Page 2277 of 2896
COMBINATION SWITCH
LT-69
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
L
MA
B
LT
Revision: June 20062007 Versa
3. HARNESS INSPECTION
1. Turn ignition switch OFF.
2. Disconnect BCM connector and combination switch connector.
3. Check for continuity between BCM harness connector of the suspect system and the corresponding com-
bination switch harness connector.
4. Check for continuity between of BCM harness connector in suspect system and ground.
OK or NG
OK >> GO TO 4.
NG >> Check harness between BCM and combination switch for open or short circuit.
Suspect
systemAB
Continuity
Connector Terminal Connector Terminal
1
M18Input 1 6
M286
Ye s Output 1 36 1
2Input 2 5 7
Output 2 35 2
3Input 3 4 10
Output 3 34 3
4Input 4 3 9
Output 4 33 4
5Input 5 2 8
Output 5 32 5
Suspect
systemBCM
Continuity
Connector Terminal
1
M18Input 1 6
Ground No Output 1 36
2Input 2 5
Output 2 35
3Input 3 4
Output 3 34
4Input 4 3
Output 4 33
5Input 5 2
Output 5 32
WKIA5497E
WKIA5500E
Page 2474 of 2896
MTC-62
CONTROLLER
Revision: June 20062007 Versa
Disassembly and AssemblyEJS00581
CAUTION:
Install inner cable of each door cable to the corresponding
lever, as shown in the figure. Press outer cable until it hooks on
the tabs and becomes secure.
1. Air mix door cable 2. Intake door cable 3. Mode door cable
4. A/C controller assembly 5. Mode control dial 6. Rear DEF button
7. A/C button 8. Temperature control dial 9. Illumination bulb
10. Intake door lever knob 11. Fan control dial
ZJIA0106J
MJIA0038E
Page 2487 of 2896
DUCTS AND GRILLES
MTC-75
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
K
L
MA
B
MTC
Revision: June 20062007 Versa
DUCTS AND GRILLESPFP:27860
Removal and InstallationEJS0058C
Floor Ducts - Canada Only
1. Side defroster duct (right) 2. Defroster nozzle 3. Side defroster duct (left)
4. Side defroster grille (left) 5. Instrument side panel (left) 6. Instrument panel and pad
7. Side ventilator assembly (left) 8. Cluster lid C 9. Side ventilator assembly (right)
10. Instrument finisher E 11. Instrument side panel (right) 12. Side defroster grille (right)
13. Side ventilator duct (right) 14. Center ventilator duct (right) 15. Center ventilator duct (left)
16. Side ventilator duct (left)
SJIA0657E
WJIA2198E
Page 2492 of 2896
MTC-80
REFRIGERANT LINES
Revision: June 20062007 Versa
REFRIGERANT LINESPFP:92600
HFC-134a (R-134a) Service ProcedureEJS0058D
SETTING OF SERVICE TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT
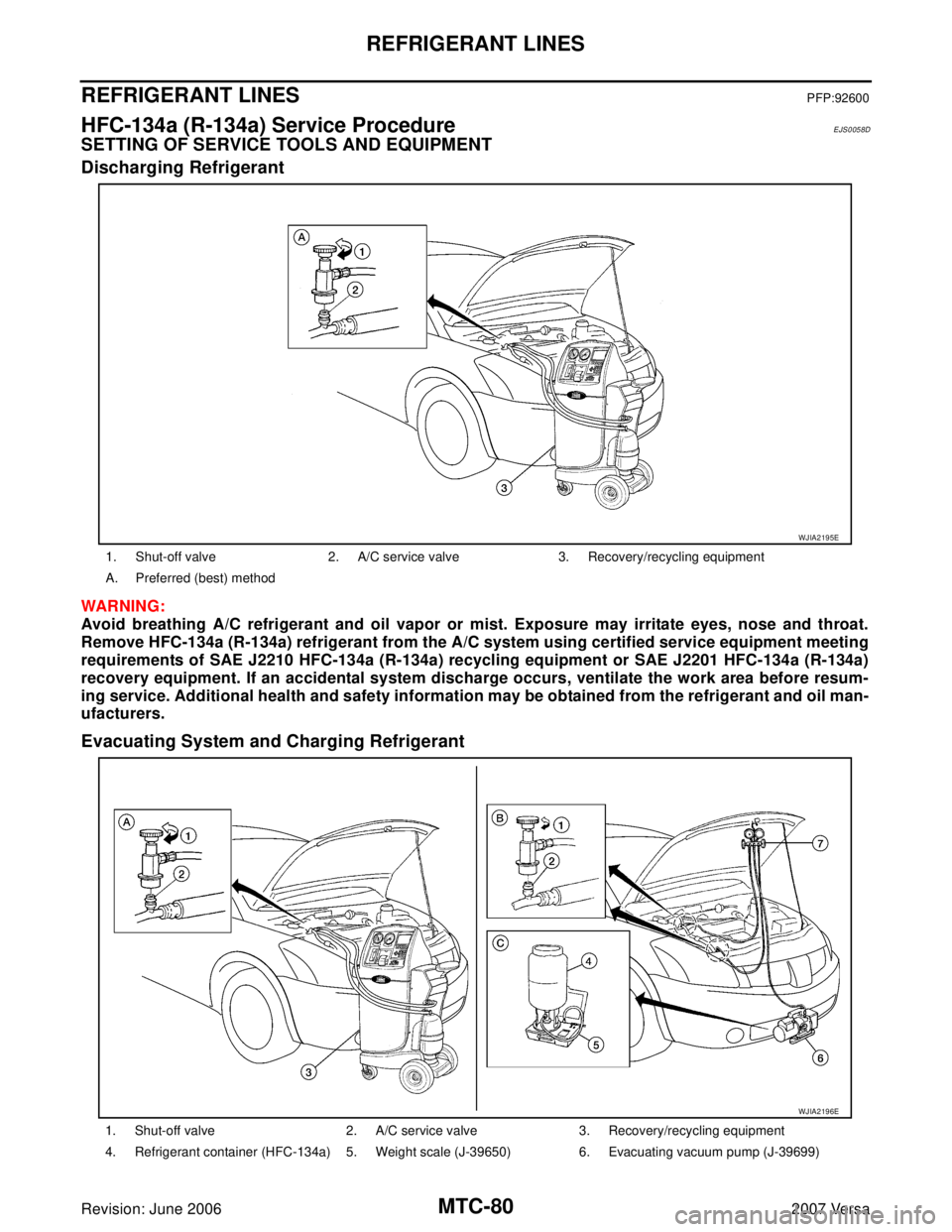
Discharging Refrigerant
WAR NIN G:
Avoid breathing A/C refrigerant and oil vapor or mist. Exposure may irritate eyes, nose and throat.
Remove HFC-134a (R-134a) refrigerant from the A/C system using certified service equipment meeting
requirements of SAE J2210 HFC-134a (R-134a) recycling equipment or SAE J2201 HFC-134a (R-134a)
recovery equipment. If an accidental system discharge occurs, ventilate the work area before resum-
ing service. Additional health and safety information may be obtained from the refrigerant and oil man-
ufacturers.
Evacuating System and Charging Refrigerant
1. Shut-off valve 2. A/C service valve 3. Recovery/recycling equipment
A. Preferred (best) method
WJIA2195E
1. Shut-off valve 2. A/C service valve 3. Recovery/recycling equipment
4. Refrigerant container (HFC-134a) 5. Weight scale (J-39650) 6. Evacuating vacuum pump (J-39699)
WJIA2196E
Page 2532 of 2896
PG-16
POWER SUPPLY ROUTING CIRCUIT
Revision: June 20062007 Versa
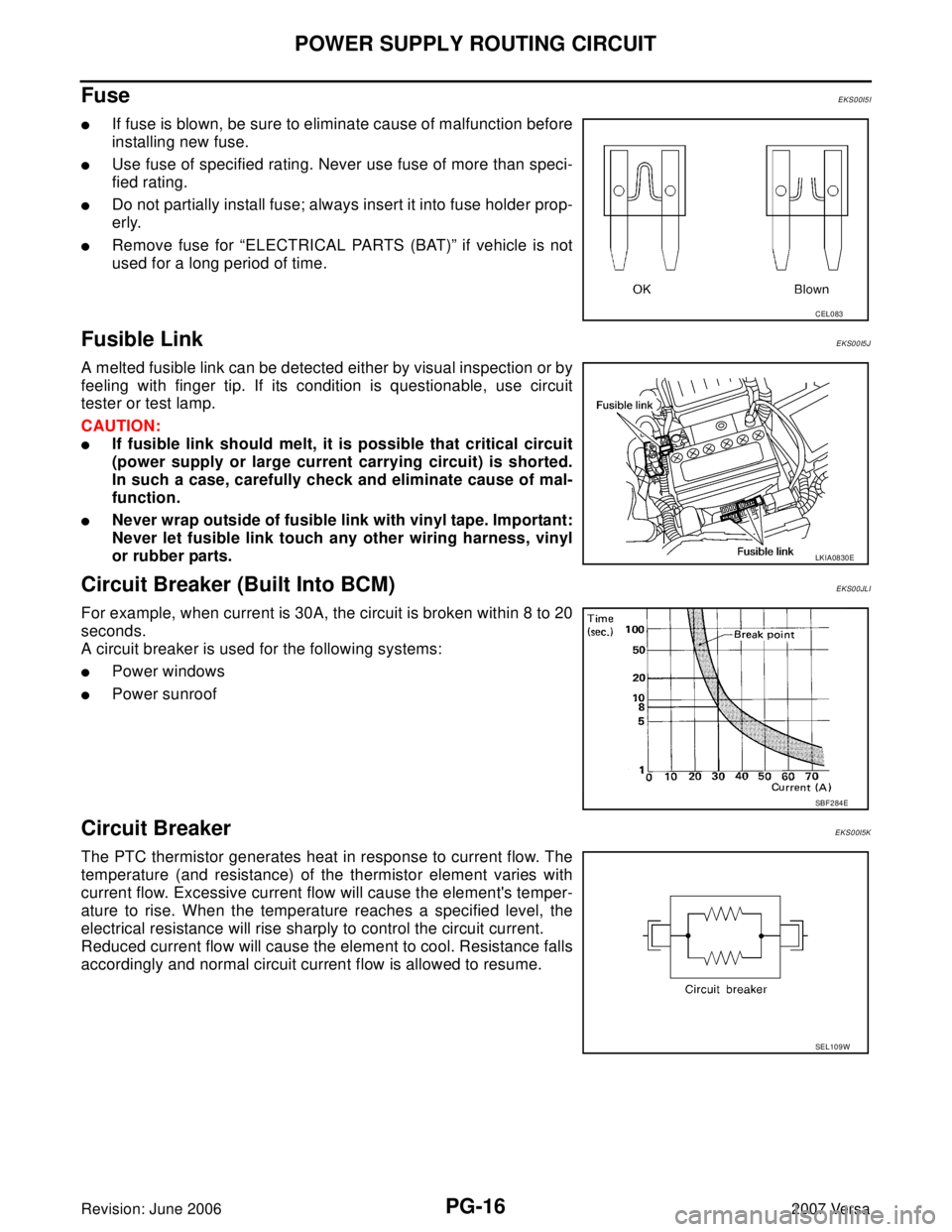
Fuse EKS00I5I
�If fuse is blown, be sure to eliminate cause of malfunction before
installing new fuse.
�Use fuse of specified rating. Never use fuse of more than speci-
fied rating.
�Do not partially install fuse; always insert it into fuse holder prop-
erly.
�Remove fuse for “ELECTRICAL PARTS (BAT)” if vehicle is not
used for a long period of time.
Fusible Link EKS00I5J
A melted fusible link can be detected either by visual inspection or by
feeling with finger tip. If its condition is questionable, use circuit
tester or test lamp.
CAUTION:
�If fusible link should melt, it is possible that critical circuit
(power supply or large current carrying circuit) is shorted.
In such a case, carefully check and eliminate cause of mal-
function.
�Never wrap outside of fusible link with vinyl tape. Important:
Never let fusible link touch any other wiring harness, vinyl
or rubber parts.
Circuit Breaker (Built Into BCM)EKS00JLI
For example, when current is 30A, the circuit is broken within 8 to 20
seconds.
A circuit breaker is used for the following systems:
�Power windows
�Power sunroof
Circuit Breaker EKS00I5K
The PTC thermistor generates heat in response to current flow. The
temperature (and resistance) of the thermistor element varies with
current flow. Excessive current flow will cause the element's temper-
ature to rise. When the temperature reaches a specified level, the
electrical resistance will rise sharply to control the circuit current.
Reduced current flow will cause the element to cool. Resistance falls
accordingly and normal circuit current flow is allowed to resume.
CEL083
LKIA0830E
SBF 2 84 E
SEL109W
Page 2585 of 2896
HARNESS CONNECTOR
PG-69
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
L
MA
B
PG
Revision: June 20062007 Versa
HARNESS CONNECTOR (SLIDE-LOCKING TYPE)
�A new style slide-locking type connector is used on certain systems and components, especially those
related to OBD.
�The slide-locking type connectors help prevent incomplete locking and accidental looseness or discon-
nection.
�The slide-locking type connectors are disconnected by pushing or pulling the slider. Refer to the figure
below.
CAUTION:
�Do not pull the harness or wires when disconnecting the connector.
�Be careful not to damage the connector support bracket when disconnecting the connector.
[Example]
SEL769V
Page 2622 of 2896
RF-4
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
Revision: June 20062007 Versa
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSESPFP:00000
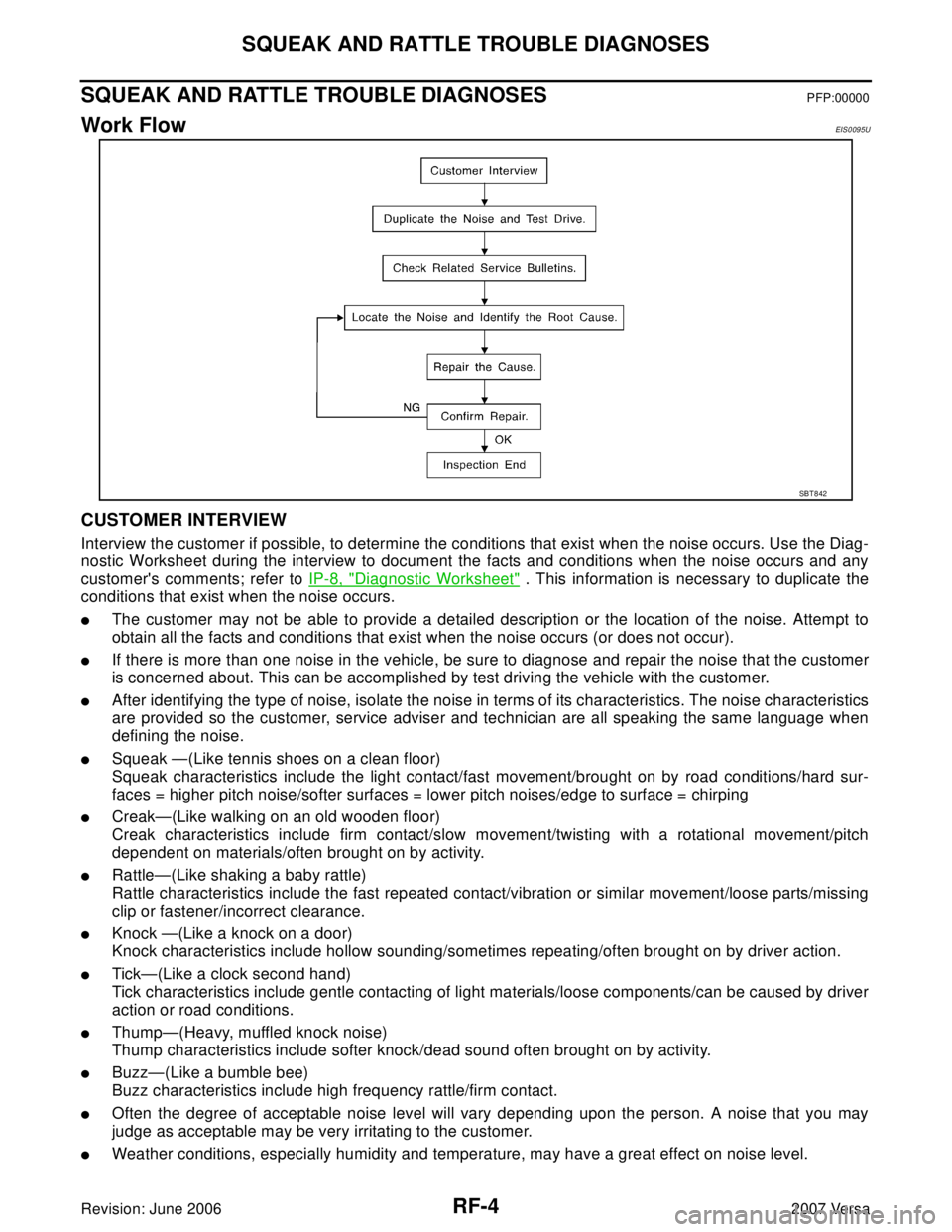
Work FlowEIS0095U
CUSTOMER INTERVIEW
Interview the customer if possible, to determine the conditions that exist when the noise occurs. Use the Diag-
nostic Worksheet during the interview to document the facts and conditions when the noise occurs and any
customer's comments; refer to IP-8, "
Diagnostic Worksheet" . This information is necessary to duplicate the
conditions that exist when the noise occurs.
�The customer may not be able to provide a detailed description or the location of the noise. Attempt to
obtain all the facts and conditions that exist when the noise occurs (or does not occur).
�If there is more than one noise in the vehicle, be sure to diagnose and repair the noise that the customer
is concerned about. This can be accomplished by test driving the vehicle with the customer.
�After identifying the type of noise, isolate the noise in terms of its characteristics. The noise characteristics
are provided so the customer, service adviser and technician are all speaking the same language when
defining the noise.
�Squeak —(Like tennis shoes on a clean floor)
Squeak characteristics include the light contact/fast movement/brought on by road conditions/hard sur-
faces = higher pitch noise/softer surfaces = lower pitch noises/edge to surface = chirping
�Creak—(Like walking on an old wooden floor)
Creak characteristics include firm contact/slow movement/twisting with a rotational movement/pitch
dependent on materials/often brought on by activity.
�Rattle—(Like shaking a baby rattle)
Rattle characteristics include the fast repeated contact/vibration or similar movement/loose parts/missing
clip or fastener/incorrect clearance.
�Knock —(Like a knock on a door)
Knock characteristics include hollow sounding/sometimes repeating/often brought on by driver action.
�Tick—(Like a clock second hand)
Tick characteristics include gentle contacting of light materials/loose components/can be caused by driver
action or road conditions.
�Thump—(Heavy, muffled knock noise)
Thump characteristics include softer knock/dead sound often brought on by activity.
�Buzz—(Like a bumble bee)
Buzz characteristics include high frequency rattle/firm contact.
�Often the degree of acceptable noise level will vary depending upon the person. A noise that you may
judge as acceptable may be very irritating to the customer.
�Weather conditions, especially humidity and temperature, may have a great effect on noise level.
SBT 8 42
Page 2712 of 2896
SE-4
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
Revision: June 20062007 Versa
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSESPFP:00000
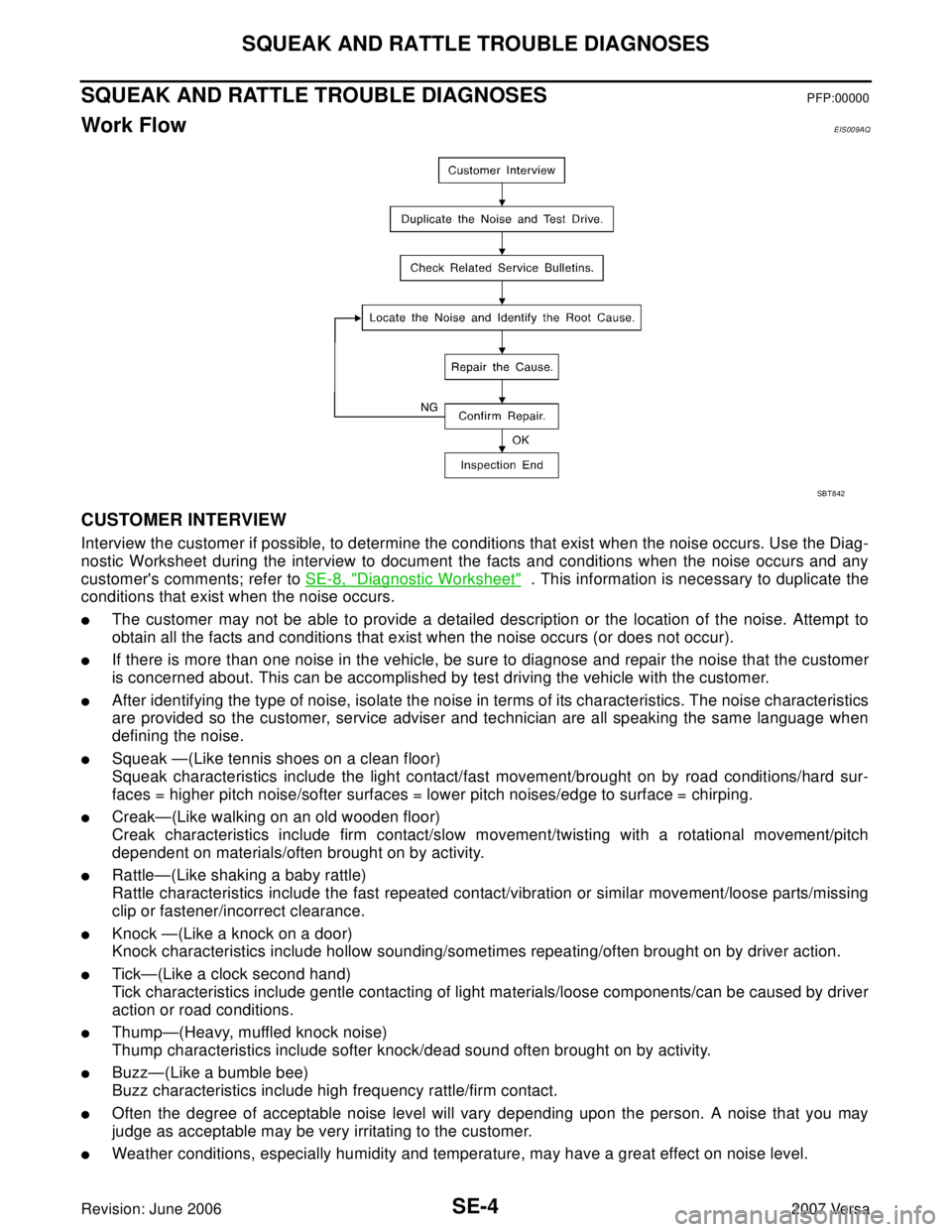
Work FlowEIS009AQ
CUSTOMER INTERVIEW
Interview the customer if possible, to determine the conditions that exist when the noise occurs. Use the Diag-
nostic Worksheet during the interview to document the facts and conditions when the noise occurs and any
customer's comments; refer to SE-8, "
Diagnostic Worksheet" . This information is necessary to duplicate the
conditions that exist when the noise occurs.
�The customer may not be able to provide a detailed description or the location of the noise. Attempt to
obtain all the facts and conditions that exist when the noise occurs (or does not occur).
�If there is more than one noise in the vehicle, be sure to diagnose and repair the noise that the customer
is concerned about. This can be accomplished by test driving the vehicle with the customer.
�After identifying the type of noise, isolate the noise in terms of its characteristics. The noise characteristics
are provided so the customer, service adviser and technician are all speaking the same language when
defining the noise.
�Squeak —(Like tennis shoes on a clean floor)
Squeak characteristics include the light contact/fast movement/brought on by road conditions/hard sur-
faces = higher pitch noise/softer surfaces = lower pitch noises/edge to surface = chirping.
�Creak—(Like walking on an old wooden floor)
Creak characteristics include firm contact/slow movement/twisting with a rotational movement/pitch
dependent on materials/often brought on by activity.
�Rattle—(Like shaking a baby rattle)
Rattle characteristics include the fast repeated contact/vibration or similar movement/loose parts/missing
clip or fastener/incorrect clearance.
�Knock —(Like a knock on a door)
Knock characteristics include hollow sounding/sometimes repeating/often brought on by driver action.
�Tick—(Like a clock second hand)
Tick characteristics include gentle contacting of light materials/loose components/can be caused by driver
action or road conditions.
�Thump—(Heavy, muffled knock noise)
Thump characteristics include softer knock/dead sound often brought on by activity.
�Buzz—(Like a bumble bee)
Buzz characteristics include high frequency rattle/firm contact.
�Often the degree of acceptable noise level will vary depending upon the person. A noise that you may
judge as acceptable may be very irritating to the customer.
�Weather conditions, especially humidity and temperature, may have a great effect on noise level.
SBT 8 42