2006 GREAT WALL HOVER wheel
[x] Cancel search: wheelPage 38 of 425

Clutch-8
b. Use special tools to install the guide bearing
Remarks: Install the guide bearing into the flywheel, make
sure that the bearing can rotate well.
6. Check to see whether there is wearing of the diaphragm spring
Use caliper to check the wearing depth and width of the diaphragm
spring
Limit value: maximum depth 0.6mm
Maximum width 5.0mm
7. Check the throwout bearing
Rotate the bearing with hand along the axis direction.
If the bearing can not rotate or the resistance is too large, it is necessary
to replace the throwout bearing.
Remarks: The bearing is permanent lubricated, so cleaning
and lubricating is unnecessary.
special tools
Page 39 of 425
Clutch-9
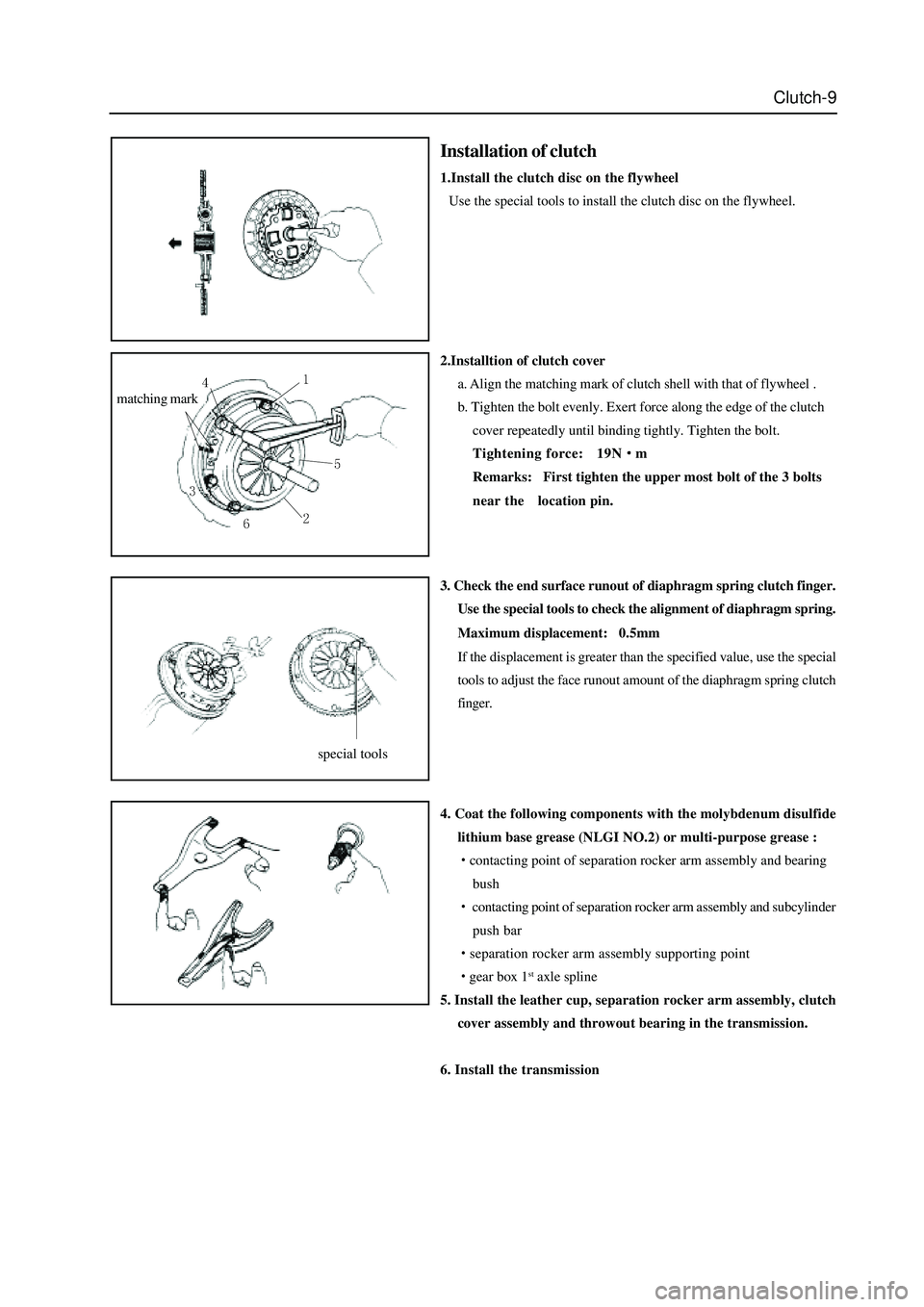
2.Installtion of clutch cover
a. Align the matching mark of clutch shell with that of flywheel .
b. Tighten the bolt evenly. Exert force along the edge of the clutch
cover repeatedly until binding tightly. Tighten the bolt.
Tightening force: 19N
m
Remarks: First tighten the upper most bolt of the 3 bolts
near thelocation pin.
3. Check the end surface runout of diaphragm spring clutch finger.
Use the special tools to check the alignment of diaphragm spring.
Maximum displacement: 0.5mm
If the displacement is greater than the specified value, use the special
tools to adjust the face runout amount of the diaphragm spring clutch
finger.
4. Coat the following components with the molybdenum disulfide
lithium base grease (NLGI NO.2) or multi-purpose grease :
contacting point of separation rocker arm assembly and bearing
bush
contacting point of separation rocker arm assembly and subcylinder
push bar
separation rocker arm assembly supporting point
gear box 1st axle spline
5. Install the leather cup, separation rocker arm assembly, clutch
cover assembly and throwout bearing in the transmission.
6. Install the transmission
matching mark
Installation of clutch
1.Install the clutch disc on the flywheel
Use the special tools to install the clutch disc on the flywheel.
special tools
Page 78 of 425

Automatic transmission-2
Instruction for automatic transmission
1. M88 4-speed automatic transmission is equipped with the hydraulic torque converter and electric control system with locking.
When keep the stable forward status, the hydraulic torque converter can be locked automatically when the engine operates in low
speed, then reduce the unnecessary slide.
Figure 1.1 Electric automatic transmission control system
Figure 1.2 M88 4 speeds automatic transmission appearance figure (applied to 2 wheels driving)
2. The main advantage of the transmission is the application of transmission control unit (TCU). The control unit is the control
system based on the microprocessor system.. TCU control the shifting sensing and realize the Gear position shifting through the
signal of opening degree of throttle position, opening frequency of throttle position, engine speed, vehicle speed, transmission oil
temperature, gear position, mode selection and forced Gear reduction application.
3. TCU drives a variable pressure regulating solenoid valve to control three regulation valves and control the feeling of shifting.
Different transmission fluid temperatures are taken as one the main parameters to control the output pressure of the solenoid
valve, so as to keep consistent feeling of shifting within the normal operation scope.
4. The planning of shifting is very flexible. According to the car model, the different shifting plan is stored in the same TCU.
Generally speaking, the “economical mode” can increase the economical efficiency of the fuel and the driving performance of the
car to the maximum limit. The “dynamic mode” can bring into full play the drive performance of the car to the maximum limit. The
“winter mode” can make the car starting from shift 2.
Page 98 of 425

Automatic transmission-22
Power transmission system
The power transmission system includes:
Torque converter equipped with single lock clutch.
4 multi-plate clutch assemblies
2 brake belts
2 one-way clutches
Planetary gear assembly
parking mechanism
A traditional planetary gear assembly composed by six pinions is used in four-speed transmission. It realizes the 4 Gear power
transmission through the drive gear bracket.
So, the cross arrangement is the main arranging method. In the box, there are four subassemblies, shown as follows:
Gear bank central support
C1-C2-C3-clutch C4 subassembly
Pump assembly
Valve assembly
One piece or one set of optional shim is located between the input shaft flange and center of stator support shaft axle of and used
to control the end flotation of transmission. The structure arrangement allows the inspection for the subassembly during the
product manufacturing period.
For description of power transmission system refer to table 4.1 and Figure 4.1:
When the clutch C2 is engaged and 1-2 one-way clutch is engaged, the gear is in 2nd-Gear at this time. During the 1-2 shifting
process, B1 brake belt is combined and the 1-2 one-way clutch is separated (OWC). During the 2-3 shifting period, the clutch
C1 is engaged and the B1brake belt is released. During the 3-4 shifting period, B1brake belt is engaged and 3-4 one-way clutch
is released. For reverse gear, the clutch C3 and B2brake belt is engaged.
When the gear position is in manual 1st, 2
nd and 3rd gear position, the engagement of the clutch C4 can provide the brake of
engine. Additionally, in the drive scope of 2
nd and 3rd Gear, the engagement of clutch C4 can eliminate the unfavorable freewheel
inertia. In the scope of manual 1
st-Gear, the low speed shifting is realized by the engagement of B2brake belt.
The front and rear servo has the figure surface design which requires the accurate friction and need not the secondary regulating
valve. When use the transmission fluid with new static factor, the design of the friction unit can meet the requirement that need
low shifting energy and high static holding force. The transmission uses the non-asbestos friction material.
LUGear position Gear ratio
1st-Gear 2.393
2
nd-Gear 1.450
3
rd-Gear 1.000
4
th-Gear 0.677
R-Gear 2.093
Manual 1 2.393
C3C4 B1 B2
Name of participated unit
* For operation of specified vehicle refer to user’operation manual.
LU: hydraulic torque converter lock clutch
Table 4.1 Participated unit and gear ratio in different gear position
Page 99 of 425

Automatic transmission-23
Figure 4.1 Power flow chart
Torque converter
The torque converter (refer to Figure 4.2) consists of the turbine, stator, impeller and a lock throttle brake and piston assembly.
Same as that of the traditional torque converter, the impeller is connected to the end cover of the torque converter. The turbine is
connected to the input shaft through the spline. The stator is installed on the pump housing through the one-way clutch .
Figure 4.2 Section of torque converter
The buffer and piston assembly can make the torque converter is locked in proper condition. The locking action only occurs
in the condition of specified throttle position opening and vehicle speed. When the hydraulic force makes the buffer and piston
assembly is coupled on the cover of torque converter, it can acquire the locking status. In this status, it can eliminate the
unnecessary sliding. It can increase the economical efficiency of fuel oil when the locking action is generated. When in locking
status, the torque buffer spring in the buffer and piston can absorb the torque fluctuation of engine
.
Clutch assembly
It has four types of clutch assembly (refer to Figure 4.3). All clutch assemblies are composed of several layers of steel plate and
friction disk.
Clutch C1 When it is engaged, the drive shaft drive the planet carrier. The condition occurs in 3
rd and 4th Gear.
Clutch C2 When it is engaged, the drive shaft drive the forward central gear through the 3-4 one-way clutch. The conditio
occurs in 1
st, 2nd and 3rd-Gear condition.
Clutch C3 When it is engaged, the drive shaft drive the backward central gear. The condition occurs in R-Gear position.
Clutch C4 It can provide the brake of engine during overspeed when is engaged, The condition occurs in manual 1
st, 2nd and 3rd
–Gear, also in automatic 2nd and 3rd-Gear to avoid the unfavorable inertia rotation of freewheel.
Page 125 of 425

Automatic transmission-49
The distribution of FAQ table is shown as follows:
Table 6.2.1 Drive failure Table 6.2.3 Shift quality failure
Table 6.2.2 Shift mode failure Table 6.2.4 Disassembly failure
failure Possible reason Corresponding measure
“D”-Gear operation
has not drive The automatic transmission fluid is insufficient.
The oil-entering of C1/C2 piston is blocked.
The “Z” is assembled incorrectly.
The primary regulating valve plug is opened.
The overspeed shaft or input shaft sealing ring is
failure.
3→4, 1→2 single-way clut ch is installed in revers e or
failure. Check the liquid level. Fill it up if necessary.
Check and wash the C1/C2 oil inlet device.
Reinstall the “Z” connection.
Remove, wash and reinstall the primary
regulating valve.
Check and replace it if necessary.
Check and replace it if necessary.
The reverse shifting
operation is without
drive.
The manual 1
st-Gear
has not engine
brake.
The engine brake is
normal in manual
1
st-Gear. The input shaft oil seal ring is damaged.
The rear brake belt or servo system is faulty.
C3, C3 wheel shaft or C1/C2 cylinder are out of work. Check and replace it if necessary.
Test the servo system or replace the rear brake
belt according to the requirement.
Test the failure C3, C3 wheel axle or C1/C2
cylinder.
Repair it in time if necessary.
“D” –Gear and reverse
–Gear operation is
without drive. The primary regulating valve is blocked.
The pump gear is damaged.
Take out the output shaft clasp. Det ect and clean the primary regulating valve.
Check and replace the pump gear if necessary.
Check and repair it if necessary.
Only can 2→3 shifting
(can not realize the
4
th-Gear and 1st-Gear) S1 is closed always. Test the S1. Repair or replace it if necessary.
Test the failure of S1 12V power supply
voltage or wire bundle.
Only can 1→4 shifting
1→3→4 shifting (1
→2 shifting delay). S1 is opened always Test the S1. Repair or replace it if necessary.
Test the failure of S1 12V power supply
voltage or wire bundle.
Only can 4→3 shifting S2 is closed always.
Test the S2. Repair or replace it if necessary.
Test the failure of circuit break or wire bundle.
1→2→neutral position
shifting (1st-Gear
transition) S2 is opened always Test the S2. Repair or replace it if necessary.
Test the failure of circuit break or wire bundle.
Only can 1→3 shifting B1 is out of work
The brake belt is loose.
The front servo piston or oil s eal is out of work.
S1/S2 ball spool is reinstalled in wrong place. Test and adjust it according to the requirement.
Test and maintain it according to the
requirement. Test and replace or reinstall it according
to the requirement.
Only can 1→3→4
shifting The small O-ring of front s ervo piston is invalid or
lost.
2→3 Gear position shifting valve is blocked. Det ect the O-ring. Process the replacement or
reinstallation if necessary. Detect the 2→3
Gear shifting valve; Process the maintenance
or replacement according to the requirement.
Only can 1→2→1
shifting C1 is invalid or 3rd-Gear and 4th-Gear is loose. (give
to 1st-Gear in 3rd-gear; give to 2nd-Gear in 4th-Gear) Det ect the clutch C1. Repair or replace it if
necessary.
Can not realize the
man ual 4→3, 3→2, 2
→1 Overspeed clutch /ball spool has displacement.
C4 is invalid. Detect the ball spool. Process the replacement
or reinstallation according to the requirement.
Det ect the C4. Repair C4 or r eplace the C4
wave pan according to the necessary.
Page 133 of 425
e. Take out the manual-operated valve operating lever and parking operating lever.
f. Take out the 10 pin socket connector form the wire bunch bracket adjacent gear sensor.
g. Press down the raised part of 10-pin plug and take out the 10-pin connecting plug from the box.
h. Separate the NO.7 solenoid valve wire bunch form the front end of housing.
i. Remove the brake bar pivot, brake shaft and spring.
j. Remove the shaft and rear servo operating lever.
k. Remove the rear servo cover and piston assembly.
l. Remove the BIR circlip, valve and spring.
m. Remove two brake belt adjusting shims.
n. Check the output shaft bush in box, replace it if necessary.
o. Check the cooler pipeline, replace it if necessary.
p. Check the box for damage.
Caution:
It must not remove the operating lever of parking gear in normal condition.
q. It needs to remove the P-Gear operating lever: take out the circlip from the pivot, knock the external of shaft until it can move
freely in box. Then use a width and thin object to table out the bolt form the box, operating lever and spring.
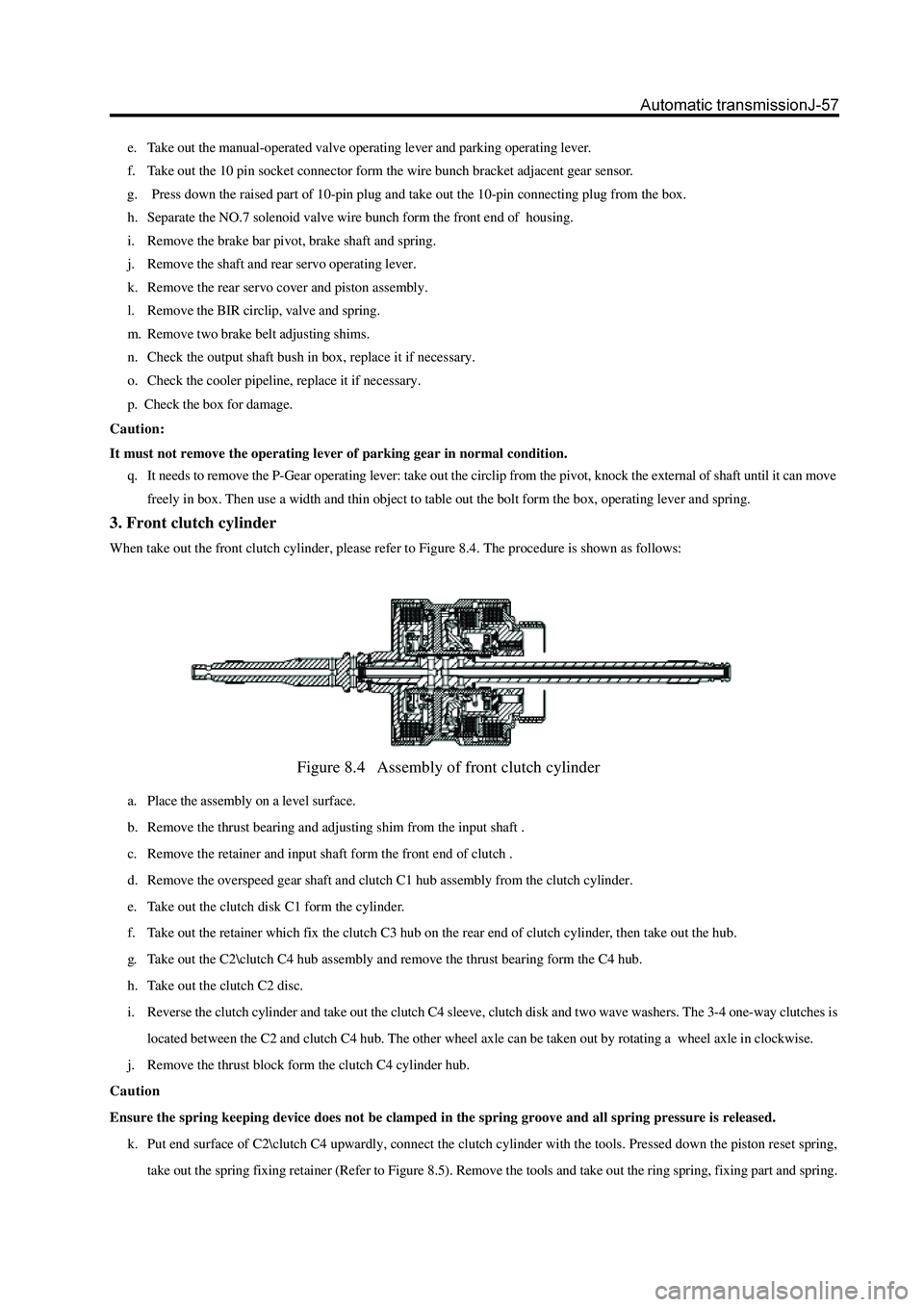
3. Front clutch cylinder
When take out the front clutch cylinder, please refer to Figure 8.4. The procedure is shown as follows:
Figure 8.4 Assembly of front clutch cylinder
a. Place the assembly on a level surface.
b. Remove the thrust bearing and adjusting shim from the input shaft .
c. Remove the retainer and input shaft form the front end of clutch .
d. Remove the overspeed gear shaft and clutch C1 hub assembly from the clutch cylinder.
e. Take out the clutch disk C1 form the cylinder.
f. Take out the retainer which fix the clutch C3 hub on the rear end of clutch cylinder, then take out the hub.
g. Take out the C2\clutch C4 hub assembly and remove the thrust bearing form the C4 hub.
h. Take out the clutch C2 disc.
i. Reverse the clutch cylinder and take out the clutch C4 sleeve, clutch disk and two wave washers. The 3-4 one-way clutches is
located between the C2 and clutch C4 hub. The other wheel axle can be taken out by rotating a wheel axle in clockwise.
j. Remove the thrust block form the clutch C4 cylinder hub.
Caution
Ensure the spring keeping device does not be clamped in the spring groove and all spring pressure is released.
k. Put end surface of C2\clutch C4 upwardly, connect the clutch cylinder with the tools. Pressed down the piston reset spring,
take out the spring fixing retainer (Refer to Figure 8.5). Remove the tools and take out the ring spring, fixing part and spring.
Page 139 of 425

Figure 8.15 manual-operated valve brake lever
k. Install the manual-operated valve detent connecting rod (shown as Figure 8.15), align it with the cross shaft hole.
l. Push the shaft by the positioning operating lever, until start from one side of box operating lever.
m. Use the special tools to install the operating lever drive bolt on the shaft, and ensure the adaptor covers the bolt.
n. Press the bolt into the shaft until the tools reaches the bottom.
o. Take out the tools and install the spring fixing ring spring on the shaft
p . Use the tools to install the new cross shaft seal.
q. Install the Gear-position sensor on the box; install the screw according to the specified torque. Use the tools to press the bolt
on the shaft.
r. Check the connection of wire bunch port completely to ensure the normal operation.
s. Install the wire bunch and install the connecting point of solenoid valve 7 and ring flange matched to the pump. Refer to Figure
8.16. The connecting wire of solenoid valve 7 is organized under the parking lever and in box cross shaft.
t . Install the 10-pin connecting socket in the box, ensure the flange of connecting socket matches to the notch on box.
u. Pull out the wire bunch part form the box and prohibition switches; install the 10-pin connecting socket on the wire bunch
bracket (only for rear-wheel drive mode).
Figure 8.16 Connecting position of coil 7Figure 8.17 Installation of 10-pin
connecting plug