2007 ISUZU KB P190 brakes
[x] Cancel search: brakesPage 4171 of 6020

7A4–36 UNIT REPAIR (AW30–40LE)
Diaassembly, Inspection and
Reassembly of minor Components
NOTE: The instructions here are organized so that you
work on only one component group at a time.
This will help avoid confusion from similar-looking parts
of different subassemblies being on your workbench at
the same time.
The component groups are inspected and repaired from
the converter housing side.
As much as possible, complete the inspection, repair
and reassembly before proceeding to the next
component group. If a component group cannot be
reassembled because parts are being ordered, be sure
to keep all parts of that group in separate container
while proceeding with disassembly, inspection, repair
and reassembly of other component groups.
Recommended ATF type DEXRON III.
General Cleaning Notes:
1. All disassembled parts should be washed clean and any fluid passages and holes should be blown
through with compressed air.
2. When using compressed air to dry parts, always aim away from yourself to prevent accidentally spraying
automatic transmission fluid in your face.
3. The recommended automatic transmission fluid should be used for cleaning.
Parts Arrangement:
1. After cleaning, the parts should be arranged inproper order to allow performing inspection, repairs,
and reassembly with efficiency.
2. When disassembling a valve body, be sure to keep each valve together with the corresponding spring.
3. New brakes and clutches that are to be used for replacement must be soaked in transmission fluid
for at least thirty minutes before assembly.
General Assembly:
1. All oil seal rings, clutch discs, clutch plates, rotating parts, and sliding surfaces should be coated with
transmission fluid prior to reassembly.
2. All gaskets and rubber O-ring should be replaced.
3. Make sure that the ends of a snap ring are not aligned with one of the cutouts and are installed in
the groove correctly.
4. If a worn bushing is to be replaced, the subassembly containing that bushing must be
replaced.
5. Check thrust bearings and races for wear or damage. Replace if necessary.
6. Use petroleum jelly or vaseline to keep parts in place.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4242 of 6020
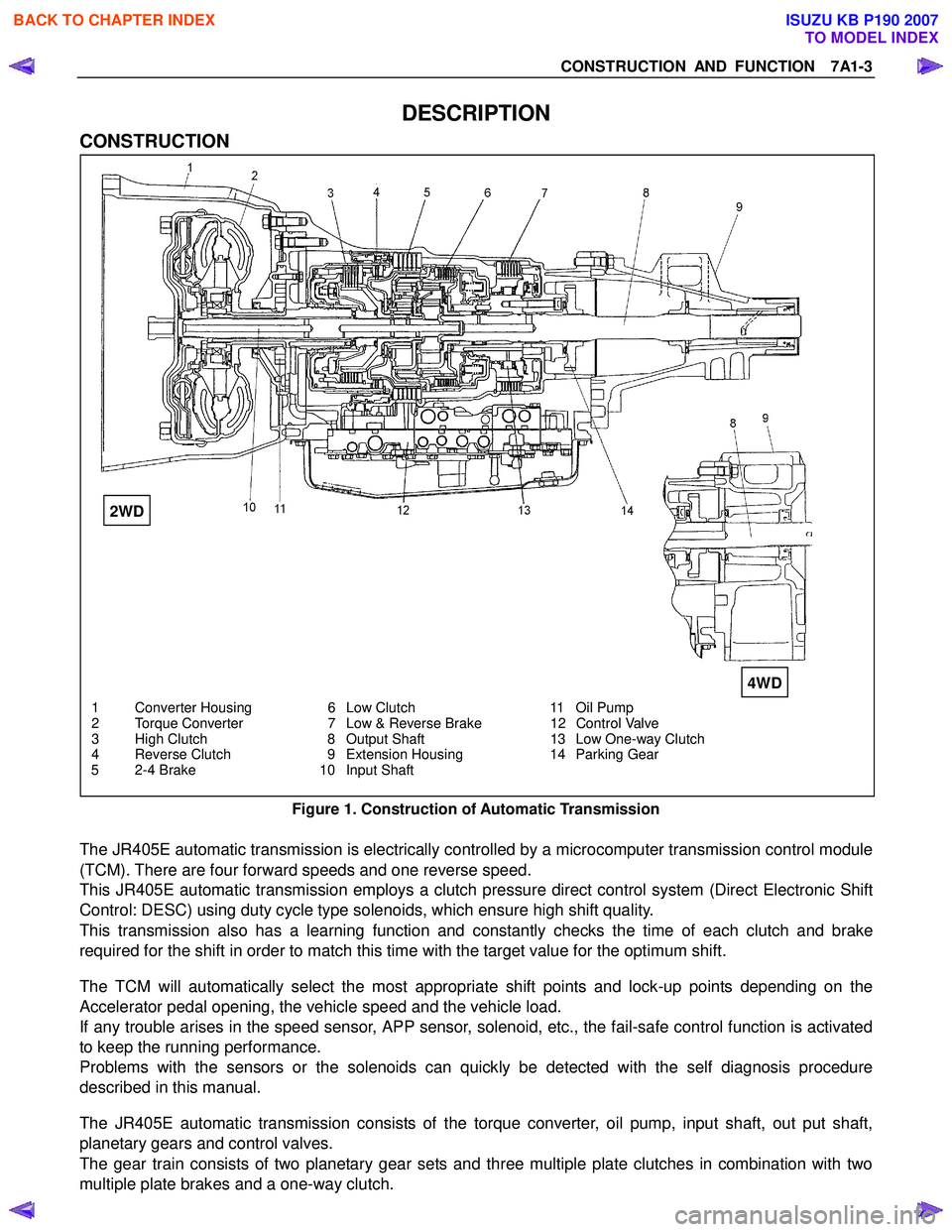
CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION 7A1-3
DESCRIPTION
CONSTRUCTION
1 Converter Housing 6 Low Clutch 11 Oil Pump
2 Torque Converter 7 Low & Reverse Brake 12 Control Valve
3 High Clutch 8 Output Shaft 13 Low One-way Clutch
4 Reverse Clutch 9 Extension Housing 14 Parking Gear
5 2-4 Brake 10 Input Shaft
Figure 1. Construction of Automatic Transmission
The JR405E automatic transmission is electrically controlled by a microcomputer transmission control module
(TCM). There are four forward speeds and one reverse speed.
This JR405E automatic transmission employs a clutch pressure direct control system (Direct Electronic Shift
Control: DESC) using duty cycle type solenoids, which ensure high shift quality.
This transmission also has a learning function and constantly checks the time of each clutch and brake
required for the shift in order to match this time with the target value for the optimum shift.
The TCM will automatically select the most appropriate shift points and lock-up points depending on the
Accelerator pedal opening, the vehicle speed and the vehicle load.
If any trouble arises in the speed sensor, APP sensor, solenoid, etc., the fail-safe control function is activated
to keep the running performance.
Problems with the sensors or the solenoids can quickly be detected with the self diagnosis procedure
described in this manual.
The JR405E automatic transmission consists of the torque converter, oil pump, input shaft, out put shaft,
planetary gears and control valves.
The gear train consists of two planetary gear sets and three multiple plate clutches in combination with two
multiple plate brakes and a one-way clutch.
2WD
4WD
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4249 of 6020

7A1-10 CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION
INPUT SHAFT
• The input shaft has some oil holes, through which lubricating ATF is supplied to the torque converter, the
bearings, etc.
• The input shaft is fitted to the turbine runner in the torque converter, the reverse & high clutch drum and
the rear sun gear by means of the spline. Therefore, the engine driving force received by the torque
converter is transmitted to the reverse & high clutch drum and rear sun gear.
OUTPUT SHAFT
• The output shaft has some oil holes, through which the lubricating ATF is supplied to the bearings, the
planetary gear unit, etc.
• The output shaft transmits the engine driving force from the planetary gear to the propeller shaft.
• The front internal gear is fitted with the rear carrier assembly by spline. The parking gear is also fitted by
spline. By fixing this gear mechanically, the output shaft is fixed as required when parking the vehicle.
GEAR SHIFTING MECHANISM
• The JR405E consists of two sets of planetary gears, three multiple plate clutches, two multiple plate
brakes and a one-way clutch. They are activated in different combinations in any of four forward and one
reverse gear positions.
Principle of gear shifting (Figure 12) • Planetary gears have the advantage of a compact configuration because of the way they are constructed
with a single central shaft.
• Also, unlike the manual transmission gears that require changing of the gear mesh, the gear ratio of the
planetary gears can be changed more easily by locking, releasing or rotating only some of their parts.
• A planetary gear is made up of a sun gear (1) at its center, and pinion gears (2) each of which rotates
about its own center and around the sun gear, as shown. They are all contained within the internal gear
(3).
• Also, since the pinion gears are further supported by the planetary carrier (4), they rotate as a unit in the
same direction, and at the same rate.
• As shown below, each planetary gear is constructed of three elements; a sun gear, pinion gears, an
internal gear and a planetary carrier. Gear shifting is achieved by conditioning two of the three elements,
namely the sun gear, the internal gear and planetary carrier.
• The planetary gears are locked by the clutch, brake and one-way clutch according to the gear shifting.
1. Sun Gear
2. Pinion Gear
3. Internal Gear
4. Planetary Carrier
Figure 12. Planetary Gear
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4252 of 6020
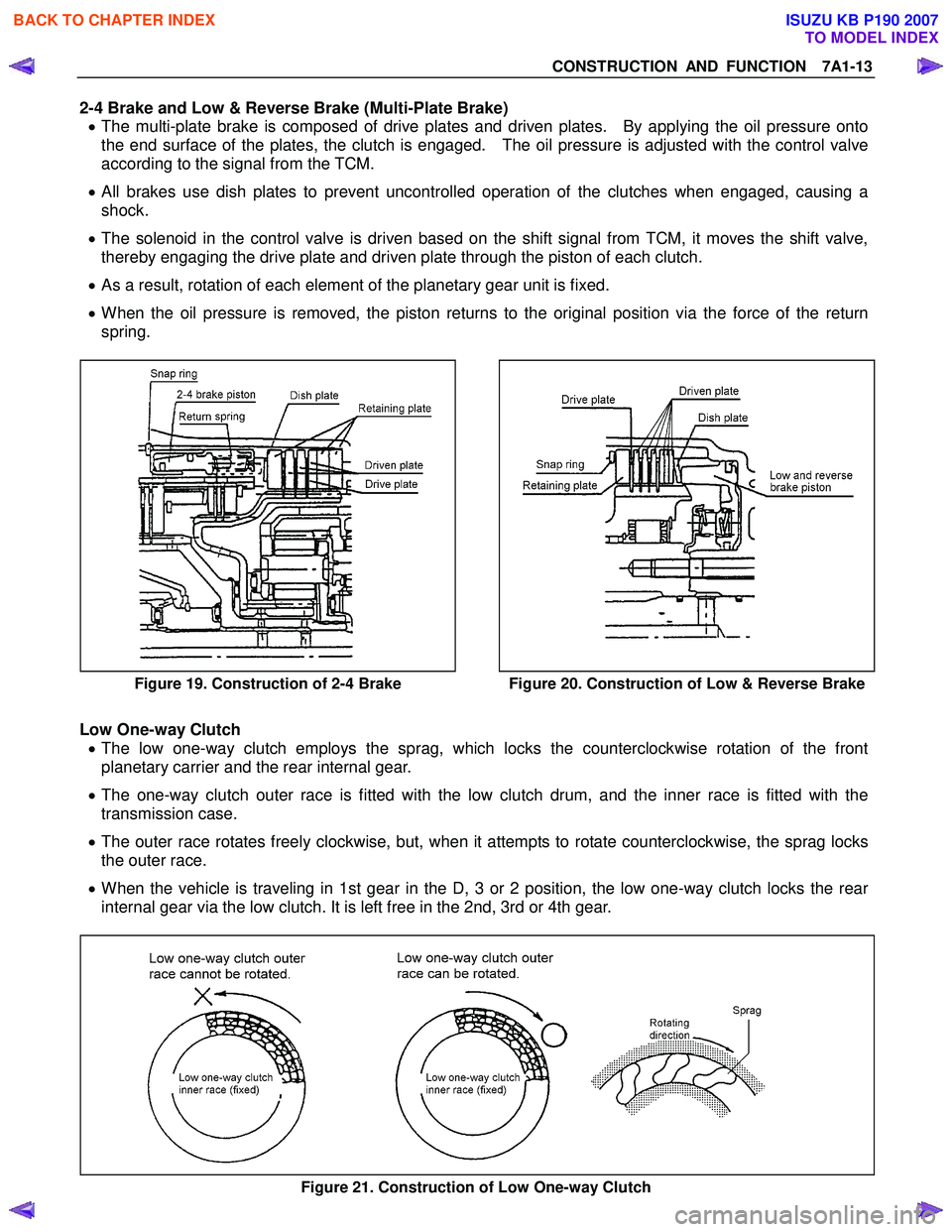
CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION 7A1-13
2-4 Brake and Low & Reverse Brake (Multi-Plate Brake) • The multi-plate brake is composed of drive plates and driven plates. By applying the oil pressure onto
the end surface of the plates, the clutch is engaged. The oil pressure is adjusted with the control valve
according to the signal from the TCM.
• All brakes use dish plates to prevent uncontrolled operation of the clutches when engaged, causing a
shock.
• The solenoid in the control valve is driven based on the shift signal from TCM, it moves the shift valve,
thereby engaging the drive plate and driven plate through the piston of each clutch.
• As a result, rotation of each element of the planetary gear unit is fixed.
• When the oil pressure is removed, the piston returns to the original position via the force of the return
spring.
Figure 19. Construction of 2-4 Brake
Figure 20. Construction of Low & Reverse Brake
Low One-way Clutch
• The low one-way clutch employs the sprag, which locks the counterclockwise rotation of the front
planetary carrier and the rear internal gear.
• The one-way clutch outer race is fitted with the low clutch drum, and the inner race is fitted with the
transmission case.
• The outer race rotates freely clockwise, but, when it attempts to rotate counterclockwise, the sprag locks
the outer race.
• When the vehicle is traveling in 1st gear in the D, 3 or 2 position, the low one-way clutch locks the rear
internal gear via the low clutch. It is left free in the 2nd, 3rd or 4th gear.
Figure 21. Construction of Low One-way Clutch
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4255 of 6020
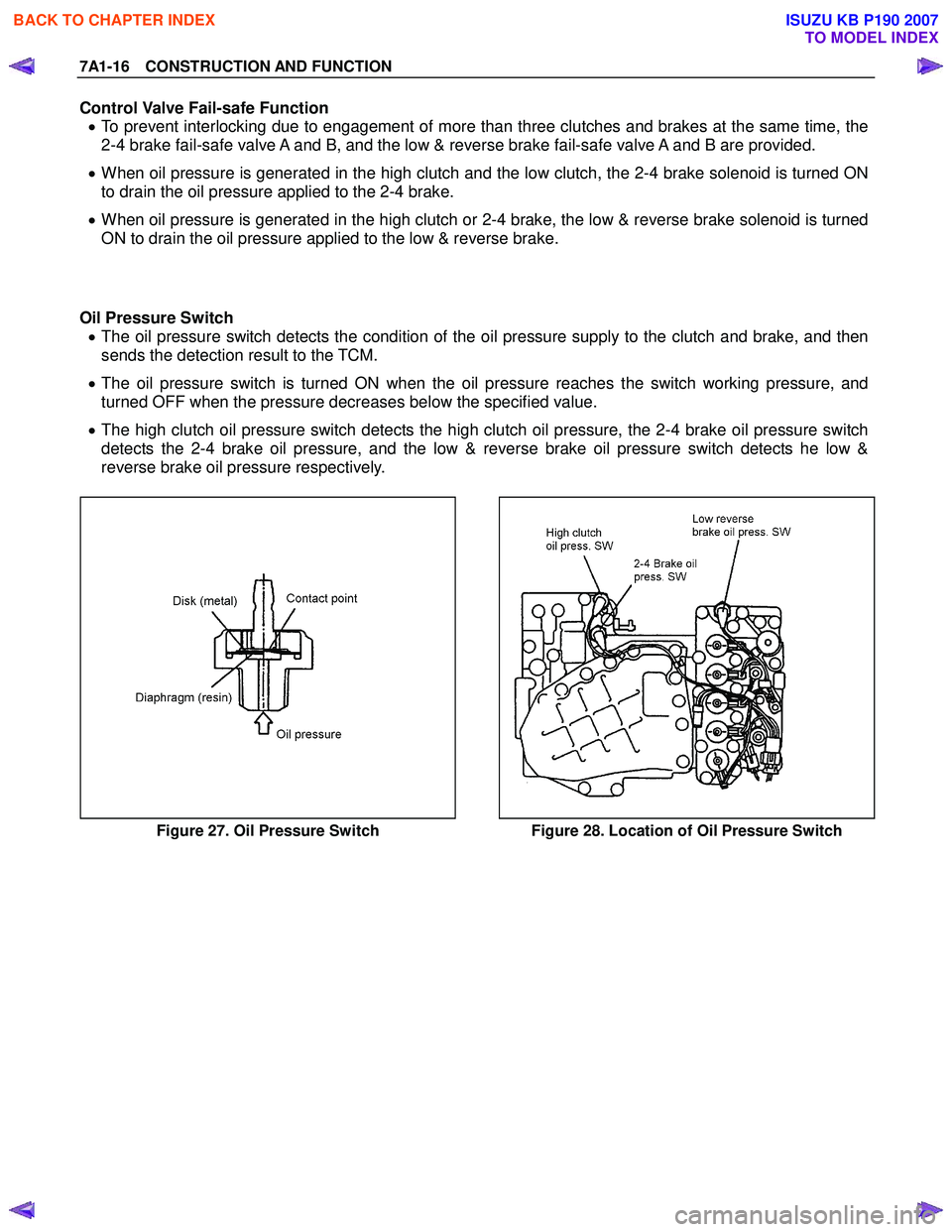
7A1-16 CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION
Control Valve Fail-safe Function • To prevent interlocking due to engagement of more than three clutches and brakes at the same time, the
2-4 brake fail-safe valve A and B, and the low & reverse brake fail-safe valve A and B are provided.
• When oil pressure is generated in the high clutch and the low clutch, the 2-4 brake solenoid is turned ON
to drain the oil pressure applied to the 2-4 brake.
• When oil pressure is generated in the high clutch or 2-4 brake, the low & reverse brake solenoid is turned
ON to drain the oil pressure applied to the low & reverse brake.
Oil Pressure Switch • The oil pressure switch detects the condition of the oil pressure supply to the clutch and brake, and then
sends the detection result to the TCM.
• The oil pressure switch is turned ON when the oil pressure reaches the switch working pressure, and
turned OFF when the pressure decreases below the specified value.
• The high clutch oil pressure switch detects the high clutch oil pressure, the 2-4 brake oil pressure switch
detects the 2-4 brake oil pressure, and the low & reverse brake oil pressure switch detects he low &
reverse brake oil pressure respectively.
Figure 27. Oil Pressure Switch Figure 28. Location of Oil Pressure Switch
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4275 of 6020
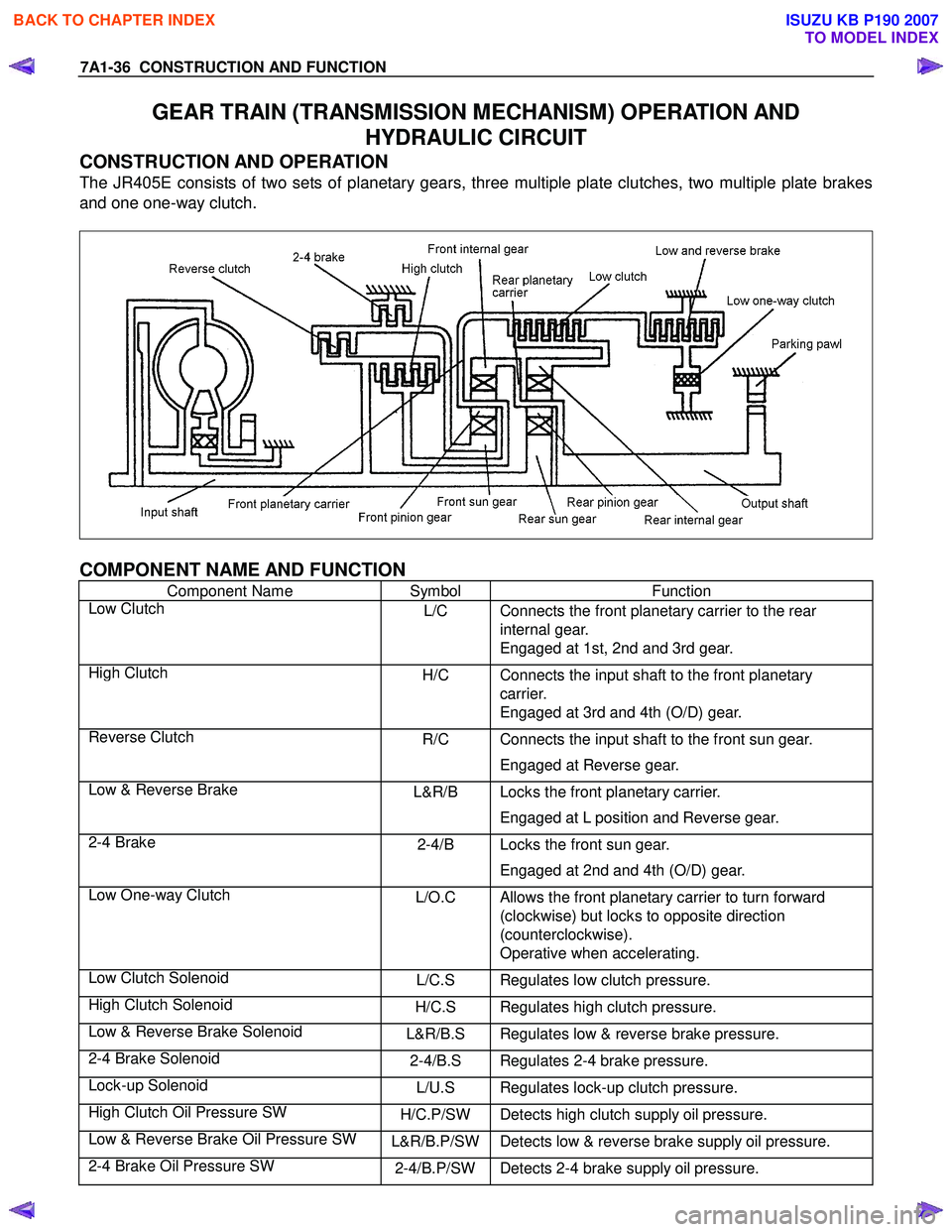
7A1-36 CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION
GEAR TRAIN (TRANSMISSION MECHANISM) OPERATION AND
HYDRAULIC CIRCUIT
CONSTRUCTION AND OPERATION
The JR405E consists of two sets of planetary gears, three multiple plate clutches, two multiple plate brakes
and one one-way clutch.
COMPONENT NAME AND FUNCTION
Component Name Symbol Function
Low Clutch L/C Connects the front planetary carrier to the rear
internal gear.
Engaged at 1st, 2nd and 3rd gear.
High Clutch H/C Connects the input shaft to the front planetary
carrier.
Engaged at 3rd and 4th (O/D) gear.
Reverse Clutch R/C Connects the input shaft to the front sun gear.
Engaged at Reverse gear.
Low & Reverse Brake L&R/B Locks the front planetary carrier.
Engaged at L position and Reverse gear.
2-4 Brake 2-4/B Locks the front sun gear.
Engaged at 2nd and 4th (O/D) gear.
Low One-way Clutch L/O.C Allows the front planetary carrier to turn forward
(clockwise) but locks to opposite direction
(counterclockwise).
Operative when accelerating.
Low Clutch Solenoid L/C.S Regulates low clutch pressure.
High Clutch Solenoid H/C.S Regulates high clutch pressure.
Low & Reverse Brake Solenoid L&R/B.S Regulates low & reverse brake pressure.
2-4 Brake Solenoid 2-4/B.S Regulates 2-4 brake pressure.
Lock-up Solenoid L/U.S Regulates lock-up clutch pressure.
High Clutch Oil Pressure SW H/C.P/SW Detects high clutch supply oil pressure.
Low & Reverse Brake Oil Pressure SW L&R/B.P/SWDetects low & reverse brake supply oil pressure.
2-4 Brake Oil Pressure SW 2-4/B.P/SWDetects 2-4 brake supply oil pressure.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4277 of 6020
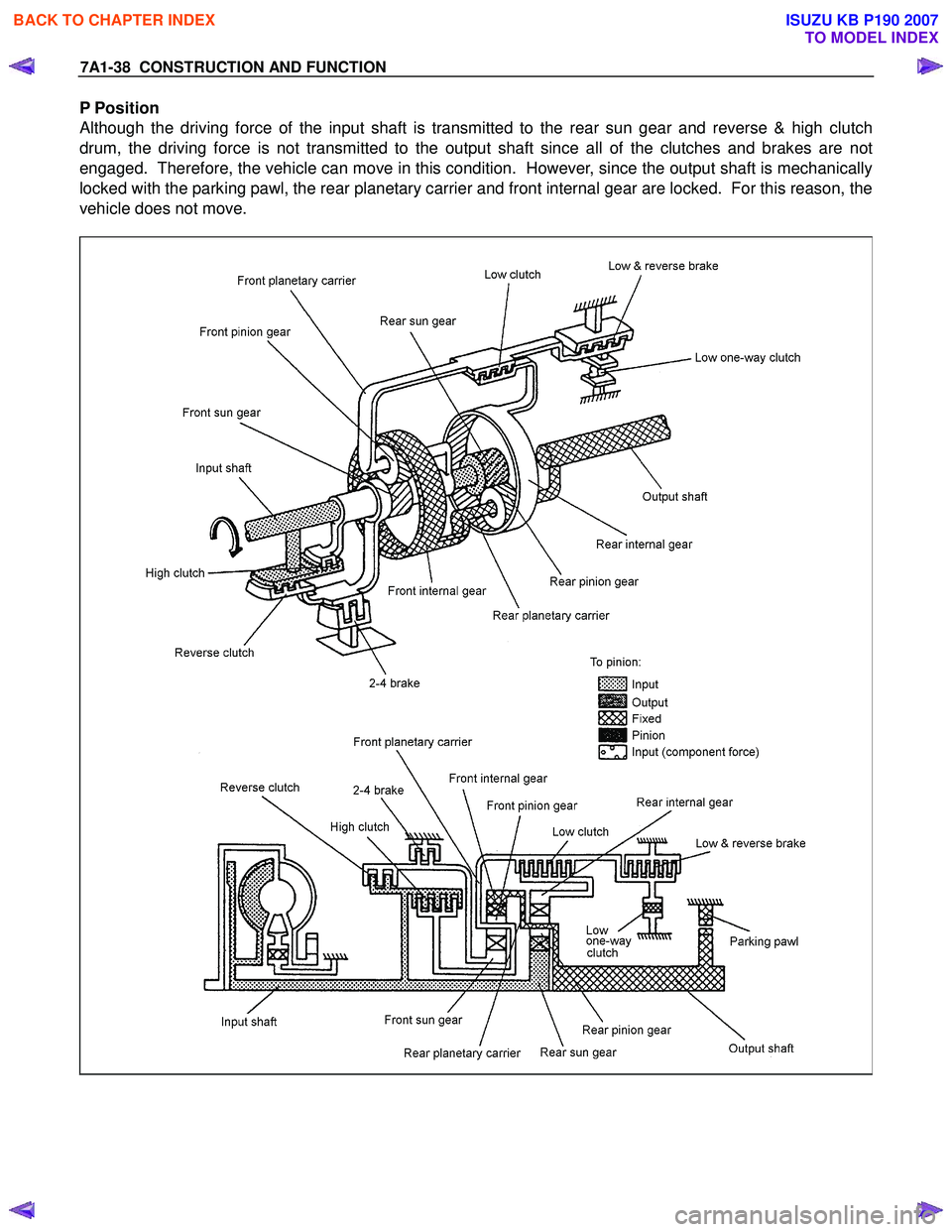
7A1-38 CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION
P Position
Although the driving force of the input shaft is transmitted to the rear sun gear and reverse & high clutch
drum, the driving force is not transmitted to the output shaft since all of the clutches and brakes are not
engaged. Therefore, the vehicle can move in this condition. However, since the output shaft is mechanically
locked with the parking pawl, the rear planetary carrier and front internal gear are locked. For this reason, the
vehicle does not move.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4278 of 6020
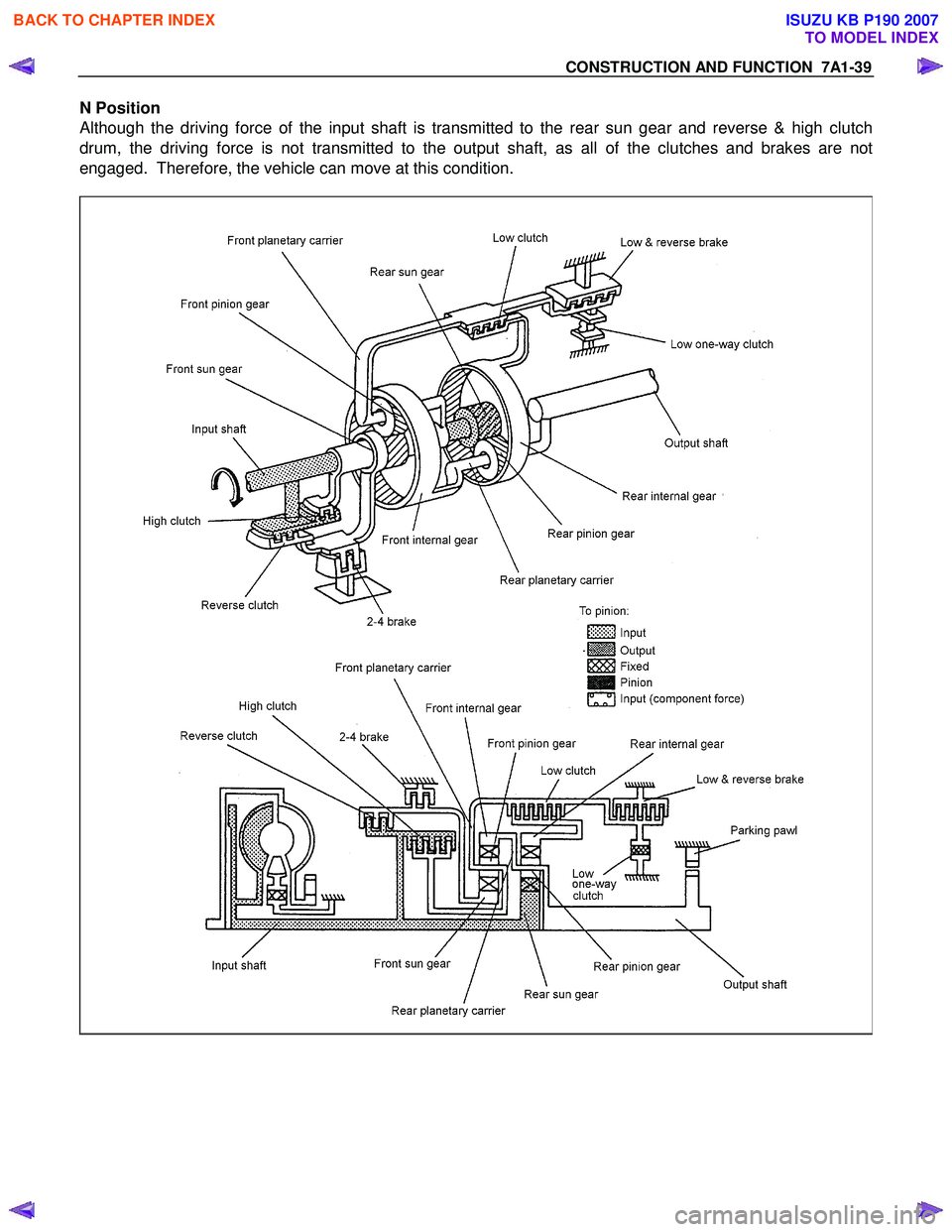
CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION 7A1-39
N Position
Although the driving force of the input shaft is transmitted to the rear sun gear and reverse & high clutch
drum, the driving force is not transmitted to the output shaft, as all of the clutches and brakes are not
engaged. Therefore, the vehicle can move at this condition.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007