Page 358 of 2893

����
��������
M/T
Secondary Heated Oxygen Sensor (Secondary HO2S)
Accelerator Pedal Position (APP) Sensor
Electronic Throttle Control System
11-35
TERMINAL
MAGNET O-RING O-RING
ZIRCONIA
ELEMENT SENSOR
TERMINALS
HEATER
TERMINALS
HEATER
APP SENSOR A/B
ACCELERATOR
PEDAL MODULE
The secondary HO2S detects the oxygen content in the
exhaust gas downstream of the three way catalytic
converter (TWC), and sends signals to the ECM/PCM
which varies the duration of fuel injection accordingly.
To stabilize its output, the sensor has an internal heater.
The ECM/PCM compares the HO2S output with the A/F
sensor output to determine catalyst efficiency. The
secondary HO2S is on the TWC. The throttle is electronically controlled by the electronic
throttle control system. Refer to the system diagram to
see a functional layout of the system.
Idle control: When the engine is idling, the ECM/PCM
controls the throttle actuator to maintain the proper idle
speed according to engine loads.
Acceleration control: When the accelerator pedal is
pressed, the ECM/PCM opens the throttle valve,
depending on the accelerator pedal position (APP)
sensor signal.
Cruise control: The ECM/PCM controls the throttle
actuator to maintain the set speed when the cruise
control is operating. The throttle actuator takes the
place of the cruise control actuator.
As the accelerator pedal position changes, the sensor
varies the signal voltage to the ECM/PCM.
(cont’d)
08/08/21 14:13:39 61SNR030_110_0035
ProCarManuals.com
DYNOMITE -2009-
Page 359 of 2893

����Throttle Body
Brake Pedal Position Switch
Electrical Power Steering (EPS) Signal
Fuel Cutoff Control
Fuel Pump Control
PGM-FI Main Relay 1 and 2
Idle Control System
Fuel Supply System
11-36Fuel and Emissions Systems
System Description (cont’d)
THROTTLE VALVE
THROTTLE POSITION
(TP) SENSOR and
THROTTLE ACTUATOR
The throttle body is a single-barrel side draft type. The
lower portion of the throttle valve is heated by engine
coolant from the cylinder head to prevent icing of the
throttle plate. When the engine is cold, the A/C compressor is on, the
transmission is in gear, the brake pedal is pressed, the
power steering load is high, or the alternator is
charging, the ECM/PCM sends signal to the throttle
position to maintain the correct idle speed.
The brake pedal position switch signals the ECM/PCM
when the brake pedal is pressed.
The EPS signals the ECM/PCM when the power steering
load is high.
During deceleration with the throttle valve closed,
current to the injectors is cut off to improve fuel
economy at engine speeds over 1,000 rpm. Fuel cutoff
control also occurs when the engine speed exceeds
6,900 rpm (K20Z3: 8,200 rpm), regardless of the
position of the throttle valve, to protect the engine from
over-revving. When the vehicle is st
opped, the ECM/
PCM cuts the fuel at engine speeds over 5,000 rpm
(K20Z3: 7,700 rpm). On a cold engine, fuel cut occurs at
a lower engine speed.
When the ignition switch is turned to ON (II), the ECM/
PCM grounds PGM-FI main relay 2 (FUEL PUMP) which
feeds current to the fuel pump for 2 seconds to
pressurize the fuel system. With the engine running, the
ECM/PCM grounds PGM-FI main relay 2 (FUEL PUMP)
and feeds current to the fuel pump. When the engine is
not running and the ignition is turned to ON (II), the
ECM/PCM cuts ground to PGM-FI main relay 2 (FUEL
PUMP) which cuts current to the fuel pump.
PGM-FI main relay 1 is energized whenever the ignition
switch is ON (II), to supply battery voltage to the ECM/
PCM, power to the injectors, and power for PGM-FI
main relay 2 (FUEL PUMP). PGM-FI main relay 2 (FUEL
PUMP) is energized to supply power to the fuel pump
for 2 seconds when the ignition switch is turned to
ON (II), and when the engine is cranking or running.
08/08/21 14:13:39 61SNR030_110_0036
ProCarManuals.com
DYNOMITE -2009-
Page 360 of 2893

����
i-VTEC
11-37
LOW SPEED CAMHIGH SPEED CAM
HIGH
ENGINE SPEED HIGH
LOW
LOW
ENGINE
LOAD
TORQUE CURVE
The i-VTEC system has a variable valve timing control (VTC) mechanism on the intake camshaft in addition to the
usual VTEC.
This system improves fuel efficiency and reduces exhaust emissions at all levels of engine speed, vehicle speed,
and engine load.
The VTEC system changes the valve lift and timing by using more than one cam profile.
The VTC system changes the phase of the intake camshaft via oil pressure. It changes the intake valve timing continuously.
Driving Condition VTC Control Description
Light-load Base Position For stable combustion, the cam angle is retarded, and reduces the entry of exhaust gas into the cylinder.
Medium/high-load Advance Control Cam phase angle is controlled to optimize valve timing, improving fuel efficiency and reducing
emissions.
High speed Advance-Base Position To reduce pumping loss, the intake valve is closed quickly. This gives the air/fuel mixture a charging
effect that helps to maximize engine power.
(cont’d)
08/08/21 14:13:39 61SNR030_110_0037
ProCarManuals.com
DYNOMITE -2009-
Page 361 of 2893

����
�
�
�
�
VTC System
VTEC System
K20Z2 engine
K20Z3 engine
11-38
Fuel and Emissions Systems
System Description (cont’d)
MAXIMUM VTC ADVANCE 25 °
TDC
EX IN 1IN 2
EX IN 2IN 1
MAXIMUM VTC ADVANCE 25 °
SHORT OVERLAP
LONG OVERLAP
LOW SPEED VALVE TIMING HIGH SPEED VALVE TIMING
EX IN EXIN
IN (LOW LIFT)
LOW SPEED VALVE TIMING HIGH SPEED VALVE TIMING
EX IN EX IN
The VTC system makes continuous intake valve timing changes based on operating conditions.
Intake valve timing is optimized to allow the engine to produce maximum power.
Cam angle is advanced to obtain the EGR effect and reduce pumping loss. The intake valve is closed quickly to
reduce the entry of the air/fuel mixture into the intake port and improve the charging effect.
The system reduces the cam advance at idle, stabilizes combustion, and reduces engine speed.
If a malfunction occurs, the VTC system control is disabled and the valve timing is fixed at the fully retarded position.
The VTEC system changes the cam profile to correspond to the engine speed. It maximizes torque at low engine speed and output at high engine speed.
The low lift cam is used at low engine speeds, and the high lift cam is used at high engine speeds.
08/08/21 14:13:40 61SNR030_110_0038
ProCarManuals.com
DYNOMITE -2009-
Page 363 of 2893
�
������
�
��
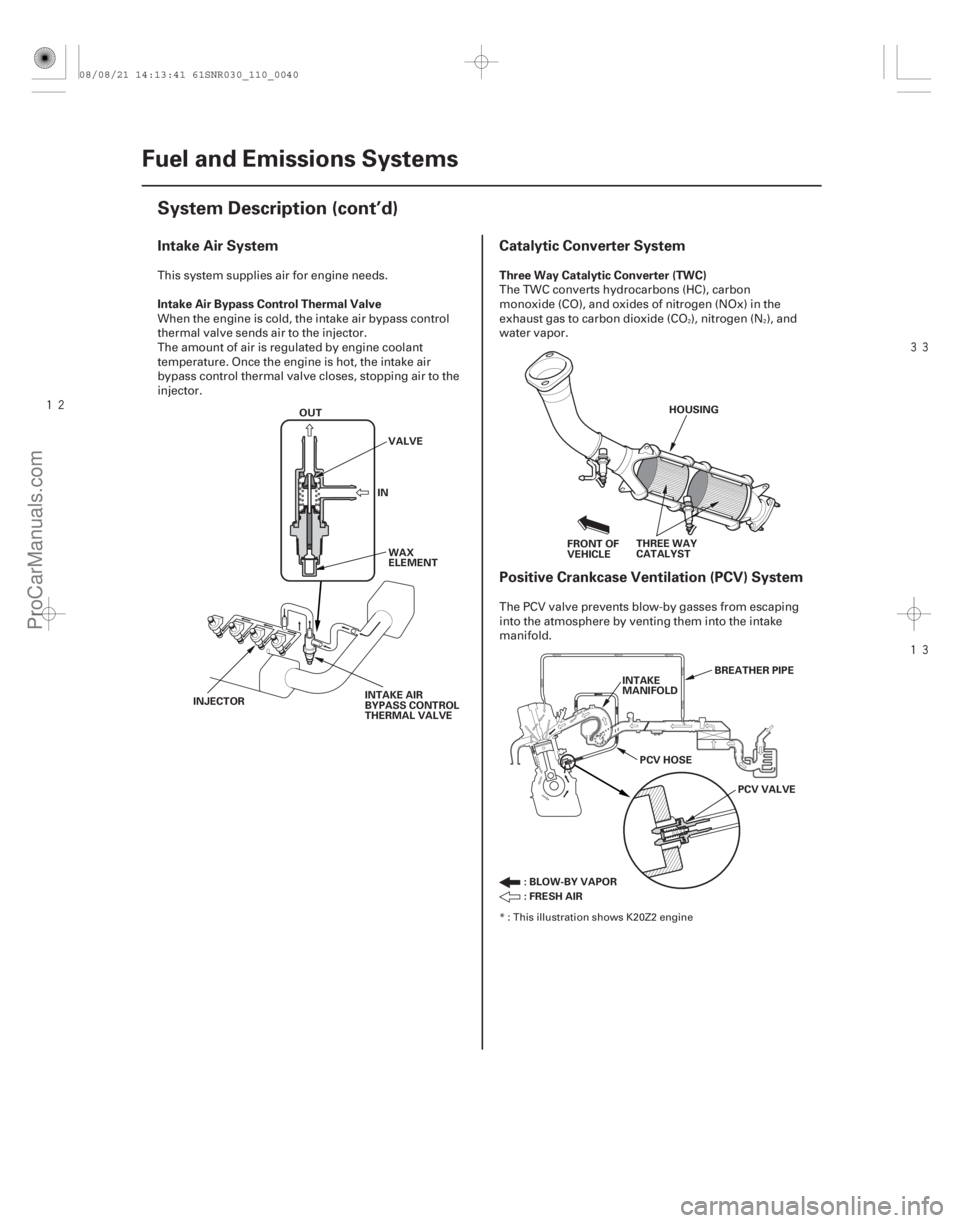
Intake Air System
Catalytic Converter System
Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) System
Intake Air Bypass Control Thermal Valve Three Way Catalytic Converter (TWC)
11-40Fuel and Emissions Systems
System Description (cont’d)
OUT
INVALVE
WAX
ELEMENT
INJECTOR INTAKE AIR
BYPASS CONTROL
THERMAL VALVE FRONT OF
VEHICLE
HOUSING
THREE WAY
CATALYST BREATHER PIPE
INTAKE
MANIFOLD
PCV HOSE PCV VALVE
:BLOW-BYVAPOR
:FRESHAIR
This system supplies air for engine needs.
When the engine is cold, the intake air bypass control
thermal valve sends air to the injector.
The amount of air is regulated by engine coolant
temperature. Once the engine is hot, the intake air
bypass control thermal valve closes, stopping air to the
injector. The TWC converts hydrocarbons (HC), carbon
monoxide (CO), and oxides of nitrogen (NOx) in the
exhaust gas to carbon dioxide (CO ), nitrogen (N ), and
water vapor.
The PCV valve prevents blow-by gasses from escaping
into the atmosphere by venting them into the intake
manifold.
22
* : This illustration shows K20Z2 engine
08/08/21 14:13:41 61SNR030_110_0040
ProCarManuals.com
DYNOMITE -2009-
Page 364 of 2893

��������
����
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System
(K20Z2 engine)
Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Control
System
EGR Valve
EVAP Canister
EVAP Canister Purge Valve
Fuel Tank Pressure (FTP) Sensor
EVAP Canister Vent Shut Valve
11-41
TERMINAL
COIL
OUT
IN O-RING
TERMINAL
SENSOR UNIT
O-RING VALVE O-RING TERMINAL
Refer to the system diagram to see a functional layout
of the system.
The EGR valve lowers peak combustion temperatures
and reduces oxides of nitrogen emissions (NOx) by
recirculating exhaust gas through the intake manifold
and into the combustion chambers.
Refer to the system diagram to see a functional layout
of the system.
The EVAP canister temporarily stores fuel vapor from
the fuel tank until it can be purged back into the engine
and burned.
When the engine coolant temperature is below 60 °C
(140 °F), the ECM/PCM turns off the EVAP canister
purge valve which cuts vacuum to the EVAP canister. The FTP sensor converts fuel tank absolute pressure
into an electrical input to the ECM/PCM.
The EVAP canister vent shut valve is on the EVAP
canister.
The EVAP canister vent shut valve controls the venting
of the EVAP canister.
(cont’d)
08/08/21 14:13:42 61SNR030_110_0041
ProCarManuals.com
DYNOMITE -2009-
Page 365 of 2893

��
��
Fuel Cap Warning MessageTo make the message go off (with the HDS)
To make the message go off (without the
HDS) (’06 model)
To make the message go off (without the
HDS) (’07-09 models)
First drive cycle Procedure
Procedure
Procedure
11-42Fuel and Emissions Systems
System Description (cont’d)
A
Shows CHECK FUEL CAP
in the gauge display.
The ECM/PCM detects a loose or missing fuel fill cap as
an evaporative system leak, and alarts the driver by
showing a warning message in the gauge display.
The first time a leak is detected a CHECK FUEL CAP
message is shown in the gauge display (A). To scroll to
another message, press the select/reset button. The
CHECK FUEL CAP message appears each time you
restart the engine until the system turns the message
off. Turn the engine off, then replace or tighten the fuel
fill cap until it clicks at least once.
1. Tighten the fuel fill cap until it clicks.
2. Clear the Temporary DTC with the HDS.
3. Verify there is no leak by doing the EVAP
FUNCTION TEST in the INSPECTION MENU with
the HDS.
1. Tighten the fuel fill cap until it clicks.
2. The message should go off after s everal days of
normal driving.
1. Tighten the fuel fill cap until it clicks.
2. Start the engine, then turn the ignition switch to LOCK (0).
3. Repeat step 2 two more times.
08/08/21 14:13:43 61SNR030_110_0042
ProCarManuals.com
DYNOMITE -2009-
Page 367 of 2893
��
�
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) System Diagram (K20Z2 engine)
11-44Fuel and Emissions Systems
System Description (cont’d)
INTAKE MANIFOLD
EGR VALVE
EGR VALVE
POSITION SENSOR
YEL/BLU
GRN/BLK
WHT/BLK
BLU/RED
BLK/RED
(BLK)
BLK
ECM/PCM
VARIOUS
SENSORS
* : ’07-09 models
*
The EGR system reduces oxides of nitrogen (NOx) emissions by recirculating exhaust gas through the EGR valve and
the intake manifold into the combustion chambers. The ECM/PCM memory includes the ideal EGR valve position for
varying operating conditions.
The EGR valve position sensor detects the amount of EGR valve lift and sends it to the ECM/PCM. The ECM/PCM then
compares it with the ideal lift in its memory (based on signals sent from other sensors). If there is any difference
between the two, the ECM/PCM cuts current to the EGR valve.
08/08/21 14:13:43 61SNR030_110_0044
ProCarManuals.com
DYNOMITE -2009-