2007 ISUZU KB P190 Fuel line
[x] Cancel search: Fuel linePage 2219 of 6020

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–49
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)
The TPS is a potentiometer connected to throttle shaft
on the throttle body.
The engine control module (ECM) monitors the voltage
on the signal line and calculates throttle position. As the
throttle valve angle is changed when accelerator pedal
moved. The TPS signal also changed at a moved
throttle valve. As the throttle valve opens, the output
increases so that the output voltage should be high.
The throttle body has a throttle plate to control the
amount of the air delivered to the engine.
Engine coolant is directed through a coolant cavity in
the throttle body to warm the throttle valve and to
prevent icing.
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
The idle air control valve (IAC) valve is two directional
and gives 2-way control. With power supply to the coils
controlled steps by the engine control module (ECM),
the IAC valve's pintle is moved to adjust idle speed,
raising it for fast idle when cold or there is extra load
from the air conditioning or power steering.
By moving the pintle in (to decrease air flow) or out (to
increase air flow), a controlled amount of the air can
move around the throttle plate. If the engine speed is
too low, the engine control module (ECM) will retract the
IAC pintle, resulting in more air moving past the throttle
plate to increase the engine speed.
If the engine speed is too high, the engine control
module (ECM) will extend the IAC pintle, allowing less
air to move past the throttle plate, decreasing the
engine speed.
The IAC pintle valve moves in small step called counts.
During idle, the proper position of the IAC pintle is
calculated by the engine control module (ECM) based
on battery voltage, coolant temperature, engine load,
and engine speed.
If the engine speed drops below a specified value, and
the throttle plate is closed, the engine control module
(ECM) senses a near-stall condition. The engine control
module (ECM) will then calculate a new IAC pintle valve
position to prevent stalls.
If the IAC valve is disconnected and reconnected with
the engine running, the idle speed will be wrong. In this
case, the IAC must be reset. The IAC resets when the
key is cycled “On” then “Off”. When servicing the IAC, it
should only be disconnected or connected with the
ignition “Off”.
The position of the IAC pintle valve affects engine start-
up and the idle characteristic of the vehicle.
If the IAC pintle is fully open, too much air will be
allowed into the manifold. This results in high idle
speed, along with possible hard starting and lean air/
fuel ratio.
(1) Throttle Position Sensor
(2) Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
1
2
C harac teris t ic of TPS -R ef erenc e-
0
0.5
1
1.5 2
2.5
3
3.5 4
4.5 5
0 10 2030 405060 7080 90100 Throt t le Angle (% ) (Tec h2 R eading)
Output Voltage (V)
StepCoilAB CDCoil A H igh
(ECM J1-28) On On
Coil A Low
(ECM J1-30) On On
Coil B H igh
(ECM J1-13) On On
Coil B Low
(ECM J1-29) On On
(IAC Valve Close Direction)
(IAC Valve Open Direction)
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2221 of 6020
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–51
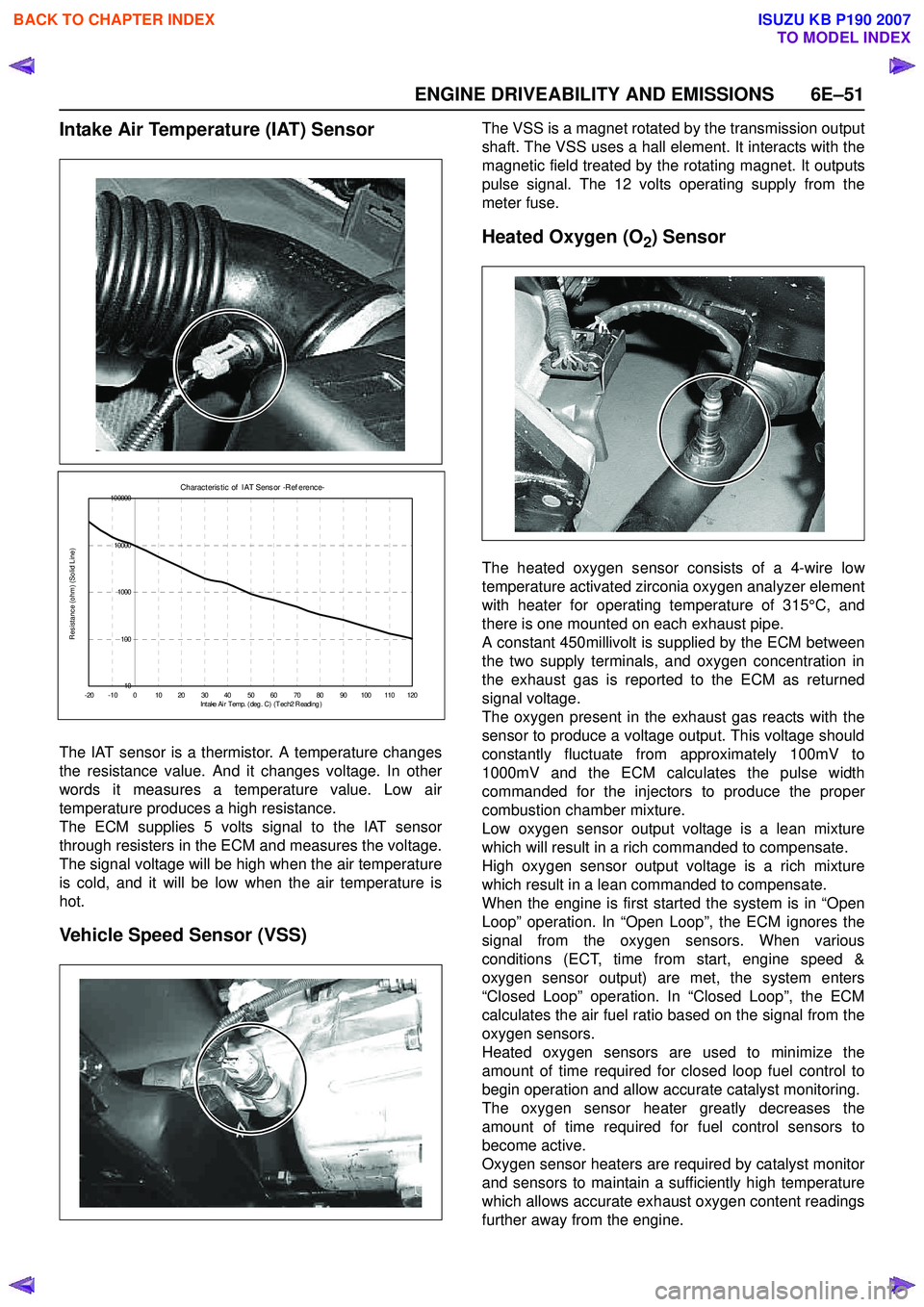
Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
The IAT sensor is a thermistor. A temperature changes
the resistance value. And it changes voltage. In other
words it measures a temperature value. Low air
temperature produces a high resistance.
The ECM supplies 5 volts signal to the IAT sensor
through resisters in the ECM and measures the voltage.
The signal voltage will be high when the air temperature
is cold, and it will be low when the air temperature is
hot.
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS)
The VSS is a magnet rotated by the transmission output
shaft. The VSS uses a hall element. It interacts with the
magnetic field treated by the rotating magnet. It outputs
pulse signal. The 12 volts operating supply from the
meter fuse.
Heated Oxygen (O2) Sensor
The heated oxygen sensor consists of a 4-wire low
temperature activated zirconia oxygen analyzer element
with heater for operating temperature of 315°C, and
there is one mounted on each exhaust pipe.
A constant 450millivolt is supplied by the ECM between
the two supply terminals, and oxygen concentration in
the exhaust gas is reported to the ECM as returned
signal voltage.
The oxygen present in the exhaust gas reacts with the
sensor to produce a voltage output. This voltage should
constantly fluctuate from approximately 100mV to
1000mV and the ECM calculates the pulse width
commanded for the injectors to produce the proper
combustion chamber mixture.
Low oxygen sensor output voltage is a lean mixture
which will result in a rich commanded to compensate.
High oxygen sensor output voltage is a rich mixture
which result in a lean commanded to compensate.
When the engine is first started the system is in “Open
Loop” operation. In “Open Loop”, the ECM ignores the
signal from the oxygen sensors. When various
conditions (ECT, time from start, engine speed &
oxygen sensor output) are met, the system enters
“Closed Loop” operation. In “Closed Loop”, the ECM
calculates the air fuel ratio based on the signal from the
oxygen sensors.
Heated oxygen sensors are used to minimize the
amount of time required for closed loop fuel control to
begin operation and allow accurate catalyst monitoring.
The oxygen sensor heater greatly decreases the
amount of time required for fuel control sensors to
become active.
Oxygen sensor heaters are required by catalyst monitor
and sensors to maintain a sufficiently high temperature
which allows accurate exhaust oxygen content readings
further away from the engine.
Charac t eris t ic of I AT Sens or -R ef erenc e-
10
100
1000
10000
100000
- 20 - 10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 Intake Ai r T emp. ( deg . C ) ( T ec h2 R eadi ng )
Resistance (ohm) (Solid Line)
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2222 of 6020

6E–52 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION FOR FUEL
METERING
The fuel metering system starts with the fuel in the fuel
tank. An electric fuel pump, located in the fuel tank,
pumps fuel to the fuel rail through an in-line fuel filter.
The pump is designed to provide fuel at a pressure
above the pressure needed by the injectors.
A fuel pressure regulator in the fuel rail keeps fuel
available to the fuel injectors at a constant pressure.
A return line delivers unused fuel back to the fuel tank.
The basic function of the air/fuel metering system is to
control the air/fuel delivery to the engine. Fuel is
delivered to the engine by individual fuel injectors
mounted in the intake manifold.
The main control sensor is the heated oxygen sensor
located in the exhaust system. The heated oxygen
sensor reports to the ECM how much oxygen is in the
exhaust gas. The ECM changes the air/fuel ratio to the
engine by controlling the amount of time that fuel
injector is “On”.
The best mixture to minimize exhaust emissions is 14.7
parts of air to 1 part of gasoline by weight, which allows
the catalytic converter to operate most efficiently.
Because of the constant measuring and adjusting of the
air/fuel ratio, the fuel injection system is called a “closed
loop” system.
The ECM monitors signals from several sensors in
order to determine the fuel needs of the engine. Fuel is
delivered under one of several conditions called “mode”.
All modes are controlled by the ECM.
Battery Voltage Correction Mode
When battery voltage is low, the ECM will compensate
for the weak spark by increasing the following:
• The amount of fuel delivered.
• The idle RPM.
Clear Flood Mode
Clear a flooded engine by pushing the accelerator pedal
down all the way. The ECM then de-energizes the fuel
injectors. The ECM holds the fuel injectors de-energized
as long as the throttle remains above 75% and the
engine speed is below 800 RPM. If the throttle position
becomes less than 75%, the ECM again begins to pulse
the injectors ON and OFF, allowing fuel into the
cylinders.
Deceleration Fuel Cutoff (DFCO) Mode
The ECM reduces the amount of fuel injected when it
detects a decrease in the throttle position and the air
flow. When deceleration is very fast, the ECM may cut
off fuel completely. Until enable conditions meet the
engine revolution less 1000 rpm or manifold absolute
pressure less than 10 kPa.
Engine Speed/ Vehicle Speed/ Fuel Disable
Mode
The ECM monitors engine speed. It turns off the fuel
injectors when the engine speed increases above 6000
RPM. The fuel injectors are turned back on when
engine speed decreases below 3500 RPM.
Acceleration Mode
The ECM provides extra fuel when it detects a rapid
increase in the throttle position and the air flow.
Fuel Cutoff Mode
No fuel is delivered by the fuel injectors when the
ignition is OFF. This prevents engine run-on. In addition,
the ECM suspends fuel delivery if no reference pulses
are detected (engine not running) to prevent engine
flooding.
Starting Mode
When the ignition is first turned ON, the ECM energizes
the fuel pump relay for two seconds to allow the fuel
pump to build up pressure. The ECM then checks the
engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor and the
throttle position sensor to determine the proper air/fuel
ratio for starting.
The ECM controls the amount of fuel delivered in the
starting mode by adjusting how long the fuel injectors
are energized by pulsing the injectors for very short
times.
Run Mode
The run mode has the following two conditions:
• Open loop
• Closed loop
When the engine is first started, the system is in “open
loop” operation. In “Open Loop,” the ECM ignores the
signal from the heated oxygen sensor (HO2S). It
calculates the air/fuel ratio based on inputs from the TP,
ECT, and MAP sensors.
The system remains in “Open Loop” until the following
conditions are met:
• The HO2S has a varying voltage output showing that it is hot enough to operate properly (this depends on
temperature).
• The ECT has reached a specified temperature.
• A specific amount of time has elapsed since starting the engine.
• Engine speed has been greater than a specified RPM since start-up.
The specific values for the above conditions vary with
different engines and are stored in the programmable
read only memory (PROM). When these conditions are
met, the system enters “closed loop” operation. In
“closed loop,” the ECM calculates the air/fuel ratio
(injector on-time) based on the signal from the HO2S.
This allows the air/fuel ratio to stay very close to 14.7:1.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2223 of 6020

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–53
Fuel Metering System Components
The fuel metering system is made up of the following
parts.
• Fuel injector
• Throttle body
•Fuel rail
• Fuel pressure regulator
•ECM
• Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor
• Idle air control (IAC) valve
•Fuel pump
Fuel Injector
The group fuel injection fuel injector is a solenoid
operated device controlled by the ECM. The ECM
energizes the solenoid, which opens a valve to allow
fuel delivery.
The fuel is injected under pressure in a conical spray
pattern at the opening of the intake valve. Excess fuel
not used by the injectors passes through the fuel
pressure regulator before being returned to the fuel
tank.
Fuel Pressure Regulator
The fuel pressure regulator is a diaphragm-operated
relief valve mounted on the fuel rail with fuel pump
pressure on one side and manifold pressure on the
other side. The fuel pressure regulator maintains the
fuel pressure available to the injector at three times
barometric pressure adjusted for engine load. It may be
serviced separately.
If the pressure is too low or poor performance, DTC
P0131 or P1171 will be the result. If the pressure is too
high, DTC P0132 or P1167 will be the result. Refer to
Fuel System Diagnosis for information on diagnosing
fuel pressure conditions.
Fuel Rail
The fuel rail is mounted to the top of the engine and
distributes fuel to the individual injectors. Fuel is
delivered to the fuel inlet tube of the fuel rail by the fuel
lines. The fuel goes through the fuel rail to the fuel
pressure regulator. The fuel pressure regulator
maintains a constant fuel pressure at the injectors.
Remaining fuel is then returned to the fuel tank.
Fuel Pump Electrical Circuit
When the key is first turned ON, the ECM energizes the
fuel pump relay for two seconds to build up the fuel
pressure quickly. If the engine is not started within two
seconds, the ECM shuts the fuel pump off and waits
until the engine is cranked. When the engine is cranked
and the 58X crankshaft position signal has been
detected by the ECM, the ECM supplies 12 volts to the
fuel pump relay to energize the electric in-tank fuel
pump.
An inoperative fuel pump will cause a “no-start”
condition. A fuel pump which does not provide enough pressure will result in poor performance.
Thottle Body Unit
The throttle body has a throttle plate to control the
amount of air delivered to the engine. The Thottle
position sensor and IAC valve are also mounted on the
throttle body.
Vacuum ports located behind the throttle plate provide
the vacuum signals needed by various components.
Engine coolant is directed through a coolant cavity in
the throttle body to warm the throttle valve and to
prevent icing.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2227 of 6020
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–57
GENERAL DESCRIPTION FOR
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION SYSTEM
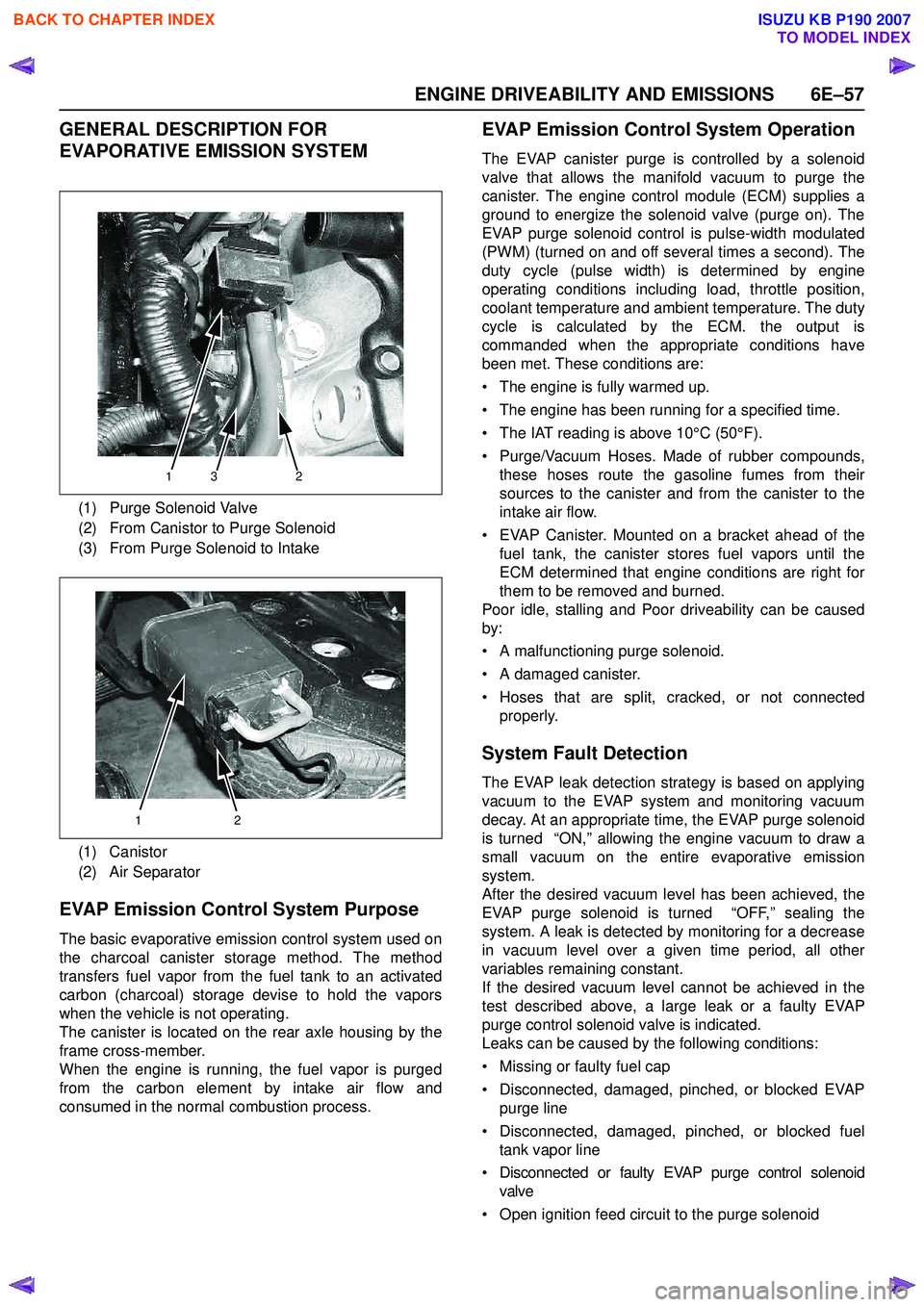
EVAP Emission Control System Purpose
The basic evaporative emission control system used on
the charcoal canister storage method. The method
transfers fuel vapor from the fuel tank to an activated
carbon (charcoal) storage devise to hold the vapors
when the vehicle is not operating.
The canister is located on the rear axle housing by the
frame cross-member.
When the engine is running, the fuel vapor is purged
from the carbon element by intake air flow and
consumed in the normal combustion process.
EVAP Emission Control System Operation
The EVAP canister purge is controlled by a solenoid
valve that allows the manifold vacuum to purge the
canister. The engine control module (ECM) supplies a
ground to energize the solenoid valve (purge on). The
EVAP purge solenoid control is pulse-width modulated
(PWM) (turned on and off several times a second). The
duty cycle (pulse width) is determined by engine
operating conditions including load, throttle position,
coolant temperature and ambient temperature. The duty
cycle is calculated by the ECM. the output is
commanded when the appropriate conditions have
been met. These conditions are:
• The engine is fully warmed up.
• The engine has been running for a specified time.
• The IAT reading is above 10°C (50°F).
• Purge/Vacuum Hoses. Made of rubber compounds, these hoses route the gasoline fumes from their
sources to the canister and from the canister to the
intake air flow.
• EVAP Canister. Mounted on a bracket ahead of the fuel tank, the canister stores fuel vapors until the
ECM determined that engine conditions are right for
them to be removed and burned.
Poor idle, stalling and Poor driveability can be caused
by:
• A malfunctioning purge solenoid.
• A damaged canister.
• Hoses that are split, cracked, or not connected properly.
System Fault Detection
The EVAP leak detection strategy is based on applying
vacuum to the EVAP system and monitoring vacuum
decay. At an appropriate time, the EVAP purge solenoid
is turned “ON,” allowing the engine vacuum to draw a
small vacuum on the entire evaporative emission
system.
After the desired vacuum level has been achieved, the
EVAP purge solenoid is turned “OFF,” sealing the
system. A leak is detected by monitoring for a decrease
in vacuum level over a given time period, all other
variables remaining constant.
If the desired vacuum level cannot be achieved in the
test described above, a large leak or a faulty EVAP
purge control solenoid valve is indicated.
Leaks can be caused by the following conditions:
• Missing or faulty fuel cap
• Disconnected, damaged, pinched, or blocked EVAP purge line
• Disconnected, damaged, pinched, or blocked fuel tank vapor line
• Disconnected or faulty EVAP purge control solenoid valve
• Open ignition feed circuit to the purge solenoid
(1) Purge Solenoid Valve
(2) From Canistor to Purge Solenoid
(3) From Purge Solenoid to Intake
(1) Canistor
(2) Air Separator
132
12
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2228 of 6020

6E–58 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
• Damaged EVAP canister
• Leaking fuel sender assembly O-ring
• Leaking fuel tank or fuel filler neck
The ECM supplies a ground to energize the purge
control solenoid valve (purge “ON” ). The EVAP purge
control is turned “ON” and “OFF,” several times a
second. The duty cycle (pulse width) is determined by
engine operating conditions including load, throttle
position, coolant temperature and ambient temperature.
The duty cycle is calculated by the ECM and the output
is commanded when the appropriate conditions have
been met.
The system checks for conditions that cause the EVAP
system to purge continuously by commanding the EVAP
purge solenoid “OFF”, EVAP purge solenoid duty ratio
“0%”. If fuel tank vacuum level increases during the test,
a continuous purge flow condition is indicated. This can
be caused by the following conditions:
• EVAP purge solenoid leaking
• EVAP purge and engine vacuum lines switched at the EVAP purge control solenoid valve
• EVAP purge control solenoid valve driver circuit grounded
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2237 of 6020

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–67
GENERAL SERVICE INFORMATION
Aftermarket Electrical and Vacuum
Equipment
Aftermarket (add-on) electrical and vacuum equipment
is defined as any equipment which connects to the
vehicle's electrical or vacuum systems that is installed
on a vehicle after it leaves the factory. No allowances
have been made in the vehicle design for this type of
equipment.
NOTE: No add-on vacuum equipment should be added
to this vehicle.
NOTE: Add-on electrical equipment must only be
connected to the vehicle's electrical system at the
battery (power and ground).
Add-on electrical equipment, even when installed to
these guidelines, may still cause the electric system to
malfunction. This may also include equipment not
connected to the vehicle electrical system such as
portable telephones and radios. Therefore, the first step
in diagnosing any electric problem is to eliminate all
aftermarket electrical equipment from the vehicle. After
this is done, if the problem still exists, it may be
diagnosed in the normal manner.
Electrostatic Discharge Damage
Electronic components used in the ECM are often
designed to carry very low voltage. Electronic
components are susceptible to damage caused by
electrostatic discharge. Less than 100 volts of static
electricity can cause damage to some electronic
components. By comparison, it takes as much as 4000
volts for a person to feel even the zap of a static
discharge.
There are several ways for a person to become
statically charged. The most common methods of
charging are by friction and induction.
• An example of charging by friction is a person sliding across a vehicle seat.
• Charge by induction occurs when a person with well- insulated shoes stands near a highly charged object
and momentarily touches ground. Charges of the
same polarity are drained off leaving the person
highly charged with the opposite polarity. Static
charges can cause damage, therefore it is important
to use care when handling and testing electronic
components. Non-OEM Parts
All of the OBD diagnostics have been calibrated to run
with OEM parts. Accordingly, if commercially sold
sensor or switch is installed, it makes a wrong diagnosis
and turns on the check engine lamp.
Aftermarket electronics, such as cellular phones,
stereos, and anti-theft devices, may radiate EMI into the
control system if they are improperly installed. This may
cause a false sensor reading and turn on the check
engine lamp.
Poor Vehicle Maintenance
The sensitivity of OBD diagnostics will cause the check
engine lamp to turn on if the vehicle is not maintained
properly. Restricted oil filters, fuel filters, and crankcase
deposits due to lack of oil changes or improper oil
viscosity can trigger actual vehicle faults that were not
previously monitored prior to OBD. Poor vehicle
maintenance can not be classified as a “non-vehicle
fault”, but with the sensitivity of OBD diagnostics,
vehicle maintenance schedules must be more closely
followed.
Related System Faults
Many of the OBD system diagnostics will not run if the
ECM detects a fault on a related system or component.
Visual/Physical Engine Compartment
Inspection
Perform a careful visual and physical engine
compartment inspection when performing any
diagnostic procedure or diagnosing the cause of an
emission test failure. This can often lead to repairing a
problem without further steps. Use the following
guidelines when performing a visual/physical
inspection:
• Inspect all vacuum hoses for punches, cuts, disconnects, and correct routing.
• Inspect hoses that are difficult to see behind other components.
• Inspect all wires in the engine compartment for proper connections, burned or chafed spots, pinched
wires, contact with sharp edges or contact with hot
exhaust manifolds or pipes.
Basic Knowledge of Tools Required
NOTE: Lack of basic knowledge of this powertrain
when performing diagnostic procedures could result in
an incorrect diagnosis or damage to powertrain
components. Do not attempt to diagnose a powertrain
problem without this basic knowledge.
A basic understanding of hand tools is necessary to
effectively use this section of the Service Manual.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2268 of 6020
6E–98 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
FUEL METERING SYSTEM CHECK
Some failures of the fuel metering system will result in
an “Engine Cranks But Will Not Run” symptom. If this
condition exists, refer to the Cranks But Will Not Run
chart. This chart will determine if the problem is caused
by the ignition system, the ECM, or the fuel pump
electrical circuit.
Refer to Fuel System Electrical Test for the fuel system
wiring schematic.
If there is a fuel delivery problem, refer to Fuel System
Diagnosis , which diagnoses the fuel injectors, the fuel
pressure regulator, and the fuel pump.
Followings are applicable to the vehicles with
closed Loop System:
If a malfunction occurs in the fuel metering system, it
usually results in either a rich HO2S signal or a lean
HO2S signal. This condition is indicated by the HO2S
voltage, which causes the ECM to change the fuel
calculation (fuel injector pulse width) based on the
HO2S reading. Changes made to the fuel calculation
will be indicated by a change in the long term fuel trim
values which can be monitored with a Scan Tool. Ideal
long term fuel trim values are around 0%; for a lean
HO2S signal, the ECM will add fuel, resulting in a fuel
trim value above 0%. Some variations in fuel trim values
are normal because all engines are not exactly the
same. If the evaporative emission canister purge is 02
status may be rich condition. 02 status indicates the
lean condition, refer to DTC P1171 for items which can
cause a lean HO2S signal.
FUEL INJECTOR COIL TEST PROCEDURE
AND FUEL INJECTOR BALANCE TEST
PROCEDURE
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart:
2. Relieve the fuel pressure by connecting 5-8840- 0378-0 T-Joint to the fuel pressure connection on the
fuel rail.
Caution: In order to reduce the risk of fire and
personal injury, wrap a shop towel around the
fuel pressure connection. The towel will absorb
any fuel leakage that occurs during the
connection of the fuel pressure gauge. Place the
towel in an approved container when the
connection of the fuel pressure gauge is
complete.
Place the fuel pressure gauge bleed hose in an
approved gasoline container.
With the ignition switch OFF open the valve on the
fuel pressure gauge.
3. Record the lowest voltage displayed by the DVM after the first second of the test. (During the first
second, voltage displayed by the DVM may be
inaccurate due to the initial current surge.)
Injector Specifications:
• The voltage displayed by the DVM should be within the specified range.
• The voltage displayed by the DVM may increase throughout the test as the fuel injector windings
warm and the resistance of the fuel injector
windings changes. Resistance Ohms
Voltage Specification at
10°C-35°C (50°F-95°F)
11.8-12.6 5.7-6.6
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007