2007 ISUZU KB P190 battery replacement
[x] Cancel search: battery replacementPage 3592 of 6020

Charging System – V6 Page 6D1-1-5
• Death or injury to other people in or near the workplace area, and / or
• Death or injury to the driver / or passenger(s) of the vehicle or other people, if the vehicle has been improperly
repaired.
CAUTION defined
A CAUTION statement immediately precedes an operating procedure or maintenance practice which, if not correctly
followed, could result in damage to or destruction of equipment, or corruption of data. If a CAUTION statement is
ignored, the following consequences may occur:
• Damage to the vehicle,
• Unnecessary vehicle repairs or component replacement,
• Faulty operation or performance of any system or component being repaired,
• Damage to any system or components which depend on the proper operation of the system or component being
repaired,
• Faulty operation or performance of any systems or components which depend on the proper operation or
performance of the system or component under repair,
• Damage to fasteners, basic tools or special tools and / or
• Leakage of coolant, lubricant or other vital fluids.
NOTE defined
A NOTE statement immediately precedes or follows an operating procedure, maintenance practice or condition that
requires highlighting. A NOTE statement also emphasises necessary characteristics of a diagnostic or repair procedure.
A NOTE statement is designed to:
• Clarify a procedure,
• Present additional information for accomplishing a procedure,
• Give insight into the reasons for performing a procedure in the recommended manner, and / or
• Present information that gives the technician the benefit of past experience in accomplishing a procedure with
greater ease.
1.3 System Operation
Operation
W ith the ignition switch in the ON position and the engine at rest, current is supplied via the regulator to generator
connector E-4 pin 1 and to the engine control module ECM connector E-60 pin 43. This initiates current flow (within the
regulator) from the generator connection P-9, to the brushes and rotor winding, to ‘excite’ the circuit.
The current in the rotor winding creates magnetic fields between adjacent rotor poles.
W ith the engine running, the rotor spins, the stator windings cut through this field and induce voltage. As the engine
speed is increased, this induced voltage increases. Current then flows through the three-phase diode bridge in the
rectifier to convert the AC voltage to DC. This is supplied to the generator connector P-9 output and then to the battery
terminal via fuse SBF1.
The regulator monitors the voltage to the battery. W hen this voltage reaches approximately 14.5 V, the regulator opens
the circuit through the rotor winding, causing the generator output voltage to drop. W hen the regulator senses a voltage
below a preset voltage, the regulator closes the circuit through the rotor winding and voltage to the battery again
increases. This cycle repeats very rapidly.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3643 of 6020

Battery Page 6D1-3–3
1 General Information
The vehicle is fitted with a 12 V battery located in the front right-hand corner of the engine compartment. The battery
provides:
• power for cranking the engine,
• power for a limited time when the electrical load exceeds the generator output,
• power for the accessories when the engine is not running, and
• a voltage stabilising load for the electrical system.
1.1 WARNING, CAUTION and NOTES
This Section contains various W ARNINGS, CAUTIONS and NOTE statements that you must observe carefully to reduce
the risk of death or injury during service, repair procedures or vehicle operation. Incorrect service or repair procedures
may damage the vehicle or cause operational faults. W ARNINGS, CAUTION and NOTE statements are not exhaustive.
HOLDEN LTD can not possibly warn of all the potentially hazardous consequences of failure to follow these instructions.
Definition of WARNING, CAUTION and NOTE Statements
Diagnosis and repair procedures in this Section contain both general and specific W ARNING, CAUTION and NOTE
statements. HOLDEN LTD is dedicated to the presentation of service information that helps the technician to diagnose
and repair the systems necessary for proper operation of the vehicle. Certain procedures may present a hazard to the
technician if they are not followed in the recommended manner. W ARNING, CAUTION and NOTE statements are
designed to help prevent these hazards from occurring, but not all hazards can be foreseen.
WARNING defined
A W ARNING statement immediately precedes an operating procedure or maintenance practice which, if not correctly
followed, could result in death or injury. A W ARNING statement alerts you to take necessary action or not to take a
prohibited action. If a W ARNING statement is ignored, the following consequences may occur:
• Death or injury to the technician or other personnel working on the vehicle,
• Death or injury to other people in or near the workplace area, and / or
• Death or injury to the driver / or passenger(s) of the vehicle or other people, if the vehicle has been improperly
repaired.
CAUTION defined
A CAUTION statement immediately precedes an operating procedure or maintenance practice which, if not correctly
followed, could result in damage to or destruction of equipment, or corruption of data. If a CAUTION statement is ignored,
the following consequences may occur:
• Damage to the vehicle,
• Unnecessary vehicle repairs or component replacement,
• Faulty operation or performance of any system or component being repaired,
• Damage to any system or components which depend on the proper operation of the system or component being
repaired,
• Faulty operation or performance of any systems or components which depend on the proper operation or
performance of the system or component under repair,
• Damage to fasteners, basic tools or special tools and / or
• Leakage of coolant, lubricant or other vital fluids.
NOTE defined
A NOTE statement immediately precedes or follows an operating procedure, maintenance practice or condition that
requires highlighting. A NOTE statement also emphasises necessary characteristics of a diagnostic or repair procedure.
A NOTE statement is designed to:
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3644 of 6020
Battery Page 6D1-3–4
• Clarify a procedure,
• Present additional information for accomplishing a procedure,
• Give insight into the reasons for performing a procedure in the recommended manner, and / or
Present information that gives the technician the benefit of past experience in accomplishing a procedure with greater
ease.
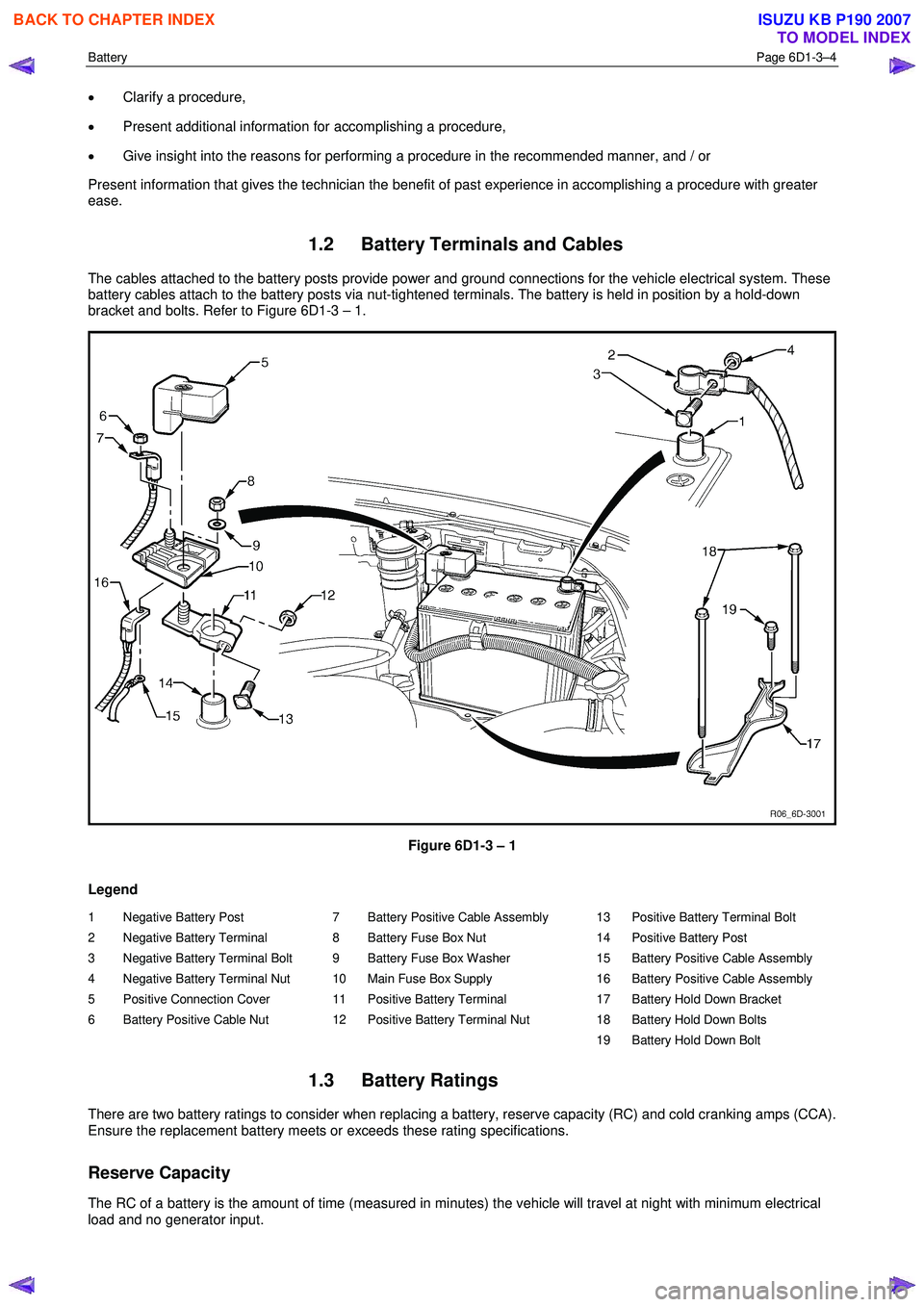
1.2 Battery Terminals and Cables
The cables attached to the battery posts provide power and ground connections for the vehicle electrical system. These
battery cables attach to the battery posts via nut-tightened terminals. The battery is held in position by a hold-down
bracket and bolts. Refer to Figure 6D1-3 – 1.
Figure 6D1-3 – 1
Legend
1 Negative Battery Post
2 Negative Battery Terminal
3 Negative Battery Terminal Bolt
4 Negative Battery Terminal Nut
5 Positive Connection Cover
6 Battery Positive Cable Nut 7 Battery Positive Cable Assembly
8 Battery Fuse Box Nut
9 Battery Fuse Box Washer
10 Main Fuse Box Supply
11 Positive Battery Terminal
12 Positive Battery Terminal Nut 13 Positive Battery Terminal Bolt
14 Positive Battery Post
15 Battery Positive Cable Assembly
16 Battery Positive Cable Assembly
17 Battery Hold Down Bracket
18 Battery Hold Down Bolts
19 Battery Hold Down Bolt
1.3 Battery Ratings
There are two battery ratings to consider when replacing a battery, reserve capacity (RC) and cold cranking amps (CCA).
Ensure the replacement battery meets or exceeds these rating specifications.
Reserve Capacity
The RC of a battery is the amount of time (measured in minutes) the vehicle will travel at night with minimum electrical
load and no generator input.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3753 of 6020

Exhaust System – V6 Page 6F – 5
Service Notes
1. Vehicles fitted with catalytic converters should not be operated with leaded petrol. Lead will contaminate
the ceramic monolith.
2. Do not drop the catalytic converter as it will damage the ceramic monolith.
3. Replace the catalytic converter if it is damaged.
4. Do not allow water, oil or fuel to enter the converter as the ceramic monolith will be contaminated.
5. Do not use engine and/or fuel additives unless approved by General Motors. Many additives contain phosphorous that will contaminate the ceramic monolith.
6. The vehicle must not be started by pushing or towing, as unburned fuel could reach the catalytic converter and destroy the ceramic monolith. Always use jumper leads to start a vehicle that has a flat or
defective battery.
7. W hen carrying out a compression test, for V6 engines use Tech 2 to ensure the output control Engine Compression Test is set to enable, refer to 6A1 Engine Mechanical. This prevents fuel injection and
ignition during engine cranking.
8. Do not drive the vehicle with the engine misfiring or with any of the spark plug leads disconnected, as the catalytic converter will overheat.
9. Do not coast downhill with the engine misfiring or with any of the spark plug leads disconnected.
10. The catalytic converter is serviceable as part of the front exhaust assembly only. Refer to the service operations in this section for details of front exhaust pipe assembly removal and reinstallation.
11. The exhaust flange gaskets must be replaced whenever a new exhaust pipe, muffler or catalytic converter is installed.
1.3 WARNING, CAUTION and NOTES
This Section contains various W ARNINGS, CAUTIONS and NOTE statements that you must observe carefully to reduce
the risk of death or injury during service, repair procedures or vehicle operation. Incorrect service or repair procedures
may damage the vehicle or cause operational faults. W ARNINGS, CAUTION and NOTE statements are not exhaustive.
HOLDEN LTD can not possibly warn of all the potentially hazardous consequences of failure to follow these instructions.
1.1 Definition of WARNING, CAUTION and NOTE Statements
Diagnosis and repair procedures in this Section contain both general and specific W ARNING, CAUTION and NOTE
statements. HOLDEN LTD is dedicated to the presentation of service information that helps the technician to diagnose
and repair the systems necessary for proper operation of the vehicle. Certain procedures may present a hazard to the
technician if they are not followed in the recommended manner. W ARNING, CAUTION and NOTE statements are
designed to help prevent these hazards from occurring, but not all hazards can be foreseen.
WARNING defined
A W ARNING statement immediately precedes an operating procedure or maintenance practice which, if not correctly
followed, could result in death or injury. A W ARNING statement alerts you to take necessary action or not to take a
prohibited action. If a W ARNING statement is ignored, the following consequences may occur:
• Death or injury to the technician or other personnel working on the vehicle,
• Death or injury to other people in or near the workplace area, and / or
• Death or injury to the driver / or passenger(s) of the vehicle or other people, if the vehicle has been improperly
repaired.
CAUTION defined
A CAUTION statement immediately precedes an operating procedure or maintenance practice which, if not correctly
followed, could result in damage to or destruction of equipment, or corruption of data. If a CAUTION statement is
ignored, the following consequences may occur:
• Damage to the vehicle,
• Unnecessary vehicle repairs or component replacement,
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3814 of 6020

Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–28
7 Ensure that all wiring harness connectors are fitted correctly and secure.
8 W hen steam or pressure cleaning vehicle components, such as engines, transmissions, etc., do not direct the cleaning nozzle at any system electrical wiring harness connectors or components.
9 Do not clear any DTCs unless instructed.
10 The fault must be present when using the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Diagnostic Tables. Otherwise, misdiagnosis or replacement of good parts may occur.
11 Do not touch any electronic control module connector pins or soldered components on the circuit board. This is required to avoid the possibility of electrostatic discharge damage.
12 Use only the test equipment specified in the diagnostic tables, as other test equipment may give incorrect results or damage good components.
13 Electronic control modules are designed to withstand normal current draws associated with vehicle operation. However, the following fault conditions or incorrect test procedure may overload internal control module circuits and
irreparably damage the control module:
• A short to voltage fault condition in any of the control module low reference circuits may cause internal and/or
sensor damage. Therefore, any short to voltage fault condition in the control module low reference circuits
must be rectified before replacing a faulty component.
• A short to ground fault condition in any of the control module 5 volts reference circuits may cause internal
control module and/or sensor damage. Therefore, any short to ground fault condition in the control module 5
volt reference circuits must be rectified before replacing a faulty component.
• W hen using a test light to test an electrical circuit, do not use any of the control module low reference circuits
or 5 volts reference circuits as a reference point. Otherwise, excessive current draw from the test light may
damage the control module.
14 Disregard DTCs that set while performing the following diagnostic Steps:
• Using the Tech 2 output control function, or
• Disconnecting a control module system sensor connector then switching the ignition ON.
15 After completing the required diagnostics and service operations, road test the vehicle to ensure correct system operation.
4.4 Preliminary Checks
The Preliminary Checks is a set of visual and physical checks or inspections that may quickly identify a control module
system fault condition:
1 Refer to relevant Service Techlines for information regarding the fault condition.
2 Ensure that the battery is fully charged.
3 Inspect the battery connections for corrosion or a loose terminal.
4 Ensure that all relevant control module system related fuses are serviceable.
5 Inspect for incorrect aftermarket theft deterrent devices, lights or mobile phone installation.
6 Ensure that there is no speaker magnet positioned too close to any electronic module that contains relays.
7 Inspect the system wiring harness for proper connections, pinches or cuts.
8 Ensure that all control module related electrical wiring connectors are fitted correctly.
9 Inspect the control module ground connections for corrosion, loose terminal or incorrect position.
10 Ensure that the resistance between the control module housing and the battery ground cable is less than 0.5 ohms.
11 Check that the control module and its mounting bracket is secure.
12 Check all control module related components for correct installation.
13 Check the control module and related wiring harness routing to ensure that no rubbing or cutting of the wiring harness by sharp body components can occur.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3834 of 6020
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–48
Diagnostic Aids
• Verify if the brake pedal position sensor is
adjusted properly, refer to 8B Cruise
Control.
• Test drive the vehicle if a switch or circuit
condition cannot be located. An
intermittent condition may be duplicated
during a test drive.
• Application of the brake pedal while
accelerating may cause this DTC to set.
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
2 Checks the stop lamp switch is serviceable.
4 Checks if there is a stop lamp switch signal to the TCM.
DTC P0719 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2 Refer to
4.7 Diagnostic System Check
2 1 Connect Tech 2 to the DLC.
2 On Tech 2 select: Engine / V6 Engine / Data Display / Cruise / Traction Data.
3 Turn on the ignition, with the engine off.
NOTE
Ensure the brake pedal is in the rest position.
Does the Stop Lamp Pedal Switch parameter indicate Inactive? Check for an
intermittent fault in
the circuit, refer to
8A Electrical-Body and Chassis Go to Step 3
3 Test the stop lamp switch assembly, refer to 8B Cruise Control.
Is the stop lamp switch assembly serviceable? Go to Step 4 Replace the stop
lamp switch
assembly.
4 1 Disconnect connector C-96 from the TCM.
2 Using a multimeter set to measure voltage, probe between harness connector C-96 pin 42 and a known ground.
NOTE
Ensure the brake pedal is in the rest position.
Does the multimeter display battery voltage? Repair or replace
affected circuit
Go to Step 6 Go to Step 5
5
Replace the TCM, refer to 7C4 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E –
On-vehicle Service.
Did you complete the replacement? Go to Step 6
—
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3841 of 6020
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–55
Step Action Yes No
6 1 Disconnect connector C-96 from the TCM.
2 Test circuits speed sensor circuits (between C-96 pin 16 and E-44 pin 2; C-96 pin 41 and E-44 pin 1) for the following
conditions:
• Short to ground,
• Short to battery,
• Open circuit, and
• Short together.
Did you find and correct the condition? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
7 Replace the vehicle speed sensor, refer to 7C4 Automatic
Transmission – 4L60E – On-vehicle Service.
Did you complete the replacement? Go to Step 9 —
8 Replace the TCM, refer to 7C4 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E –
On-vehicle Service.
Did you complete the replacement? Go to Step 9 —
9 Perform the following procedure to verify the repair:
1 On Tech 2 select: Diagnostic Trouble Codes / Clear Engine & Transmission
DTCs.
2 Follow the instructions on Tech 2 and clear any DTCs.
3 On Tech 2 select: Data Display / Transmission Data.
4 Operate the vehicle ensuring the transmission output speed drop is less than 500 r.p.m. for 2 seconds and output speed is
greater than 500 r.p.m.
5 On Tech 2 select:
Diagnostic Trouble Codes / Read DTC Information.
Has DTC P0723 set? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 10
10 On Tech 2 select:
Diagnostic Trouble Codes / Read DTC Information.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs you have not diagnosed? Refer to
4.8 Diagnostic Trouble Code List System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
4.17 DTC P0724 – Brake Switch Circuit Low
Input (Stuck Off)
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports DTC P0724 Brake Switch Circuit Low Voltage.
Circuit Description
The transmission control module receives a direct input from the stop lamp switch assembly. When the brake pedal is
pressed, 12 V is supplied to the TCM through connector C-96 pin 42.
When the TCM detects an open or short to ground on the stop lamp signal circuit during stopping then DTC P0724 sets.
DTC P0724 is a type C DTC.
Refer to 2 W iring Diagrams and Connector Chart to aid in diagnosis.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3843 of 6020
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–57
Step Action Yes No
3 Test the stop lamp switch assembly, refer to 8B Cruise Control.
Is the stop lamp switch assembly serviceable? Go to Step 4 Replace the stop
lamp switch assembly
4 1 Disconnect connector C-96 from the TCM.
2 Using a multimeter set to measure voltage, probe between harness connector C-96 pin 42 and a known ground.
3 Press the brake pedal.
Does the multimeter display battery voltage? Go to Step 5 Repair or replace
affected circuit
Go to Step 6
5 Replace the TCM, refer to 7C4 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E –
On-vehicle Servicing.
Did you complete the replacement? Go to Step 6 —
6 Perform the following procedure to verify the repair:
1 On Tech 2 select: Diagnostic Trouble Codes / Clear Engine & Transmission
DTCs.
2 Follow the instructions on Tech 2 and clear any DTCs.
3 Operate the vehicle under the following conditions:
• Turn on the ignition, with the engine off for at least
2 seconds.
• Start the vehicle and idle for 5 seconds.
• Drive in D4 from 0 – 60 km/h then brake, eight times in one
ignition cycle.
4 On Tech 2 select:
Diagnostic Trouble Codes / Read DTC Information.
Has DTC P0724 set? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 7
7 On Tech 2 select:
Diagnostic Trouble Codes / Read DTC Information.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs you have not diagnosed? Refer to
4.8 Diagnostic Trouble Code List System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the
system for correct operation.
4.18 DTC P0741 – Torque Converter Clutch
System – Stuck Off
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports DTC P0741 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) System - Stuck Off.
Circuit Description
The torque converter clutch (TCC) solenoid valve is a normally-open exhaust valve that is used with the torque converter
clutch pulse width modulation (TCC PWM) solenoid valve to control fluid acting on the converter clutch apply valve. The
TCC solenoid valve attaches to the transmission case assembly extending into the pump cover. W hen grounded by the
transmission control module (TCM), the TCC solenoid valve stops converter signal oil from exhausting. This causes
converter signal oil pressure to increase and move the converter clutch apply valve against spring force and into the
apply position. In this position, release fluid is open to an exhaust port and converter feed fluid fills the apply fluid circu it.
The converter feed fluid applies the TCC. When the TCM no longer provides a ground path, the TCC solenoid valve de-
energizes and apply fluid exhausts, releasing the TCC.
When the TCM detects high torque converter slip when the TCC is commanded off, then DTC P0741 sets. DTC P0741 is
a type B DTC.
Refer to 2 W iring Diagrams and Connector Chart to aid in diagnosis.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007