2007 ISUZU KB P190 ESP
[x] Cancel search: ESPPage 1295 of 6020
Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-261
Checks Action
Fuel System Checks Inspect the fuel system for the following conditions. Refer to the Fuel System section.
• Inspect for water contamination in the fuel.
• Inspect for external fuel leaks or fuel leakage into the engine oil.
• Inspect the fuel lines between the fuel tank and fuel injection pump for tightness and all
fuel hoses for cuts, cracks and for the use of proper clamps.
Notice: The fuel system from the fuel tank(s) to the fuel injection pump is under a slight
vacuum with the engine running. As a result, air can enter the fuel system if these
connections are not tight. Air in the fuel system will cause fuel injection pump internal
pressure fluctuations especially at high engine speed and load.
• Inspect for air in the fuel system.
Notice: If many air bubbles appear in the fuel, check the fuel system line connections
between the fuel tank and the fuel injection pump for tightness and all fuel hoses for cuts,
cracks and for the use of proper clamps.
a. Remove the fuel hose that connects to the fuel injection pump suction side.
b. Substitute a clear hose.
Notice: A hose must be cleaned.
d. Connect the clear hose to the fuel injection pump.
c. Bleed the fuel system.
e. Let the engine run at idle for at least 2 minutes.
f. Accelerator the engine between idle and W .O.T. (accelerator pedal full travel) many times while observing the clear hose.
• Inspect the fuel tank vent hose for a plugged or kinked.
• Inspect inside the fuel tank for any foreign material that may be getting drawn into the
fuel line pickup causing a blocked condition. Draw fuel from the fuel tank at the fuel line
(as close to the fuel tank as possible) going to the fuel pickup tube to verify a clean
stream of fuel comes out (use the hand-held vacuum pump 5-8840-0279-0/J-23738-A
with a clear hose or equivalent). This will ensure the fuel pickup tube is not cracked
drawing air into the fuel line.
• Inspect the fuel injection pump operation.
Notice: The fuel injection pump must be timed to the engine.
• Inspect the eye bolt for any type of restriction or collapsed gauze filter.
Notice: If any type of restriction found, check for a condition that causes contaminated
fuel, such as the customer is using an aftermarket fuel filter or extended maintenance
interval. Also inspect fuel waxing or icing that is caused by an incorrect fuel type used in
winter season or water intrusion in the fuel system.
• Inspect the fuel injection nozzle(s) for proper splay condition or operating pressure.
Notice: Only first stage of operating pressure can be checked.
Air Intake System Checks Inspect the air intake system for the following conditions.
• Inspect the air cleaner and air intake ducts for a restriction, holes, or leaks.
• Inspect for a restriction in the turbocharger inlet duct.
• Inspect for a restriction or deposit in the intake throttle bore.
• Inspect for a restriction or leak in the intake manifold.
• Inspect for a restriction or damage at MAF sensor.
Exhaust System Checks Inspect the exhaust system for a possible restriction. Refer to the Exhaust System section.
• Inspect for a restriction in the catalytic converter or exhaust pipes.
Engine Mechanical Checks Inspect the engine mechanical for the following conditions. Refer to the Engine Mechanical
section.
• Inspect for poor cylinder compression. Proper compression is more than 2100 kPa (309
psi).
• Improper mechanical timing
• Improper valve gap
• Broken or weak valve springs
• W orn camshaft lobes
• Inspect for incorrect basic engine parts.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1297 of 6020
Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-263
Checks Action
Fuel System Checks Inspect the fuel system for the following conditions. Refer to the Fuel System section.
• Inspect for water contamination in the fuel.
• Inspect for external fuel leaks or fuel leakage into the engine oil.
• Inspect the fuel lines between the fuel tank and fuel injection pump for tightness and
all fuel hoses for cuts, cracks and for the use of proper clamps.
Notice: The fuel system from the fuel tank(s) to the fuel injection pump is under a
slight vacuum with the engine running. As a result, air can enter the fuel system if
these connections are not tight. Air in the fuel system will cause fuel injection pump
internal pressure fluctuations especially at high engine speed and load.
• Inspect for air in the fuel system.
Notice: If many air bubbles appear in the fuel, check the fuel system line connections
between the fuel tank and the fuel injection pump for tightness and all fuel hoses for
cuts, cracks and for the use of proper clamps.
a. Remove the fuel hose that connects to the fuel injection pump suction side.
b. Substitute a clear hose.
Notice: A hose must be cleaned.
c. Connect the clear hose to the fuel injection pump.
d. Bleed the fuel system.
e. Let the engine run at idle for at least 2 minutes.
f. Accelerator the engine between idle and W .O.T. (accelerator pedal full travel) many times while observing the clear hose.
• Inspect the fuel tank vent hose for a plugged or kinked.
• Inspect inside the fuel tank for any foreign material that may be getting drawn into
the fuel line pickup causing a blocked condition. Draw fuel from the fuel tank at the
fuel line (as close to the fuel tank as possible) going to the fuel pickup tube to verify a
clean stream of fuel comes out (use the hand-held vacuum pump 5-8840-0279-0/J-
23738-A with a clear hose or equivalent). This will ensure the fuel pickup tube is not
cracked drawing air into the fuel line.
• Inspect the fuel injection pump operation.
Notice: The fuel injection pump must be timed to the engine.
Inspect the eye bolt for any type of restriction or collapsed gauze filter.
Notice: If any type of restriction found, check for a condition that causes contaminated
fuel, such as the customer is using an aftermarket fuel filter or extended maintenance
interval. Also inspect fuel waxing or icing that is caused by an incorrect fuel type used
in winter season or water intrusion in the fuel system.
Air Intake System Checks Inspect the air intake system for the following conditions.
• Inspect the air cleaner and air intake ducts for a restriction, holes, or leaks.
• Inspect for a restriction in the turbocharger inlet duct.
• Inspect for a restriction or deposit in the intake throttle bore.
• Inspect for a restriction or leak in the intake manifold.
• Inspect for a restriction or damage at mass air flow (MAF) sensor.
Additional Checks •
Inspect the generator output voltage. Repair if less than 9 volts or more than 16
volts.
• Electromagnetic interference (EMI) on the reference circuit can cause an engine
miss condition. The scan tool can usually detect EMI by monitoring the engine
speed. A sudden increase in speed with little change in actual engine speed change
indicates that EMI is present. If a problem exists, check routing of high voltage
components, such as fuel injection solenoid wiring, near the sensor circuits.
Surges/Chuggles
Checks Action
DIFINITION:The engine has a power variation under a steady throttle or cruise. The vehicle seems to speed up and slow down
with no change in the accelerator pedal.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1299 of 6020
Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-265
Checks Action
Fuel System Checks Inspect the fuel system for the following conditions. Refer to the Fuel System section.
• Inspect for water contamination in the fuel.
• Inspect for external fuel leaks or fuel leakage into the engine oil.
• Inspect the fuel lines between the fuel tank and fuel injection pump for tightness and
all fuel hoses for cuts, cracks and for the use of proper clamps.
Notice: The fuel system from the fuel tank(s) to the fuel injection pump is under a
slight vacuum with the engine running. As a result, air can enter the fuel system if
these connections are not tight. Air in the fuel system will cause fuel injection pump
internal pressure fluctuations especially at high engine speed and load.
• Inspect for air in the fuel system.
Notice: If many air bubbles appear in the fuel, check the fuel system line connections
between the fuel tank and the fuel injection pump for tightness and all fuel hoses for
cuts, cracks and for the use of proper clamps.
a. Remove the fuel hose that connects to the fuel injection pump suction side.
b. Substitute a clear hose.
Notice: A hose must be cleaned.
c. Connect the clear hose to the fuel injection pump.
d. Bleed the fuel system.
e. Let the engine run at idle for at least 2 minutes.
f. Accelerator the engine between idle and W .O.T. (accelerator pedal full travel) many times while observing the clear hose.
• Inspect the fuel tank vent hose for a plugged or kinked.
• Inspect inside the fuel tank for any foreign material that may be getting drawn into
the fuel line pickup causing a blocked condition. Draw fuel from the fuel tank at the
fuel line (as close to the fuel tank as possible) going to the fuel pickup tube to verify a
clean stream of fuel comes out (use the hand-held vacuum pump 5-8840-0279-0/J-
23738-A with a clear hose or equivalent). This will ensure the fuel pickup tube is not
cracked drawing air into the fuel line.
• Inspect the fuel injection pump operation.
Notice: The fuel injection pump must be timed to the engine.
• Inspect the eye bolt for any type of restriction or collapsed gauze filter.
Notice: If any type of restriction found, check for a condition that causes contaminated
fuel, such as the customer is using an aftermarket fuel filter or extended maintenance
interval. Also inspect fuel waxing or icing that is caused by an incorrect fuel type used
in winter season or water intrusion in the fuel system.
• Inspect the fuel injection nozzle(s) for proper splay condition or operating pressure.
Notice: Only first stage of operating pressure can be checked.
• Inspect the timing device operating correctly. Observe the Actual Injection Timing
parameter with the scan tool while running the engine. The Actual Injection Timing
parameter must follow the Desired Injection Timing within 2°CA on each engine
speed. Engine idle > around 2000 RPM> around 3000 RPM. If not, inspect the fuel
system restriction, air in the fuel or fuel injection pump operation.
Air Intake System Checks Inspect the air intake system for the following conditions.
• Inspect the air cleaner and air intake ducts for a restriction, holes, or leaks.
• Inspect for a restriction in the turbocharger inlet duct.
• Inspect for a restriction or deposit in the intake throttle bore.
• Inspect for a restriction or leak in the intake manifold.
• Inspect for a restriction or damage at MAF sensor.
Additional Checks •
Inspect the generator output voltage. Repair if less than 9 volts or more than 16
volts.
• Inspect the EGR system operating correctly.
• Inspect the A/C operation.
• Inspect the torque converter clutch (TCC) operation. (A/T only)
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1301 of 6020
Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-267
Checks Action
Fuel System Checks Inspect the fuel system for the following conditions. Refer to the Fuel System section.
• Inspect for water contamination in the fuel.
• Inspect for external fuel leaks or fuel leakage into the engine oil.
• Inspect the fuel lines between the fuel tank and fuel injection pump for tightness and
all fuel hoses for cuts, cracks and for the use of proper clamps.
Notice: The fuel system from the fuel tank(s) to the fuel injection pump is under a
slight vacuum with the engine running. As a result, air can enter the fuel system if
these connections are not tight. Air in the fuel system will cause fuel injection pump
internal pressure fluctuations especially at high engine speed and load.
• Inspect for air in the fuel system.
Notice: If many air bubbles appear in the fuel, check the fuel system line connections
between the fuel tank and the fuel injection pump for tightness and all fuel hoses for
cuts, cracks and for the use of proper clamps.
a. Remove the fuel hose that connects to the fuel injection pump suction side.
b. Substitute a clear hose.
Notice: A hose must be cleaned.
c. Connect the clear hose to the fuel injection pump.
d. Bleed the fuel system.
e. Let the engine run at idle for at least 2 minutes.
f. Accelerator the engine between idle and W .O.T. (accelerator pedal full travel) many times while observing the clear hose.
• Inspect the fuel tank vent hose for a plugged or kinked.
• Inspect inside the fuel tank for any foreign material that may be getting drawn into
the fuel line pickup causing a blocked condition. Draw fuel from the fuel tank at the
fuel line (as close to the fuel tank as possible) going to the fuel pickup tube to verify a
clean stream of fuel comes out (use the hand-held vacuum pump 5-8840-0279-0/J-
23738-A with a clear hose or equivalent). This will ensure the fuel pickup tube is not
cracked drawing air into the fuel line.
• Inspect the fuel injection pump operation.
Notice: The fuel injection pump must be timed to the engine.
• Inspect the eye bolt for any type of restriction or collapsed gauze filter.
Notice: If any type of restriction found, check for a condition that causes contaminated
fuel, such as the customer is using an aftermarket fuel filter or extended maintenance
interval. Also inspect fuel waxing or icing that is caused by an incorrect fuel type used
in winter season or water intrusion in the fuel system.
Inspect the fuel injection nozzle(s) for proper splay condition or operating pressure.
Notice: Only first stage of operating pressure can be checked.
• Inspect the timing device operating correctly. Observe the Actual Injection Timing
parameter with the scan tool while running the engine. The Actual Injection Timing
parameter must follow the Desired Injection Timing within 2°CA on each engine
speed. Engine idle > around 2000 RPM> around 3000 RPM. If not, inspect the fuel
system restriction, air in the fuel or fuel injection pump operation.
Air Intake System Checks Inspect the air intake system for the following conditions.
• Inspect the air cleaner and air intake ducts for a restriction, holes, or leaks.
• Inspect for a restriction or leak in the intercooler.
• Inspect for a restriction in the turbocharger inlet duct.
• Inspect for a restriction or deposit in the intake throttle bore.
• Inspect for a restriction or leak in the intake manifold.
• Inspect for a restriction or damage at MAF sensor.
• Inspect for a worn or damaged turbocharger turbine wheel, shaft or compressor
wheel. Refer to turbocharger inspection in the Engine Mechanical section.
• Inspect for turbocharger wastegate valve operation. Refer to wastegate valve
inspection in the Engine Mechanical section.
Exhaust System Checks Inspect the exhaust system for a possible restriction. Refer to the Exhaust System
section.
• Inspect for a restriction in the catalytic converter or exhaust pipes.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1302 of 6020
6E-268 Engine Control System (4JH1)
Checks Action
Engine Mechanical Check Inspect the engine mechanical for the following conditions. Refer to the Engine
Mechanical section.
• Inspect for poor cylinder compression. Proper compression is more than 2100 kPa
(309 psi).
• Improper mechanical timing
• Improper valve gap
• Broken or weak valve springs
• W orn camshaft lobes
Additional Checks •
Inspect the generator output voltage. Repair if less than 9 volts or more than 16
volts.
• Inspect the EGR system operating correctly.
• Inspect the engine overheat condition. Refer to the Engine Cooling section.
• Inspect the A/C operation.
• Inspect the torque converter clutch (TCC) operation (A/T only).
Hesitation, Sag, Stumble
Checks Action
DEFINITION:The vehicle has a momentary lack of response when pushing down on the accelerator. The condition can occur
at any vehicle speed. The condition is usually most severe when trying to make the vehicle move from a stop. If severe
enough, the condition may cause the engine to stall.
Preliminary Checks • Diagnostic System Check - Engine Controls.
• Compare the vehicle with a similar unit. Ensure the vehicle has an actual problem.
• Remove the air cleaner and check for dirt, or for air ducts being plugged or
restricted. Replace as necessary.
• Inspect for a proper transmission shift pattern and down shift operation.
• Inspect the fuel quality (cetane index).
• Inspect the engine oil level and quality.
• Inspect the scan tool Data List in this section.
• Inspect the engine control module (ECM) and fuel injection pump control unit (PCU)
grounds for being clean, tight, and in their proper locations.
• Inspect the Service Bulletins for ECM software updates.
Sensor Checks Inspect the engine control sensors for the following conditions. Refer to the scan tool
Data List in this section.
• Use the scan tool to compare the Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) with the Intake
Air Temperature (IAT) and Fuel Temperature (FT) on a cold engine condition. If the
difference among temperature reading is more than 5°C (9°F) on a cold engine,
check for high resistance on the low reference circuit and signal circuit or for a
skewed sensor.
Notice: The mass air flow (MAF) sensor is heated and as a result the IAT sensor may
indicate a higher than normal intake air temperature if the ignition switch is being ON.
FT sensor is internal to the PCU and it is part of the fuel injection pump assembly.
• Use the scan tool to compare the MAF Sensor parameter with the Desired MAF
parameter. Start the engine and warm up (allow engine coolant temperature to reach
at least 60°C [140°F]). The MAF Sensor parameter must follow the Desired MAF
parameter within 100 mg/strk. If not, inspect the air intake system, EGR system
components and contaminated, skewed or slow MAF sensor.
• Use the scan tool to observe the Accelerator Pedal Position Accelerator Pedal
Position. Accelerator Pedal Position parameter should change linearly from 0% to
100% according to the accelerator pedal operation.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1303 of 6020
Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-269
Checks Action
Fuel System Checks Inspect the fuel system for the following conditions. Refer to the Fuel System section.
• Inspect for water contamination in the fuel.
• Inspect for external fuel leaks or fuel leakage into the engine oil.
• Inspect the fuel lines between the fuel tank and fuel injection pump for tightness and
all fuel hoses for cuts, cracks and for the use of proper clamps.
Notice: The fuel system from the fuel tank(s) to the fuel injection pump is under a
slight vacuum with the engine running. As a result, air can enter the fuel system if
these connections are not tight. Air in the fuel system will cause fuel injection pump
internal pressure fluctuations especially at high engine speed and load.
• Inspect for air in the fuel system.
Notice: If many air bubbles appear in the fuel, check the fuel system line connections
between the fuel tank and the fuel injection pump for tightness and all fuel hoses for
cuts, cracks and for the use of proper clamps.
a. Remove the fuel hose that connects to the fuel injection pump suction side.
b. Substitute a clear hose.
Notice: A hose must be cleaned.
c. Connect the clear hose to the fuel injection pump.
d. Bleed the fuel system.
e. Let the engine run at idle for at least 2 minutes.
f. Accelerator the engine between idle and W .O.T. (accelerator pedal full travel) many times while observing the clear hose.
• Inspect the fuel tank vent hose for a plugged or kinked.
• Inspect inside the fuel tank for any foreign material that may be getting drawn into
the fuel line pickup causing a blocked condition. Draw fuel from the fuel tank at the
fuel line (as close to the fuel tank as possible) going to the fuel pickup tube to verify a
clean stream of fuel comes out (use the hand-held vacuum pump 5-8840-0279-0/J-
23738-A with a clear hose or equivalent). This will ensure the fuel pickup tube is not
cracked drawing air into the fuel line.
• Inspect the fuel injection pump operation.
Notice: The fuel injection pump must be timed to the engine.
• Inspect the eye bolt for any type of restriction or collapsed gauze filter.
Notice: If any type of restriction found, check for a condition that causes contaminated
fuel, such as the customer is using an aftermarket fuel filter or extended maintenance
interval. Also inspect fuel waxing or icing that is caused by an incorrect fuel type used
in winter season or water intrusion in the fuel system.
• Inspect the fuel injection nozzle(s) for proper splay condition or operating pressure.
Notice: Only first stage of operating pressure can be checked.
• Inspect the timing device operating correctly. Observe the Actual Injection Timing
parameter with the scan tool while running the engine. The Actual Injection Timing
parameter must follow the Desired Injection Timing within 2°CA on each engine
speed. Engine idle > around 2000 RPM> around 3000 RPM. If not, inspect the fuel
system restriction, air in the fuel or fuel injection pump operation.
Air Intake System Checks Inspect the air intake system for the following conditions.
• Inspect the air cleaner and air intake ducts for a restriction, holes, or leaks.
• Inspect for a restriction or leak in the intercooler.
• Inspect for a restriction in the turbocharger inlet duct.
• Inspect for a restriction or deposit in the intake throttle bore.
• Inspect for a restriction or leak in the intake manifold.
• Inspect for a restriction or damage at MAF sensor.
• Inspect for a worn or damaged turbocharger turbine wheel, shaft or compressor
wheel. Refer to turbocharger inspection in the Engine Mechanical section.
• Inspect for turbocharger wastegate valve operation. Refer to wastegate valve
inspection in the Engine Mechanical section.
Exhaust System Checks Inspect the exhaust system for a possible restriction. Refer to the Exhaust System
section.
• Inspect for a restriction in the catalytic converter or exhaust pipes.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1328 of 6020
6E-294 Engine Control System (4JH1)
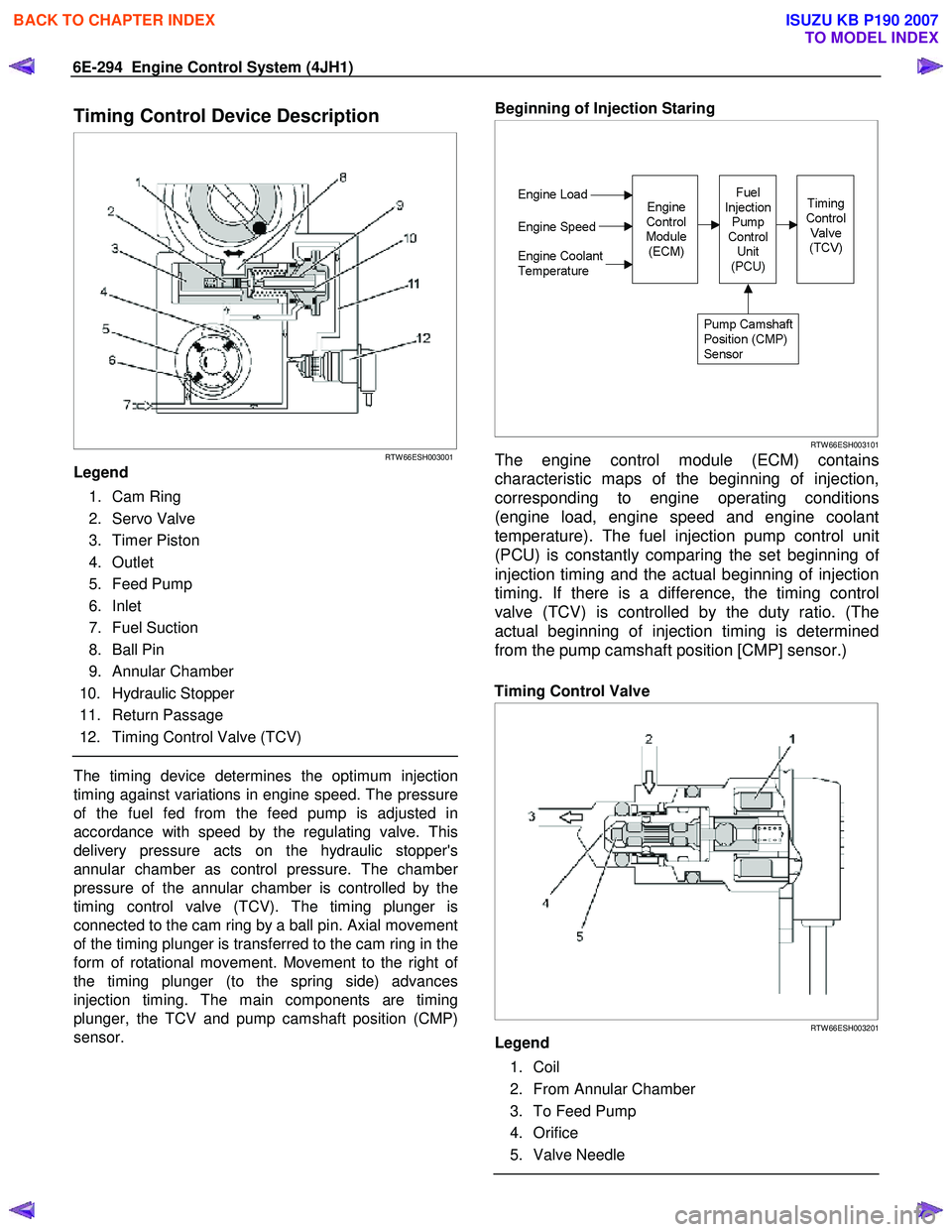
Timing Control Device Description
RTW 66ESH003001
Legend
1. Cam Ring
2. Servo Valve
3. Timer Piston
4. Outlet
5. Feed Pump
6. Inlet
7. Fuel Suction
8. Ball Pin
9. Annular Chamber
10. Hydraulic Stopper
11. Return Passage
12. Timing Control Valve (TCV)
The timing device determines the optimum injection
timing against variations in engine speed. The pressure
of the fuel fed from the feed pump is adjusted in
accordance with speed by the regulating valve. This
delivery pressure acts on the hydraulic stopper's
annular chamber as control pressure. The chambe
r
pressure of the annular chamber is controlled by the
timing control valve (TCV). The timing plunger is
connected to the cam ring by a ball pin. Axial movement
of the timing plunger is transferred to the cam ring in the
form of rotational movement. Movement to the right o
f
the timing plunger (to the spring side) advances
injection timing. The main components are timing
plunger, the TCV and pump camshaft position (CMP)
sensor.
Beginning of Injection Staring
RTW 66ESH003101
The engine control module (ECM) contains
characteristic maps of the beginning of injection,
corresponding to engine operating conditions
(engine load, engine speed and engine coolant
temperature). The fuel injection pump control unit
(PCU) is constantly comparing the set beginning o
f
injection timing and the actual beginning of injection
timing. If there is a difference, the timing control
valve (TCV) is controlled by the duty ratio. (The
actual beginning of injection timing is determined
from the pump camshaft position [CMP] sensor.)
Timing Control Valve
RTW 66ESH003201
Legend
1. Coil
2. From Annular Chamber
3. To Feed Pump
4. Orifice
5. Valve Needle
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1330 of 6020

6E-296 Engine Control System (4JH1)
• Momentary Cam Ring Angular Position
The momentary angular position of the cam ring is input into the fuel injection PCU as a fuel injection
solenoid valve control signal. From momentar
y
input of angular position for fluctuations in running
conditions, the fuel injection solenoid valve open
and close intervals corresponding to the cam ring's
cam lift can be accurately determined.
• Actual Injection Pump Speed
W hen the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor is faulty, the engine control module (ECM) uses the
pump CMP signal as a replacement signal.
• Actual Timing Plunger Position
The actual timing plunger position can be determined by comparing the CKP sensor signal
with the pump CMP sensor angle. This position is
used for timer control.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007