Page 17 of 2000
ENGINE - 2AZ-FE ENGINE
01NEG37Y
Mesh Type Gasket
01NEG38Y
TWC EG-20
4. Intake Manifold
The intake manifold has been made of plastic to reduce the weight and the amount of heat transferred from
the cylinder head. As a result, it has become possible to reduce the intake air temperature and improve the
intake volumetric efficiency.
A mesh type gasket is used, in order to reduce the intake noise.
5. Exhaust Manifold
A stainless steel exhaust manifold is used for improving the warm-up of TWC (Three-Way Catalytic
converter) and for weight reduction.
Page 133 of 2000
CHASSIS - 4WD SYSTEM CH-66
4WD SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
The 4WD system of the ’06 RAV4 uses an active torque control 4WD system.
It is a compact, lightweight, and high performance 4WD system that optimally controls the torque
distribution to the front and rear wheels through the electric control coupling in the rear differential.
ACTIVE TORQUE CONTROL 4WD SYSTEM
1. General
Based on information provided by various sensors, the 4WD ECU controls the amperage that is applied
to the electric control coupling, in order to transmit drive torque to the rear wheels when needed, and in
the amount needed. The following describes the features of the active torque control 4WD system.
Traction performance
Realizes stable start-off and acceleration performance
Driving stability performanceRealizes stable cornering performance
Fuel economyRealizes better fuel economy by transmitting drive torque to the rear
wheels when needed, in the amount needed.
A four-wheel drive lock switch has been provided. This enables the driver to select between the AUTO
and LOCK modes by operating the switch. The system optimally controls the torque distribution to the
front and rear wheels in the respective modes.
Mode
Four-wheel Drive
Lock Switch and
Indicator Light
Outline
AUTOOFF
Optimally distributes drive torque to the front and rear wheels.
Ensures optimal start-off performance during a start-off, based on
information provided by various sensors.
Suppresses the tight corner braking phenomenon* during low-speed
cornering.
Reduces the amount of torque distribution to the rear wheels and
improves fuel economy when the system judges that the vehicle is
traveling steadily.
Disengages the 4WD during braking deceleration.
LOCKON
Distributes the maximum torque limit to the rear wheels.
Distributes the maximum torque limit to the rear wheels during
start-off.
Distributes optimal torque during low-speed cornering.
Disengages the 4WD during braking deceleration.
Disengages the LOCK mode and transfers to the AUTO mode when
the vehicle speed exceeds 40 km / h (25 mph).
*: Tight corner braking phenomenon: a condition in which the brakes are applied due to a rotational difference
between the front and rear wheels, such as during low-speed cornering in the 4WD mode.
The 4WD ECU effects cooperative control with the skid control ECU, in order to control the drive torque
distribution to the front and rear wheels in accordance with information received from the skid control
ECU. These controls ensure a smooth acceleration and driving stability.
Page 138 of 2000

CHASSIS - 4WD SYSTEM
Service Tip
When the 4WD ECU judges that the vehicle has become stable, it cancels the stopping of the 4WD
control and transfers to AUTO control. If the 4WD warning light blinks, take the following actions
without turning the engine OFF:
Drop the vehicle speed until the light goes out
Stop the vehicle and stay there until the light goes out
CH-71
6. Diagnosis
When the 4WD ECU detects a malfunction, the 4WD ECU makes a diagnosis and memorizes the failed
section. Furthermore, the 4WD warning light in the combination meter illuminates to inform the driver.
At the same time, the DTCs (Diagnosis Trouble Codes) are stored in memory. The DTCs can be read by
connecting a hand-held tester, or by connecting the SST (09843-18040) to the TC and CG terminals of
DLC3 and observing the blinks of the 4WD warning light.
For details of the DTCs that are stored in 4WD ECU memory, see the 2006 RAV4 Repair Manual (Pub. No.
RM01M1U).
7. Fail-safe
When there is a possibility of causing damage to the drive system due to a malfunction in the 4WD system
or rough driving, the system illuminates or blinks the 4WD warning light to inform the driver, stops the 4WD
controls, and enables the vehicle to operate in the front-wheel-drive mode.
Malfunction
4WD Warning Light
4WD System MalfunctionIlluminate
Rough driving in 4WDPre-warning for stopping 4WD controlSlow blinkingRough driving in 4WDStopping 4WD controlFast blinking
Page 196 of 2000

2GR-FE ENGINE MECHANICAL – ENGINE ASSEMBLYEM–21
EM
REMOVAL
1. DISCHARGE REFRIGERANT FROM
REFRIGERATION SYSTEM (See page AC-172)
2. DISCHARGE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE (See page
FU-13)
3. DISCONNECT CABLE FROM NEGATIVE BATTERY
TERMINAL
CAUTION:
Wait at least 90 seconds after disconnecting the
cable from the negative (-) battery terminal to
prevent airbag and seat belt pretensioner activation.
4. REMOVE NO. 1 ENGINE UNDER COVER
(a) Remove the 4 bolts, 12 clips and under cover.
5. REMOVE REAR ENGINE UNDER COVER RH
(a) Remove the 2 clips and under cover.
6. REMOVE REAR ENGINE UNDER COVER LH
(a) Remove the 2 clips and under cover.
7. REMOVE NO. 2 ENGINE UNDER COVER
(a) Remove the 2 clips and under cover.
8. REMOVE FRONT FLOOR COVER (See page FU-34)
9. DRAIN ENGINE COOLANT (See page CO-8)
10. DRAIN ENGINE OIL (See page LU-4)
11. DRAIN AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE FLUID
(a) 2WD:
Drain automatic transaxle fluid (see page AX-172).
(b) 4WD:
Drain automatic transaxle fluid (see page AX-173)
12. DRAIN TRANSFER OIL (for 4WD)
13. REMOVE HOOD SUB-ASSEMBLY (See page ED-4)
14. REMOVE V-BANK COVER SUB-ASSEMBLY
(a) Detach the 3 clips and remove the V-bank cover.
A137900
Page 201 of 2000
EM–262GR-FE ENGINE MECHANICAL – ENGINE ASSEMBLY
EM
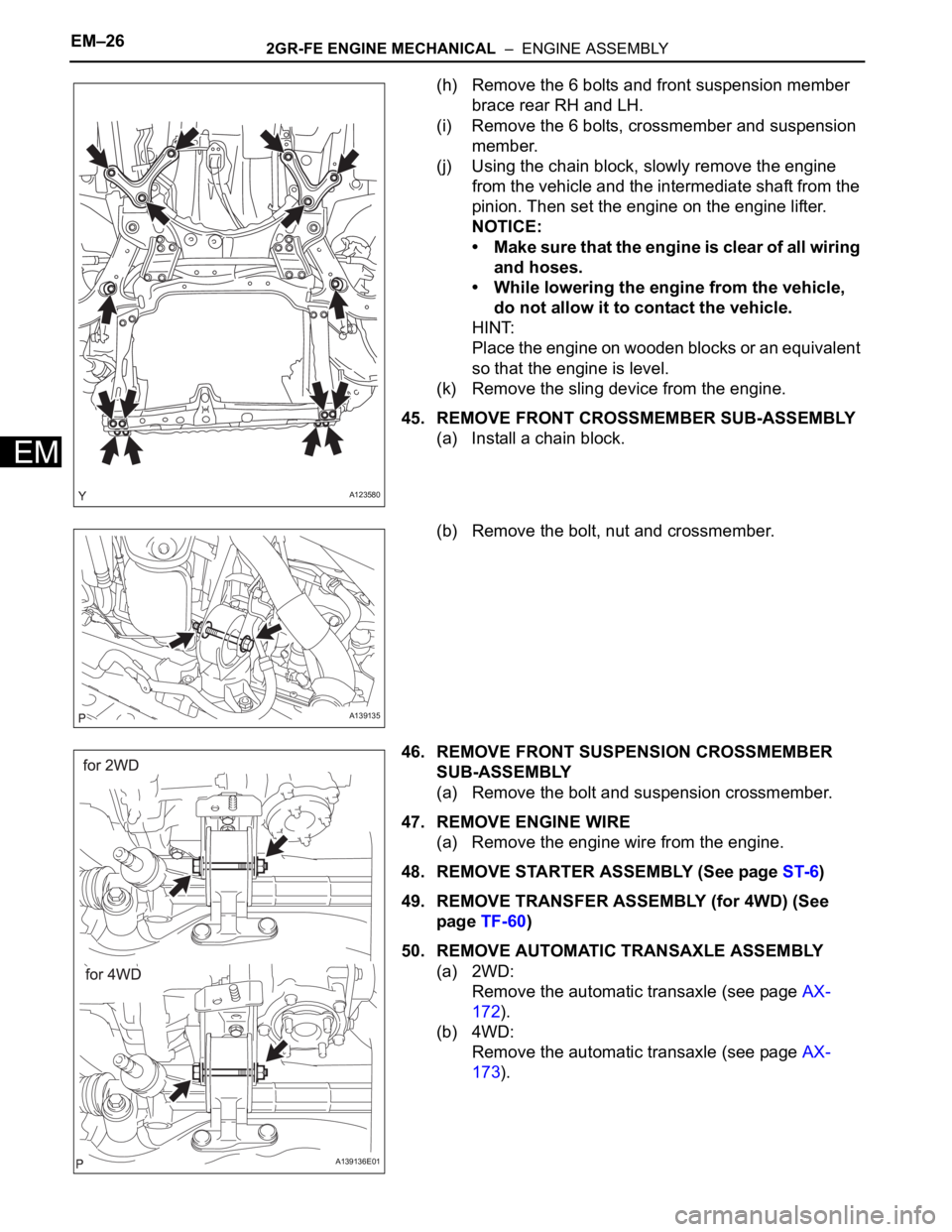
(h) Remove the 6 bolts and front suspension member
brace rear RH and LH.
(i) Remove the 6 bolts, crossmember and suspension
member.
(j) Using the chain block, slowly remove the engine
from the vehicle and the intermediate shaft from the
pinion. Then set the engine on the engine lifter.
NOTICE:
• Make sure that the engine is clear of all wiring
and hoses.
• While lowering the engine from the vehicle,
do not allow it to contact the vehicle.
HINT:
Place the engine on wooden blocks or an equivalent
so that the engine is level.
(k) Remove the sling device from the engine.
45. REMOVE FRONT CROSSMEMBER SUB-ASSEMBLY
(a) Install a chain block.
(b) Remove the bolt, nut and crossmember.
46. REMOVE FRONT SUSPENSION CROSSMEMBER
SUB-ASSEMBLY
(a) Remove the bolt and suspension crossmember.
47. REMOVE ENGINE WIRE
(a) Remove the engine wire from the engine.
48. REMOVE STARTER ASSEMBLY (See page ST-6)
49. REMOVE TRANSFER ASSEMBLY (for 4WD) (See
page TF-60)
50. REMOVE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE ASSEMBLY
(a) 2WD:
Remove the automatic transaxle (see page AX-
172).
(b) 4WD:
Remove the automatic transaxle (see page AX-
173).
A123580
A139135
A139136E01
Page 326 of 2000
PREPARATION – GF1A TRANSFERPP–63
PP
RECOMMENDED TOOLS
09904-00010 Expander Set
09905-00012 Snap Ring No.1 Expander
Page 327 of 2000
PP–64PREPARATION – GF1A TRANSFER
PP
EQUIPMENT
Dial indicator or dial indicator with magnetic base
Plastic-faced hammer
Hammer
Press
To r q u e w r e n c h
Page 382 of 2000
GF1A TRANSFER – TRANSFER SYSTEMTF–3
TF
PROBLEM SYMPTOMS TABLE
(2006/01- )
HINT:
Use the table below to help determine the cause of the
problem symptom. The potential causes of the symptoms are
listed in order of probability in the "Suspected area" column of
the table. Check each symptom by checking the suspected
areas in the order they are listed. Replace parts as
necessary.
Transfer system
Symptom Suspected Area See page
Noise1. Oil (level low)TF-45
2. Oil (wrong)TF-45
3. Transfer (faulty)TF-60
Oil leakage1. Oil (level too high)TF-45
2. Gasket (damaged)TF-55
3. Oil seal (worn or damaged)TF-55
4. O-ring (worn or damaged)TF-55