2007 INFINITI QX56 light
[x] Cancel search: lightPage 2025 of 3061
GW-6
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
If the noise can be duplicated easily during the test drive, to help identify the source of the noise, try to dupli-
cate the noise with the vehicle stopped by doing one or all of the following:
1) Close a door.
2) Tap or push/pull around the area where the noise appears to be coming from.
3) Rev the engine.
4) Use a floor jack to recreate vehicle “twist”.
5) At idle, apply engine load (electrical load, half-clutch on M/T model, drive position on A/T model).
6) Raise the vehicle on a hoist and hit a tire with a rubber hammer.
• Drive the vehicle and attempt to duplicate the conditions the customer states exist when the noise occurs.
• If it is difficult to duplicate the noise, drive the vehicle slowly on an undulating or rough road to stress the
vehicle body.
CHECK RELATED SERVICE BULLETINS
After verifying the customer concern or symptom, check ASIST for Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) related
to that concern or symptom.
If a TSB relates to the symptom, follow the procedure to repair the noise.
LOCATE THE NOISE AND IDENTIFY THE ROOT CAUSE
1. Narrow down the noise to a general area.To help pinpoint the source of the noise, use a listening tool
(Chassis Ear: J-39570, Engine Ear: J-39565 and mechanic's stethoscope).
2. Narrow down the noise to a more specific area and identify the cause of the noise by:
• removing the components in the area that you suspect the noise is coming from.
Do not use too much force when removing clips and fasteners, otherwise clips and fasteners can be broken
or lost during the repair, resulting in the creation of new noise.
• tapping or pushing/pulling the component that you suspect is causing the noise.
Do not tap or push/pull the component with excessive force, otherwise the noise will be eliminated only tem-
porarily.
• feeling for a vibration with your hand by touching the component(s) that you suspect is (are) causing the
noise.
• placing a piece of paper between components that you suspect are causing the noise.
• looking for loose components and contact marks.
Refer to GW-7, "
Generic Squeak and Rattle Troubleshooting".
REPAIR THE CAUSE
• If the cause is a loose component, tighten the component securely.
• If the cause is insufficient clearance between components:
- separate components by repositioning or loosening and retightening the component, if possible.
- insulate components with a suitable insulator such as urethane pads, foam blocks, felt cloth tape or urethane
tape. A NISSAN Squeak and Rattle Kit (J-43980) is available through your authorized NISSAN Parts Depart-
ment.
CAUTION:
Do not use excessive force as many components are constructed of plastic and may be damaged.
Always check with the Parts Department for the latest parts information.
The following materials are contained in the NISSAN Squeak and Rattle Kit (J-43980). Each item can be
ordered separately as needed.
URETHANE PADS [1.5 mm (0.059 in) thick]
Insulates connectors, harness, etc.
76268-9E005: 100×135 mm (3.94×5.31 in)/76884-71L01: 60×85 mm (2.36×3.35 in)/76884-71L02: 15×25
mm (0.59×0.98 in)
INSULATOR (Foam blocks)
Insulates components from contact. Can be used to fill space behind a panel.
73982-9E000: 45 mm (1.77 in) thick, 50×50 mm (1.97×1.97 in)/73982-50Y00: 10 mm (0.39 in) thick,
50×50 mm (1.97×1.97 in)
INSULATOR (Light foam block)
80845-71L00: 30 mm (1.18 in) thick, 30×50 mm (1.18×1.97 in)
FELT CLOTH TAPE
Used to insulate where movement does not occur. Ideal for instrument panel applications.
68370-4B000: 15×25 mm (0.59×0.98 in) pad/68239-13E00: 5 mm (0.20 in) wide tape roll. The following mate-
rials not found in the kit can also be used to repair squeaks and rattles.
UHMW (TEFLON) TAPE
Insulates where slight movement is present. Ideal for instrument panel applications.
Page 2027 of 3061

GW-8
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
Most of these incidents can be repaired by adjusting, securing or insulating the item(s) or component(s) caus-
ing the noise.
SUNROOF/HEADLINER
Noises in the sunroof/headliner area can often be traced to one of the following:
1. Sunroof lid, rail, linkage or seals making a rattle or light knocking noise
2. Sun visor shaft shaking in the holder
3. Front or rear windshield touching headliner and squeaking
Again, pressing on the components to stop the noise while duplicating the conditions can isolate most of these
incidents. Repairs usually consist of insulating with felt cloth tape.
OVERHEAD CONSOLE (FRONT AND REAR)
Overhead console noises are often caused by the console panel clips not being engaged correctly. Most of
these incidents are repaired by pushing up on the console at the clip locations until the clips engage.
In addition look for:
1. Loose harness or harness connectors.
2. Front console map/reading lamp lense loose.
3. Loose screws at console attachment points.
SEATS
When isolating seat noise it's important to note the position the seat is in and the load placed on the seat when
the noise is present. These conditions should be duplicated when verifying and isolating the cause of the
noise.
Cause of seat noise include:
1. Headrest rods and holder
2. A squeak between the seat pad cushion and frame
3. The rear seatback lock and bracket
These noises can be isolated by moving or pressing on the suspected components while duplicating the con-
ditions under which the noise occurs. Most of these incidents can be repaired by repositioning the component
or applying urethane tape to the contact area.
UNDERHOOD
Some interior noise may be caused by components under the hood or on the engine wall. The noise is then
transmitted into the passenger compartment.
Causes of transmitted underhood noise include:
1. Any component mounted to the engine wall
2. Components that pass through the engine wall
3. Engine wall mounts and connectors
4. Loose radiator mounting pins
5. Hood bumpers out of adjustment
6. Hood striker out of adjustment
These noises can be difficult to isolate since they cannot be reached from the interior of the vehicle. The best
method is to secure, move or insulate one component at a time and test drive the vehicle. Also, engine RPM
or load can be changed to isolate the noise. Repairs can usually be made by moving, adjusting, securing, or
insulating the component causing the noise.
Page 2079 of 3061
GW-60
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
FRONT DOOR GLASS AND REGULATOR
Fitting Inspection
• Check that the glass is securely fit into the glass run groove.
• Lower the glass slightly [approximately 10 to 20 mm (0.39 to 0.79 in)] and check that the clearance to the
sash is parallel. If the clearance between the glass and sash is not parallel, loosen the regulator bolts, guide
rail bolts, and glass and guide rail bolts to correct the glass position.
FRONT DOOR GLASS REGULATOR
Removal
1. Remove the front door speaker. Refer to AV-46, "Removal and Installation".
2. Remove the hole cover over rear glass bolt.
3. Temporarily reconnect the power window switch.
4. Operate the power window main switch to raise/lower the door window until the glass bolts can be seen.
5. Partially remove the inside seal.
6. Remove the glass bolts.
7. Raise the front door glass and hold it in place with suitable tool.
8. Disconnect the harness connector from the regulator assembly.
9. Remove the bolts and the regulator assembly.
Disassembly And Assembly
Remove the regulator motor from the regulator assembly.
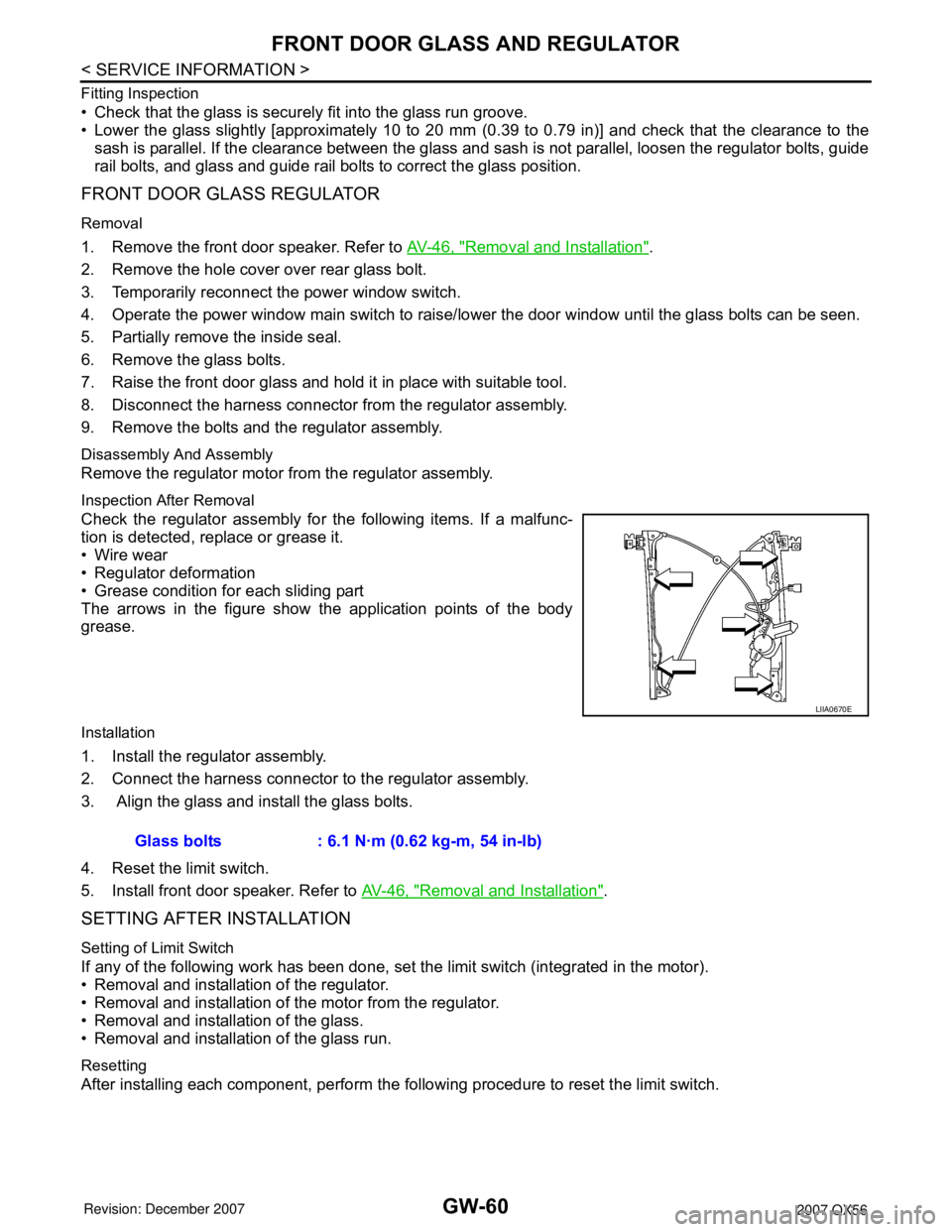
Inspection After Removal
Check the regulator assembly for the following items. If a malfunc-
tion is detected, replace or grease it.
• Wire wear
• Regulator deformation
• Grease condition for each sliding part
The arrows in the figure show the application points of the body
grease.
Installation
1. Install the regulator assembly.
2. Connect the harness connector to the regulator assembly.
3. Align the glass and install the glass bolts.
4. Reset the limit switch.
5. Install front door speaker. Refer to AV-46, "
Removal and Installation".
SETTING AFTER INSTALLATION
Setting of Limit Switch
If any of the following work has been done, set the limit switch (integrated in the motor).
• Removal and installation of the regulator.
• Removal and installation of the motor from the regulator.
• Removal and installation of the glass.
• Removal and installation of the glass run.
Resetting
After installing each component, perform the following procedure to reset the limit switch.
LIIA0670E
Glass bolts : 6.1 N·m (0.62 kg-m, 54 in-lb)
Page 2081 of 3061
GW-62
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
REAR DOOR GLASS AND REGULATOR
REAR DOOR GLASS AND REGULATOR
Removal and InstallationINFOID:0000000003533062
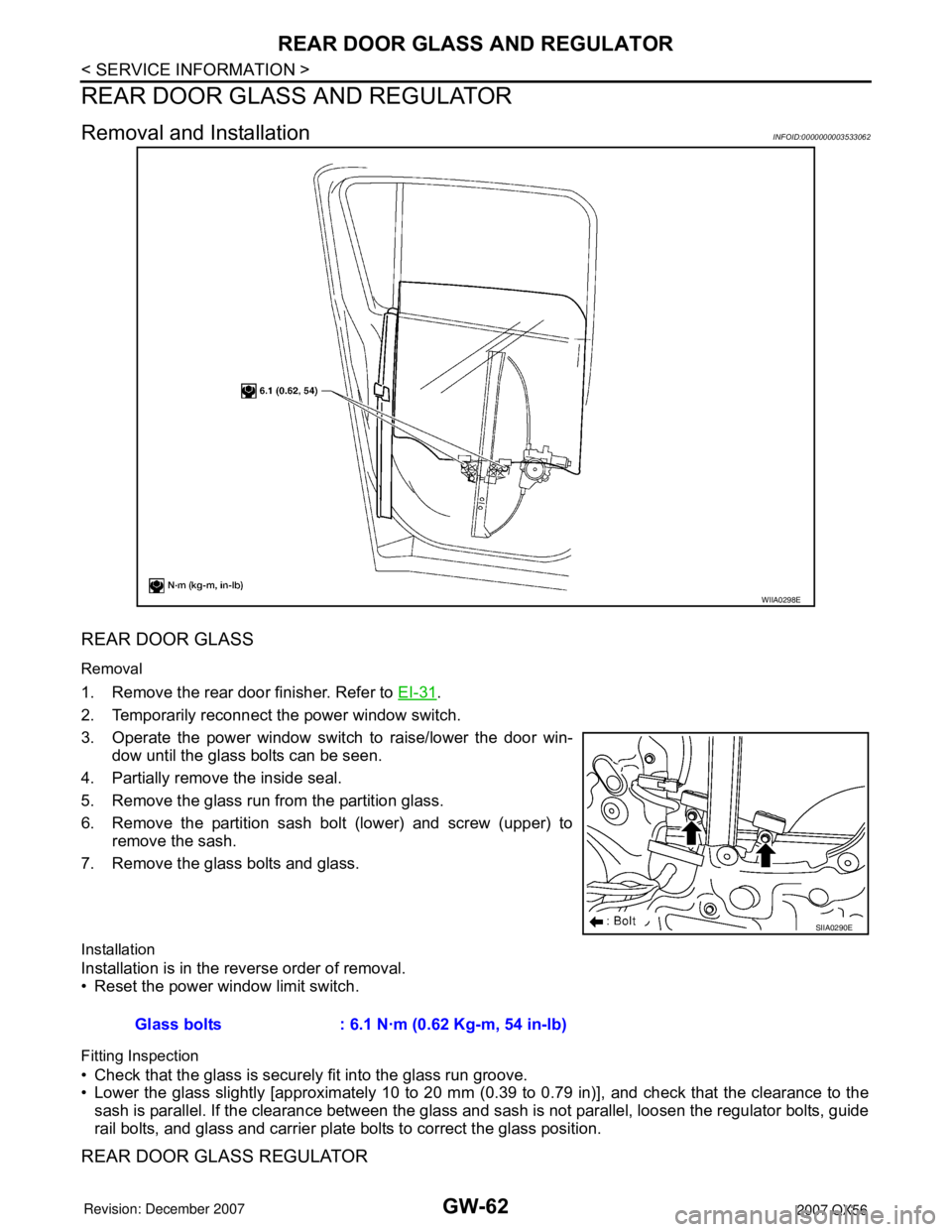
REAR DOOR GLASS
Removal
1. Remove the rear door finisher. Refer to EI-31.
2. Temporarily reconnect the power window switch.
3. Operate the power window switch to raise/lower the door win-
dow until the glass bolts can be seen.
4. Partially remove the inside seal.
5. Remove the glass run from the partition glass.
6. Remove the partition sash bolt (lower) and screw (upper) to
remove the sash.
7. Remove the glass bolts and glass.
Installation
Installation is in the reverse order of removal.
• Reset the power window limit switch.
Fitting Inspection
• Check that the glass is securely fit into the glass run groove.
• Lower the glass slightly [approximately 10 to 20 mm (0.39 to 0.79 in)], and check that the clearance to the
sash is parallel. If the clearance between the glass and sash is not parallel, loosen the regulator bolts, guide
rail bolts, and glass and carrier plate bolts to correct the glass position.
REAR DOOR GLASS REGULATOR
WIIA0298E
SIIA0290E
Glass bolts : 6.1 N·m (0.62 Kg-m, 54 in-lb)
Page 2094 of 3061
REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER
GW-75
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
MA
B
GW
N
O
P
BCM Power Supply and Ground Circuit InspectionINFOID:0000000003533076
Refer to BCS-15, "BCM Power Supply and Ground Circuit Inspection".
Rear Window Defogger Switch Circuit InspectionINFOID:0000000003533077
1.CHECK REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER SWITCH OPERATION
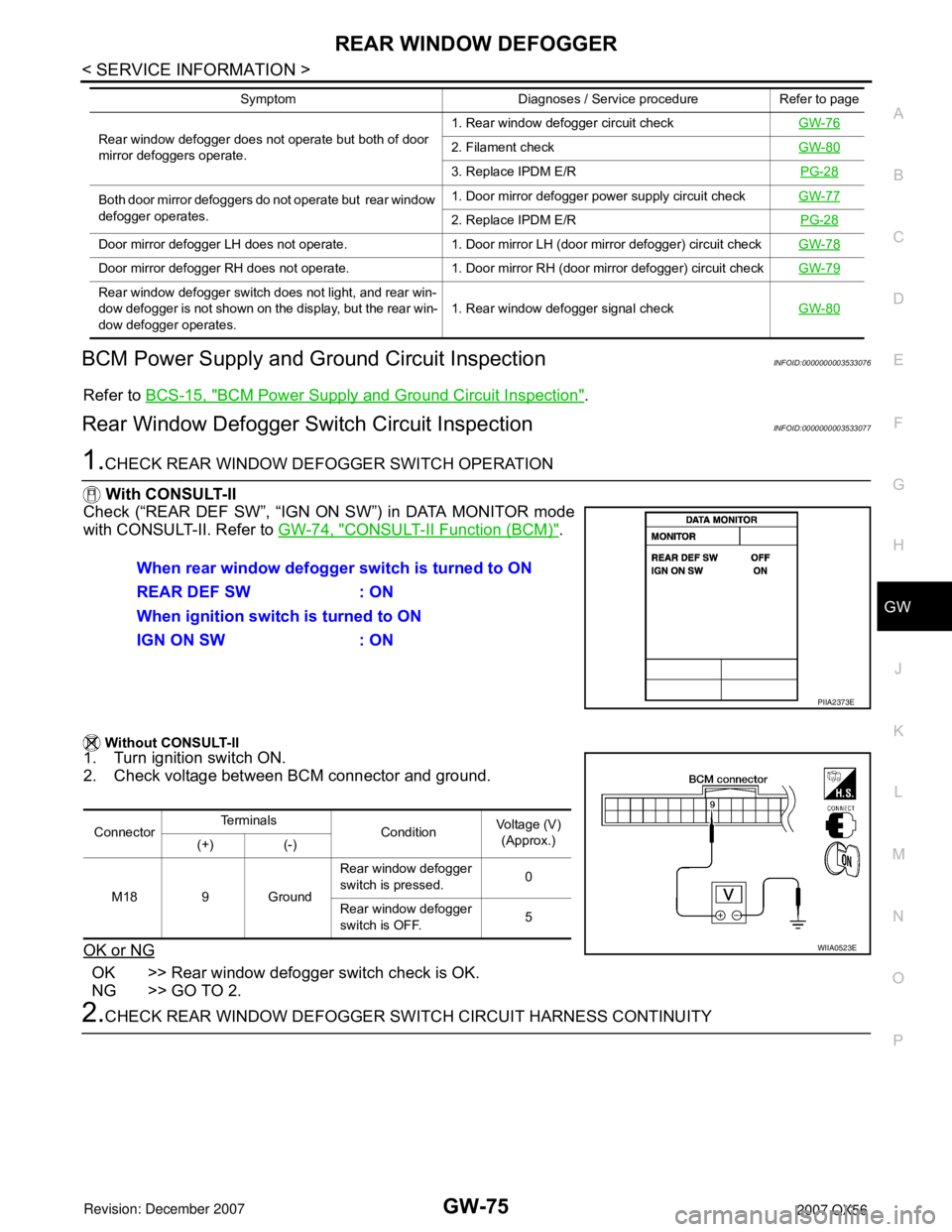
With CONSULT-II
Check (“REAR DEF SW”, “IGN ON SW”) in DATA MONITOR mode
with CONSULT-II. Refer to GW-74, "
CONSULT-II Function (BCM)".
Without CONSULT-II
1. Turn ignition switch ON.
2. Check voltage between BCM connector and ground.
OK or NG
OK >> Rear window defogger switch check is OK.
NG >> GO TO 2.
2.CHECK REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER SWITCH CIRCUIT HARNESS CONTINUITY
Rear window defogger does not operate but both of door
mirror defoggers operate.1. Rear window defogger circuit checkGW-762. Filament checkGW-80
3. Replace IPDM E/RPG-28
Both door mirror defoggers do not operate but rear window
defogger operates.1. Door mirror defogger power supply circuit checkGW-77
2. Replace IPDM E/RPG-28
Door mirror defogger LH does not operate. 1. Door mirror LH (door mirror defogger) circuit checkGW-78
Door mirror defogger RH does not operate. 1. Door mirror RH (door mirror defogger) circuit checkGW-79
Rear window defogger switch does not light, and rear win-
dow defogger is not shown on the display, but the rear win-
dow defogger operates. 1. Rear window defogger signal checkGW-80
Symptom Diagnoses / Service procedure Refer to page
When rear window defogger switch is turned to ON
REAR DEF SW : ON
When ignition switch is turned to ON
IGN ON SW : ON
PIIA2373E
ConnectorTe r m i n a l s
ConditionVoltage (V)
(Approx.)
(+) (-)
M18 9 GroundRear window defogger
switch is pressed.0
Rear window defogger
switch is OFF.5
WIIA0523E
Page 2100 of 3061
REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER
GW-81
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
MA
B
GW
N
O
P
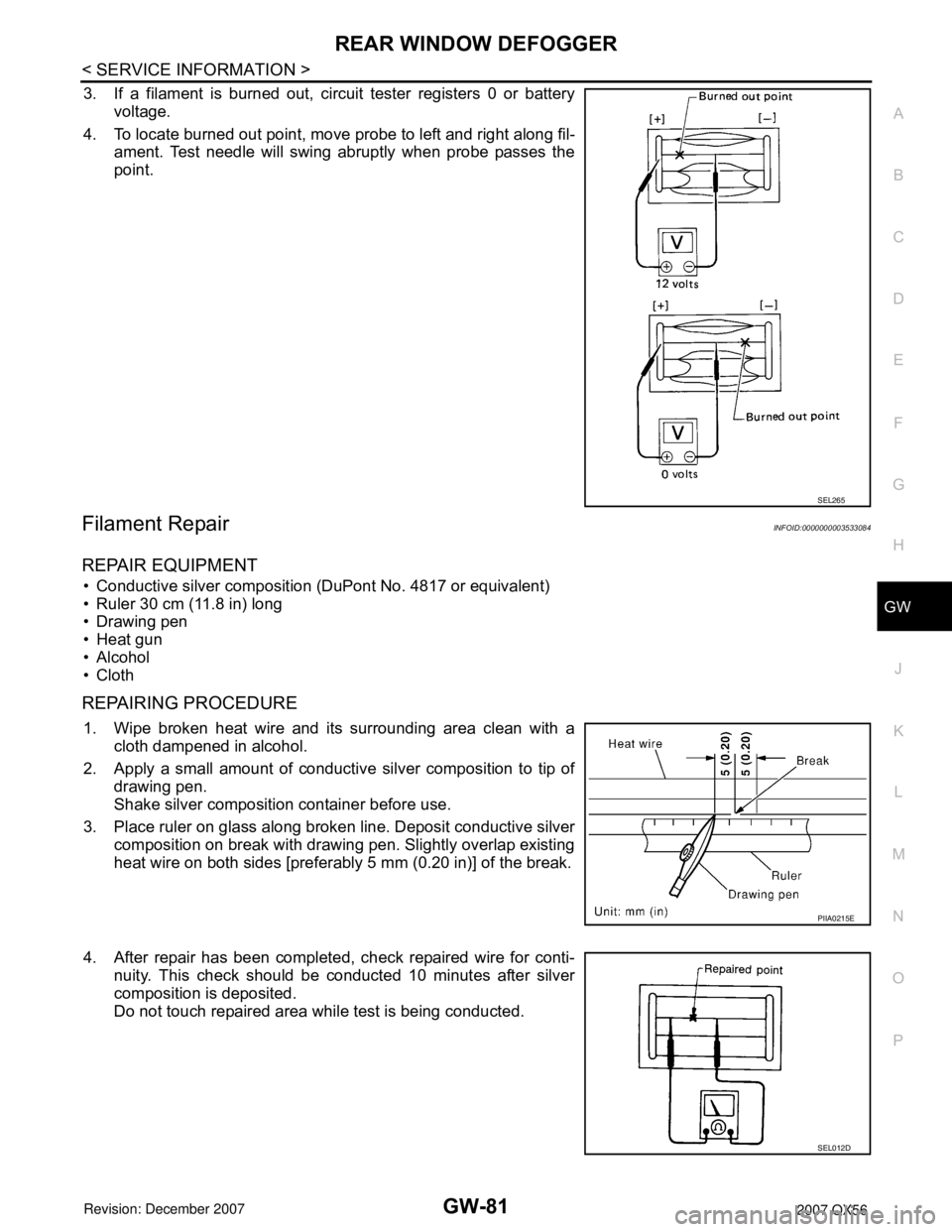
3. If a filament is burned out, circuit tester registers 0 or battery
voltage.
4. To locate burned out point, move probe to left and right along fil-
ament. Test needle will swing abruptly when probe passes the
point.
Filament RepairINFOID:0000000003533084
REPAIR EQUIPMENT
• Conductive silver composition (DuPont No. 4817 or equivalent)
• Ruler 30 cm (11.8 in) long
• Drawing pen
• Heat gun
• Alcohol
• Cloth
REPAIRING PROCEDURE
1. Wipe broken heat wire and its surrounding area clean with a
cloth dampened in alcohol.
2. Apply a small amount of conductive silver composition to tip of
drawing pen.
Shake silver composition container before use.
3. Place ruler on glass along broken line. Deposit conductive silver
composition on break with drawing pen. Slightly overlap existing
heat wire on both sides [preferably 5 mm (0.20 in)] of the break.
4. After repair has been completed, check repaired wire for conti-
nuity. This check should be conducted 10 minutes after silver
composition is deposited.
Do not touch repaired area while test is being conducted.
SEL265
PIIA0215E
SEL012D
Page 2107 of 3061
IDX-3
A
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L B
IDX
ALPHABETICAL INDEX
Brake fluid level ................................................. MA-28
Brake hydraulic line ........................................... BR-12
Brake inspection ................................................ MA-28
Brake lines and cables inspection ..................... MA-28
Brake master cylinder ....................................... BR-15
Brake switch ...................................... EC-572, EC-584
BRK/SW - Wiring diagram ............................... EC-585
Bulb specifications ........................................... LT-148
Bumper, front ...................................................... EI-13
Bumper, rear ....................................................... EI-15
C
Cabin air filter .................................................... MA-21
Camshaft ........................................................... EM-46
Camshaft inspection .......................................... EM-49
Camshaft position sensor (PHASE) ................ EC-369
CAN - Wiring diagram .............. EC-157, AT-93, AT-94
CAN communication EC-32, EC-156, EC-159, TF-112,
RSU-6
Canister-See EVAP canister ............................. EC-36
Center case (Transfer) ....................... TF-154, TF-167
CHARGE - Wiring diagram ............................... SC-19
Charging system ............................................... SC-17
Chassis and body maintenance ........................ MA-21
Chassis and body maintenanceSchedule 1 ........ MA-8
Chassis and body maintenanceSchedule 2 ...... MA-10
CHIME - Wiring diagram ..................................... DI-41
Circuit breaker ................................................... PG-17
Clock ................................................................... DI-61
CLOCK - Wiring diagram .................................... DI-61
Closed loop control ............................. EC-26, EC-501
Closed loop control (Bank 1) ........................... EC-501
Closed loop control (Bank 2) ........................... EC-501
Clutch drum (Transfer) ....................... TF-154, TF-167
Clutch pressure switch (Transfer) ...... TF-154, TF-167
Coil spring (front) ............................................. FSU-10
Collision diagnosis .......................................... SRS-53
Combination lamp, front, removal and installation . LT-
25
Combination lamp, rear, removal and installation .. LT-
101
Combination meter ................................................ DI-5
Combination switch ............................................ LT-79
COMBSW - Wiring diagram ............................... LT-79
COMM - Wiring diagram ................................... AV-94
COMPAS - Wiring diagram ................................. DI-24
Compass ............................................................. DI-23
Component Location (auto A/C) ...................... ATC-38
Compressor clutch removal and installation . ATC-180
Compressor mounting ................................... ATC-179
Compressor precaution ................................... ATC-11
Compressor special service tool ..................... ATC-14
Condenser ..................................................... ATC-184
Connecting rod .................................................. EM-96
Connecting rod bearing clearance .................... EM-96
Connecting rod bushing clearance .................... EM-96
Console box - See Instrument panel ................... IP-10
CONSULT for VDC ......................................... BRC-27
CONSULT general information ........................... GI-37
CONSULT-II for engine ................................... EC-118
Control units (terminal arrangement) ................. PG-71
Control valve (A/T) ............................................. AT-36
Control valve (Transfer) ...................... TF-154, TF-167
Converter housing installation ............ AT-240, AT-244
COOL/F - Wiring diagram ................................ EC-507
Coolant mixture ratio ......................................... MA-12
Coolant replacement ............................ CO-10, MA-13
Cooling circuit (engine) ........................................ CO-8
Cooling fan ........................................................ CO-17
Cooling fan control ........................................... EC-504
Cooling fan motor ............................................ EC-513
Cooling unit (A/C evaporator) ....... ATC-157, ATC-186
Corrosion protection ......................................... BL-157
Crankcase ventilation system - See Positive crankcase
ventilation .......................................................... EC-46
Crankshaft ......................................................... EM-79
Crankshaft position sensor (POS) ................... EC-362
Crash zone sensor .......................................... SRS-48
CUR/SE - Wiring diagram ... EC-522, EC-529, EC-536,
EC-543
Cylinder block .................................................... EM-78
Cylinder block boring ......................................... EM-99
D
D/LOCK - Wiring diagram ................................... BL-19
Data link connector for Consult ......... EC-120, EC-132
Daytime light system .......................................... LT-27
Daytime running light - See Daytime light system .. LT-
27
DEF - Wiring diagram ....................................... GW-74
Diagnosis sensor unit ...................................... SRS-51
Diagnostic trouble code (DTC) for OBD system . EC-9,
EC-54
Diagnostic trouble code (DTC) inspection priority chart
EC-91
Differential carrier assembly ............................ RFD-15
Differential gear oil replacement ........................ MA-26
Dimensions ......................................................... GI-51
Direct clutch solenoid valve ................ AT-143, AT-145
Display and amp.assembly .............................. ATC-59
Display Control Unit ........................................... AV-83
Display Unit ....................................................... AV-83
Dome light - See Interior lamp .......................... LT-110
Door glass .......................................... GW-62, GW-65
Door lock .......................................................... BL-121
Door mirror lamp ............................................... LT-110
Door trim .............................................................. EI-32
Door, front ........................................... BL-117, GW-62
Door, rear ........................................... BL-117, GW-65
Drive belt ........................................................... EM-13
Drive chain (Transfer) ......................... TF-149, TF-176
Drive pinion diff. inspection .............................. RFD-18
Drive shaft (rear) ................................................ RAX-7
Driver air bag ................................................... SRS-39
DTC work support ............................................ EC-128
DTRL - Wiring diagram ....................................... LT-31
Page 2116 of 3061
IP-4
< SERVICE INFORMATION >
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
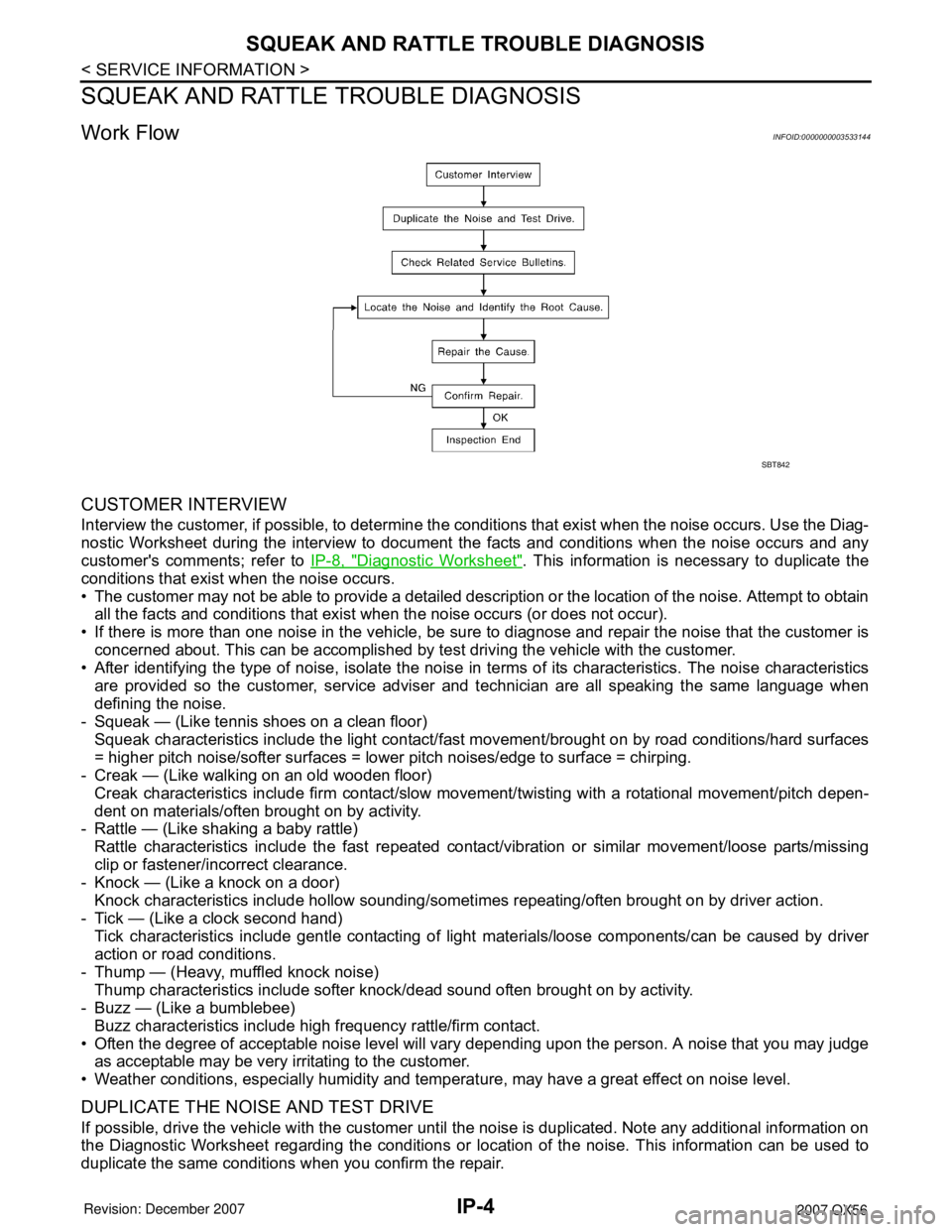
Work FlowINFOID:0000000003533144
CUSTOMER INTERVIEW
Interview the customer, if possible, to determine the conditions that exist when the noise occurs. Use the Diag-
nostic Worksheet during the interview to document the facts and conditions when the noise occurs and any
customer's comments; refer to IP-8, "
Diagnostic Worksheet". This information is necessary to duplicate the
conditions that exist when the noise occurs.
• The customer may not be able to provide a detailed description or the location of the noise. Attempt to obtain
all the facts and conditions that exist when the noise occurs (or does not occur).
• If there is more than one noise in the vehicle, be sure to diagnose and repair the noise that the customer is
concerned about. This can be accomplished by test driving the vehicle with the customer.
• After identifying the type of noise, isolate the noise in terms of its characteristics. The noise characteristics
are provided so the customer, service adviser and technician are all speaking the same language when
defining the noise.
- Squeak — (Like tennis shoes on a clean floor)
Squeak characteristics include the light contact/fast movement/brought on by road conditions/hard surfaces
= higher pitch noise/softer surfaces = lower pitch noises/edge to surface = chirping.
- Creak — (Like walking on an old wooden floor)
Creak characteristics include firm contact/slow movement/twisting with a rotational movement/pitch depen-
dent on materials/often brought on by activity.
- Rattle — (Like shaking a baby rattle)
Rattle characteristics include the fast repeated contact/vibration or similar movement/loose parts/missing
clip or fastener/incorrect clearance.
- Knock — (Like a knock on a door)
Knock characteristics include hollow sounding/sometimes repeating/often brought on by driver action.
- Tick — (Like a clock second hand)
Tick characteristics include gentle contacting of light materials/loose components/can be caused by driver
action or road conditions.
- Thump — (Heavy, muffled knock noise)
Thump characteristics include softer knock/dead sound often brought on by activity.
- Buzz — (Like a bumblebee)
Buzz characteristics include high frequency rattle/firm contact.
• Often the degree of acceptable noise level will vary depending upon the person. A noise that you may judge
as acceptable may be very irritating to the customer.
• Weather conditions, especially humidity and temperature, may have a great effect on noise level.
DUPLICATE THE NOISE AND TEST DRIVE
If possible, drive the vehicle with the customer until the noise is duplicated. Note any additional information on
the Diagnostic Worksheet regarding the conditions or location of the noise. This information can be used to
duplicate the same conditions when you confirm the repair.
SBT842