2006 NISSAN PATROL lock
[x] Cancel search: lockPage 761 of 1226

WHEEL BEARING
Wheel bearing axial end play
mm (in)0 (0)
Wheel bearing lock nuts
Tightening torque
Nzm (kg-m, ft-lb)167 - 196 (17 - 20, 123 - 145)
Retightening torque after
untightened
Nzm (kg-m, in-lb)3 - 5 (0.3 - 0.5, 26 - 43)
Measured starting force
At wheel hub bolt
N (kg, lb)A
Turning adjusting nut in tightening
direction and measuring starting
force
At wheel hub bolt
N (kg, lb)B
Calculated wheel bearing preload;
BþA
At wheel hub bolt
N (kg, lb)0 - 18.6 (0 - 1.9, 0 - 4.2)
KNUCKLE FLANGE BEARING
Flange turning torque
Without trunnion seal
and drive shaft
Nzm (kg-m, ft-lb)1 - 3 (0.1 - 0.3, 0.7 - 2.2)
At knuckle arm ``F''
N (kg, lb)4.9 - 14.7 (0.5 - 1.5, 1.1 - 3.3)
Adjusting shims mm (in)Thickness Part number
0.075 (0.0030)
0.127 (0.0050)
0.254 (0.0100)
0.500 (0.0197)
0.762 (0.0300)40606-44000
40605-44000
40604-44000
40571-01J00
40603-44000
SFA882B
DRIVE SHAFT
Bir®eld joint axial end play
mm (in)0 (0)
Grease
Type Multi-purpose grease
Capacity g (oz) 50 - 60 (1.76 - 2.12)
Drive shaft axial end play
mm (in)0.4 (0.016) or less
Adjusting snap rings
mm (in)Thickness Part number
1.1 (0.043)
1.3 (0.051)
1.5 (0.059)
1.7 (0.067)
1.9 (0.075)
2.1 (0.083)39253-01J00
39253-01J01
39253-01J02
39253-01J03
39253-01J04
39253-01J05
SERVICE DATA AND SPECIFICATIONS (SDS)
Inspection and Adjustment (Cont'd)
FA-28
Page 769 of 1226
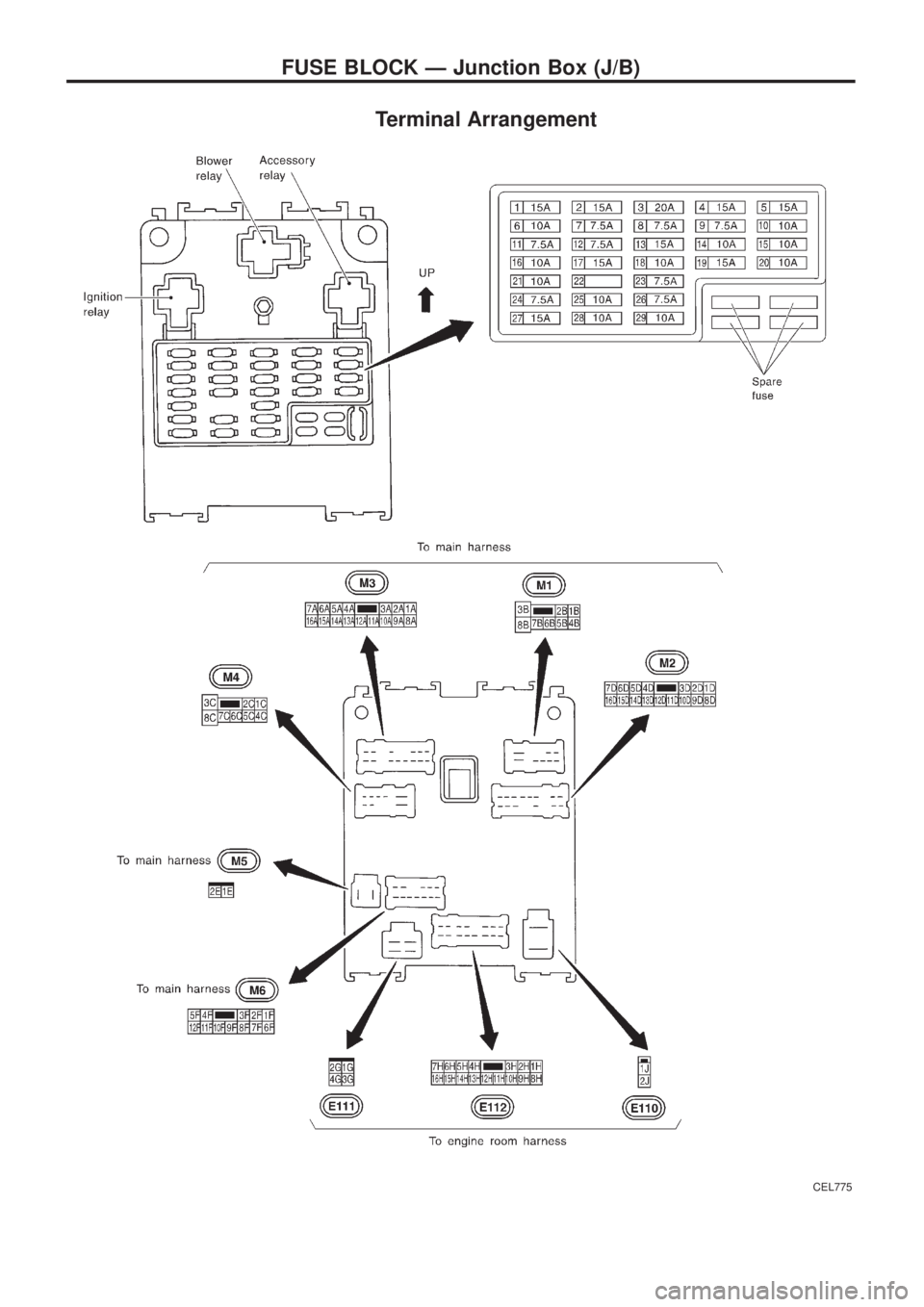
Terminal Arrangement
CEL775
FUSE BLOCK Ð Junction Box (J/B)
Page 773 of 1226

GENERAL INFORMATION
SECTION
GI
CONTENTS
PRECAUTIONS...............................................................1
Precaution for Supplemental Restraint System
(SRS) ``AIR BAG'' and ``SEAT BELT
PRE-TENSIONER'' ......................................................1
General Precautions ....................................................2
Precautions for Multiport Fuel Injection System
or ECCS Engine ..........................................................3
Precautions for Three Way Catalyst
(If so equipped)............................................................4
Precautions for Engine Oils .........................................4
Precautions for Fuel ....................................................5
Precautions for Air Conditioning ..................................5
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL........................................6
HOW TO READ WIRING DIAGRAMS............................8
Sample/Wiring Diagram Ð EXAMPL Ð......................8
Description .................................................................10
HOW TO CHECK TERMINAL.......................................17
How to Probe Connectors .........................................17
How to Check Enlarged Contact Spring of
Terminal .....................................................................18
Waterproof Connector Inspection ..............................19
Terminal Lock Inspection ...........................................19
HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSIS FOR
AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT........................................20Work Flow ..................................................................20
Incident Simulation Tests ...........................................21
Circuit Inspection .......................................................24
HOW TO FOLLOW FLOW CHART IN TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES..................................................................30
How to Follow This Flow Chart .................................31
CONSULT CHECKING SYSTEM..................................33
Function and System Application ..............................33
Lithium Battery Replacement ....................................33
Checking Equipment..................................................33
Loading Procedure ....................................................34
CONSULT Data Link Connector (DLC) Circuit..........34
IDENTIFICATION INFORMATION.................................35
Model Variation ..........................................................35
Identi®cation Number .................................................36
Dimensions ................................................................38
Wheels & Tires ..........................................................38
LIFTING POINTS AND TOW TRUCK TOWING...........39
Screw Jack ................................................................39
Garage Jack and Safety Stand .................................39
2-pole Lift ...................................................................40
Tow Truck Towing ......................................................41
SAE J1930 TERMINOLOGY LIST................................43
SAE J1930 Terminology List .....................................43
GI
Page 775 of 1226

General Precautions
+Do not operate the engine for an extended period of time with-
out proper exhaust ventilation.
Keep the work area well ventilated and free of any in¯ammable
materials. Special care should be taken when handling any
in¯ammable or poisonous materials, such as gasoline, refriger-
ant gas, etc. When working in a pit or other enclosed area, be
sure to properly ventilate the area before working with hazard-
ous materials.
Do not smoke while working on the vehicle.
+Before jacking up the vehicle, apply wheel chocks or other tire
blocks to the wheels to prevent the vehicle from moving. After
jacking up the vehicle, support the vehicle weight with safety
stands at the points designated for proper lifting before work-
ing on the vehicle.
These operations should be done on a level surface.
+When removing a heavy component such as the engine or
transaxle/transmission, be careful not to lose your balance and
drop it. Also, do not allow it to strike adjacent parts, especially
the brake tubes and master cylinder.
+Before starting repairs which do not require battery power:
Turn off ignition switch.
Disconnect the negative battery terminal.
+To prevent serious burns:
Avoid contact with hot metal parts.
Do not remove the radiator cap when the engine is hot.
+Before servicing the vehicle:
Protect fenders, upholstery and carpeting with appropriate cov-
ers.
Take caution that keys, buckles or buttons do not scratch paint.
SGI285
SGI231
SEF289H
SGI233
SGI234
PRECAUTIONS
GI-2
Page 776 of 1226

+Clean all disassembled parts in the designated liquid or solvent
prior to inspection or assembly.
+Replace oil seals, gaskets, packings, O-rings, locking washers,
cotter pins, self-locking nuts, etc. with new ones.
+Replace inner and outer races of tapered roller bearings and
needle bearings as a set.
+Arrange the disassembled parts in accordance with their
assembled locations and sequence.
+Do not touch the terminals of electrical components which use
microcomputers (such as ECMs).
Static electricity may damage internal electronic components.
+After disconnecting vacuum or air hoses, attach a tag to indi-
cate the proper connection.
+Use only the ¯uids and lubricants speci®ed in this manual.
+Use approved bonding agent, sealants or their equivalents
when required.
+Use tools and recommended special tools where speci®ed for
safe and efficient service repairs.
+When repairing the fuel, oil, water, vacuum or exhaust systems,
check all affected lines for leaks.
+Dispose of drained oil or the solvent used for cleaning parts in
an appropriate manner.
WARNING:
To prevent ECM from storing the diagnostic trouble codes, do
not carelessly disconnect the harness connectors which are
related to the ECCS system and TCM (Transmission Control
Module) system. The connectors should be disconnected only
when working according to the WORK FLOW of TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES in EC and AT sections.
Precautions for Multiport Fuel Injection System
or ECCS Engine
+Before connecting or disconnecting any harness connector for
the multiport fuel injection system or ECM (Engine Control
Module):
Turn ignition switch to ``OFF'' position.
Disconnect negative battery terminal.
Otherwise, there may be damage to ECM.
+
Before disconnecting pressurized fuel line from fuel pump to
injectors, be sure to release fuel pressure.
+Be careful not to jar components such as ECM and mass air
¯ow sensor.SGI787
PRECAUTIONS
General Precautions (Cont'd)
GI-3
Page 792 of 1226

Waterproof Connector Inspection
If water enters the connector, it can short interior circuits. This may
lead to intermittent problems.
Check the following items to maintain the original waterproof char-
acteristics.
RUBBER SEAL INSPECTION
+Most waterproof connectors are provided with a rubber seal
between the male and female connectors. If the seal is missing,
the waterproof performance may not meet speci®cations.
+The rubber seal may come off when connectors are discon-
nected. Whenever connectors are reconnected, make sure the
rubber seal is properly installed on either side of male or female
connector.
WIRE SEAL INSPECTION
The wire seal must be installed on the wire insertion area of a
waterproof connector. Be sure that the seal is installed properly.
Terminal Lock Inspection
Check for unlocked terminals by pulling wire at the end of connec-
tor. An unlocked terminal may create intermittent signals in the cir-
cuit.
SEL275V
SEL330V
HOW TO CHECK TERMINAL
GI-19
Page 797 of 1226

Circuit Inspection
INTRODUCTION
In general, testing electrical circuits is an easy task if it is approached in a logical and organized method. Before
beginning it is important to have all available information on the system to be tested. Also, get a thorough
understanding of system operation. Then you will be able to use the appropriate equipment and follow the
correct test procedure.
You may have to simulate vehicle vibrations while testing electrical components.Gently shakethe wiring
harness or electrical component to do this.
OPEN A circuit is open when there is no continuity through a section of the circuit.
SHORT There are two types of shorts.
+SHORT CIRCUITWhen a circuit contacts another circuit and causes the
normal resistance to change.
+SHORT TO GROUNDWhen a circuit contacts a ground source and grounds the
circuit.
TESTING FOR ``OPENS'' IN THE CIRCUIT
Before you begin to diagnose and test the system, you should rough sketch a schematic of the system. This
will help you to logically walk through the diagnosis process. Drawing the sketch will also reinforce your work-
ing knowledge of the system.
Continuity check method
The continuity check is used to ®nd an open in the circuit. The Digital Multimeter (DMM) set on the resistance
function will indicate an open circuit as over limit (OL, no beep tone or no ohms symbol). Make sure to always
start with the DMM at the highest resistance level.
To help in understanding the diagnosis of open circuits please refer to the schematic above.
1. Disconnect the battery negative cable.
2. Start at one end of the circuit and work your way to the other end. (At the fuse block in this example)
3. Connect one probe of the DMM to the fuse block terminal on the load side.
4. Connect the other probe to the fuse block (power) side of SW1. Little or no resistance will indicate that
portion of the circuit has good continuity. If there were an open in the circuit, the DMM would indicate an
over limit or in®nite resistance condition. (point A)
5. Connect the probes between SW1 and the relay. Little or no resistance will indicate that portion of the cir-
cuit has good continuity. If there were an open in the circuit, the DMM would indicate an over limit or in®-
nite resistance condition. (point B)
6. Connect the probes between the relay and the solenoid. Little or no resistance will indicate that portion of
the circuit has good continuity. If there were an open in the circuit, the DMM would indicate an over limit
or in®nite resistance condition. (point C)
Any circuit can be diagnosed using the approach in the above example.
SGI846
HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSIS FOR AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
GI-24
Page 798 of 1226
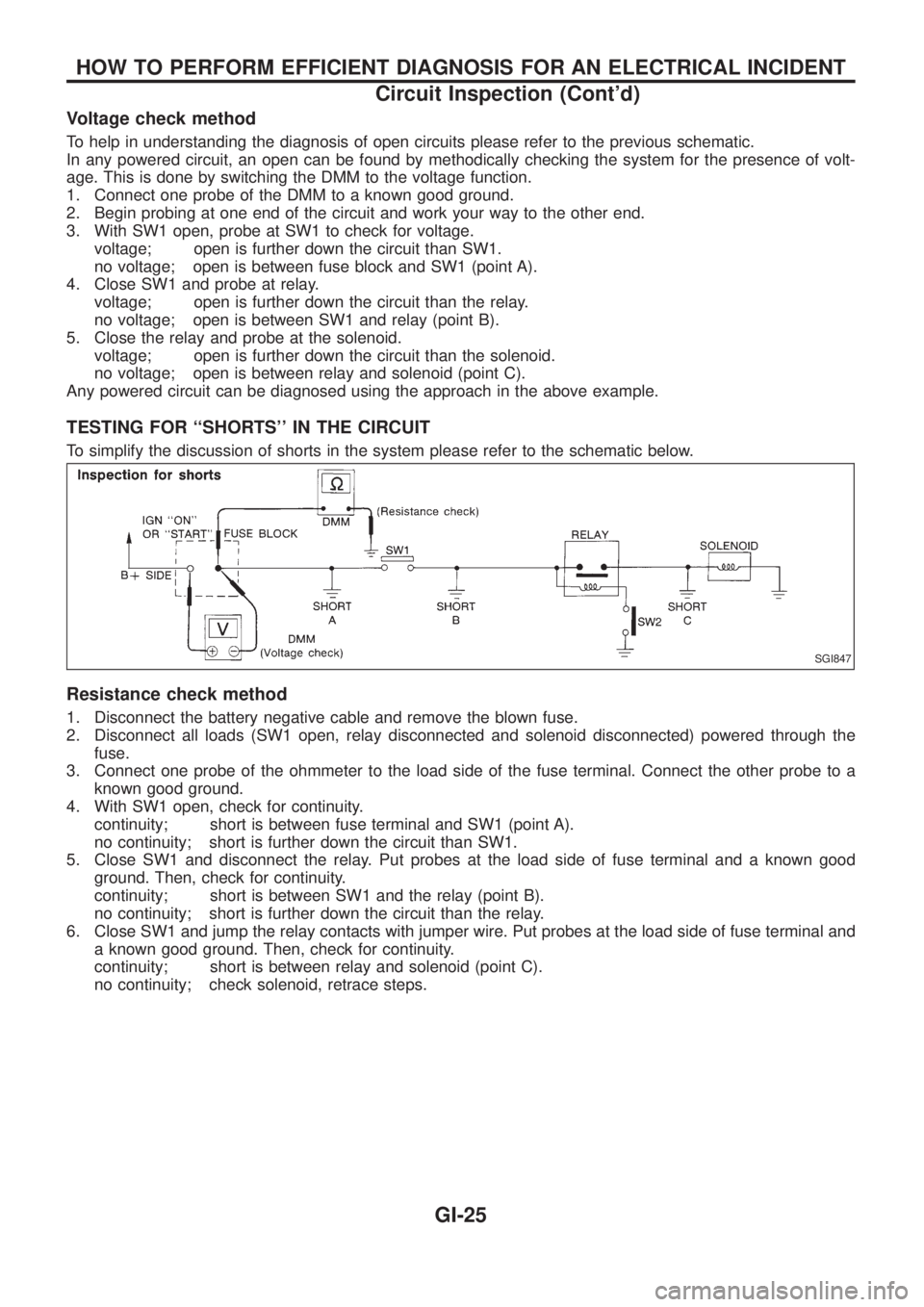
Voltage check method
To help in understanding the diagnosis of open circuits please refer to the previous schematic.
In any powered circuit, an open can be found by methodically checking the system for the presence of volt-
age. This is done by switching the DMM to the voltage function.
1. Connect one probe of the DMM to a known good ground.
2. Begin probing at one end of the circuit and work your way to the other end.
3. With SW1 open, probe at SW1 to check for voltage.
voltage; open is further down the circuit than SW1.
no voltage; open is between fuse block and SW1 (point A).
4. Close SW1 and probe at relay.
voltage; open is further down the circuit than the relay.
no voltage; open is between SW1 and relay (point B).
5. Close the relay and probe at the solenoid.
voltage; open is further down the circuit than the solenoid.
no voltage; open is between relay and solenoid (point C).
Any powered circuit can be diagnosed using the approach in the above example.
TESTING FOR ``SHORTS'' IN THE CIRCUIT
To simplify the discussion of shorts in the system please refer to the schematic below.
Resistance check method
1. Disconnect the battery negative cable and remove the blown fuse.
2. Disconnect all loads (SW1 open, relay disconnected and solenoid disconnected) powered through the
fuse.
3. Connect one probe of the ohmmeter to the load side of the fuse terminal. Connect the other probe to a
known good ground.
4. With SW1 open, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between fuse terminal and SW1 (point A).
no continuity; short is further down the circuit than SW1.
5. Close SW1 and disconnect the relay. Put probes at the load side of fuse terminal and a known good
ground. Then, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between SW1 and the relay (point B).
no continuity; short is further down the circuit than the relay.
6. Close SW1 and jump the relay contacts with jumper wire. Put probes at the load side of fuse terminal and
a known good ground. Then, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between relay and solenoid (point C).
no continuity; check solenoid, retrace steps.
SGI847
HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSIS FOR AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Circuit Inspection (Cont'd)
GI-25