2006 FORD TRANSIT lock
[x] Cancel search: lockPage 184 of 234
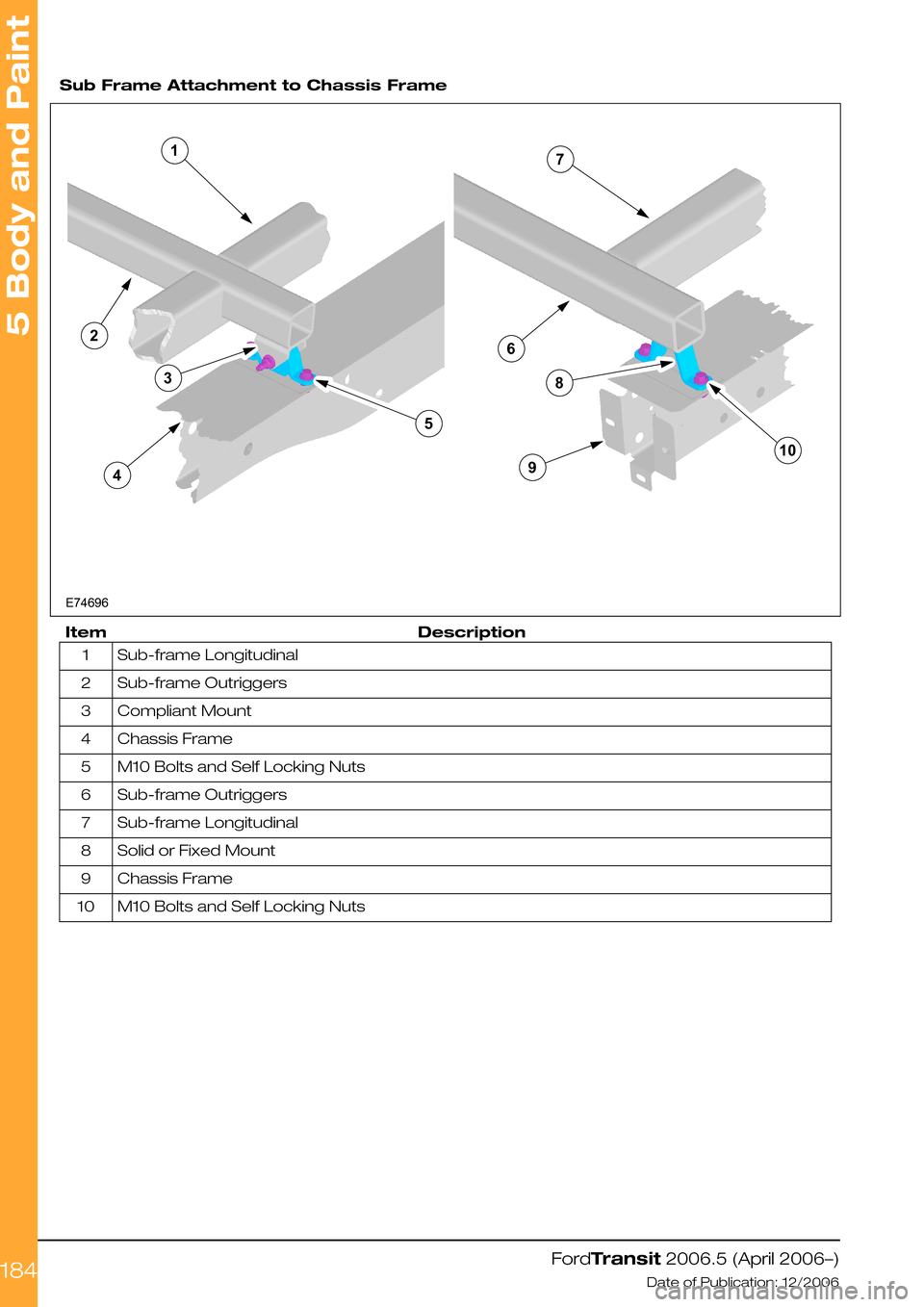
Sub Frame Attachment to Chassis Frame
DescriptionItem
Sub-frame Longitudinal1
Sub-frame Outriggers2
Compliant Mount3
Chassis Frame4
M10 Bolts and Self Locking Nuts5
Sub-frame Outriggers6
Sub-frame Longitudinal7
Solid or Fixed Mount8
Chassis Frame9
M10 Bolts and Self Locking Nuts10
FordTransit 2006.5 (April 2006–)
Date of Publication: 12/2006
5 Body and Paint
184E7469617689102345
Page 190 of 234

Sub-frame Mounted on Floor - Compliant Mount
DescriptionItem
Sub-frame Longitudinal1
Sub-frame Outriggers2
Floor of Van3
Load Compartment Tie Down (Load Lashing Point)4
Captive Compliant Bush5
For Van, Bus and Kombi:
•It is recommended to fix every mount with M8
bolt grade 8.8 minimum. For load
compartment tie down locations.
Refer to: 5.2 (page 200).
(Figures E74505 - E74508)
•It is recommended to fix sub-frame to the floor
at the load compartment tie downs only. Any
other floor contact should be padded to
prevent local stress and to allow function of
compliant mounts.
•It is not recommended to engineer through
the floor fixings to clamp around side
members.
•If the load compartment tie downs are not
suitable see, Frame Drilling and Tube
Reinforcing.
Refer to: 5.11 Frame and Body Mounting (page
222).
•Very stiff sub-frames should not be rigidly
mounted to the floor, please refer to Figure
E75876 for an example of a compliant mount.
Compliant bushes should allow up to +/-12mm
movement at a rate of 100kg per 1.0mm
deflection with only the rear pair of load
compartment tie down mounting brackets
being fixed.
•Support legs, if required, must be fitted directly
to the sub-frame
•Support legs must be designed to prevent any
adverse strain on the vehicle structure when
operating the equipment
CAUTIONS:
Safety devices must ensure the legs
are deployed when operating the
lifting equipment.
Safety devices must ensure the legs
are stowed and locked away prior
to engaging vehicle drive.
For Chassis Cab:
FordTransit 2006.5 (April 2006–)
Date of Publication: 12/2006
5 Body and Paint
190E7587642351
Page 199 of 234

Static & Dynamic Sealing and
Finishing
Use Ford approved sealing and finishing material,
and underbody corrosion protection.
Refer to: 5.10 Corrosion Prevention (page 221).
Ensure proper sealing against ingress of water,
salt, dust etc. after cutting or drilling the body.
5.1.10 Tipper Bodies
For tipper conversions single an double Chassis
Cab versions except extended rear chassis
frame can be used. All variants allow single and
three way tipping.
It is recommended to have the tipping system
operative only when the engine is running. It is
also recommended to have the master control
switch in the security of the cab. According
routing of wires and hydraulic lines please refer
to section hydraulic lift.
Ensure that axle plated weights including the
front axle minimum are not exceeded.
For tipper sub-frames please refer to the
following guidelines:
•Design for full length continuous frame with
mountings for motor, pump unit, reservoir,
pivot points and ram
•Use all mounting points on chassis frame to
mount sub-frame
•The rear two sets of chassis frame mounting
brackets should have a full torque with 100%
grip. The attachment to the remaining forward
chassis frame brackets must be precisely
located and retained, but allow some relative
flexing between the sub-frame and chassis
frame. That is clamp control devices such as
conical washer stacks or machine springs with
self locking fastenings.
•Very stiff sub-frames may damage the chassis
frame by preventing its natural flexing,
therefore compliant mounts should be captive
fail safe with up to plus and minus 12mm
compliance, vehicle laden or un-laden
whichever is worst case, rated 2mm
deflection minimum per 200kg mass at each
chassis frame forward mount, please see also
Figures E74696 Sub-frame attachment to
Chassis frame and Figure E75880 Rigid or
Torsion Stiff sub-frame for Chassis Cab.
•Use two M10 grade 8.8 minimum bolts,
washers and self locking nuts at each solid
and compliant chassis frame location.
•Sub-frame must extend to the back of the
cab and attach to all mounting locations, with
the forward end designed to minimize local
frame stress, please refer to Figure E74575
Sub-frame for low floor or other equipment.
However it is preferable to mount the
sub-frame onto the mounting brackets with
a clearance to the chassis frame top surface.
•Side tipping loads/forces must be resolved
by the sub-frame. It is not recommended to
strain the chassis frame.
5.1.11 Tank and Dry Bulk Carriers
Due to the high rigidity of tanks it is necessary to
isolate the tank and its sub-frame from the
chassis frame allowing the chassis frame to
naturally flex. Please refer to the following
guidelines:
•Mount tank to full length of sub-frame.
•Mount sub-frame to all chassis frame
mounting points.
•The rear two sets of chassis frame mounting
brackets should have solid full bolts torque
with 100% grip.
•The remaining forward location mounts must
be compliant to allow relative chassis frame
to sub-frame deflections.
•Sub-frame must extend to the back of the
cab and not contact chassis frame at forward
end under worst case deflection.
•Compliant mounts should have captive fail
safe through bolts, please refer to Figures
E74696 Sub-frame attachment to Chassis
frame and Figure E75880 Rigid or Torsion Stiff
sub-frame for Chassis Cab, with up to
plus/minus 12mm compliance, vehicle laden
or un-laden whatever is worst case, rated at
2.0mm minimum deflection per 200kg mass
each.
•Use two M10 grade 8.8 minimum bolts,
washers and self lock nuts per chassis frame
mount bracket at each solid and compliant
location.
FordTransit 2006.5 (April 2006–)
Date of Publication: 12/2006
5 Body and Paint
199
Page 203 of 234

5.3 Body Closures
Authoring Template
5.3.1 Load Compartment Interior
Lining
Do not damage the lock or latch system
(electrical cables, release system) when applying
interior lining.
WARNING: Plan fixing points for
other fitments such as racking to
ensure through bolting can be
achieved. Fixing to the lining
material may be inadequate for
normal safe operation of the vehicle.
The additional weight of the linings on doors may
require additional reinforcements to the door and
pillar at the hinge and check mechanism.
5.3.2 Security, Anti Theft and
Locking System Security
NOTE: It is not recommended to alter the
locking system.
However, in case a modification is required for
the conversions, please consult the Vehicle
Converter Advisory Service [email protected].
To avoid locking system security complications,
it is recommended to discuss with the local Ford
dealer prior to modifications taking place.
The Central Junction Box is designed to work
specifically with the Ford Transit lock and latch
mechanisms and therefore drives latches to lock
and unlock for specific time periods. Additional
power locking functionality should be based
around the use of additional Ford Transit latch
mechanisms. Additional latches can be driven
via relays connected in parallel with existing
latches.
On Chassis Cabs fitted with a high-level
Passenger Junction Box, the cargo door latch
driver is not used by the base vehicle and can
be used by Body Builders wishing to add power
locking capability to the vehicle load space. This
latch can be controlled via the driver's door key
barrel or the cargo unlock button on the remote
key fob (dependent on vehicle configuration).
The following figures outline the areas in which
it is not advisable to drill:
FordTransit 2006.5 (April 2006–)
Date of Publication: 12/2006
5 Body and Paint
203
Page 216 of 234

5.7.5 Roof Racks
Roof racks may be fitted to all van, bus and kombi
variants as illustrated in figure E75917, providing
the following is satisfied:
•The carried load does not exceed 100kg (Body
Builder to ensure owner’s hand book identifies
this limitation).
•The carried load does not exceed 300mm
load height (converter to ensure owner’s
information book identifies this limitation).
•The load is evenly distributed (converter to
ensure owner’s information book identifies this
limitation).
•The rack and subsequent carried load is
supported in the roof drip rails irrespective of
rack retaining method.
•The unit load on the roof drip, under worst
case loading, must not exceed 75kg per rack
foot.
•The rack is clamped to the drip rail at six (6)
points per illustration, or alternatively bolted
through the roof panel with minimum six (6)
M8 bolts, self locking nuts and 3mm X 50mm
square spread plates.
•The rack leading edge preferably should not
be located forward of the rear edge of the
driver’s door, or “B” pillar as shown.
Double Cab
The forgoing limitations are based on ensuring
body structure integrity, vehicle handling, braking
and plated axle weights. Such considerations
must also be applied to any double cab
applications, in particular steering, braking and
front axle plated weight and the extra continuous
loads on the “A” pillar, which should not exceed
60 kg total incremental load.
Ensure that the planned loaded vehicle operates
within its designed Center of Gravity condition.
For details please consult the Vehicle Converter
Advisory Service [email protected].
FordTransit 2006.5 (April 2006–)
Date of Publication: 12/2006
5 Body and Paint
216
Page 220 of 234

5.9 Safety Belt System
WARNING: Follow removal and
installation procedures for the seat
belt system to ensure correct
function of the restraints system.
The removal and reinstallation of the seat belt,
strainer or any component of the seat belt system
should be avoided. In case the removal and
re-installation system is required during the
conversion, however, follow the guidelines for
removal and installation of the seat belt system
as described in the workshop manual. Please
consult your local National Sales Company
representative for further information
When removing the seat belt system, a seat belt
webbing forked retainer should be applied to the
webbing 200mm below the webbing button stop.
This prevents a situation where all the webbing
runs back into the retractor and the retractor
becomes locked.
When reinstalling, fit the retractor to the body first
and gently pull the webbing out of the retractor
to allow fitment of the D loop. Then remove the
forked retainer. If the retractor is locked, allow a
small amount of webbing to reel back into the
retractor to allow the webbing lock to release. Do
not attempt to release the retractor by pulling on
the webbing with significant force or by manually
interfering with the locking mechanism.
FordTransit 2006.5 (April 2006–)
Date of Publication: 12/2006
5 Body and Paint
220
Page 228 of 234

•It is recommended that the altered extension
has a similar closed section, material thickness
and properties to the existing chassis frame.
•An equivalent open section for the extension
assembly is at the vehicle converters
discretion.
•Lightening holes in new extension and cross
members are discretional.
•Do not weld original chassis frame except as
specified when adding reinforcing tubes,
please refer to Figure E745171.
•Do not drill the top or bottom surface of the
chassis frame, including the flanges turned
out, except as recommended above for
continuity of closure.
•Any alternative finish such as hot dip
galvanizing is at the discretion of the Body
Builder providing it does not have a detrimental
effect on the original Ford product.
Refer to: 5.10 Corrosion Prevention (page 221).
5.11.5 Frame Drilling and Tube
Reinforcing
The chassis frame may be drilled and reinforcing
spacer tubes may be welded in place, providing
the following is applied:
•Adhere to all details shown in Figure E74517.
•Drill and weld only side walls of the chassis
frame.
•Locate and drill holes accurately, using a drill
guide to ensure holes are square to frame
vertical centre line (note: allow for side member
draft angle).
•Drill undersize and ream out to size.
•Endeavor to remove all swarf from inside side
member, and treat to prevent corrosion.
•Fully weld each end of the tube and grind flat
and square, in groups if applicable. Be aware
of side member draft angle.
•Apply corrosion protection inside and outside
of the chassis frame.
Refer to: 5.10 Corrosion Prevention (page 221).
•Holes should be in groups of two (2), either
vertically spaced at 30 to 35mm from chassis
frame top and/or bottom surface, or
horizontally at 50mm minimum pitch, 30 to
35mm from top and/or bottom chassis frame
surface, please refer to Figure E74517.
•Always use M10 bolts with grade 8.8 minimum.
•Do not position tubes at the medium chassis
frame height, this may create “oil canning” of
the deep section side walls.
•Where possible, the outrigger moments should
be resolved by matching inner cross members
between the chassis side members inline with
the outriggers, please refer to Figure E74577-
Low Floor.
•A diameter of 16.5mm is the maximum
allowable hole size in the chassis frame side
wall, irrespective of the usage.
Avoid drilling into closed frame body members
to avoid the risk of corrosion from swarf.
Refer to: 5.10 Corrosion Prevention (page 221).
Drilling and welding of frames and body structure
have to be conducted following the program
guidelines. Please consult the Vehicle Converter
Advisory Service [email protected] for details.
5.11.6 Ancillary Equipment - Sub
Frame Mounting
Typical sub-frames and longitudinal members for
flatbed and low or drop-side bodies or equipment
exceeding the standard or Regular Production
Order frame length should adhere to the following
guidelines:
•Flat-beds and low bodies mounted on integral
longitudinal members (channel or box section
metal – not wood) must use both sides of all
frame mounting brackets, see Figure E74575.
•Longitudinal members must be relieved at the
front end if they are to contact the chassis
frame top surface, to minimize stress
concentrations, see Figure E74575. However,
it is preferable to mount the longitudinal onto
the mounting brackets, with a clearance to the
chassis frame top surface.
•Each set of brackets must use two (2) x M10
bolts grade 8.8 minimum.
•The rear two (2) sets of chassis frame
mounting holes / locations should have a full
bolt torque with 100% grip. The attachment to
the remaining forward chassis frame holes /
locations must be precisely located and
retained, but allow some relative flexing
between the sub-frame and chassis frame.
For example, clamp control devices such as
conical washer stacks or machine springs with
self locking fasteners.
•Minimum floor heights will require wheel arch
boxes to clear the rear tires, see Vehicle Data
sheets for relevant tire jounce.
•Chassis frame, for example: clamp control
devices such as conical washer stacks or
machine springs with self locking fastenings.
•Minimum floor heights will require wheel arch
boxes to clear the rear tires.
Pedestal mounted low or drop side bodies – (not
illustrated)
For bodies or equipment not exceeding the
standard or Regular Production Order chassis
frame length.
FordTransit 2006.5 (April 2006–)
Date of Publication: 12/2006
5 Body and Paint
228
Page 230 of 234

A
About This Manual................................................6
Accessory Drive..................................................77
Adding Connectors, Terminals and Wiring....
162
Additional 'Theatre Lighting' for rear of vehicle
interior...............................................................118
Additional External Lamps...............................116
Additional Ignition, Instrument Panel Illumination
and Air Conditioning On Signals...................124
Additional Internal Lamps ................................118
Additional Vehicle Signals / Features.............147
Aids for Vehicle Entry and Exit..........................33
Air Bags..............................................................218
Air Bag Supplemental Restraint System (SRS)..
218
Air Flow Restrictions...........................................76
Alternative Type Approval....................................7
Ancillary Equipment - Sub Frame Mounting....
228
Antenna Location...............................................24
Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist..................65
Auxiliary Fuses, Fuse Box and Relays (Fuses -
Standard)..........................................................119
Auxiliary Heater Installation...............................76
Auxiliary Heater Systems..................................75
B
Back Panel Removal................................177, 214
Battery and Cables............................................98
Battery Information............................................98
Body....................................................................175
Body Closures..................................................203
Body Structures - General Information.........175
Body System - General
Information—Specifications.........................200
Brake Hoses General........................................62
Brake System.....................................................62
C
Cab Roof Removal...........................................214
Cab Van Floor....................................................185
CAN-Bus System Description and Interface....
90
Cellular Phone....................................................115
Center of Gravity ...............................................46
Central Junction Box (CJB)...............................91
Charge Balance Guidelines..............................97
Charging System...............................................95
Chassis Cab.......................................................179
Circit Diagram.....................................................94
Circuit Diagram...................................................93
Circuit Diagrams.................................................97
Climate Control System..................................106
Clutch...................................................................82
Commercial and Legal Aspects.........................7
Communications Network...............................90
Connectors........................................................133
Contact Corrosion............................................221
Contact Information.............................................9
Conversion Affect on Fuel Economy and
Performance.....................................................25
Conversion Affects on Parking Aids................33
Conversion Homologation...............................23
Conversion Type.................................................14
Corrosion Prevention.......................................221
Customer Connection Points.........................120
D
Drilling and Welding..............................................8
Driver's Standing Head Room........................214
Driver Field of View.............................................33
Driver Reach Zones...........................................33
Driveshaft.............................................................61
E
Electrical Conversions.......................................95
Electrically operated Door Mirrors..................117
Electrics for Tow bar........................................136
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)............24
Electronic Engine Controls................................81
End of Life Vehicle (ELV) Directive...................26
Engine Cooling....................................................75
Engine..................................................................66
Engine Power Curves.......................................66
Engine RPM (Revs Per Minute) Speed
Controller..........................................................157
Engine Run Signal (D+ Alternative)................132
Exhaust Heat Shields.........................................86
Exhaust Pipes and Supports............................86
Exhaust System.................................................86
Extended Chassis Frame...............................226
Extensions and Optional Exhausts..................86
Exterior Lighting.................................................116
F
Fitting of Equipment Containing an Electric
Motor..................................................................97
Frame and Body Mounting............................222
Frame Drilling and Tube Reinforcing.............228
Front, Rear and Side Under-run Protection....
38
Front and Rear Brakes......................................64
Front End Accessory Drive 2.2l Diesel............79
Front End Accessory Drive 2.4l Diesel and 2.3l
Petrol...................................................................77
Front End Integrity for Cooling, Crash,
Aerodynamics and Lighting..........................198
Front Suspension...............................................58
Fuel System........................................................88
Fuses and Relays..............................................119
G
General........................................................62, 221
General Component Package Guidelines.....33
General Information and Specific Warnings....
95
General........................................................62, 221
General Product Safety Requirement...............7
Index
230