O
2 SENSOR
EB-11 10A H/LIGHT-RH- HIGH *2
EB-12 10A H/LIGHT-LH- HIGH *2
EB-13 10A A/C
EB-14 10A 4WD
EB-15 10A HORN
EB-16 10A HAZARD
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2235 of 6020

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–65
Step 3: Simulate the symptom and isolate the
problem
Simulate the symptom and isolate the system by
reproducing all possible conditions suggested in Step 1
while monitoring suspected circuits/components/
systems to isolate the problem symptom. Begin with the
most logical circuit/component.
Isolate the circuit by dividing the suspect system into
simpler circuits. Next, confine the problem into a smaller
area of the system. Begin at the most logical point (or
point of easiest access) and thoroughly check the
isolated circuit for the fault, using basic circuit tests.
Hints
You can isolate a circuit by:
• Unplugging connectors or removing a fuse to separate one part of the circuit from another
• If only component fails to operate, begin testing the component
• If a number of components do not operate, begin test at areas of commonality (such as power sources,
ground circuits, switches, main connectors or major
components)
• Substitute a known good part from the parts department or the vehicle system
• Try the suspect part in a known good vehicle
See Symptom Simulation Tests on the next page for
problem simulation procedures. Refer to service manual
sections 6E and 8A for information about intermittent
diagnosis. Follow procedures for basic circuit testing in
service manual section 8A.
What resources you should use
Whenever appropriate, you should use the following
resources to assist in the diagnostic process:
• Service manual
• Bulletins
• Digital multimeter (with a MIN/MAX feature)
• Tech II and Tech II upload function
• Circuit testing tools (including connector kits/ harnesses and jumper wires)
• Experience
• Intermittent problem solving simulation methods
• Customer complaint check sheet
Symptom Simulation Tests
1. Vibration
This method is useful when the customer complaint
analysis indicates that the problem occurs when the
vehicle/system undergoes some form of vibration.
For connectors and wire harness, slightly shake
vertically and horizontally. Inspect the connector joint
and body for damage. Also, tapping lightly along a
suspected circuit may be helpful. For parts and sensors, apply slight vibration to the part
with a light tap of the finger while monitoring the system
for a malfunction.
2. Heat
This method is important when the complaint suggests
that the problem occurs in a heated environment. Apply
moderate heat to the component with a hair drier or
similar tool while monitoring the system for a
malfunction.
CAUTION: Care must be take to avoid overheating
the component.
3. Water and Moisture
This method may be used when the complaint suggests
that the malfunction occurs on a rainy day or under
conditions of high humidity. In this case, apply water in a
light spray on the vehicle to duplicate the problem.
CAUTION: Care must be take to avoid directly
exposing electrical connections to water.
4. Electrical loads
This method involves turning systems ON (such as the
blower, lights or rear window defogger) to create a load
on the vehicle electrical system at the same time you
are monitoring the suspect circuit/component.
5e. Vehicle Operates as Designed
This condition refers to instances where a system
operating as designed is perceived to be unsatisfactory
or undesirable. In general, this is due to:
• A lack of understanding by the customer
• A conflict between customer expectations and vehicle design intent
• A system performance that is unacceptable to the customer
What you should do
You can verify that a system is operating as designed
by:
• Reviewing service manual functional/diagnostic checks
• Examining bulletins and other service information for supplementary information
• Compare system operation to an identical vehicle
If the condition is due to a customer misunderstanding
or a conflict between customer expectation and system
operation, you should explain the system operation to
the customer.
If the complaint is due to a case of unsatisfactory
system performance, you should contact Technical
Assistance for the latest information.
What resources you should use
Whenever possible, you should use the following
resources to facilitate the diagnostic process:
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2373 of 6020
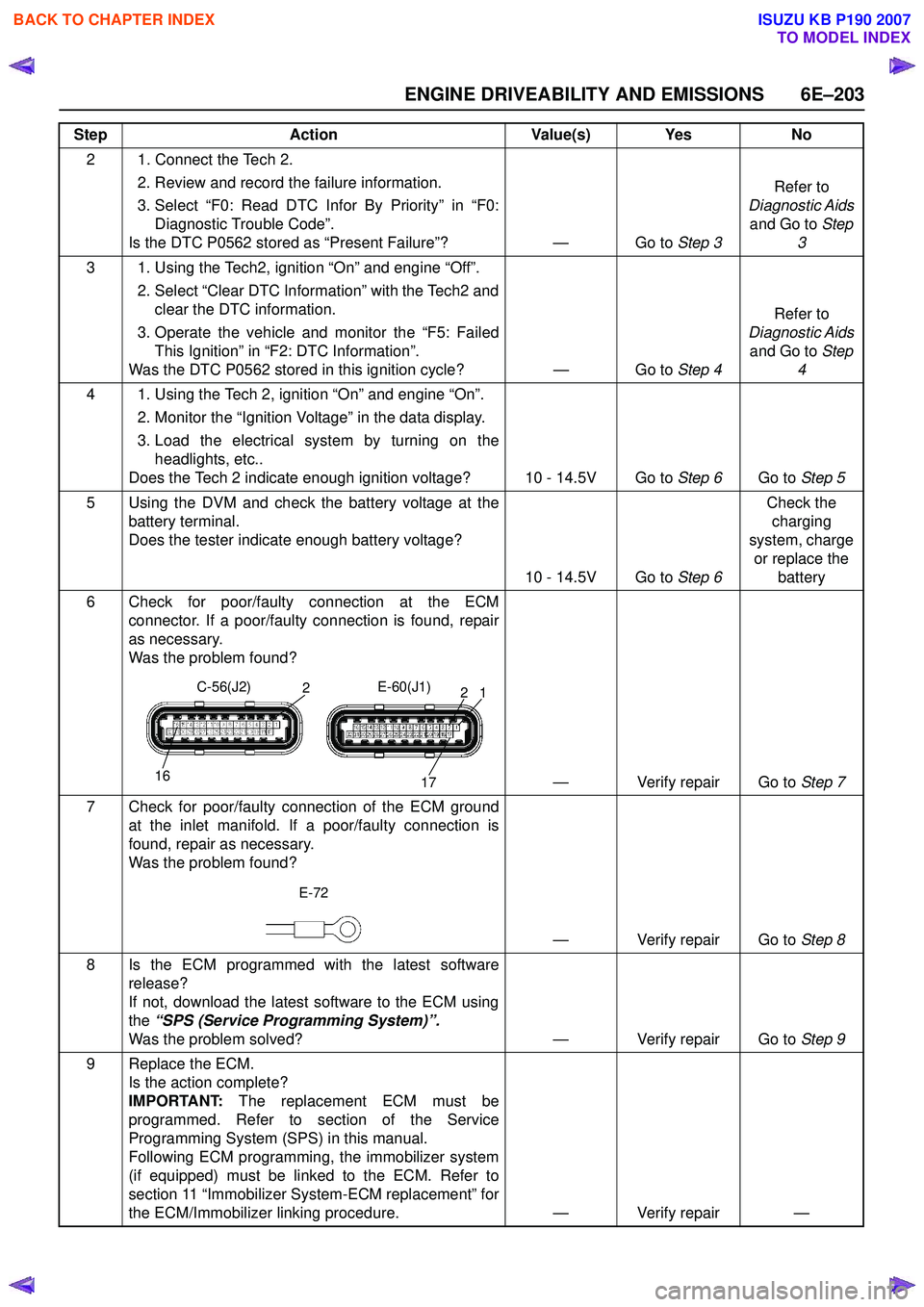
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–203
2 1. Connect the Tech 2. 2. Review and record the failure information.
3. Select “F0: Read DTC Infor By Priority” in “F0: Diagnostic Trouble Code”.
Is the DTC P0562 stored as “Present Failure”? — Go to Step 3Refer to
Diagnostic Aids and Go to Step
3
3 1. Using the Tech2, ignition “On” and engine “Off”. 2. Select “Clear DTC Information” with the Tech2 andclear the DTC information.
3. Operate the vehicle and monitor the “F5: Failed This Ignition” in “F2: DTC Information”.
Was the DTC P0562 stored in this ignition cycle? — Go to Step 4Refer to
Diagnostic Aids and Go to Step
4
4 1. Using the Tech 2, ignition “On” and engine “On”. 2. Monitor the “Ignition Voltage” in the data display.
3. Load the electrical system by turning on the headlights, etc..
Does the Tech 2 indicate enough ignition voltage? 10 - 14.5V Go to Step 6Go to Step 5
5 Using the DVM and check the battery voltage at the battery terminal.
Does the tester indicate enough battery voltage?
10 - 14.5V Go to Step 6Check the
charging
system, charge or replace the battery
6 Check for poor/faulty connection at the ECM connector. If a poor/faulty connection is found, repair
as necessary.
Was the problem found?
— Verify repair Go to Step 7
7 Check for poor/faulty connection of the ECM ground at the inlet manifold. If a poor/faulty connection is
found, repair as necessary.
Was the problem found?
— Verify repair Go to Step 8
8 Is the ECM programmed with the latest software release?
If not, download the latest software to the ECM using
the “SPS (Service Programming System)”.
Was the problem solved? — Verify repair Go to Step 9
9 Replace the ECM. Is the action complete?
IMPORTANT: The replacement ECM must be
programmed. Refer to section of the Service
Programming System (SPS) in this manual.
Following ECM programming, the immobilizer system
(if equipped) must be linked to the ECM. Refer to
section 11 “Immobilizer System-ECM replacement” for
the ECM/Immobilizer linking procedure. — Verify repair —
Step
Action Value(s) Yes No
16
2
17
12
C-56(J2)
E-60(J1)
E-72
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2375 of 6020
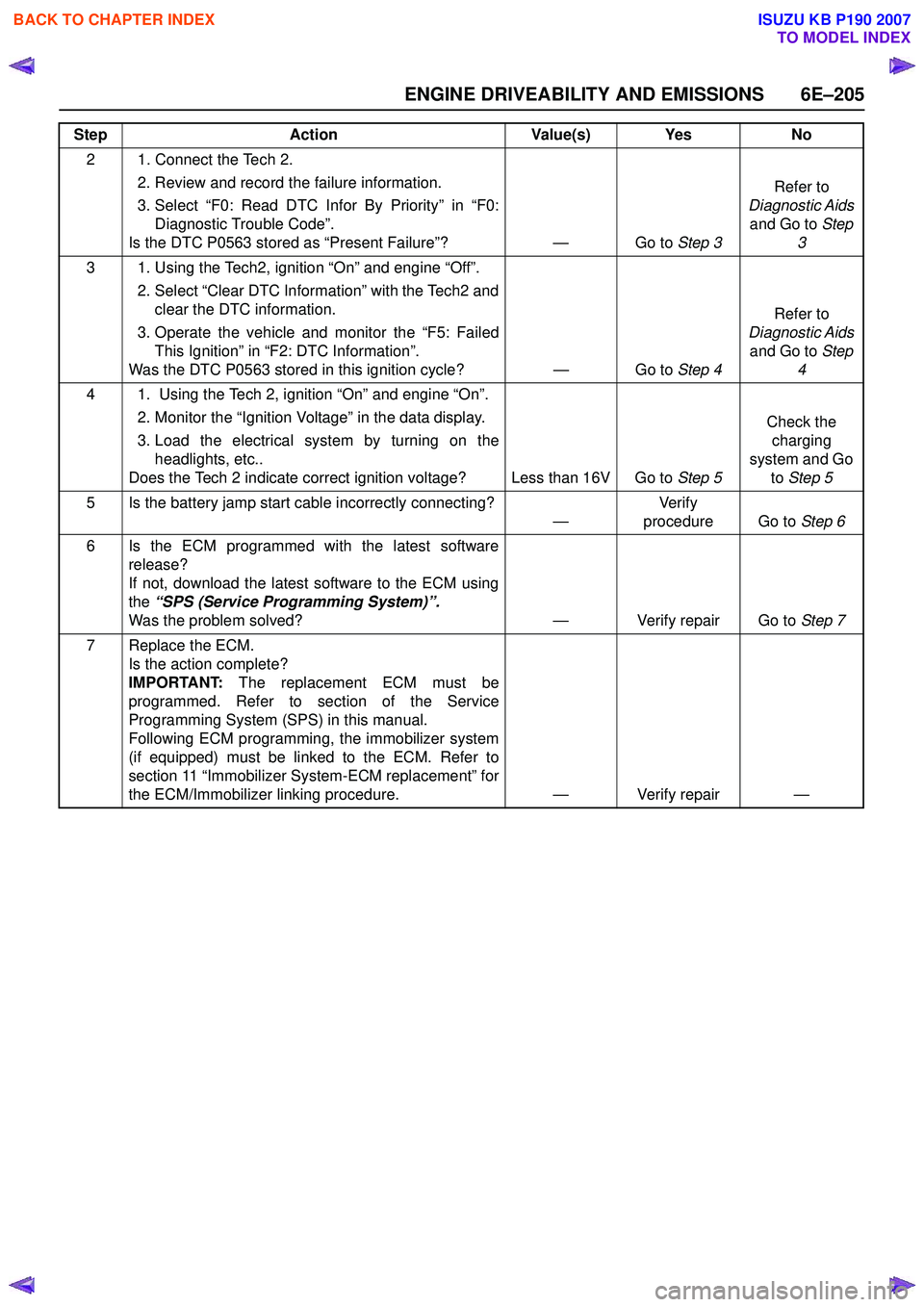
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–205
2 1. Connect the Tech 2. 2. Review and record the failure information.
3. Select “F0: Read DTC Infor By Priority” in “F0: Diagnostic Trouble Code”.
Is the DTC P0563 stored as “Present Failure”? — Go to Step 3Refer to
Diagnostic Aids and Go to Step
3
3 1. Using the Tech2, ignition “On” and engine “Off”. 2. Select “Clear DTC Information” with the Tech2 andclear the DTC information.
3. Operate the vehicle and monitor the “F5: Failed This Ignition” in “F2: DTC Information”.
Was the DTC P0563 stored in this ignition cycle? — Go to Step 4Refer to
Diagnostic Aids and Go to Step
4
4 1. Using the Tech 2, ignition “On” and engine “On”. 2. Monitor the “Ignition Voltage” in the data display.
3. Load the electrical system by turning on the headlights, etc..
Does the Tech 2 indicate correct ignition voltage? Less than 16V Go to Step 5Check the
charging
system and Go to Step 5
5 Is the battery jamp start cable incorrectly connecting? —Ve r if y
procedure Go to Step 6
6 Is the ECM programmed with the latest software release?
If not, download the latest software to the ECM using
the “SPS (Service Programming System)”.
Was the problem solved? — Verify repair Go to Step 7
7 Replace the ECM. Is the action complete?
IMPORTANT: The replacement ECM must be
programmed. Refer to section of the Service
Programming System (SPS) in this manual.
Following ECM programming, the immobilizer system
(if equipped) must be linked to the ECM. Refer to
section 11 “Immobilizer System-ECM replacement” for
the ECM/Immobilizer linking procedure. — Verify repair —
Step
Action Value(s) Yes No
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007