2007 ISUZU KB P190 turn signal
[x] Cancel search: turn signalPage 1741 of 6020
6E-124 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1)
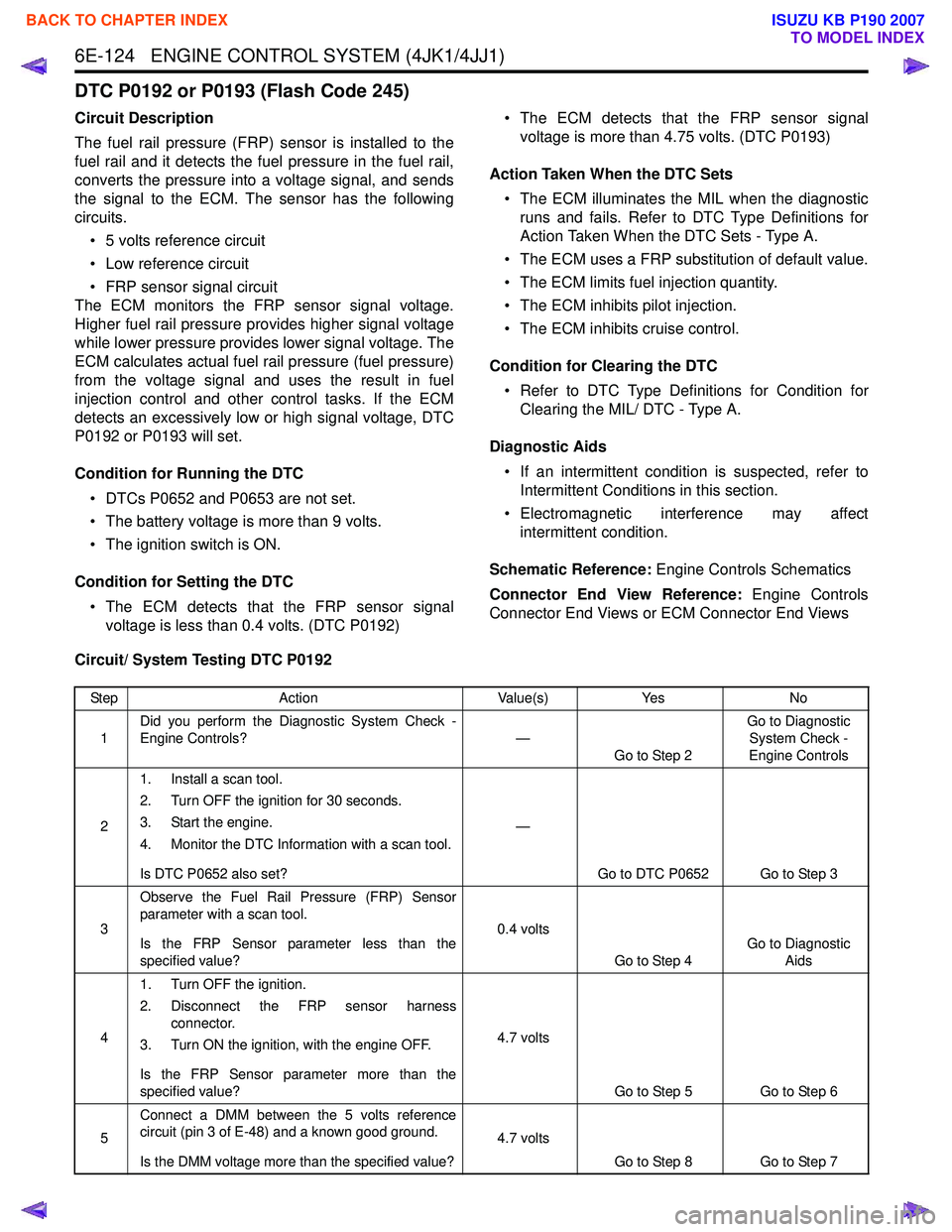
DTC P0192 or P0193 (Flash Code 245)
Circuit Description
The fuel rail pressure (FRP) sensor is installed to the
fuel rail and it detects the fuel pressure in the fuel rail,
converts the pressure into a voltage signal, and sends
the signal to the ECM. The sensor has the following
circuits.
• 5 volts reference circuit
• Low reference circuit
• FRP sensor signal circuit
The ECM monitors the FRP sensor signal voltage.
Higher fuel rail pressure provides higher signal voltage
while lower pressure provides lower signal voltage. The
ECM calculates actual fuel rail pressure (fuel pressure)
from the voltage signal and uses the result in fuel
injection control and other control tasks. If the ECM
detects an excessively low or high signal voltage, DTC
P0192 or P0193 will set.
Condition for Running the DTC • DTCs P0652 and P0653 are not set.
• The battery voltage is more than 9 volts.
• The ignition switch is ON.
Condition for Setting the DTC • The ECM detects that the FRP sensor signal voltage is less than 0.4 volts. (DTC P0192) • The ECM detects that the FRP sensor signal
voltage is more than 4.75 volts. (DTC P0193)
Action Taken When the DTC Sets • The ECM illuminates the MIL when the diagnostic runs and fails. Refer to DTC Type Definitions for
Action Taken When the DTC Sets - Type A.
• The ECM uses a FRP substitution of default value.
• The ECM limits fuel injection quantity.
• The ECM inhibits pilot injection.
• The ECM inhibits cruise control.
Condition for Clearing the DTC • Refer to DTC Type Definitions for Condition for Clearing the MIL/ DTC - Type A.
Diagnostic Aids • If an intermittent condition is suspected, refer to Intermittent Conditions in this section.
• Electromagnetic interference may affect intermittent condition.
Schematic Reference: Engine Controls Schematics
Connector End View Reference: Engine Controls
Connector End Views or ECM Connector End Views
Circuit/ System Testing DTC P0192
Step Action Value(s)Yes No
1 Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check -
Engine Controls? —
Go to Step 2 Go to Diagnostic
System Check -
Engine Controls
2 1. Install a scan tool.
2. Turn OFF the ignition for 30 seconds.
3. Start the engine.
4. Monitor the DTC Information with a scan tool.
Is DTC P0652 also set? —
Go to DTC P0652 Go to Step 3
3 Observe the Fuel Rail Pressure (FRP) Sensor
parameter with a scan tool.
Is the FRP Sensor parameter less than the
specified value? 0.4 volts
Go to Step 4 Go to Diagnostic
Aids
4 1. Turn OFF the ignition.
2. Disconnect the FRP sensor harness connector.
3. Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
Is the FRP Sensor parameter more than the
specified value? 4.7 volts
Go to Step 5 Go to Step 6
5 Connect a DMM between the 5 volts reference
circuit (pin 3 of E-48) and a known good ground.
Is the DMM voltage more than the specified value? 4.7 volts
Go to Step 8 Go to Step 7
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1742 of 6020
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1) 6E-125
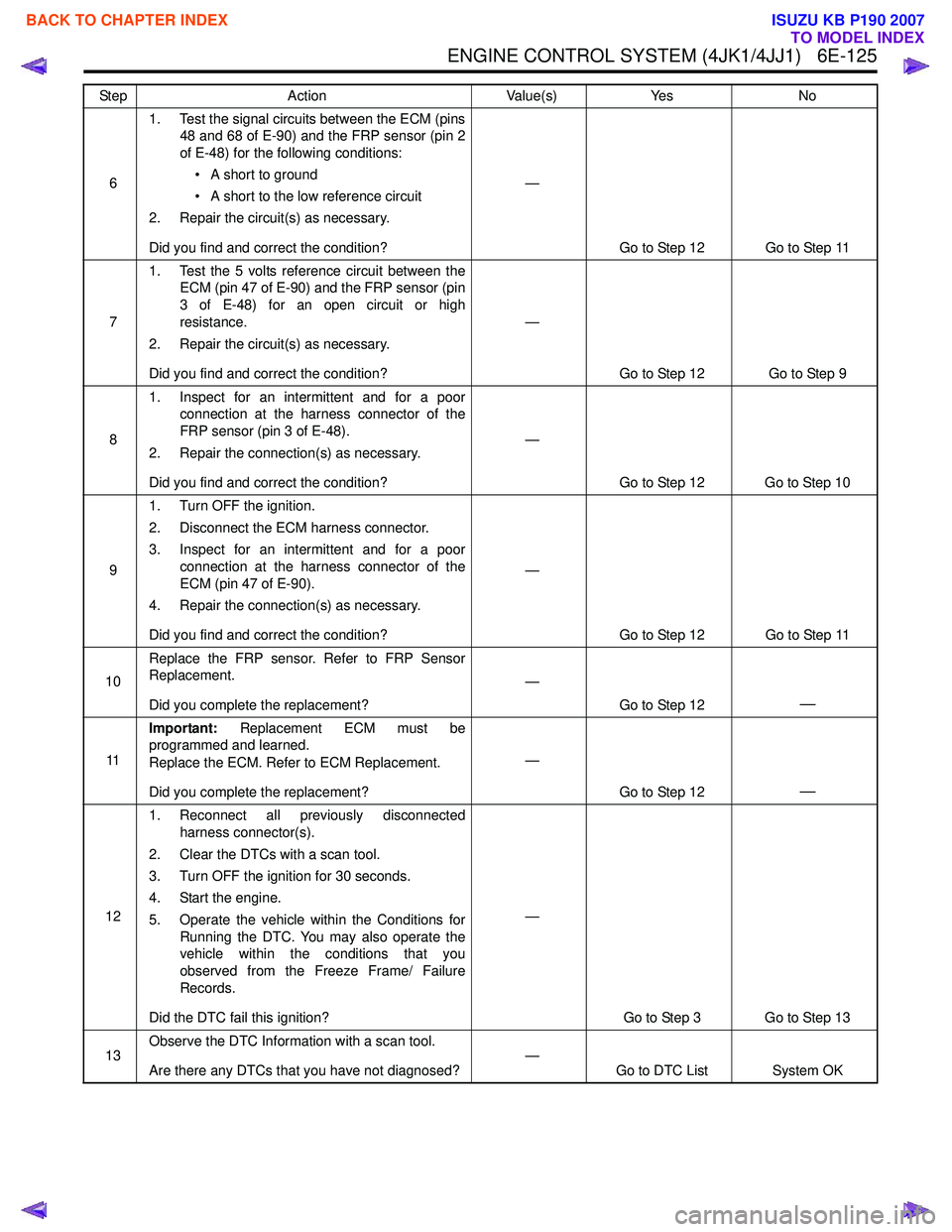
61. Test the signal circuits between the ECM (pins
48 and 68 of E-90) and the FRP sensor (pin 2
of E-48) for the following conditions:
• A short to ground
• A short to the low reference circuit
2. Repair the circuit(s) as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition? —
Go to Step 12 Go to Step 11
7 1. Test the 5 volts reference circuit between the
ECM (pin 47 of E-90) and the FRP sensor (pin
3 of E-48) for an open circuit or high
resistance.
2. Repair the circuit(s) as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition? —
Go to Step 12 Go to Step 9
8 1. Inspect for an intermittent and for a poor
connection at the harness connector of the
FRP sensor (pin 3 of E-48).
2. Repair the connection(s) as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition? —
Go to Step 12 Go to Step 10
9 1. Turn OFF the ignition.
2. Disconnect the ECM harness connector.
3. Inspect for an intermittent and for a poor connection at the harness connector of the
ECM (pin 47 of E-90).
4. Repair the connection(s) as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition? —
Go to Step 12 Go to Step 11
10 Replace the FRP sensor. Refer to FRP Sensor
Replacement.
Did you complete the replacement? —
Go to Step 12
—
11Important:
Replacement ECM must be
programmed and learned.
Replace the ECM. Refer to ECM Replacement.
Did you complete the replacement? —
Go to Step 12
—
121. Reconnect all previously disconnected
harness connector(s).
2. Clear the DTCs with a scan tool.
3. Turn OFF the ignition for 30 seconds.
4. Start the engine.
5. Operate the vehicle within the Conditions for Running the DTC. You may also operate the
vehicle within the conditions that you
observed from the Freeze Frame/ Failure
Records.
Did the DTC fail this ignition? —
Go to Step 3 Go to Step 13
13 Observe the DTC Information with a scan tool.
Are there any DTCs that you have not diagnosed? —
Go to DTC List System OK
Step
Action Value(s)Yes No
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1743 of 6020
6E-126 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1)
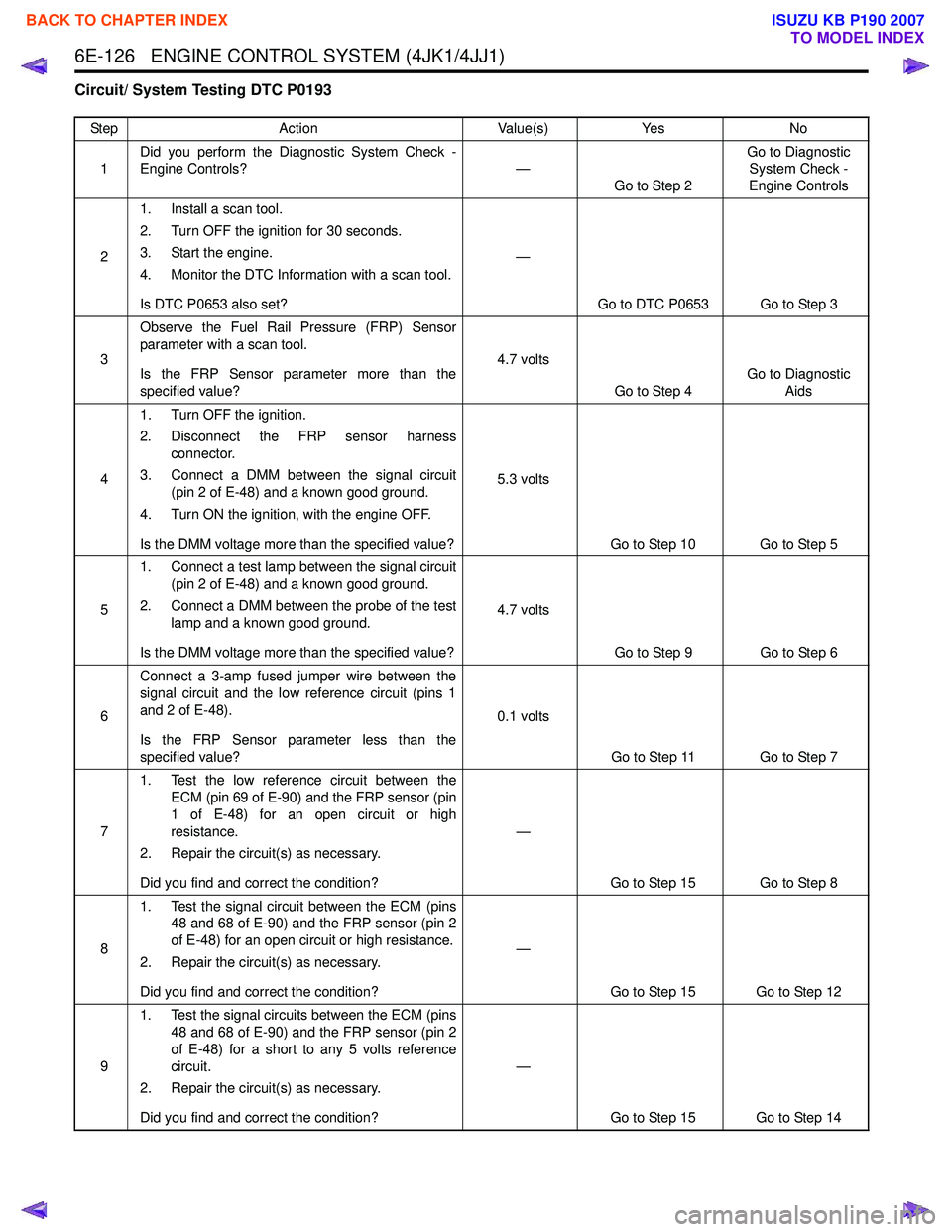
Circuit/ System Testing DTC P0193
StepAction Value(s)Yes No
1 Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check -
Engine Controls? —
Go to Step 2 Go to Diagnostic
System Check -
Engine Controls
2 1. Install a scan tool.
2. Turn OFF the ignition for 30 seconds.
3. Start the engine.
4. Monitor the DTC Information with a scan tool.
Is DTC P0653 also set? —
Go to DTC P0653 Go to Step 3
3 Observe the Fuel Rail Pressure (FRP) Sensor
parameter with a scan tool.
Is the FRP Sensor parameter more than the
specified value? 4.7 volts
Go to Step 4 Go to Diagnostic
Aids
4 1. Turn OFF the ignition.
2. Disconnect the FRP sensor harness connector.
3. Connect a DMM between the signal circuit (pin 2 of E-48) and a known good ground.
4. Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
Is the DMM voltage more than the specified value? 5.3 volts
Go to Step 10 Go to Step 5
5 1. Connect a test lamp between the signal circuit
(pin 2 of E-48) and a known good ground.
2. Connect a DMM between the probe of the test lamp and a known good ground.
Is the DMM voltage more than the specified value? 4.7 volts
Go to Step 9 Go to Step 6
6 Connect a 3-amp fused jumper wire between the
signal circuit and the low reference circuit (pins 1
and 2 of E-48).
Is the FRP Sensor parameter less than the
specified value? 0.1 volts
Go to Step 11 Go to Step 7
7 1. Test the low reference circuit between the
ECM (pin 69 of E-90) and the FRP sensor (pin
1 of E-48) for an open circuit or high
resistance.
2. Repair the circuit(s) as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition? —
Go to Step 15 Go to Step 8
8 1. Test the signal circuit between the ECM (pins
48 and 68 of E-90) and the FRP sensor (pin 2
of E-48) for an open circuit or high resistance.
2. Repair the circuit(s) as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition? —
Go to Step 15 Go to Step 12
9 1. Test the signal circuits between the ECM (pins
48 and 68 of E-90) and the FRP sensor (pin 2
of E-48) for a short to any 5 volts reference
circuit.
2. Repair the circuit(s) as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition? —
Go to Step 15 Go to Step 14
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1744 of 6020
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1) 6E-127
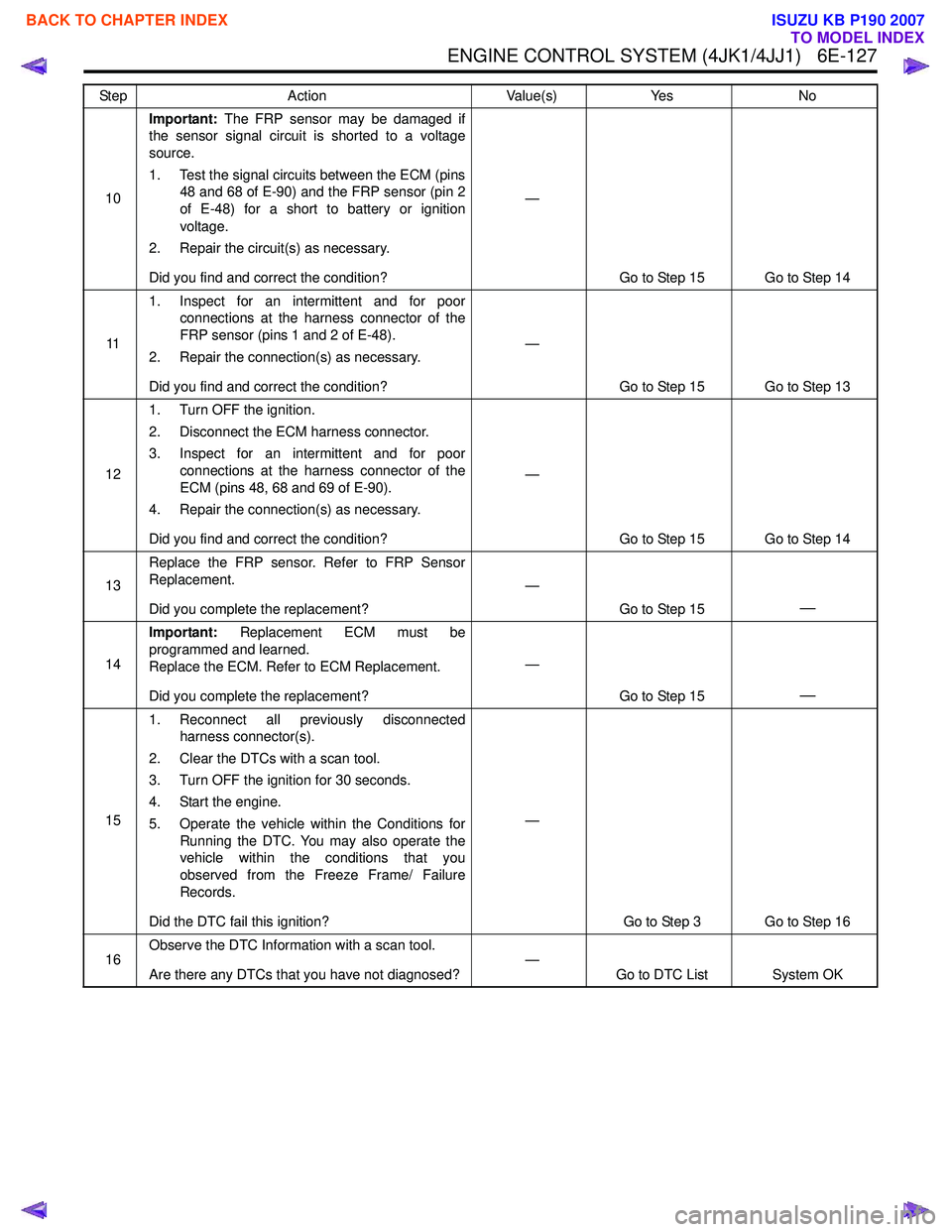
10Important:
The FRP sensor may be damaged if
the sensor signal circuit is shorted to a voltage
source.
1. Test the signal circuits between the ECM (pins 48 and 68 of E-90) and the FRP sensor (pin 2
of E-48) for a short to battery or ignition
voltage.
2. Repair the circuit(s) as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition? —
Go to Step 15 Go to Step 14
11 1. Inspect for an intermittent and for poor
connections at the harness connector of the
FRP sensor (pins 1 and 2 of E-48).
2. Repair the connection(s) as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition? —
Go to Step 15 Go to Step 13
12 1. Turn OFF the ignition.
2. Disconnect the ECM harness connector.
3. Inspect for an intermittent and for poor connections at the harness connector of the
ECM (pins 48, 68 and 69 of E-90).
4. Repair the connection(s) as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition? —
Go to Step 15 Go to Step 14
13 Replace the FRP sensor. Refer to FRP Sensor
Replacement.
Did you complete the replacement? —
Go to Step 15
—
14Important:
Replacement ECM must be
programmed and learned.
Replace the ECM. Refer to ECM Replacement.
Did you complete the replacement? —
Go to Step 15
—
151. Reconnect all previously disconnected
harness connector(s).
2. Clear the DTCs with a scan tool.
3. Turn OFF the ignition for 30 seconds.
4. Start the engine.
5. Operate the vehicle within the Conditions for Running the DTC. You may also operate the
vehicle within the conditions that you
observed from the Freeze Frame/ Failure
Records.
Did the DTC fail this ignition? —
Go to Step 3 Go to Step 16
16 Observe the DTC Information with a scan tool.
Are there any DTCs that you have not diagnosed? —
Go to DTC List System OK
Step
Action Value(s)Yes No
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1759 of 6020
6E-142 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1)
DTC P0234 (Flash Code 42)
Circuit Description
The boost pressure sensor is located in the air
induction tubing. The sensor is a transducer that varies
voltage according to changes in the air pressure inside
the air tubing. The ECM monitors the boost pressure
sensor signal for abnormal values. If the ECM detects
that the sensor signal is excessively high, this DTC will
set. This indicates excessive high boost pressure.
Condition for Running the DTC • DTCs P0045, P0107 and P0108 are not set.
• The ignition switch is ON.
• The engine is running.
Condition for Setting the DTC • The ECM detects that the actual boost pressure is more than 20 kPa (3 psi) over the desired boost
pressure under certain conditions for longer than
10 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets • The ECM illuminates the MIL when the diagnostic runs and fails. Refer to DTC Type Definitions for
Action Taken When the DTC Sets - Type A.
• The ECM limits fuel injection quantity.
• The ECM inhibits pilot injection.
Condition for Clearing the DTC • Refer to DTC Type Definitions for Condition for Clearing the MIL/ DTC - Type A.
• The ECM limits fuel injection quantity.
• The ECM inhibits pilot injection. • The ECM inhibits cruise control.
Diagnostic Aids • An open circuit or high resistance in the boost pressure low reference circuit may set this DTC.
• Misrouted vacuum hoses may set this DTC.
• Check the turbocharger nozzle control actuator for a sticking. Refer to Turbocharger in the Engine
Mechanical section.
• Use a scan tool to verify the integrity of the boost pressure sensor signal. Compare the Boost
Pressure to the Desired Boost Pressure under all
load conditions for an excessively high value.
• The fuel with which gasoline was mixed may set this DTC.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step number on the
Circuit/ System Testing.
3. A skewed boost pressure sensor value (shifted to a
higher pressure) can set this DTC. The Boost Pressure
on the scan tool should read near Barometric Pressure
(BARO) with the key ON and engine OFF.
4. A skewed BARO sensor value (shifted to a lower
pressure) may indicate a wrong boost pressure. The
BARO on the scan tool should read near surrounding
barometric pressure.
Schematic Reference: Vacuum Hose Routing
Diagram and Engine Controls Schematics
Connector End View Reference: Engine Controls
Connector End Views or ECM Connector End Views
Circuit/ System Testing DTC P0234
Step Action Value(s)Yes No
1 Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check -
Engine Controls? —
Go to Step 2 Go to Diagnostic
System - Check
Engine Controls
2 1. Install a scan tool.
2. Turn OFF the ignition for 30 seconds.
3. Start the engine.
4. Monitor the DTC Information with a scan tool.
Is DTC P0045, P0107, P0108, P0638, P1196,
P1197, P1198, P2227, P2228 or P2229 also set? —
Go to Applicable DTC Go to Step 3
3 1. Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
2. Observe the Boost Pressure and Barometric Pressure (BARO) with a scan tool.
Does the scan tool indicate that the difference
between the Boost Pressure and BARO is more
than the specified value? 10 kPa (1.5
psi)
Go to Step 4 Go to Step 5
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1760 of 6020
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1) 6E-143
4Compare the BARO value to the range specified in
the altitude vs. barometric pressure table. Refer to
Altitude vs Barometric Pressure.
Is the BARO parameter within the range specified? —
Go to Step 6 Go to Step 7
5 1. Inspect the following for possible causes of
high boost pressure.
• Misrouted turbocharger nozzle control actuator vacuum hoses
• Turbocharger nozzle control actuator or solenoid valve for a stuck condition.
Refer to Turbocharger Control System
Check in this section.
• Intake throttle valve sticking. Perform the Intake Throttle Solenoid Control with a
scan tool
• Oil in the air induction tubing causing an incorrect boost pressure sensor signal.
When there is adhesion of oil inside of
the tubing, intercooler or turbocharger it
needs to be wiped off.
2. Repair or replace as necessary.
Did you find and correction the condition? —
Go to Step 10 Go to Diagnostic
Aids
6 1. Turn OFF the ignition.
2. Disconnect the boost pressure sensor harness connector.
3. Inspect for an intermittent and for a poor connection at the harness connector of the
boost pressure sensor (pin 2 of E-107).
4. Disconnect the ECM harness connector.
5. Inspect for an intermittent, for a poor connection and corrosion at the harness
connector of the ECM (pin 23 of E-90).
6. Test for high resistance of the low reference circuit.
7. Repair the connection(s) or circuit(s) as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition? —
Go to Step 10 Go to Step 8
7 1. Turn OFF the ignition.
2. Disconnect the BARO sensor harness connector.
3. Inspect for an intermittent and for poor connections at the harness connector of the
BARO sensor (pins 2 and 3 of E-40).
4. Disconnect the ECM harness connector.
5. Inspect for an intermittent, for poor connections and corrosion at the harness
connector of the ECM (pins 18 and 19 of E-
90).
6. Test for high resistance on each circuit.
7. Repair the connection(s) or circuit(s) as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition? —
Go to Step 10 Go to Step 9
Step
Action Value(s)Yes No
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1762 of 6020
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1) 6E-145
DTC P0299 (Flash Code 65)
Circuit Description
The boost pressure sensor is located in the air
induction tubing. The sensor is a transducer that varies
voltage according to changes in the air pressure inside
the air tubing. The ECM monitors the boost pressure
sensor signal for abnormal values. If the ECM detects
that the sensor signal is excessively low, this DTC will
set. This indicates excessive low boost pressure.
Condition for Running the DTC • DTCs P0045, P0087, P0088, P0089, P0091, P0092, P0093, P0101, P0102, P0103, P0107,
P0108, P0116, P0117, P0118, P0122, P0123,
P0192, P0193, P0401, P0403, P0404, P0405,
P0406, P0638, P0652, P0653, P0698, P0699,
P1064, P1065, P1093, P1404, P2100, P2101,
P2103, P2227, P2228 and P2229 are not set.
• The ignition switch is ON.
• The engine is running.
• The fuel injection quantity is higher than a predetermined value.
Condition for Setting the DTC • The ECM detects that the actual boost pressure is more than 40 kPa (6 psi) below the desired boost
pressure under certain conditions for longer than
10 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets • The ECM illuminates the MIL when the diagnostic runs and fails. Refer to DTC Type Definitions for
Action Taken When the DTC Sets - Type A.
• The ECM limits fuel injection quantity.
• The ECM inhibits cruise control. Condition for Clearing the DTC
• Refer to DTC Type Definitions for Condition for Clearing the MIL/ DTC - Type A.
Diagnostic Aids • Induction air leakage can cause a low boost pressure condition. A whistling noise may be heard
if a component is allowing air to enter the induction
system.
• Check for cracked air tubing that may only open during certain engine movement conditions.
• Misrouted vacuum hoses may set this DTC.
• Check the turbocharger nozzle control actuator for a sticking. Refer to Turbocharger in the Engine
Mechanical section.
• Use a scan tool to verify the integrity of the boost pressure sensor signal. Compare the Boost
Pressure to the Desired Boost Pressure under all
load conditions for an excessively low value.
• Loss of vacuum pressure or vacuum pump problem sets this DTC.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step number on the
diagnostic table.
4. A skewed boost pressure sensor value (shifted to a
lower pressure) can set this DTC. The Boost Pressure
on the scan tool should read near Barometric Pressure
(BARO) with the key ON and engine OFF.
5. A skewed BARO sensor value (shifted to a higher
pressure) may indicate a wrong boost pressure. The
BARO on the scan tool should read near surrounding
barometric pressure.
Schematic Reference: Vacuum Hose Routing
Diagram and Engine Controls Schematics
Connector End View Reference: Engine Controls
Connector End Views or ECM Connector End Views
Circuit/ System Testing DTC P0299
Step Action Value(s)Yes No
1 Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check -
Engine Controls? —
Go to Step 2 Go to Diagnostic
System Check -
Engine Controls
2 1. Install a scan tool.
2. Turn OFF the ignition for 30 seconds.
3. Start the engine.
4. Monitor the DTC Information with a scan tool.
Is DTC P0045, P0107, P0108, P2227, P2228 or
P2229 also set? —
Go to Applicable DTC Go to Step 3
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1763 of 6020
6E-146 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1)
31. Inspect the following for possible causes of
low boost pressure.
• Air leakage around the boost pressure sensor or objects that block the sensor
hole.
• Air leaking around any of the air induction tubing between the turbocharger and
intake manifold. Check for damaged
components and for loose clamps.
• Misrouted, disconnected or kinked turbocharger nozzle control actuator
vacuum hose.
• Turbine shaft binding causing lower turbocharger shaft spinning speeds.
Refer to the Turbocharger in Engine
Mechanical section for diagnosis.
• Turbocharger nozzle control actuator or solenoid valve for a stuck condition.
Refer to Turbocharger Control System
Check in this section.
• Intake throttle valve sticking. Perform the Intake Throttle Solenoid Control with a
scan tool.
• Restricted air cleaner element, restricted or collapsed air tubing between the air
cleaner and the boost pressure sensor.
• Oil in the air induction tubing causing an incorrect boost pressure sensor signal.
When there is adhesion of oil inside of
the tubing, intercooler or turbocharger it
needs to be wiped off.
2. Repair or replace as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition? —
Go to Step 10 Go to Step 4
4 1. Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
2. Observe the Boost Pressure and Barometric Pressure (BARO) with a scan tool.
Does the scan tool indicate that the difference
between the Boost Pressure and BARO is more
than the specified value? 10 kPa (1.5
psi)
Go to Step 5 Go to Diagnostic
Aids
5 Compare the BARO value to the range specified in
the altitude vs. barometric pressure table. Refer to
Altitude vs Barometric Pressure.
Is the BARO parameter within the range specified? —
Go to Step 6 Go to Step 7
Step
Action Value(s)Yes No
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007