2007 ISUZU KB P190 air condition
[x] Cancel search: air conditionPage 3572 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations Page 6C1-3–48
2.22 Spark Plugs
Service Precautions
1 Allow the engine to cool (to at least 50°C) before attempting to remove spark plugs. Attempting to remove spark
plugs from a hot engine may cause the plug / cylinder head threads to bind, resulting in tearing of the alloy cylinder
head threads.
2 Clean the spark plug recess area before removing any spark plug. Failure to do so could result in engine damage because of dirt or other foreign material entering the cylinder head or by the contamination of the cylinder head
threads. The contaminated threads may then prevent the correct seating of the new or replaced plug. If required,
use a thread chaser to clean the threads of any contamination where this is suspected.
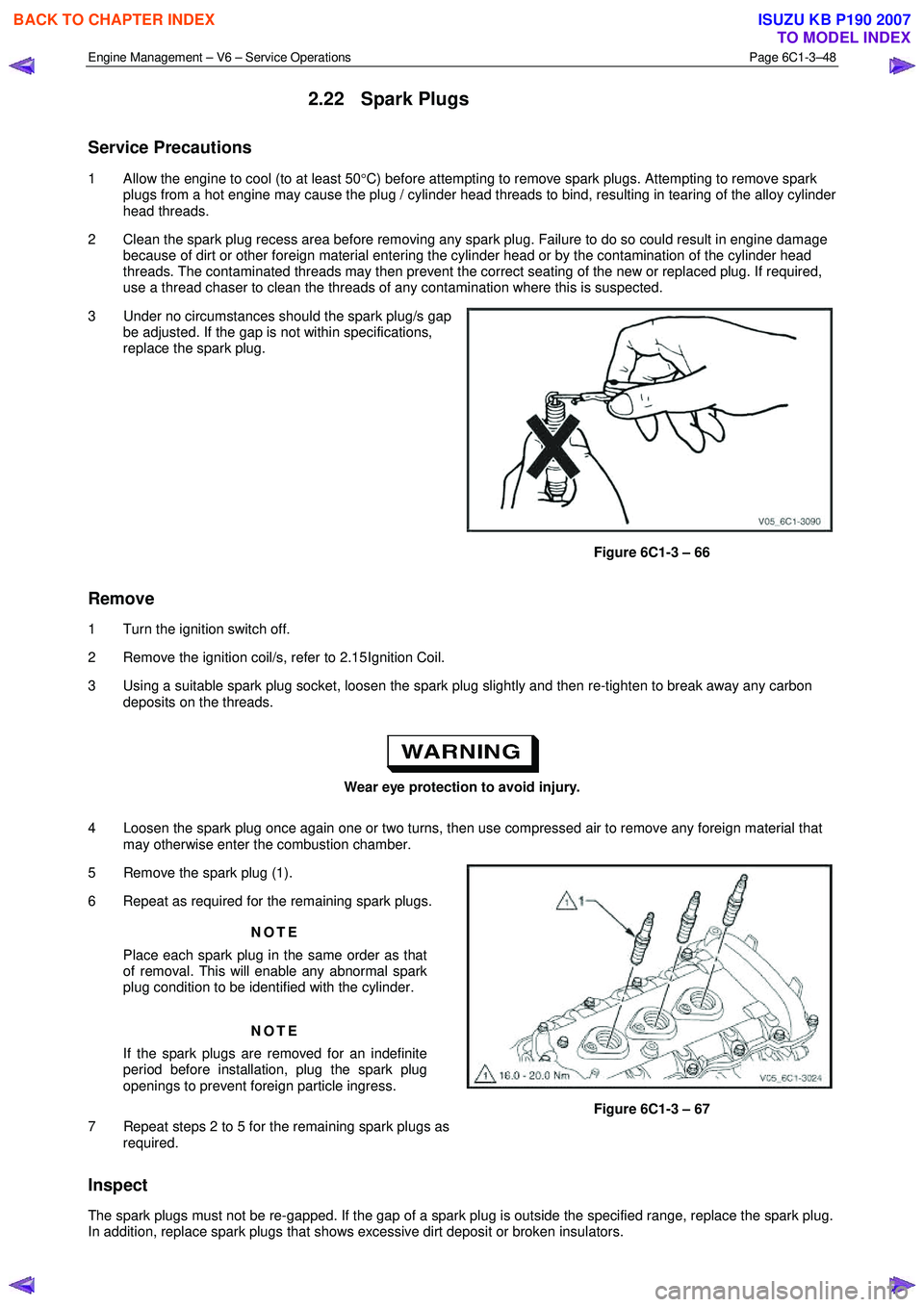
3 Under no circumstances should the spark plug/s gap be adjusted. If the gap is not within specifications,
replace the spark plug.
Figure 6C1-3 – 66
Remove
1 Turn the ignition switch off.
2 Remove the ignition coil/s, refer to 2.15 Ignition Coil.
3 Using a suitable spark plug socket, loosen the spark plug slightly and then re-tighten to break away any carbon deposits on the threads.
Wear eye protection to avoid injury.
4 Loosen the spark plug once again one or two turns, then use compressed air to remove any foreign material that may otherwise enter the combustion chamber.
5 Remove the spark plug (1).
6 Repeat as required for the remaining spark plugs.
NOTE
Place each spark plug in the same order as that
of removal. This will enable any abnormal spark
plug condition to be identified with the cylinder.
NOTE
If the spark plugs are removed for an indefinite
period before installation, plug the spark plug
openings to prevent foreign particle ingress.
7 Repeat steps 2 to 5 for the remaining spark plugs as required.
Figure 6C1-3 – 67
Inspect
The spark plugs must not be re-gapped. If the gap of a spark plug is outside the specified range, replace the spark plug.
In addition, replace spark plugs that shows excessive dirt deposit or broken insulators.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3579 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations Page 6C1-3–55
Inspect
The following throttle body inspection procedure may be carried out with the throttle body installed on the vehicle. Prior to
performing a throttle body on-vehicle inspection:
• Turn the ignition switch off.
• Disconnect the throttle body wiring harness connector. Refer to Remove in this Section.
• Remove the air intake duct, refer to 2.16 Intake Air Duct Assembly.
To avoid serious personal injury, never
attempt to rotate the throttle plate manually
whilst the throttle body harness connector is
connected to the throttle body.
1 Fully open the throttle plate by hand and inspect the throttle body bore and throttle plate for any deposits.
When cleaning / inspecting the throttle body:
• Do not subject the throttle body assembly
to an immersion cleaner or a strong
solvent. Damage to the throttle position
sensor and / or sealed throttle shaft
bearings will result.
• Never use a wire brush or scraper to clean
the throttle body. A wire brush or sharp
tool may damage the throttle body
components.
2 Use a clean shop towel and a spray type hydro-carbon cleaner to clean the throttle body bore and throttle plate. If necessary, use a parts cleaning brush to remove heavy deposits.
3 Inspect the throttle body for a binding throttle plate by fully opening and closing the throttle plate by hand. It should open and close smoothly.
4 Inspect the throttle body for a bent or damaged throttle plate, cracks, corrosion, or distortion in the throttle body housing.
NOTE
The throttle body contains no serviceable parts
and should not be disassembled. If the throttle
body is damaged it must be replaced as an
assembly.
5 If the throttle body is affected by any of the above conditions, it must be replaced.
6 If an on-vehicle throttle body inspection was performed, perform the following:
• Reinstall the air intake duct, refer to 2.16 Intake Air Duct Assembly.
• Reconnect the throttle body wiring harness connector, refer to Reinstall in this Section.
• Road test the vehicle and check for correct operation, taking particular note that no air leaks are evident.
Reinstall
Reinstallation of the throttle body assembly is the reverse of the removal procedure, noting the following:
1 Ensure the throttle body and upper intake manifold mating surfaces are clean and free of foreign material.
2 Install a new throttle body to upper intake manifold gasket.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3589 of 6020

Charging System – V6 Page 6D1-1-2
4.3 Drive Belt Routing................................................................................................................................................ 18
Without Air Conditioning ....................................................................................................... ............................. 18
6 Specifications .......................................................................................................................................19
7 Torque Wrench Specifications................................................................................................... .........20
8 Special Tools ........................................................................................................................................21
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3592 of 6020

Charging System – V6 Page 6D1-1-5
• Death or injury to other people in or near the workplace area, and / or
• Death or injury to the driver / or passenger(s) of the vehicle or other people, if the vehicle has been improperly
repaired.
CAUTION defined
A CAUTION statement immediately precedes an operating procedure or maintenance practice which, if not correctly
followed, could result in damage to or destruction of equipment, or corruption of data. If a CAUTION statement is
ignored, the following consequences may occur:
• Damage to the vehicle,
• Unnecessary vehicle repairs or component replacement,
• Faulty operation or performance of any system or component being repaired,
• Damage to any system or components which depend on the proper operation of the system or component being
repaired,
• Faulty operation or performance of any systems or components which depend on the proper operation or
performance of the system or component under repair,
• Damage to fasteners, basic tools or special tools and / or
• Leakage of coolant, lubricant or other vital fluids.
NOTE defined
A NOTE statement immediately precedes or follows an operating procedure, maintenance practice or condition that
requires highlighting. A NOTE statement also emphasises necessary characteristics of a diagnostic or repair procedure.
A NOTE statement is designed to:
• Clarify a procedure,
• Present additional information for accomplishing a procedure,
• Give insight into the reasons for performing a procedure in the recommended manner, and / or
• Present information that gives the technician the benefit of past experience in accomplishing a procedure with
greater ease.
1.3 System Operation
Operation
W ith the ignition switch in the ON position and the engine at rest, current is supplied via the regulator to generator
connector E-4 pin 1 and to the engine control module ECM connector E-60 pin 43. This initiates current flow (within the
regulator) from the generator connection P-9, to the brushes and rotor winding, to ‘excite’ the circuit.
The current in the rotor winding creates magnetic fields between adjacent rotor poles.
W ith the engine running, the rotor spins, the stator windings cut through this field and induce voltage. As the engine
speed is increased, this induced voltage increases. Current then flows through the three-phase diode bridge in the
rectifier to convert the AC voltage to DC. This is supplied to the generator connector P-9 output and then to the battery
terminal via fuse SBF1.
The regulator monitors the voltage to the battery. W hen this voltage reaches approximately 14.5 V, the regulator opens
the circuit through the rotor winding, causing the generator output voltage to drop. W hen the regulator senses a voltage
below a preset voltage, the regulator closes the circuit through the rotor winding and voltage to the battery again
increases. This cycle repeats very rapidly.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3593 of 6020

Charging System – V6 Page 6D1-1-6
Alternator Warning
NOTE
All generator faults are displayed as
Check Alternator W arning on the instrument
cluster MFD, refer to 8A Electrical Body and
Chassis.
The ECM monitors the voltage on connector E-60 pin 21 and pin 43.
The voltage at the generator connector E-4 pin 2 will remain low when a fault condition is detected in the generator or
associated external circuits. The voltage remains low (while the ignition switch is on) until the fault is repaired.
NOTE
For more information on the alternator warning
refer to 8A Electrical Body and Chassis.
Fault conditions include the following:
• open circuit or excessive voltage drop in circuit 1,
• open circuit in the generator phase connection,
• overcharging conditions,
• short circuit in the regulator output stage,
• open circuit in the rotor winding,
• poor contact between the rectifier and the regulator, and / or
• high resistance in the fusible link assembly.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3596 of 6020
Charging System – V6 Page 6D1-1-9
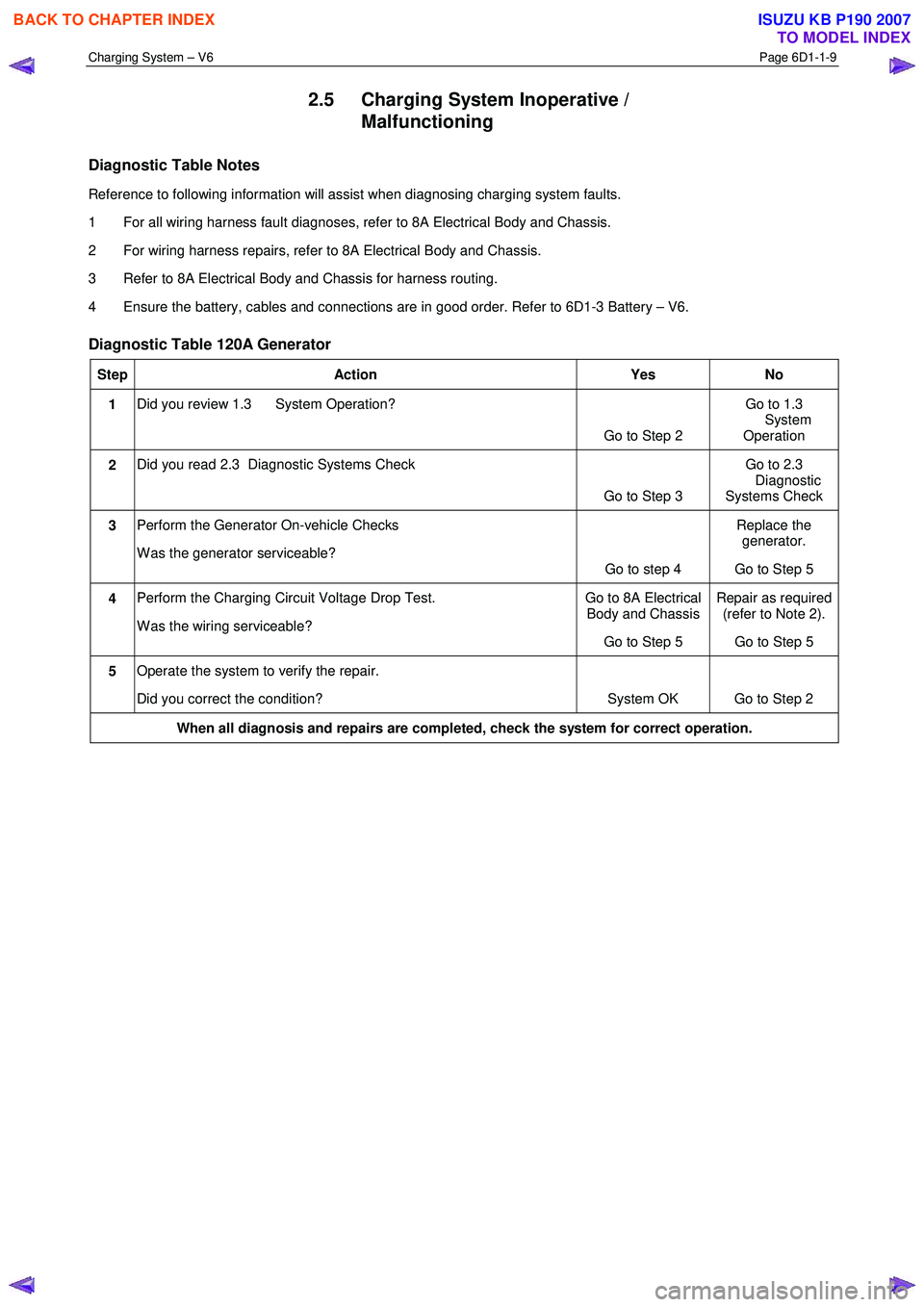
2.5 Charging System Inoperative /
Malfunctioning
Diagnostic Table Notes
Reference to following information will assist when diagnosing charging system faults.
1 For all wiring harness fault diagnoses, refer to 8A Electrical Body and Chassis.
2 For wiring harness repairs, refer to 8A Electrical Body and Chassis.
3 Refer to 8A Electrical Body and Chassis for harness routing.
4 Ensure the battery, cables and connections are in good order. Refer to 6D1-3 Battery – V6.
Diagnostic Table 120A Generator
Step Action Yes No
1 Did you review 1.3 System Operation?
Go to Step 2 Go to 1.3
System Operation
2 Did you read 2.3 Diagnostic Systems Check
Go to Step 3 Go to 2.3
Diagnostic
Systems Check
3 Perform the Generator On-vehicle Checks
W as the generator serviceable? Go to step 4 Replace the
generator.
Go to Step 5
4 Perform the Charging Circuit Voltage Drop Test.
W as the wiring serviceable? Go to 8A Electrical
Body and Chassis
Go to Step 5 Repair as required
(refer to Note 2).
Go to Step 5
5 Operate the system to verify the repair.
Did you correct the condition? System OK Go to Step 2
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3605 of 6020
Charging System – V6 Page 6D1-1-18
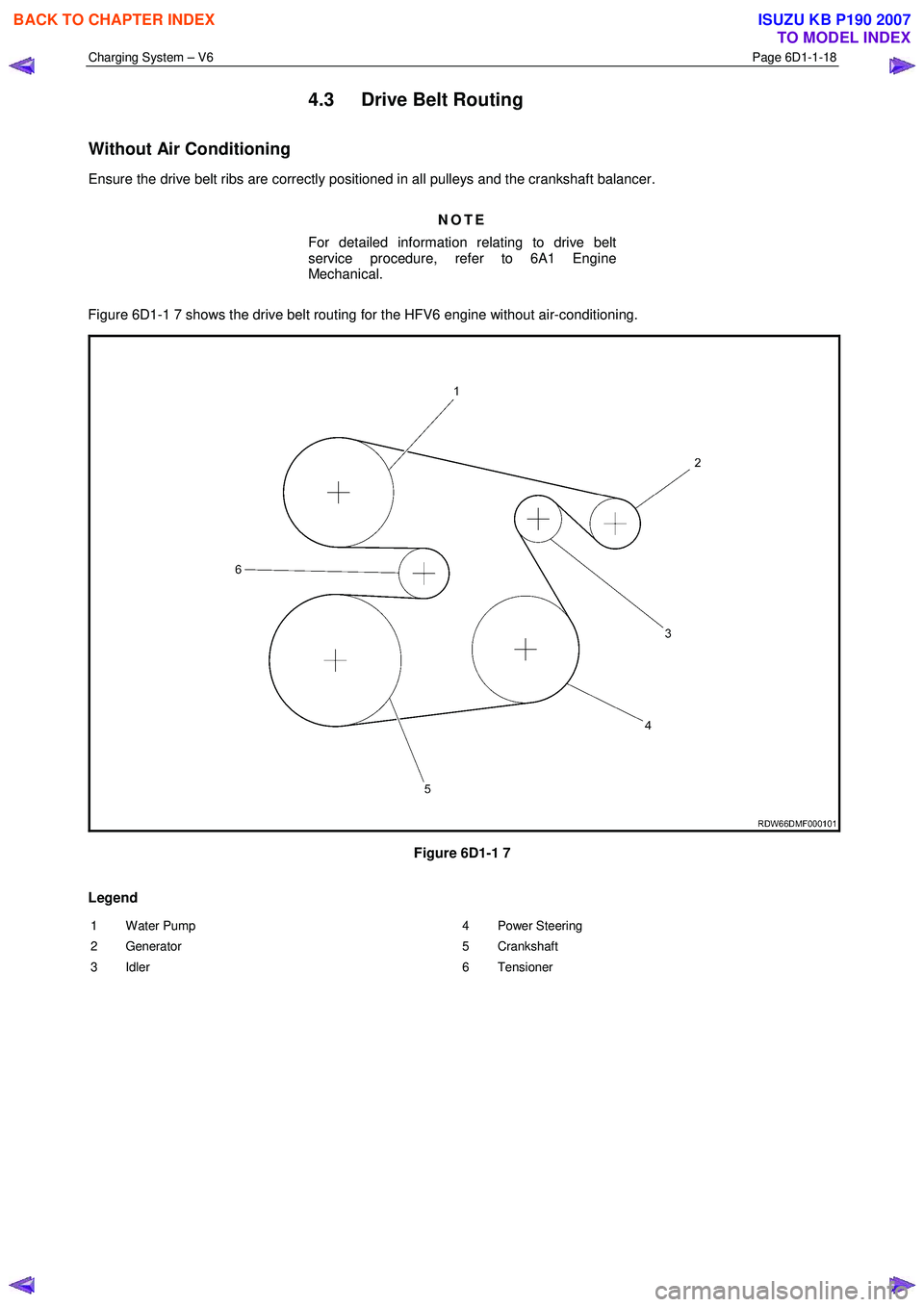
4.3 Drive Belt Routing
Without Air Conditioning
Ensure the drive belt ribs are correctly positioned in all pulleys and the crankshaft balancer.
NOTE
For detailed information relating to drive belt
service procedure, refer to 6A1 Engine
Mechanical.
Figure 6D1-1 7 shows the drive belt routing for the HFV6 engine without air-conditioning.
Figure 6D1-1 7
Legend
1 Water Pump
2 Generator
3 Idler 4 Power Steering
5 Crankshaft
6 Tensioner
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3611 of 6020

Starting System – V6 Page 6D1-2–3
1 General Information
All HFV6 engines are fitted with a Mitsubishi starter motor. This consists of a solenoid switch on a DC motor. The motor
has permanent magnet excitation, which has the advantage of low weight a with high output torque and is visually
identifiable by the absence of pole-shoe retaining screws.
The starter motor does not have field coil windings or pole shoes. These parts have been replaced by six permanent
magnets that are held in the pole housing by clips. The positive brushes are now part of the brush plate assembly.
The solenoid switch is the only component of the starter motor assembly that is serviced separately. If any other parts
require replacement, the starter motor must be replaced.
1.1 WARNING, CAUTION and NOTES
This Section contains various W ARNINGS, CAUTIONS and NOTE statements that you must observe carefully to reduce
the risk of death or injury during service, repair procedures or vehicle operation. Incorrect service or repair procedures
may damage the vehicle or cause operational faults. W ARNINGS, CAUTION and NOTE statements are not exhaustive.
HOLDEN LTD can not possibly warn of all the potentially hazardous consequences of failure to follow these instructions.
Definition of WARNING, CAUTION and NOTE Statements
Diagnosis and repair procedures in this Section contain both general and specific W ARNING, CAUTION and NOTE
statements. HOLDEN LTD is dedicated to the presentation of service information that helps the technician to diagnose
and repair the systems necessary for proper operation of the vehicle. Certain procedures may present a hazard to the
technician if they are not followed in the recommended manner. W ARNING, CAUTION and NOTE statements are
designed to help prevent these hazards from occurring, but not all hazards can be foreseen.
WARNING defined
A W ARNING statement immediately precedes an operating procedure or maintenance practice which, if not correctly
followed, could result in death or injury. A W ARNING statement alerts you to take necessary action or not to take a
prohibited action. If a W ARNING statement is ignored, the following consequences may occur:
• Death or injury to the technician or other personnel working on the vehicle,
• Death or injury to other people in or near the workplace area, and / or
• Death or injury to the driver / or passenger(s) of the vehicle or other people, if the vehicle has been improperly
repaired.
CAUTION defined
A CAUTION statement immediately precedes an operating procedure or maintenance practice which, if not correctly
followed, could result in damage to or destruction of equipment, or corruption of data. If a CAUTION statement is ignored,
the following consequences may occur:
• Damage to the vehicle,
• Unnecessary vehicle repairs or component replacement,
• Faulty operation or performance of any system or component being repaired,
• Damage to any system or components which depend on the proper operation of the system or component being
repaired,
• Faulty operation or performance of any systems or components which depend on the proper operation or
performance of the system or component under repair,
• Damage to fasteners, basic tools or special tools and / or
• Leakage of coolant, lubricant or other vital fluids.
NOTE defined
A NOTE statement immediately precedes or follows an operating procedure, maintenance practice or condition that
requires highlighting. A NOTE statement also emphasises necessary characteristics of a diagnostic or repair procedure.
A NOTE statement is designed to:
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007