2007 ISUZU KB P190 low oil pressure
[x] Cancel search: low oil pressurePage 2513 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–34
2.10 Lower Engine Noise, Regardless of
Engine Speed
NOTE
A cold piston knock which disappears in
approximately 1.5 minutes from start up should
be considered acceptable. A cold engine knock
usually disappears when the specific cylinder’s
secondary ignition circuit is grounded out during
diagnosis.
A light rattle/tapping noise may indicate a valve train/upper engine concern, while a low rumble/knocking may indicate a
crankshaft, piston or lower engine concern.
Cause Correction
Low oil pressure. 1 Perform an oil pressure test, refer to 2.19
Engine Oil Pressure Diagnosis.
2 Repair or replace the engine oil pump as required, refer to 3.17 Oil Pump Assembly.
W orn accessory drive components.
Abnormalities such as severe cracking, bumps, stretching
or missing areas on an accessory drive belt and/or
misalignment of accessory drive system components. Inspect the accessory drive system, repair or replace
components as required, refer to 3.5 Accessory
Drive Belt.
Loose or damaged crankshaft balancer and pulley
assembly. Repair or replace the crankshaft balancer and pulley
assembly as required, refer to 3.13 Crankshaft Balancer
Assembly.
Detonation or spark knock. Confirm the correct operation of the ignition system, refer to
6C1-2 Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics.
Loose torque converter bolts. Inspect and tighten the torque converter bolts to the correct
torque specification, refer to 7C4 Automatic Transmission –
4L60E – On-vehicle Servicing.
Loose or damaged flexplate. Repair or replace the flexplate as required, refer to 4.3
Flexplate Assembly.
Oil pump suction pipe loose, damaged or restricted. Clean, inspect and repair/replace the oil pump suction pipe as required, refer to 4.2 Oil Pan and Oil Pump Suction
Pipe Assembly.
Excessive piston-to-cylinder bore clearance. Inspect the piston and cylinder bore and repair/replace
components as required, refer to 4.5 Pistons, Pins,
Rings, Connecting Rods and Big-end Bearings and 4.7
Cylinder Block.
Excessive connecting rod bearing clearance. Inspect the connecting rod, crankshaft and bearings and
repair/replace components as required, refer to 4.5
Pistons, Pins, Rings, Connecting Rods and Big-
end Bearings and 4.6 Crankshaft and Main Bearings.
Excessive piston pin to bore clearance. Inspect the pistons and pins and repair/replace components
as required, refer to 4.5 Pistons, Pins, Rings,
Connecting Rods and Big-end Bearings.
Excessive crankshaft main bearing clearance. Inspect the crankshaft, cylinder block journals, main
bearings and main bearing caps and repair/replace
components as required, refer to 4.6 Crankshaft
and Main Bearings and 4.7Cylinder Block.
Incorrect piston, pin and connecting rod installation.
Pistons must be installed with the mark or dimple facing the
front of the engine. Piston pins must be centred in the
piston pin bore. Confirm the pistons, pins and connecting rods are installed
correctly and repair if required, refer to 4.5 Pistons, Pins,
Rings, Connecting Rods and Big-end Bearings.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2514 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–35
2.11 Engine Noise Under Load
NOTE
A cold piston knock which disappears in
approximately 1.5 minutes from start up, should
be considered acceptable. A cold engine knock
usually disappears when the specific cylinder’s
secondary ignition circuit is grounded out during
diagnosis.
A light rattle/tapping noise may indicate a valve train/upper engine concern, while a low rumble/knocking may indicate a
crankshaft, piston or lower engine concern.
Cause Correction
Low oil pressure. 1 Perform an oil pressure test, refer to 2.19
Engine Oil Pressure Diagnosis.
2 Repair or replace the engine oil pump as required, refer to 3.17 Oil Pump Assembly.
Detonation or spark knock. Confirm the correct operation of the ignition system, refer to
6C1-2 Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics.
Loose torque converter bolts. Inspect and tighten the torque converter bolts to the correct
torque specification, refer to 7C1 Automatic – 4L60E –
General Information – 4L60E – General Information.
Cracked flexplate. Replace the flywheel/flex-plate as required, refer to 4.3
Flexplate Assembly.
Excessive connecting rod bearing clearance. Inspect the connecting rod, crankshaft and bearings and
repair/replace components as required, refer to 4.5
Pistons, Pins, Rings, Connecting Rods and Big-
end Bearings and 4.6 Crankshaft and Main Bearings.
Excessive crankshaft bearing clearance Inspect the crankshaft, cylinder block journals, main
bearings and main bearing caps and repair/replace
components as required, refer to 4.6 Crankshaft
and Main Bearings and 4.7Cylinder Block.
2.12 Engine Will Not Crank – Crankshaft Will Not Rotate
Cause Correction
Seized accessory drive system component. 1 Remove the accessory drive belt, refer to 3.5
Accessory Drive Belt.
2 Rotate the crankshaft by hand at the balancer pulley or flywheel.
3 Repair or replace accessory drive system components as required.
Hydraulically locked cylinder caused by:
• coolant in cylinder,
• oil in cylinder, or
• fuel in cylinder. 1 Remove the spark plugs and check for fluid, refer to
6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service
Operations.
2 Inspect for broken head gasket/s.
3 Inspect for cracked engine block or cylinder head.
4 Inspect for sticking fuel injector.
5 Repair or replace components as required.
Seized torque converter. 1 Remove the torque converter bolts, refer to 7C1
Automatic – 4L60E – General Information – 4L60E –
General Information.
2 Rotate the crankshaft by hand at the balancer pulley or flywheel.
3 Repair or replace torque converter as required.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2517 of 6020

Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–38
2.15 Engine Compression Test
A compression pressure test of the engine cylinders determines the condition of the rings, the valves and the head
gasket.
Preliminary Steps
1 Ensure the battery is fully charged.
2 Remove the spark plugs from all cylinders, refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
NOTE
DTCs will set when the fuel system or the ignition
system is disabled and the engine is cranked.
Disregard DTCs that set under this condition.
3 Disable the fuel system by removing the fuel pump relay, refer to 8A Electrical Body & Chassis.
4 Start the engine to use any residual fuel from the fuel lines.
4 Disable the ignition coils by removing fuses 34 and 35, refer to 8A Electrical Body & Chassis .
5 Using Tech 2, command the throttle plate to wide open throttle.
Engine Cylinder Compression Test
1 Install the compression tester to cylinder number 1.
2 W hile observing the compression tester reading, turn the ignition to the START position for several seconds and then allow the ignition to return to the ON position.
3 Record the highest compression reading obtained.
4 Repeat the engine compression test for each cylinder.
Test Result Evaluation
Normal engine compression pressure builds quickly and evenly to over 965 kPa. In addition, the lowest reading of an
engine cylinder should not be less than 70 percent of the highest reading. If any cylinder fails the compression test,
adding 15 ml of engine oil to the suspected cylinder may help isolate the following fault condition.
1 A fault condition in the piston rings will produce the following result:
• A low compression on the first engine cycle
• The compression tends to build-up with the succeeding engine rotation.
• The compression improves with the addition of engine oil.
2 A fault condition in an intake or exhaust valve will produce the following result:
• A low compression on the first engine cycle
• The compression does not build with the succeeding engine rotation.
• The compression does not improve with the addition of engine oil.
3 A fault condition in the cylinder head gasket will produce the following result:
• A low compression on the first engine cycle
• The compression does not build with the succeeding engine rotation.
• The compression does not improve with the addition of engine oil.
• The suspected cylinders are positioned adjacent to each other.
• The engine oil may be contaminated with engine coolant.
• The engine coolant may be contaminated with engine oil.
Once the fault has been identified, refer to the relevant service procedure and reinstall the removed components.
Using Tech 2, clear DTCs.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2518 of 6020

Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–39
2.16 Cylinder Leakage Test
A leakage test may be performed to measure cylinder/combustion chamber leakage. High cylinder leakage may indicate
one or more of the following:
• worn or burnt valves,
• broken valve springs,
• stuck valve lifters,
• incorrect valve lash/adjustment,
• damaged piston,
• worn piston rings,
• worn or scored cylinder bore,
• damaged cylinder head gasket,
• cracked or damaged cylinder head, or
• cracked or damaged engine block.
1 Disconnect the battery ground negative cable.
2 Remove the spark plugs from all cylinders, refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
3 Rotate the crankshaft to place the piston in the cylinder being tested at top dead centre (TDC) of the compression stroke.
4 Install a commercially available cylinder head leak down tester into the spark plug hole.
NOTE
If required, hold the crankshaft balancer bolt to
prevent the engine from rotating.
5 Apply shop air pressure to the cylinder head leak down tester and adjust according to the manufacturers instructions.
6 Record the cylinder leakage value. Cylinder leakage that exceeds 25 percent is considered excessive and may require component service. In excessive leakage situations, inspect for the following conditions:
• air leakage sounds at the throttle body or air inlet duct that may indicate a worn or burnt intake valve or a
broken valve spring,
• air leakage sounds at the exhaust system tailpipe that may indicate a worn or burnt exhaust valve or a broken
valve spring,
• air leakage sounds from the crankcase, oil level indicator tube, or oil fill tube that may indicate worn piston
rings, a damaged piston, a worn or scored cylinder bore, a damaged engine block or a damaged cylinder
head, or
• air bubbles in the cooling system may indicate a damaged cylinder head or a damaged cylinder head gasket.
7 Perform the leakage test on the remaining cylinders and record the values.
2.17 Engine Oil Consumption Diagnosis
Definition
Excessive oil consumption (not due to leaks) is the use of 3 litres or more of engine oil within 10,000 kilometres. Prior to
performing oil pressure testing, a preliminary inspection of the vehicle should be performed. During the preliminary visual
inspection, the following likely causes of excessive oil usage should be investigated.
Cause Correction
External oil leaks. Refer to 2.18 Engine Oil Leak Diagnosis.
Incorrect oil level or reading of the oil level indicator. Check for the correct oil level, refer to 3.1 Engine Oil.
Incorrect oil viscosity. Replace the engine oil, using the recommended SAE grade
of engine oil, refer to 3.1 Engine Oil.
Continuous high-speed driving or severe usage. Service vehicle more frequently, refer to 0B Lubrication and
Service.
Crankcase ventilation system restricted or malfunctioning. Repair or replace crankcase ventilation system components as required, refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2520 of 6020

Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–41
3 W ith the vehicle parked on a flat level surface, aim the black light at the suspected component/s. The dyed fluid will
appear as a yellow path leading to the oil leak source
4 Refer to Possible Causes for Engine Oil Leaks in this Section, and repair or replace components as required.
Possible Causes for Engine Oil Leaks
Common possible causes for engine oil leaks are:
• higher than recommended fluid levels,
• higher than recommended fluid pressures,
• blocked or faulty fluid filters or pressure relief valve,
• blocked or faulty engine ventilation system,
• incorrectly tightened or damaged fasteners,
• cracked or porous components,
• incorrect gaskets or sealants used,
• incorrect gaskets or sealant installation,
• damaged or worn gaskets or seals, and
• damaged or worn sealing surfaces.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2521 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–42
2.19 Engine Oil Pressure Diagnosis
If the engine oil pressure is below the specified value, inspect the engine and components for the following:
• loose oil filter adaptor bolts,
• faulty oil filter adaptor seals,
• worn or faulty oil pump,
• loose oil pump bolts,
• loose, blocked or damaged oil pump suction pipe,
• faulty oil pump suction pipe seal,
• faulty oil pump pressure relief valve,
• faulty or incorrectly installed oil gallery plugs,
• excessive bearing clearance in one of the following:
• connecting rods big end/s,
• crankshaft main journal/s,
• camshaft/s,
• camshaft sprocket/s, and
• cracked, porous or restricted oil galleries, or broken lash adjuster/s.
2.20 Accessory Drive Belt Diagnosis
Tension Check
NOTE
An accessory drive belt that squeaks when the
engine is started or stopped is considered normal
and has no effect on drive belt durability.
1 Start the engine and switch off the air-conditioning system. Allow engine to run until normal operating temperature has been reached.
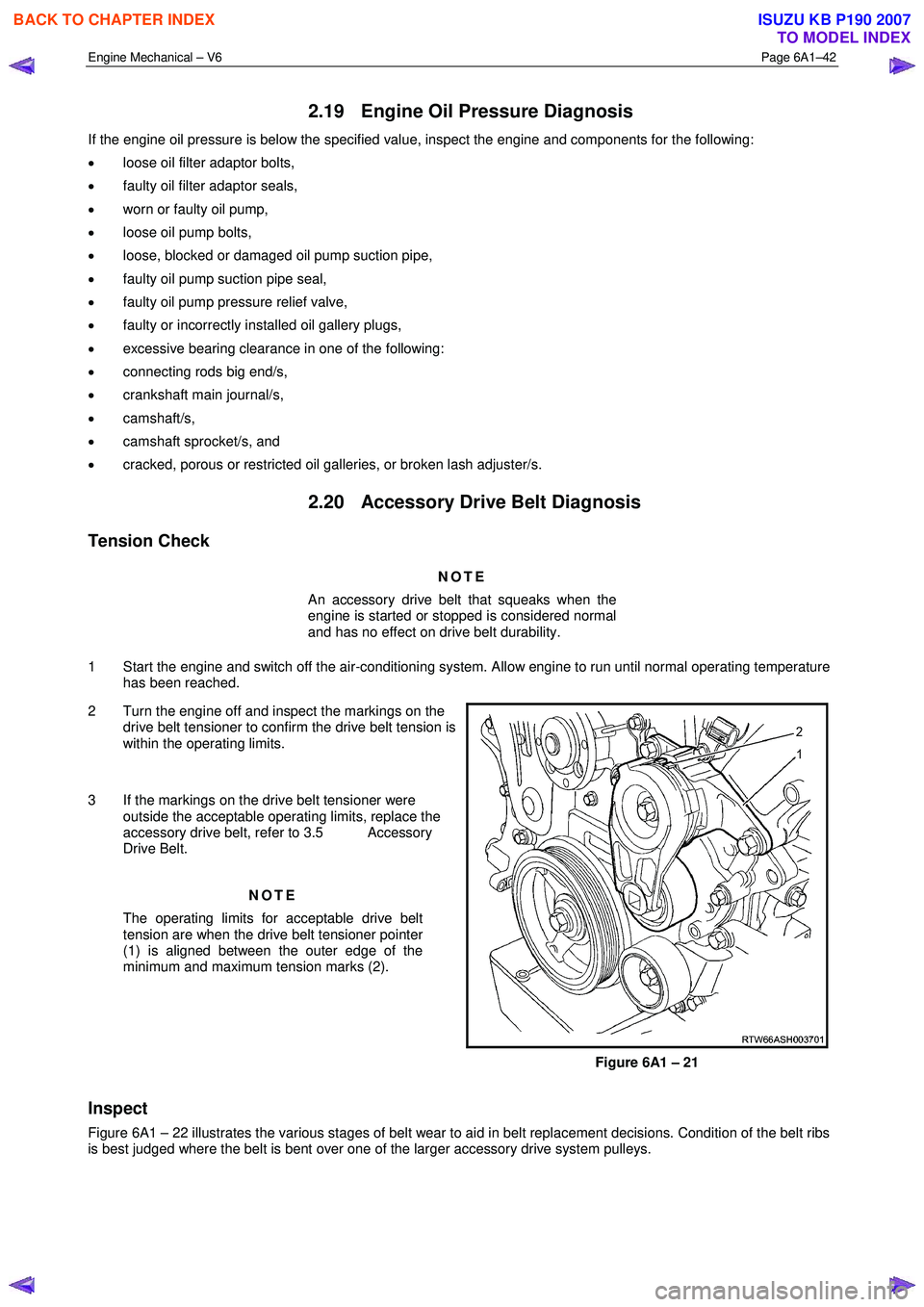
2 Turn the engine off and inspect the markings on the drive belt tensioner to confirm the drive belt tension is
within the operating limits.
3 If the markings on the drive belt tensioner were outside the acceptable operating limits, replace the
accessory drive belt, refer to 3.5 Accessory
Drive Belt.
NOTE
The operating limits for acceptable drive belt
tension are when the drive belt tensioner pointer
(1) is aligned between the outer edge of the
minimum and maximum tension marks (2).
Figure 6A1 – 21
Inspect
Figure 6A1 – 22 illustrates the various stages of belt wear to aid in belt replacement decisions. Condition of the belt ribs
is best judged where the belt is bent over one of the larger accessory drive system pulleys.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2534 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–55
Figure 6A1 – 24
6 Once the oil has completely drained, reinstall the drain plug and tighten to the correct torque specification.
Oil pan drain plug
torque specification ............................................25.0 Nm
7 Replace the oil filter, refer to 3.2 Oil Filter.
8 Lower the vehicle to the ground and fill with the specified amount of SAE 5W 30 lubricant.
Engine Oil Capacity:
With Oil Filter Change ........................................6.5 litres
9 Install the oil fill cap.
10 Start the engine and check for leaks.
Pressure Check
1 Run the engine to bring it to normal operating temperature.
2 Park the vehicle on a level surface. A vehicle not level will affect the accuracy of the level reading.
3 Stop the engine and wait 5 to 10 minutes to allow the oil to drain back into the oil pan.
4 Check the oil level and top up with the recommended engine oil as required, refer to Check, in this Section.
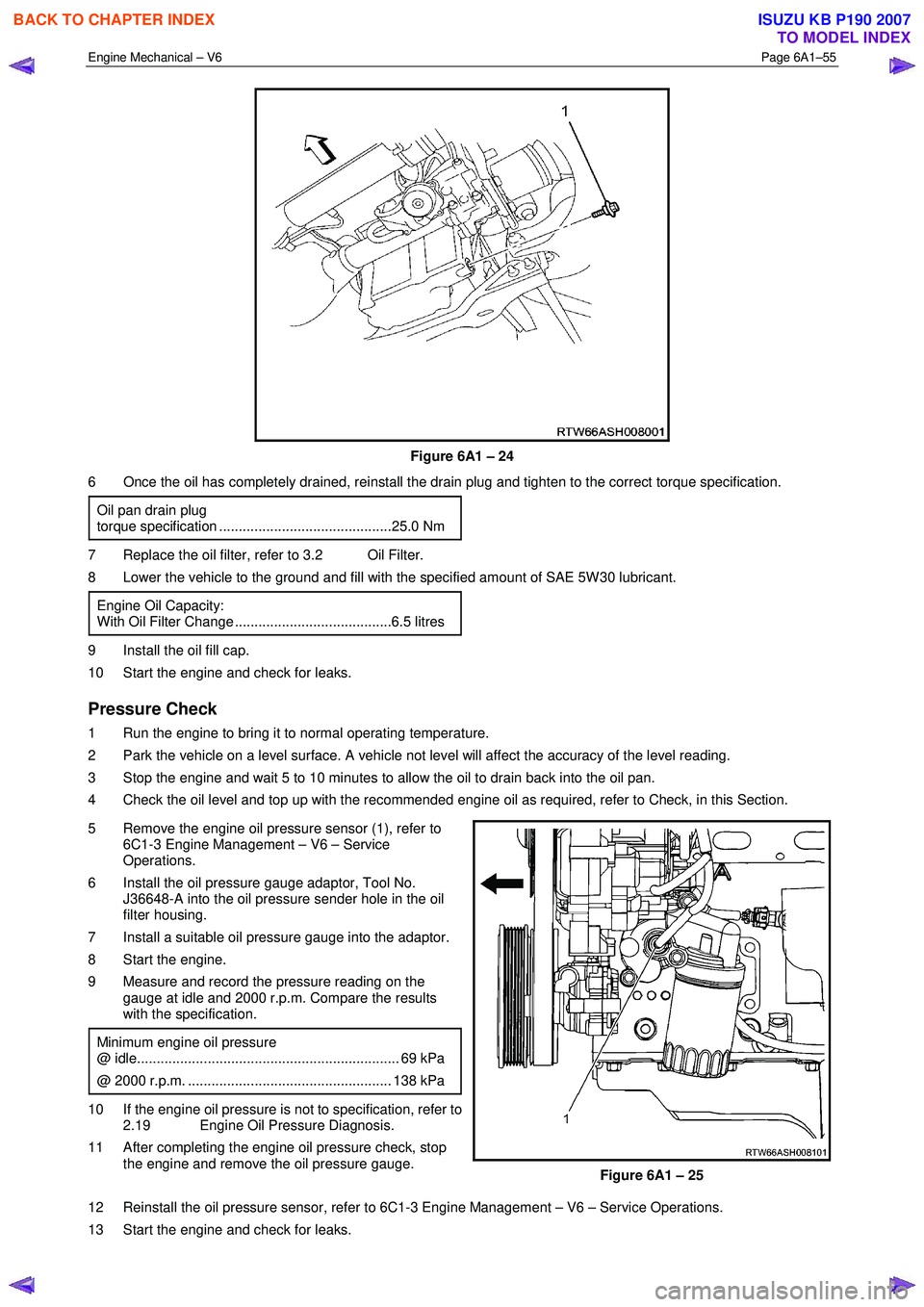
5 Remove the engine oil pressure sensor (1), refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service
Operations.
6 Install the oil pressure gauge adaptor, Tool No. J36648-A into the oil pressure sender hole in the oil
filter housing.
7 Install a suitable oil pressure gauge into the adaptor.
8 Start the engine.
9 Measure and record the pressure reading on the gauge at idle and 2000 r.p.m. Compare the results
with the specification.
Minimum engine oil pressure
@ idle................................................................... 69 kPa
@ 2000 r.p.m. .................................................... 138 kPa
10 If the engine oil pressure is not to specification, refer to 2.19 Engine Oil Pressure Diagnosis.
11 After completing the engine oil pressure check, stop the engine and remove the oil pressure gauge.
Figure 6A1 – 25
12 Reinstall the oil pressure sensor, refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
13 Start the engine and check for leaks.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2536 of 6020
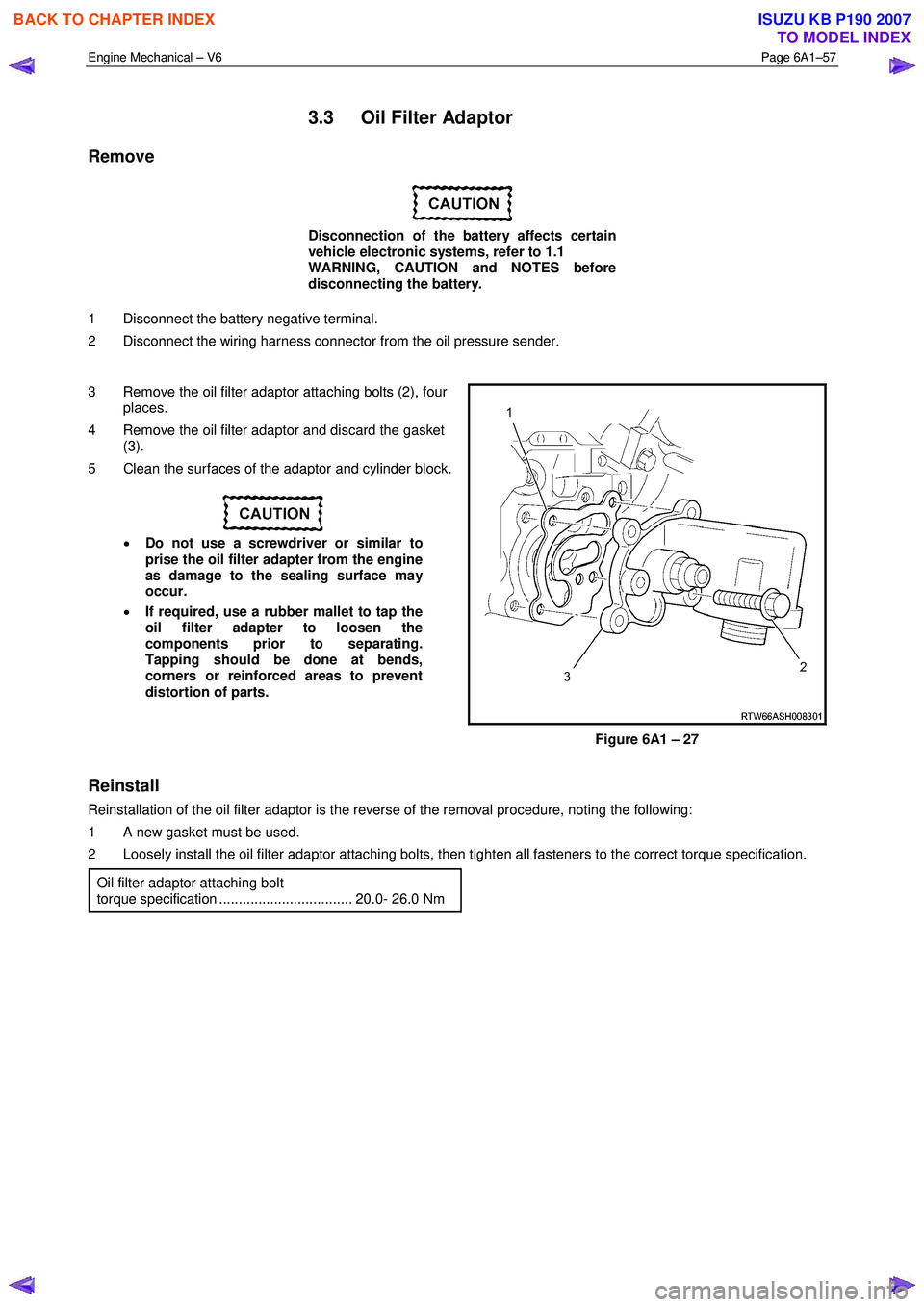
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–57
3.3 Oil Filter Adaptor
Remove
Disconnection of the battery affects certain
vehicle electronic systems, refer to 1.1
WARNING, CAUTION and NOTES before
disconnecting the battery.
1 Disconnect the battery negative terminal.
2 Disconnect the wiring harness connector from the oil pressure sender.
3 Remove the oil filter adaptor attaching bolts (2), four places.
4 Remove the oil filter adaptor and discard the gasket (3).
5 Clean the surfaces of the adaptor and cylinder block.
• Do not use a screwdriver or similar to
prise the oil filter adapter from the engine
as damage to the sealing surface may
occur.
• If required, use a rubber mallet to tap the
oil filter adapter to loosen the
components prior to separating.
Tapping should be done at bends,
corners or reinforced areas to prevent
distortion of parts.
Figure 6A1 – 27
Reinstall
Reinstallation of the oil filter adaptor is the reverse of the removal procedure, noting the following:
1 A new gasket must be used.
2 Loosely install the oil filter adaptor attaching bolts, then tighten all fasteners to the correct torque specification.
Oil filter adaptor attaching bolt
torque specification .................................. 20.0- 26.0 Nm
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007