2007 INFINITI QX56 engine
[x] Cancel search: enginePage 1715 of 3061
EC-632
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
IGNITION SIGNAL
: Average voltage for pulse signal (Actual pulse signal can be confirmed by oscilloscope.)
Diagnosis ProcedureINFOID:0000000003532179
1.CHECK ENGINE START
Turn ignition switch OFF, and restart engine.
Is engine running?
Ye s o r N o
Yes (With CONSULT-II)>>GO TO 2.
Yes (Without CONSULT-II)>>GO TO 3.
No >> GO TO 4.
2.CHECK OVERALL FUNCTION
With CONSULT-II
1. Perform “POWER BALANCE” in “ACTIVE TEST” mode with
CONSULT-II.
2. Make sure that each circuit produces a momentary engine
speed drop.
OK or NG
OK >>INSPECTION END
NG >> GO TO 10.
3.CHECK OVERALL FUNCTION
Without CONSULT-II
1. Let engine idle.
TER-
MI-
NAL
NO.WIRE
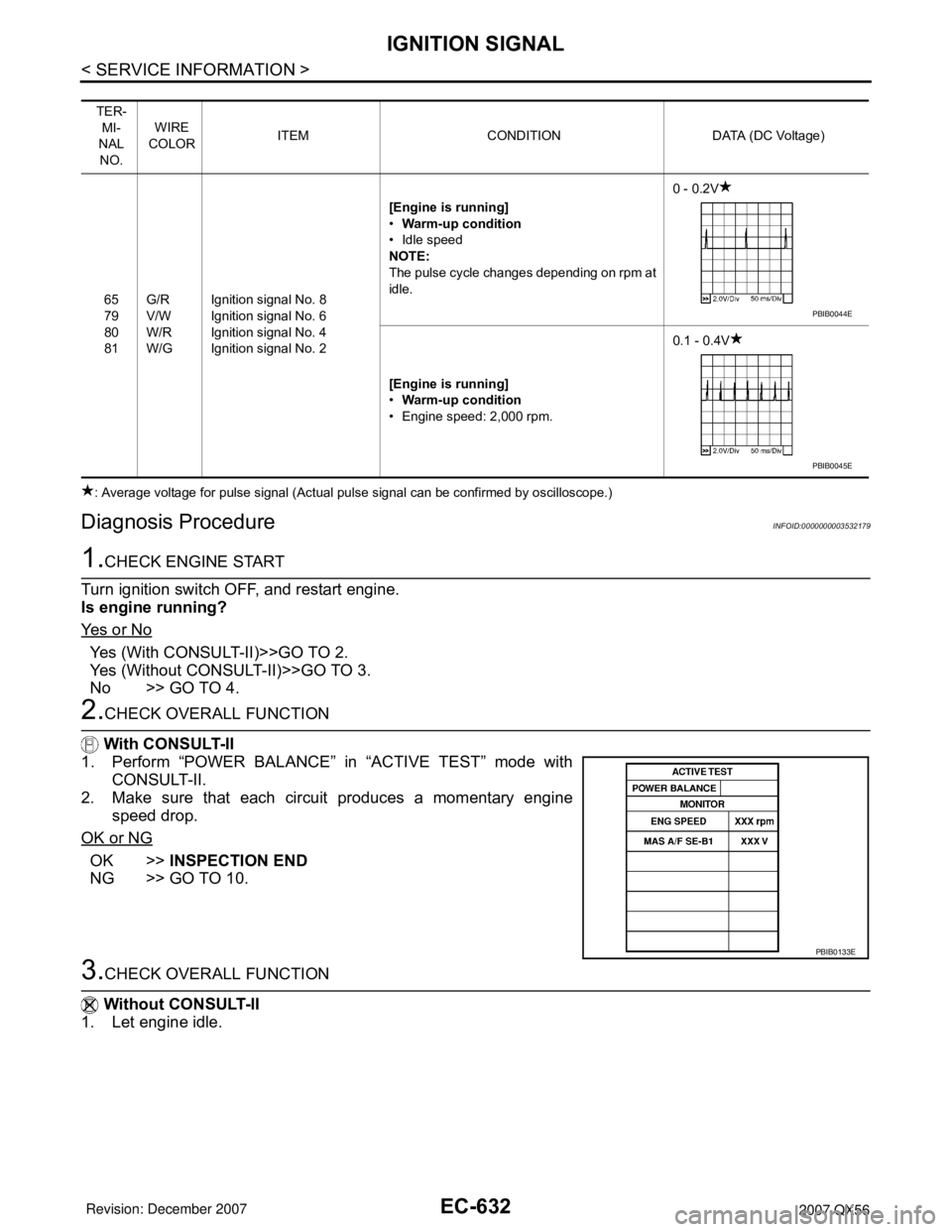
COLORITEM CONDITION DATA (DC Voltage)
65
79
80
81G/R
V/W
W/R
W/GIgnition signal No. 8
Ignition signal No. 6
Ignition signal No. 4
Ignition signal No. 2[Engine is running]
•Warm-up condition
• Idle speed
NOTE:
The pulse cycle changes depending on rpm at
idle.0 - 0.2V
[Engine is running]
•Warm-up condition
• Engine speed: 2,000 rpm.0.1 - 0.4V
PBIB0044E
PBIB0045E
PBIB0133E
Page 1719 of 3061
EC-636
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
IGNITION SIGNAL
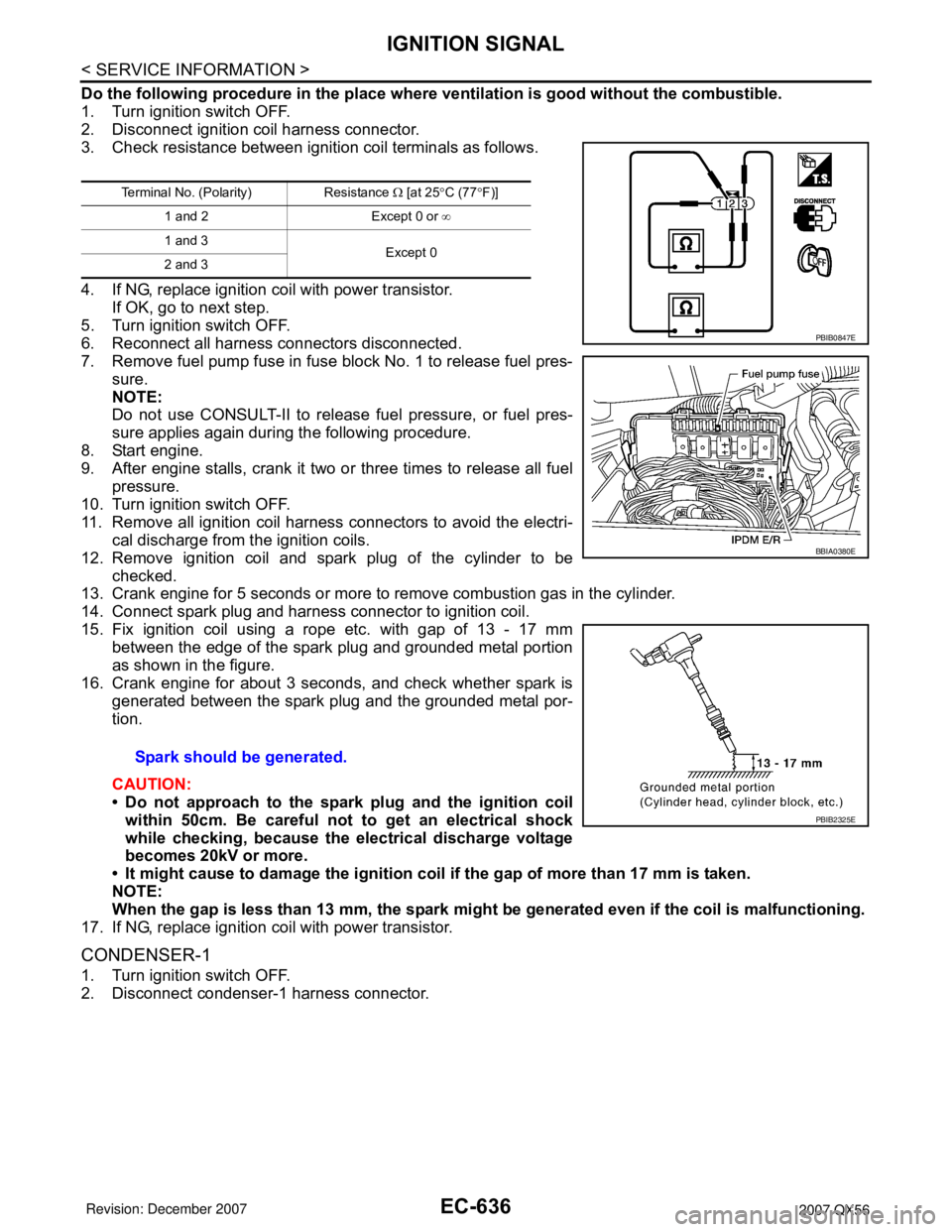
Do the following procedure in the place where ventilation is good without the combustible.
1. Turn ignition switch OFF.
2. Disconnect ignition coil harness connector.
3. Check resistance between ignition coil terminals as follows.
4. If NG, replace ignition coil with power transistor.
If OK, go to next step.
5. Turn ignition switch OFF.
6. Reconnect all harness connectors disconnected.
7. Remove fuel pump fuse in fuse block No. 1 to release fuel pres-
sure.
NOTE:
Do not use CONSULT-II to release fuel pressure, or fuel pres-
sure applies again during the following procedure.
8. Start engine.
9. After engine stalls, crank it two or three times to release all fuel
pressure.
10. Turn ignition switch OFF.
11. Remove all ignition coil harness connectors to avoid the electri-
cal discharge from the ignition coils.
12. Remove ignition coil and spark plug of the cylinder to be
checked.
13. Crank engine for 5 seconds or more to remove combustion gas in the cylinder.
14. Connect spark plug and harness connector to ignition coil.
15. Fix ignition coil using a rope etc. with gap of 13 - 17 mm
between the edge of the spark plug and grounded metal portion
as shown in the figure.
16. Crank engine for about 3 seconds, and check whether spark is
generated between the spark plug and the grounded metal por-
tion.
CAUTION:
• Do not approach to the spark plug and the ignition coil
within 50cm. Be careful not to get an electrical shock
while checking, because the electrical discharge voltage
becomes 20kV or more.
• It might cause to damage the ignition coil if the gap of more than 17 mm is taken.
NOTE:
When the gap is less than 13 mm, the spark might be generated even if the coil is malfunctioning.
17. If NG, replace ignition coil with power transistor.
CONDENSER-1
1. Turn ignition switch OFF.
2. Disconnect condenser-1 harness connector.
Terminal No. (Polarity) Resistance Ω [at 25°C (77°F)]
1 and 2 Except 0 or ∞
1 and 3
Except 0
2 and 3
Spark should be generated.
PBIB0847E
BBIA0380E
PBIB2325E
Page 1723 of 3061
EC-640
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
REFRIGERANT PRESSURE SENSOR
Diagnosis Procedure
INFOID:0000000003532184
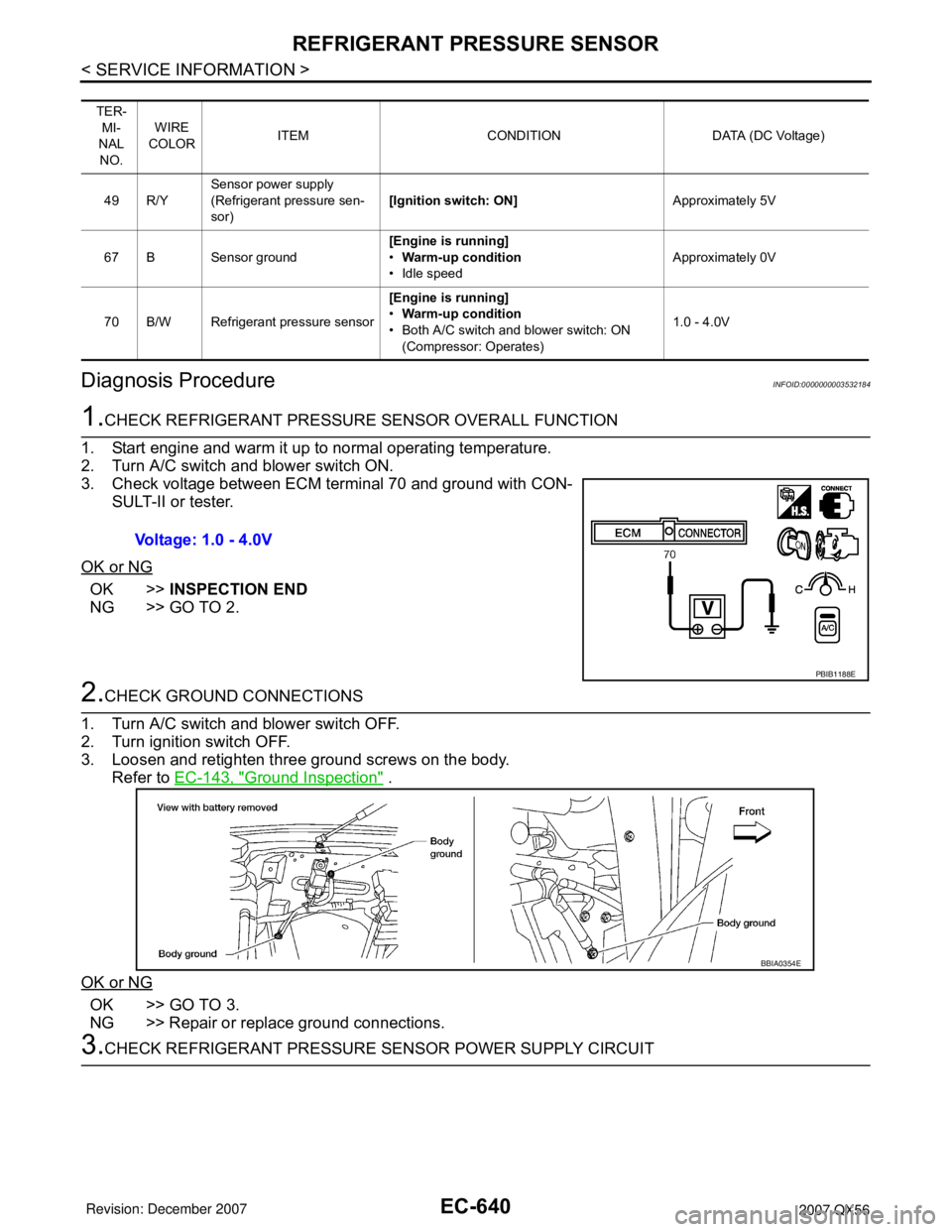
1.CHECK REFRIGERANT PRESSURE SENSOR OVERALL FUNCTION
1. Start engine and warm it up to normal operating temperature.
2. Turn A/C switch and blower switch ON.
3. Check voltage between ECM terminal 70 and ground with CON-
SULT-II or tester.
OK or NG
OK >>INSPECTION END
NG >> GO TO 2.
2.CHECK GROUND CONNECTIONS
1. Turn A/C switch and blower switch OFF.
2. Turn ignition switch OFF.
3. Loosen and retighten three ground screws on the body.
Refer to EC-143, "
Ground Inspection" .
OK or NG
OK >> GO TO 3.
NG >> Repair or replace ground connections.
3.CHECK REFRIGERANT PRESSURE SENSOR POWER SUPPLY CIRCUIT
TER-
MI-
NAL
NO.WIRE
COLORITEM CONDITION DATA (DC Voltage)
49 R/YSensor power supply
(Refrigerant pressure sen-
sor)[Ignition switch: ON]Approximately 5V
67 B Sensor ground[Engine is running]
•Warm-up condition
• Idle speedApproximately 0V
70 B/W Refrigerant pressure sensor[Engine is running]
•Warm-up condition
• Both A/C switch and blower switch: ON
(Compressor: Operates)1.0 - 4.0V
Voltage: 1.0 - 4.0V
PBIB1188E
BBIA0354E
Page 1728 of 3061

SERVICE DATA AND SPECIFICATIONS (SDS)
EC-645
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
EC
N
P O
SERVICE DATA AND SPECIFICATIONS (SDS)
Fuel PressureINFOID:0000000003532187
Idle Speed and Ignition TimingINFOID:0000000003532188
*: Under the following conditions:
• Air conditioner switch: OFF
• Electric load: OFF (Lights and heater fan)
• Steering wheel: Kept in straight-ahead position
Calculated Load ValueINFOID:0000000003532189
Mass Air Flow SensorINFOID:0000000003532190
*: Engine is warmed up to normal operating temperature and running under no load.
Intake Air Temperature SensorINFOID:0000000003532191
Engine Coolant Temperature SensorINFOID:0000000003532192
A/F Sensor 1 HeaterINFOID:0000000003532193
Heated Oxygen sensor 2 HeaterINFOID:0000000003532194
Fuel pressure at idling kPa (kg/cm2, psi)Approximately 350 (3.57, 51)
Target idle speed No-load* (in P or N position) 650±50 rpm
Air conditioner: ON In P or N position 700 rpm or more
Ignition timing In P or N position 15° ± 5° BTDC
Condition Calculated load value % (Using CONSULT-II or GST)
At idle14.0 - 33.0
At 2,500 rpm12.0 - 25.0
Supply voltage Battery voltage (11 - 14V)
Output voltage at idle1.0 - 1.3V*
Mass air flow (Using CONSULT-II or GST)3.0 - 9.0 g·m/sec at idle*
9.0 - 28.0 g·m/sec at 2,500 rpm*
Temperature °C (°F) Resistance kΩ
25 (77)1.800 - 2.200
Temperature °C (°F) Resistance kΩ
20 (68)2.1 - 2.9
50 (122)0.68 - 1.00
90 (194)0.236 - 0.260
Resistance [at 25°C (77°F)] 1.8 - 2.44Ω
Resistance [at 25°C (77°F)] 8 - 10Ω
Page 1732 of 3061
PREPARATION
EI-3
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
MA
B
EI
N
O
P
PREPARATION
Special Service ToolINFOID:0000000003533116
The actual shapes of Kent-Moore tools may differ from those of special service tools illustrated here.
Commercial Service ToolINFOID:0000000003533117
Tool number
(Kent-Moore No.)
Tool nameDescription
—
(J-39570)
Chassis earLocating the noise
—
(J-43980)
NISSAN Squeak and Rattle kitRepairing the cause of noise
SBT839
SBT840
Tool name
(Kent-Moore No.)Description
Engine ear
(J-39565)Locating the noise
SIIA0995E
Page 1734 of 3061
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
EI-5
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
MA
B
EI
N
O
P
If the noise can be duplicated easily during the test drive, to help identify the source of the noise, try to dupli-
cate the noise with the vehicle stopped by doing one or all of the following:
1) Close a door.
2) Tap or push/pull around the area where the noise appears to be coming from.
3) Rev the engine.
4) Use a floor jack to recreate vehicle “twist”.
5) At idle, apply engine load (electrical load, half-clutch on M/T model, drive position on A/T model).
6) Raise the vehicle on a hoist and hit a tire with a rubber hammer.
• Drive the vehicle and attempt to duplicate the conditions the customer states exist when the noise occurs.
• If it is difficult to duplicate the noise, drive the vehicle slowly on an undulating or rough road to stress the
vehicle body.
CHECK RELATED SERVICE BULLETINS
After verifying the customer concern or symptom, check ASIST for Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) related
to that concern or symptom.
If a TSB relates to the symptom, follow the procedure to repair the noise.
LOCATE THE NOISE AND IDENTIFY THE ROOT CAUSE
1. Narrow down the noise to a general area.To help pinpoint the source of the noise, use a listening tool
(Chassis Ear: J-39570, Engine Ear: J-39565 and mechanic's stethoscope).
2. Narrow down the noise to a more specific area and identify the cause of the noise by:
• removing the components in the area that you suspect the noise is coming from.
Do not use too much force when removing clips and fasteners, otherwise clips and fasteners can be broken
or lost during the repair, resulting in the creation of new noise.
• tapping or pushing/pulling the component that you suspect is causing the noise.
Do not tap or push/pull the component with excessive force, otherwise the noise will be eliminated only tem-
porarily.
• feeling for a vibration with your hand by touching the component(s) that you suspect is (are) causing the
noise.
• placing a piece of paper between components that you suspect are causing the noise.
• looking for loose components and contact marks.
Refer to EI-6, "
Generic Squeak and Rattle Troubleshooting".
REPAIR THE CAUSE
• If the cause is a loose component, tighten the component securely.
• If the cause is insufficient clearance between components:
- separate components by repositioning or loosening and retightening the component, if possible.
- insulate components with a suitable insulator such as urethane pads, foam blocks, felt cloth tape or urethane
tape. A NISSAN Squeak and Rattle Kit (J-43980) is available through your authorized NISSAN Parts Depart-
ment.
CAUTION:
Do not use excessive force as many components are constructed of plastic and may be damaged.
Always check with the Parts Department for the latest parts information.
The following materials are contained in the NISSAN Squeak and Rattle Kit (J-43980). Each item can be
ordered separately as needed.
URETHANE PADS [1.5 mm (0.059 in) thick]
Insulates connectors, harness, etc.
76268-9E005: 100×135 mm (3.94×5.31 in)/76884-71L01: 60×85 mm (2.36×3.35 in)/76884-71L02: 15×25
mm (0.59×0.98 in)
INSULATOR (Foam blocks)
Insulates components from contact. Can be used to fill space behind a panel.
73982-9E000: 45 mm (1.77 in) thick, 50×50 mm (1.97×1.97 in)/73982-50Y00: 10 mm (0.39 in) thick,
50×50 mm (1.97×1.97 in)
INSULATOR (Light foam block)
80845-71L00: 30 mm (1.18 in) thick, 30×50 mm (1.18×1.97 in)
FELT CLOTH TAPE
Used to insulate where movement does not occur. Ideal for instrument panel applications.
68370-4B000: 15×25 mm (0.59×0.98 in) pad/68239-13E00: 5 mm (0.20 in) wide tape roll. The following
materials not found in the kit can also be used to repair squeaks and rattles.
UHMW (TEFLON) TAPE
Insulates where slight movement is present. Ideal for instrument panel applications.
Page 1736 of 3061

SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
EI-7
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
MA
B
EI
N
O
P
Most of these incidents can be repaired by adjusting, securing or insulating the item(s) or component(s) caus-
ing the noise.
SUNROOF/HEADLINING
Noises in the sunroof/headlining area can often be traced to one of the following:
1. Sunroof lid, rail, linkage or seals making a rattle or light knocking noise
2. Sun visor shaft shaking in the holder
3. Front or rear windshield touching headliner and squeaking
Again, pressing on the components to stop the noise while duplicating the conditions can isolate most of these
incidents. Repairs usually consist of insulating with felt cloth tape.
OVERHEAD CONSOLE (FRONT AND REAR)
Overhead console noises are often caused by the console panel clips not being engaged correctly. Most of
these incidents are repaired by pushing up on the console at the clip locations until the clips engage.
In addition look for:
1. Loose harness or harness connectors.
2. Front console map/reading lamp lens loose.
3. Loose screws at console attachment points.
SEATS
When isolating seat noise it's important to note the position the seat is in and the load placed on the seat when
the noise is present. These conditions should be duplicated when verifying and isolating the cause of the
noise.
Cause of seat noise include:
1. Headrest rods and holder
2. A squeak between the seat pad cushion and frame
3. The rear seatback lock and bracket
These noises can be isolated by moving or pressing on the suspected components while duplicating the con-
ditions under which the noise occurs. Most of these incidents can be repaired by repositioning the component
or applying urethane tape to the contact area.
UNDERHOOD
Some interior noise may be caused by components under the hood or on the engine wall. The noise is then
transmitted into the passenger compartment.
Causes of transmitted underhood noise include:
1. Any component installed to the engine wall
2. Components that pass through the engine wall
3. Engine wall mounts and connectors
4. Loose radiator installation pins
5. Hood bumpers out of adjustment
6. Hood striker out of adjustment
These noises can be difficult to isolate since they cannot be reached from the interior of the vehicle. The best
method is to secure, move or insulate one component at a time and test drive the vehicle. Also, engine RPM
or load can be changed to isolate the noise. Repairs can usually be made by moving, adjusting, securing, or
insulating the component causing the noise.
Page 1741 of 3061
EI-12
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
FRONT BUMPER
FRONT BUMPER
Removal and InstallationINFOID:0000000003533122
REMOVAL
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Remove side screws from front fascia assembly.
3. Remove screws from front of fender protector. Refer to EI-22
.
4. Remove fog turn/fog lamp finisher and fog turn/fog lamp.
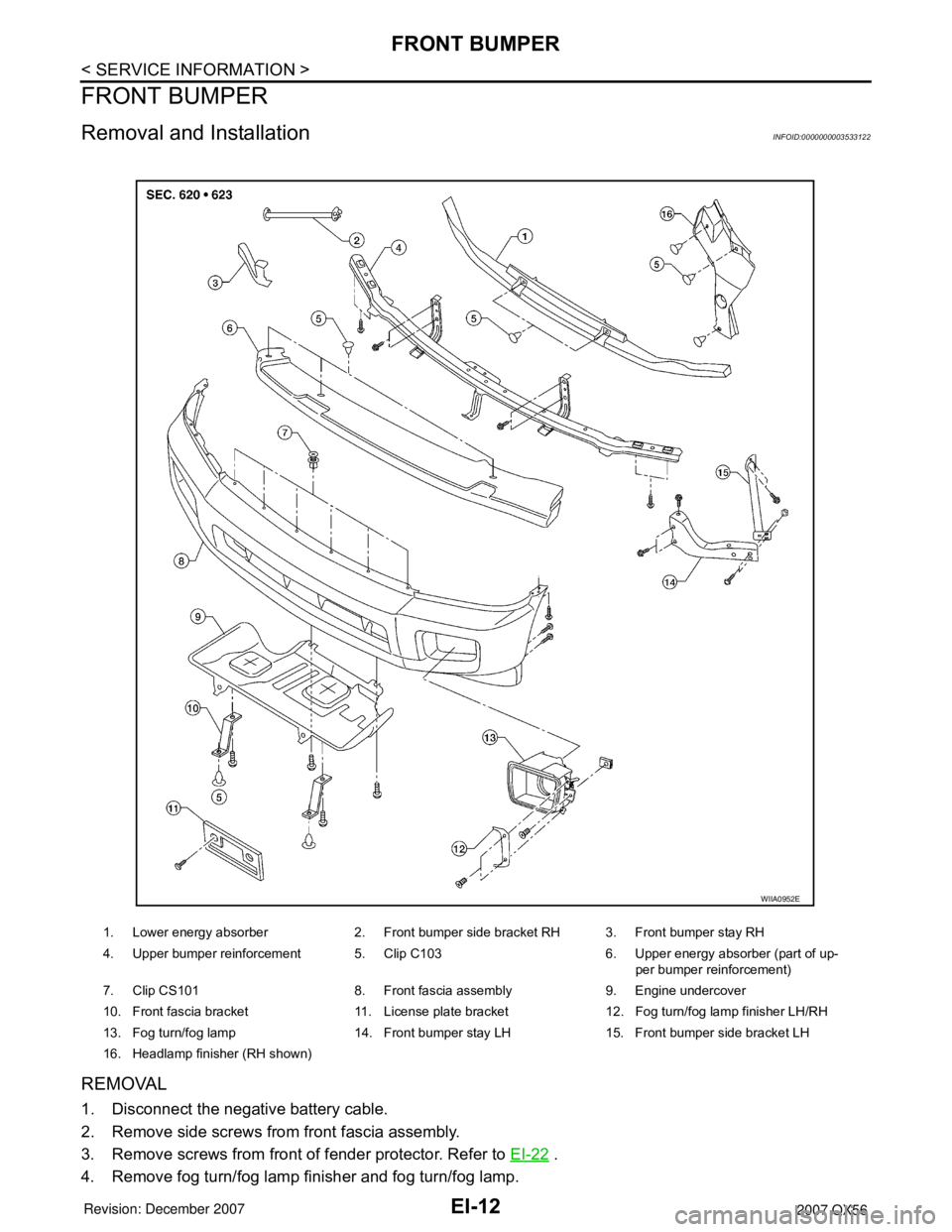
1. Lower energy absorber 2. Front bumper side bracket RH 3. Front bumper stay RH
4. Upper bumper reinforcement 5. Clip C103 6. Upper energy absorber (part of up-
per bumper reinforcement)
7. Clip CS101 8. Front fascia assembly 9. Engine undercover
10. Front fascia bracket 11. License plate bracket 12. Fog turn/fog lamp finisher LH/RH
13. Fog turn/fog lamp 14. Front bumper stay LH 15. Front bumper side bracket LH
16. Headlamp finisher (RH shown)
WIIA0952E