2007 ISUZU KB P190 turn signal
[x] Cancel search: turn signalPage 1283 of 6020
Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-249
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
39 1. Reconnect all previously disconnected fuse,
relay or harness connector(s).
2. Turn OFF the ignition for 30 seconds.
3. Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
4. Turn ON the blower motor switch.
Does the blower motor turn ON and operate
correctly?
Go to Char 1 of 2 Step 4 Refer to Applicable
Diagnostic Chart in Heating & Air Conditioning Section
Chart 2 of 2 without heater
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1 1. Turn OFF the ignition.
2. Replace the thermo relay with the horn relay or replace with a known good relay.
3. Turn OFF the blower motor switch.
4. Turn OFF the A/C switch.
5. Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
Does the A/C Request Signal parameter indicate
OFF?
Go to Step 37 Go to Step 2
2 1. Turn OFF the ignition. 2. Remove the thermo relay from the engine room relay block.
3. Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
Does the A/C Request Signal parameter indicate
OFF?
Go to Step 3 Go to Step 5
3 1. Turn OFF the ignition. 2. Reinstall the thermo relay.
3. Remove the radiator grille in order to access the pressure switch.
4. Disconnect the pressure switch harness connector (C-24).
5. Turn OFF the blower motor switch.
6. Turn OFF the A/C switch.
7. Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
Does the A/C Request Signal parameter indicate
OFF?
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 6
4 1. Turn OFF the ignition. 2. Remove the glove box in order to access the electronic thermostat.
3. Back probe a test lamp between the electronic thermostat harness (pin 2 of C-55 connector) and
battery voltage.
4. Turn ON the blower motor switch.
5. Turn OFF the A/C switch.
6. Keep the ignition OFF.
Does the test lamp illuminate?
Go to Step 8 Go to Step 9
5 Repair the short to battery or ignition voltage on the thermo relay signal input circuit between the thermo
relay (pin 1 of X-15 connector) and the engine
control module (ECM) (pin 33 of C-56 connector).
Did you complete the repair?
Go to Step 43
6 Repair the short to ground between the thermo relay
(pin 5 of X-15 connector) and pressure switch (pin 1
of C-24 connector).
Did you complete the repair?
Go to Step 43
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1289 of 6020

Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-255
Symptoms – Engine Controls
Symptoms – Engine Controls
Important Preliminary Inspections Before Starting
Perform Diagnostic System Check – Engine Controls
before using the symptom tables, and verify that all o
f
the following are true:
• The engine control module (ECM) and malfunction
indicator lamp (MIL) are operating correctly.
• There are no diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs)
stored, or a DTC exists but without the MIL.
• The scan tool data is within the normal operating
range. Refer to scan tool Data List in this section.
• Verify the customer concern and locate the correct
symptom in the table of contents. Inspect the items
indicated under that symptom.
Visual and Physical Inspection
Several of the symptom procedures ask for careful
visual and physical inspection. This step is extremel
y
important. The visual and physical inspection can lead
to correcting a problem without further inspections, and
can save valuable time. Ensure that:
• The ECM grounds are clean, tight, and in thei
r
proper location.
• The vacuum hoses are not split or kinked, and
properly connected. Inspect thoroughly for an
y
type of leak or restriction.
• The mass air flow (MAF) sensor is properl
y
installed. The arrows on the plastic portion of the
sensor must point toward the engine.
• The air intake ducts are not collapsed or damaged.
• There are no leaks at the MAF sensor, an
y
connections or intake manifold sealing surfaces.
• The engine harness wiring and terminals are
properly connected and are not pinched or cut.
Intermittent
Important:
Inspect for improper installation of electrical
components if an intermittent condition exists. Inspect
for aftermarket add-on electrical equipment devices,
lights, and cellular phones. Verify that no aftermarket
equipment is connected to the keyword 2000 serial data
circuit. If you cannot locate an intermittent condition, a
cellular phone communication signal may cause the
condition.
Important:
The problem may or may not turn ON the MIL or store a
DTC.
Faulty electrical connections or wiring cause most
intermittent problems. Perform a careful visual and
physical inspection of the suspect connectors for the
following conditions:
• Improperly mated connector halves
• Terminals that are not seated
• Terminals that are damaged or improperly formed
Reform or replace connector terminals in the problem
circuit in order to ensure proper contact tension.
Remove the terminal from the connector body in orde
r
to inspect for poor terminal wire connection.
Road test the vehicle with the DMM connected to the
suspected circuit. An abnormal reading that occurs
when the malfunction occurs is a good indication that
there is a malfunction in the circuit being monitored.
Use the scan tool in order to help detect intermittent
conditions. Useful features of the scan tool include the
following:
• Trigger the Snapshot feature in order to capture
and store engine parameters when the malfunction
occurs. Review this stored information in order to
see the specific running conditions that caused the
malfunction.
• Use the Plot Function on the scan tool in order to
plot selected data parameters. Review this stored
information to aid in locating an intermittent
problem. Refer to the scan tool Users Guide fo
r
more information.
Important:
If the intermittent condition exists as a start and then
stall, test for DTCs relating to the vehicle theft deterrent
system. Test for improper installation of electrical
options such as lights, cellular phones, etc.
Any of the following may cause an intermittent MIL with
no stored DTC:
• The ECM grounds are loose or dirty. Refer to
Engine Controls Schematics.
• The MIL circuit intermittently shorted to ground.
• Electrical system interference caused by a
malfunctioning relay, ECM driven solenoid, o
r
switch. The electrical component can cause a
sharp electrical surge. Normally, the problem will
occur when the malfunctioning component is
operating.
• There is an open diode across the A/C
compressor clutch or any other open diodes.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1312 of 6020

6E-278 Engine Control System (4JH1)
• Destination Code
j. Select Next.
k. Verify your selection on the Summary screen.
Important:
Refer to Service Bulletins before service programming is
performed if the bulletins are listed along with the
calibration files.
Important:
Select Cancel if you receive a message stating that the
calibration selected is already the current calibration in
the ECM and reprogramming with the same download is
not allowed.
l. Select Reprog.
m. The Transfer Data screen will appear until the progress bar reaches 100%.
6. Close the application and return to the TIS application selection screen after the download is
complete.
7. Turn OFF the scan tool.
8. Disconnect the scan tool from the terminal.
9. Transfer the data from the scan tool to the ECM using the following procedure:
a. Connect the scan tool to the vehicle DLC, with the engine and the scan tool OFF.
b. Turn ON the scan tool.
c. Press Enter at the Title screen.
d. Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
e. Select Service Programming System.
f. Select the Program ECU on the scan tool.
g. Follow the on-screen instructions and select Continue.
h. Programming in Process will appear until the progress bar reaches 100%.
Important:
The vehicle fitted with automatic transmission, Check
Trans lamp may blink while programming the ECM since
communication between the ECM and TCM is
interrupted. Clear DTC in any module afte
r
programming.
i. Select Continue and exit the program after the scan tool displays Programming W as
Successful.
10. Turn OFF the ignition.
11. Turn OFF the scan tool.
12. Disconnect the scan tool from the vehicle.
Service Programming System (SPS) (Pass-
Thru Procedure)
Pass-Thru programming allows the scan tool to remain
connected to the terminal and to the vehicle throughou
t
the programming process. The vehicle must be in close
proximity to the terminal while using Pass-Thru.
Important:
The TIS supports service programming with the scan
tool scan tool only.
1. Launch the TIS application at the terminal.
2. Select the Service Programming System at the main screen.
3. Highlight the following information on the Selec
t
Diagnostic Tool and Programming Process screen:
• Select Diagnostic Tool-Select Pass-Thru
• Select Programming Process-Identify whethe
r
as existing engine control module (ECM) is
being reprogrammed or an ECM is being
replaced with a new one.
• Select ECU Location-Select Vehicle.
4. Select Next.
5. Complete all vehicle data on the Preparing fo
r
Communication/Determine Vehicle screen until
Next is highlighted.
6. Select Next.
7. Follow the instruction on the Preparing fo
r
Communication screen.
Important:
In order to reduce the potential for signal loss, the RS-
232 cable should not be more than 25 feet long.
8. Select Next.
9. Verify the VIN on the Validate Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) screen and select Next.
Important:
If the ECM is replaced to new one, VIN does no
t
displayed. Input correct VIN reading from stamped VIN
or affixed VIN plate on the vehicle. If the ECM from
another vehicle is installed, input correct VIN by same
way. 10. Highlight Engine on the System Type screen and
select Next, if requested.
11. Complete the following information based on the service ID plate on the Validate Vehicle Data
screen until Next is highlighted:
• Model
• Model Year
• Engine
• Type of Transmission
• Destination Code
12. Select Next.
13. Verify your selection on the Summary screen.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1317 of 6020
Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-283
Description And Operation
Engine Control Module (ECM) Description
RTW 66ESH001201
The engine control module (ECM) is designed to
withstand normal current draws associated with vehicle
operation. Avoid overloading any circuit. W hen testing
for opens and shorts, do not ground or apply voltage to
any of the ECM circuits unless instructed to do so. In
some cases, these circuits should only be tested using
a digital multi meter (DMM). The ECM should remain
connected to the ECM harness.
The ECM is located on the floor panel. The ECM mainl
y
controls the following.
• The fuel system control
• The exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system
control
• The preheating (glow) system control
• The A/C compressor control
• On-board diagnostics for engine control
The ECM constantly observes the information from
various sensor s. The ECM controls the systems that
affect vehicle performance. The ECM performs the
diagnostic function of the system. The ECM can
recognize operational problems, alert the driver through
the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL), and store
diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). DTCs identify the
system faults to aid the technician in making repairs.
ECM Voltage Description
The ECM supplies a buffered voltage to various
switches and sensor s. The ECM can do this because
resistance in the ECM is so high in value that a test
lamp may not illuminate when connected to the circuit.
An ordinary shop voltmeter may not give an accurate
reading because the voltmeter input impedance is too
low. Use a 10-megaohm input impedance DMM, to
ensure accurate voltage readings. The input and/o
r
output devices in the ECM include analog-to-digital
converters, signal buffers, counters, and special drivers.
The ECM controls most components with electronic
switches which complete a ground circuit when turned
ON.
Aftermarket Electrical and Vacuum Equipment
Aftermarket or add-on electrical and vacuum equipment
is defined as any equipment which connects to the
vehicle's electrical or vacuum systems that is installed
on a vehicle after the vehicle leaves the factory. No
allowances have been made in the vehicle design fo
r
this type of equipment. No add-on vacuum equipment
should be added to this vehicle. Add-on electrical
equipment must only be connected to the vehicle's
electrical system at the battery power and ground. Add-
on electrical equipment, even when installed to these
guidelines, may still cause the powertrain system to
malfunction. This may also include equipment not
connected to the vehicle electrical system such as
portable telephones and audios. Therefore, the first
step in diagnosing any powertrain fault is to eliminate all
aftermarket electrical equipment from the vehicle. Afte
r
this is done, if the fault still exists, the fault may be
diagnosed in the normal manner.
Electrostatic Discharge Damage
Electronic components used in the ECM are often
designed to carry very low voltage. Electronic
components are susceptible to damage caused b
y
electrostatic discharge. By comparison, as much as
4,000 volts may be needed for a person to feel even the
zap of a static discharge. There are several ways for a
person to become statically charged. The most
common methods of charging are by friction and
induction. •
An example of charging by friction is a person
sliding across a vehicle seat.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1318 of 6020
6E-284 Engine Control System (4JH1)
Important:
To prevent possible electrostatic discharge damage,
follow these guidelines: • Do not touch the ECM connector pins or soldered
components on the ECM circuit board.
• Do not open the replacement part package until
the part is ready to be installed.
• Before removing the part from the package,
ground the package to a known good ground on
the vehicle.
• If the part has been handled while sliding across
the seat, while sitting down from a standing
position, or while walking a distance, touch a
known good ground before installing the part.
• Charge by induction occurs when a person with
well insulated shoes stands near a highly charged
object and momentarily touches ground. Charges
of the same polarity are drained off leaving the
person highly charged with opposite polarity.
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) Operation
The malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) is located in the
instrument panel cluster (IPC). The MIL will display the
following symbols when commanded ON:
RTW 76ESH004001
The MIL indicates that an emission or performance
related fault has occurred and vehicle service is
required. The following is a list of the modes o
f
operation for the MIL: • The MIL illuminates for approximately 2 seconds
when the ignition switch is turned ON, with the
engine OFF. This is a bulb test to ensure the MIL
is able to illuminate.
•
The MIL remains illuminated after the engine is
started if the ECM detects a fault. A DTC is stored
any time the ECM illuminates the MIL due to an
emission or performance related fault.
Engine Control Component Description
Accelerator Pedal Position (APP) Sensor & Idle
Switch
RTW 66ESH001301
The accelerator pedal position (APP) sensor is mounted
on the throttle assembly. The engine control module
(ECM) uses the APP sensor s to determine the amount
of acceleration or deceleration desired by the person
driving the vehicle via the fuel injection control.
The idle switch is also mounted on the intake throttle
assembly. The idle switch is part of the APP senso
r
assembly. The idle switch is a normally closed type
switch. W hen the accelerator pedal is released, the idle
switch signal to the ECM is low voltage.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1329 of 6020
Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-295
The timing control valve (TCV) acts as a variable
throttle, using the rapid opening and closing (cycling)
of the valve needle in the TCV.
At normal operation,
the TCV controls the pressure acting on the annula
r
chamber so that the hydraulic stopper cam move to
any position, from the retard position to the advance
position. At this time, the duty ratio is set by the fuel
injection pump control unit (PCU).
When control current flows to the TCV coil, the valve
needle opens and the fuel annular chamber flows
through the orifice to the feed pump inlet.
Consequently, the pressure of the annular chambe
r
decreases and the hydraulic stopper is moved to the
retard side.
When control current to the TCV coil is cut, the valve
needle closes and the return passage is closed.
Consequently, the pressure of the annular chambe
r
increases and the hydraulic stopper is moved to the
advance side.
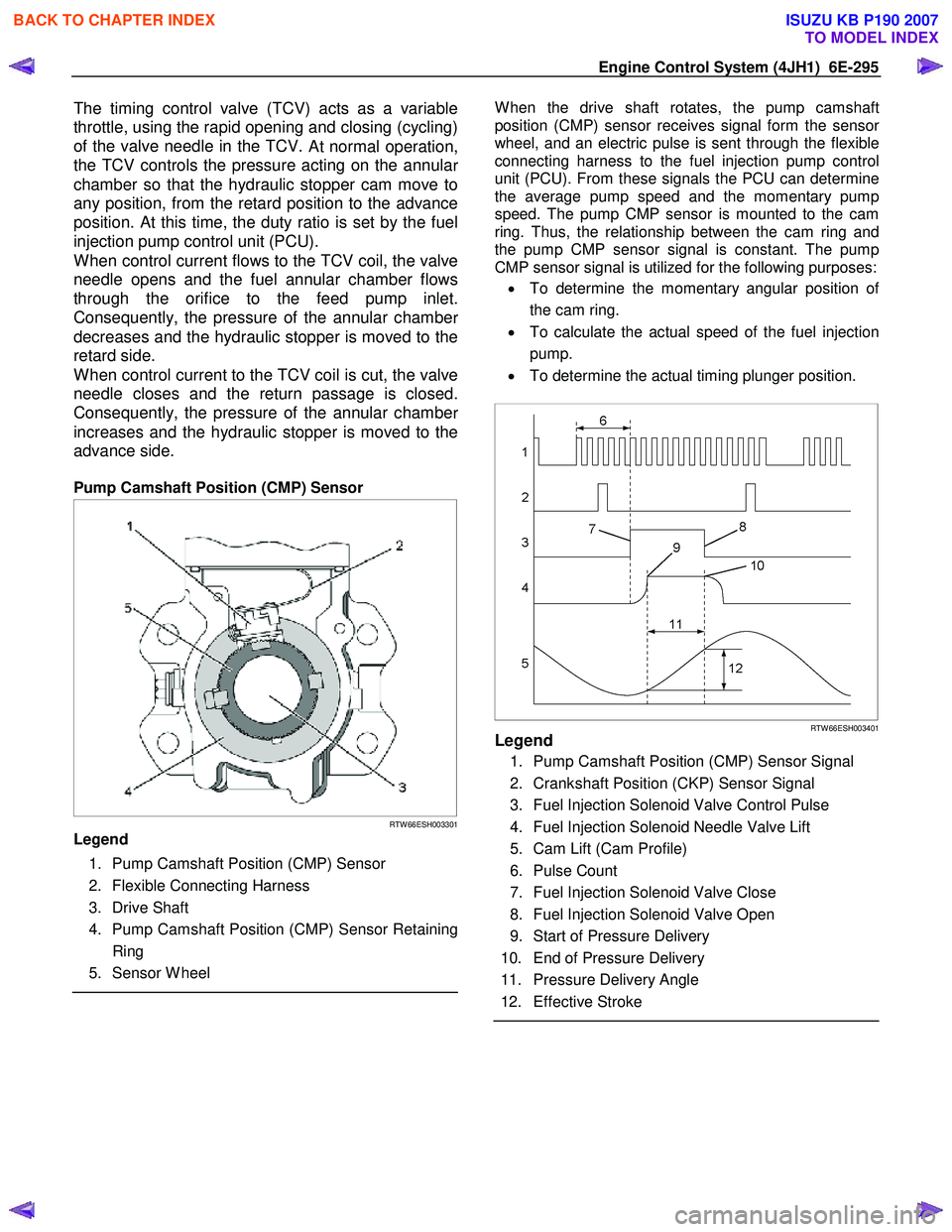
Pump Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
RTW 66ESH003301
Legend
1. Pump Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
2. Flexible Connecting Harness
3. Drive Shaft
4. Pump Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor Retaining Ring
5. Sensor W heel
W hen the drive shaft rotates, the pump camshaft
position (CMP) sensor receives signal form the senso
r
wheel, and an electric pulse is sent through the flexible
connecting harness to the fuel injection pump control
unit (PCU). From these signals the PCU can determine
the average pump speed and the momentary pump
speed. The pump CMP sensor is mounted to the cam
ring. Thus, the relationship between the cam ring and
the pump CMP sensor signal is constant. The pump
CMP sensor signal is utilized for the following purposes:
• To determine the momentary angular position o
f
the cam ring.
• To calculate the actual speed of the fuel injection
pump.
• To determine the actual timing plunger position.
RTW 66ESH003401Legend
1. Pump Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor Signal
2. Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor Signal
3. Fuel Injection Solenoid Valve Control Pulse
4. Fuel Injection Solenoid Needle Valve Lift
5. Cam Lift (Cam Profile)
6. Pulse Count
7. Fuel Injection Solenoid Valve Close
8. Fuel Injection Solenoid Valve Open
9. Start of Pressure Delivery
10. End of Pressure Delivery
11. Pressure Delivery Angle
12. Effective Stroke
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1365 of 6020

ENGINE MECHANICAL (4JK1/4JJ1) 6A-5
EGR system
Based upon data, including water temperature, engine
speeds or engine loads, it is controlled via Engine
Control Module (ECM) to purify exhaust by recycling
part of it.
Its main components include an EGR valve, an EGR
cooler and various sensors.
Connecting rod cap bolt
The angular tightening method of the connecting rod
cap bolt further increases reliability and durability.
Fuel rail-type electronic control injection system
The fuel rail-type electronic control injection system is
composed of a fuel supply pump that sets the target
pressure of high-pressure fuel and supply it, a fuel rail
that measures such high-pressure fuel and a fuel
injector that turns it into a fine spray and injects it. Each
is controlled via ECM based upon various signals, while
injection timing or fuel injection quantity is controlled
under every possible driving condition.
Fuel injector
The fuel injector is a 6-hole nozzle that adjusts fuel
injection quantity or injection timing by opening o
r
closing an electromagnetic valve on the head of the fuel
injector.
ECM corrects the dispersion of fuel injection quantit
y
between fuel injector according to ID code data in
memory. At the replacement of fuel injector, ID code
data should be stored in ECM.
Fuel filter with sedimenter
It is a fuel filter with sedimenter that gets rid of water by
making use of the difference in specific gravity between
light oil and water, which comes with an indicator that
notifies you that it is filled with water.
Preheating system
The preheating system consists of the ECM, the glow
relay, glow plugs and the glow indicator lamp. The
preheating system is operated when the engine coolant
temperature is low, and makes the engine easy to start.
Lubrication system
It is an oil filter with full-flow bypass, which uses a
water-cool oil cooler and oil jet to cool the piston.
Functional inspection
Inspection/adjustment of valve clearance 1. Inspection of valve clearance
• Remove the fuel injector harness assembly.
• Remove the leak off hose.
• Remove the cylinder head cover.
• Rotate the crankshaft to make the No.1
cylinder meet the compression top dead cente
r
(TDC).
RTW 76ASH001301
Legend
1. TDC
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1623 of 6020
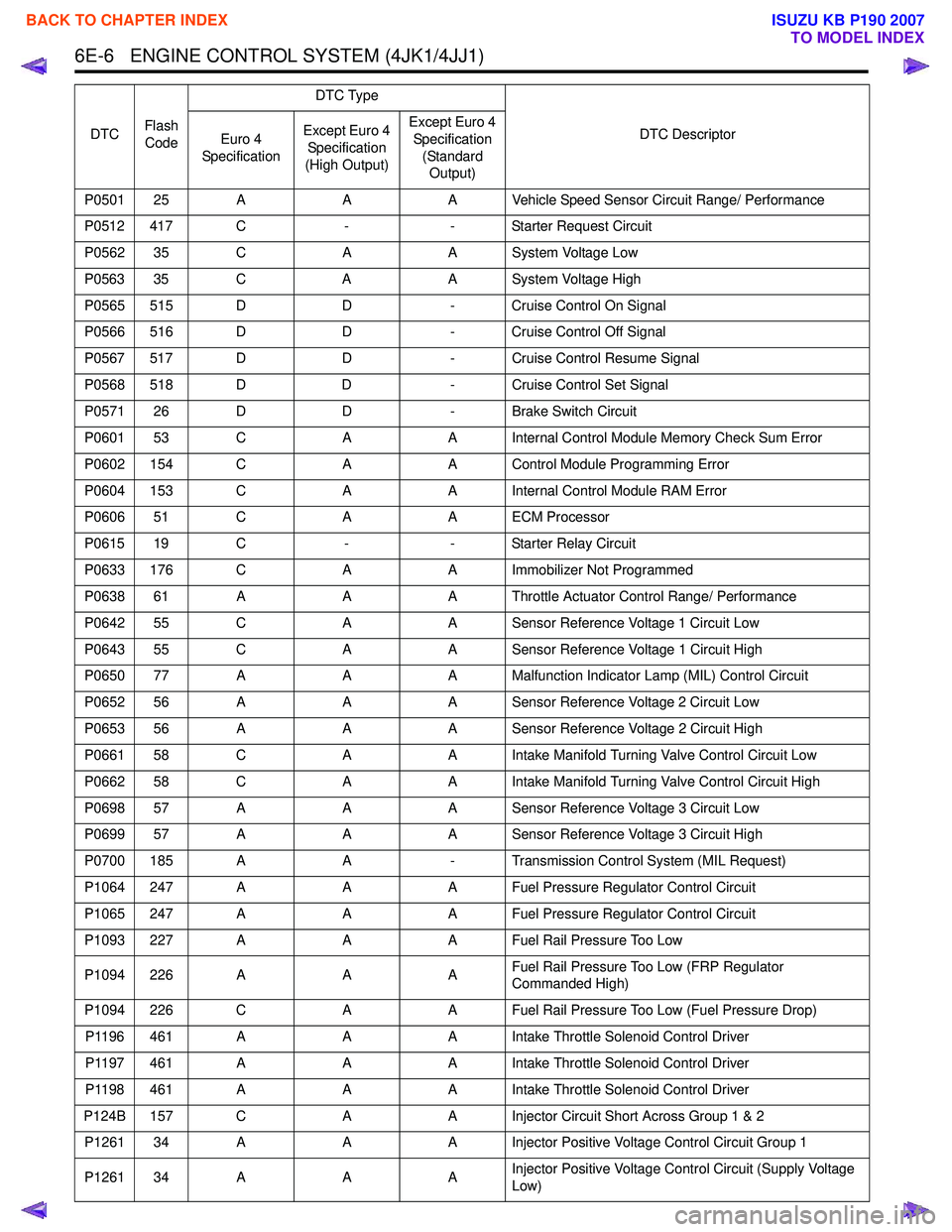
6E-6 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1)
P0501 25 AAA Vehicle Speed Sensor Circuit Range/ Performance
P0512 417 C -- Starter Request Circuit
P0562 35 C AA System Voltage Low
P0563 35 C AA System Voltage High
P0565 515 D D- Cruise Control On Signal
P0566 516 D D- Cruise Control Off Signal
P0567 517 D D- Cruise Control Resume Signal
P0568 518 D D- Cruise Control Set Signal
P0571 26 D D- Brake Switch Circuit
P0601 53 C AA Internal Control Module Memory Check Sum Error
P0602 154 C AA Control Module Programming Error
P0604 153 C AA Internal Control Module RAM Error
P0606 51 C AA ECM Processor
P0615 19 C -- Starter Relay Circuit
P0633 176 C AA Immobilizer Not Programmed
P0638 61 A AA Throttle Actuator Control Range/ Performance
P0642 55 C AA Sensor Reference Voltage 1 Circuit Low
P0643 55 C AA Sensor Reference Voltage 1 Circuit High
P0650 77 A AA Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) Control Circuit
P0652 56 A AA Sensor Reference Voltage 2 Circuit Low
P0653 56 A AA Sensor Reference Voltage 2 Circuit High
P0661 58 C AA Intake Manifold Turning Valve Control Circuit Low
P0662 58 C AA Intake Manifold Turning Valve Control Circuit High
P0698 57 A AA Sensor Reference Voltage 3 Circuit Low
P0699 57 A AA Sensor Reference Voltage 3 Circuit High
P0700 185 A A- Transmission Control System (MIL Request)
P1064 247 A AA Fuel Pressure Regulator Control Circuit
P1065 247 A AA Fuel Pressure Regulator Control Circuit
P1093 227 A AA Fuel Rail Pressure Too Low
P1094 226 A AAFuel Rail Pressure Too Low (FRP Regulator
Commanded High)
P1094 226 C AA Fuel Rail Pressure Too Low (Fuel Pressure Drop)
P1196 461 A AA Intake Throttle Solenoid Control Driver
P1197 461 A AA Intake Throttle Solenoid Control Driver
P1198 461 A AA Intake Throttle Solenoid Control Driver
P124B 157 C AA Injector Circuit Short Across Group 1 & 2
P1261 34 A AA Injector Positive Voltage Control Circuit Group 1
P1261 34 A AAInjector Positive Voltage Control Circuit (Supply Voltage
Low)
DTC
Flash
Code DTC Type
DTC Descriptor
Euro 4
Specification Except Euro 4
Specification
(High Output) Except Euro 4
Specification (Standard Output)
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007