Page 4396 of 5135
−
DIAGNOSTICS ECD SYSTEM (1CD −FTV)(From September, 2003)
05 −465
AVENSIS Supplement (RM 1045E)
DTC P 160 1 INJECTOR CORRECTION CIRCUIT
MALFUNCTION (EEPROM)
NOTICE:
S If an incorrect injector compensation code was registered with the ECM, it may rattle the engine
assembly or the engine idling may become rough. In addition, it may become a cause of engine
failure or shorten the life of the engine.
1 . If you replace the ECM with a new one, register all the injector compensation codes with the
new ECM as follows:
(a) Prior to replacing the ECM, read all the compensation codes stored in the existing ECM using the hand−held tester, and then write them down (see page 05 −273).
(b) After replacing the ECM, enter the written compensation codes into the ECM using the hand −held tes-
ter (see page 05 −277).
(c) Turn the ignition switch to OFF and wait for 30 seconds or more.
(d) Turn the ignition switch to ON, then clear DTC P 160 1 using the hand −held tester (see page 05 −290).
HINT:
S In order to optimize the injector ’s fuel injection characteristic, the ECM compensates the injection dura-
tion by each cylinder. The ECM stores and uses compensating data in the form of a 30 −digit −alphanu-
meric value that is imprinted on the head portion of each injector as the injector compensation code.
S If you installed a new injector, its own injector compensation code is needed to register with the ECM.
Also, if you replaced the ECM, the compensation codes of all the injectors are needed to register be-
cause the new ECM dose not have the codes until they are registered.
S Once the ECM is replaced, DTC P 160 1 will be present when turning the ignition switch to ON. This
is to inform you that the injector compensation codes are required to register with the ECM. In order
to clear the DTC, register the compensation codes first, then turn the ignition switch to OFF and wait
for 30 seconds or more.
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
DTC No.DTC Detection ConditionTrouble Area
P 160 1
Injector compensation code is not registered
(1 trip detection logic)
S Injector compensation codeP 160 1Wrong injector compensation code is registered
(1 trip detection logic)
Injector compensation code
S ECM
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Read freeze frame data using the hand−held tester. Freeze frame data records the engine conditions when
a malfunction is detected. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can help determine if the vehicle was
running or stopped, if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air −fuel ratio was lean or rich, and other data
from the time the malfunction occurred.
1 CHECK INJECTOR COMPENSATION CODE (See page 05 −273)
NG SET INJECTOR COMPENSATION CODE
(See page 05 −277)
OK
REPLACE ECM (See page 10− 29)
05CQ2 −03
Page 4397 of 5135
−
DIAGNOSTICS ECD SYSTEM (1CD −FTV)(From September, 2003)
05 −457
AVENSIS Supplement (RM 1045E)
DTC P 1425 DIFFERENTIAL PRESSURE SENSOR
CIRCUIT
DTC P 1427 DIFFERENTIAL PRESSURE SENSOR
CIRCUIT LOW
DTC P 1428 DIFFERENTIAL PRESSURE SENSOR
CIRCUIT HIGH
HINT:
S For more information on the differential pressure sensor and TOYOTA D −CAT (* 1), see page 05 −255.
S If P 1425, P 1427 and/or P 1428 is present, refer to the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) table for TOYO-
TA D −CAT on page 05 −255.
* 1 : Diesel Clean Advanced Technology.
05I82 −01
Page 4398 of 5135
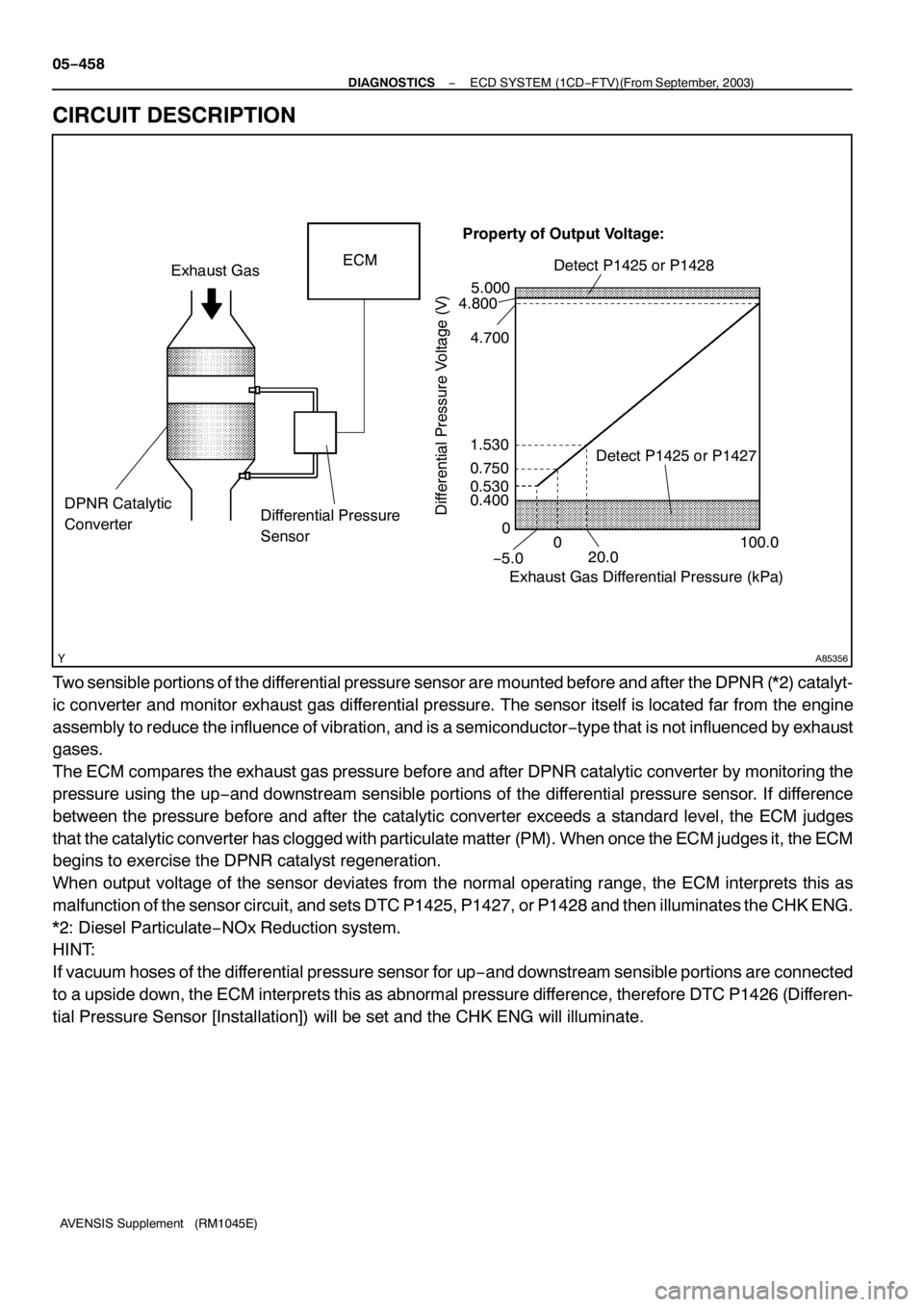
A85356
ECM
Exhaust Gas
Exhaust Gas Differential Pressure (kPa)
Differential Pressure Voltage (V)
1.530
0.750
0.530
0
−5.020.0100.0 Detect P1425 or P1428
5.000
4.700 4.800
0 0.400
Differential Pressure
Sensor
Property of Output Voltage:
Detect P1425 or P1427
DPNR Catalytic
Converter 05−458
− DIAGNOSTICSECD SYSTEM (1CD−FTV)(From September, 2003)
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E)
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
Two sensible portions of the differential pressure sensor are mounted before and after the DPNR (*2) catalyt-
ic converter and monitor exhaust gas differential pressure. The sensor itself is located far from the engine
assembly to reduce the influence of vibration, and is a semiconductor−type that is not influenced by exhaust
gases.
The ECM compares the exhaust gas pressure before and after DPNR catalytic converter by monitoring the
pressure using the up−and downstream sensible portions of the differential pressure sensor. If difference
between the pressure before and after the catalytic converter exceeds a standard level, the ECM judges
that the catalytic converter has clogged with particulate matter (PM). When once the ECM judges it, the ECM
begins to exercise the DPNR catalyst regeneration.
When output voltage of the sensor deviates from the normal operating range, the ECM interprets this as
malfunction of the sensor circuit, and sets DTC P1425, P1427, or P1428 and then illuminates the CHK ENG.
*2: Diesel Particulate−NOx Reduction system.
HINT:
If vacuum hoses of the differential pressure sensor for up−and downstream sensible portions are connected
to a upside down, the ECM interprets this as abnormal pressure difference, therefore DTC P1426 (Differen-
tial Pressure Sensor [Installation]) will be set and the CHK ENG will illuminate.
Page 4399 of 5135
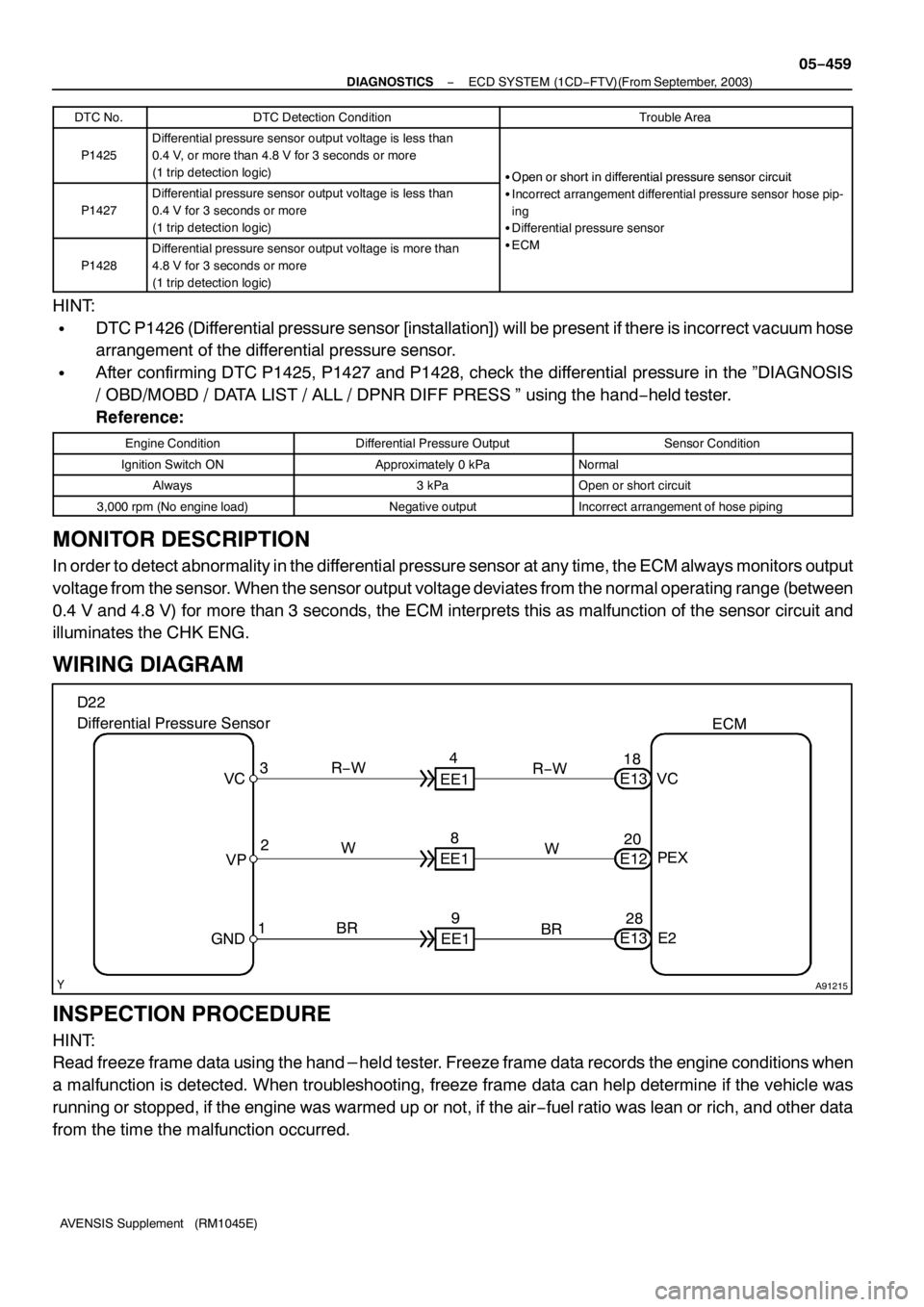
A91215
VCECM
PEX
E2 W R−W
BR D22
Differential Pressure Sensor
13
218
E13
20
E12
28
E13 VC
GNDVPR−W
W
BR EE1
EE1
EE1 4
9 8
− DIAGNOSTICSECD SYSTEM (1CD−FTV)(From September, 2003)
05−459
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E) DTC No.
DTC Detection ConditionTrouble Area
P1425
Differential pressure sensor output voltage is less than
0.4 V, or more than 4.8 V for 3 seconds or more
(1trip detection logic)
SOpen or short in differentialpressure sensor circuit
P1427
Differential pressure sensor output voltage is less than
0.4 V for 3 seconds or more
(1trip detection logic)
SOpenorshortindifferentialpressuresensorcircuit
SIncorrect arrangement differential pressure sensor hose pip-
ing
SDifferential pressure sensor
P1428
Differential pressure sensor output voltage is more than
4.8 V for 3 seconds or more
(1trip detection logic)
ee tap essu ese so
SECM
HINT:
SDTC P1426 (Differential pressure sensor [installation]) will be present if there is incorrect vacuum hose
arrangement of the differential pressure sensor.
SAfter confirming DTC P1425, P1427 and P1428, check the differential pressure in the ”DIAGNOSIS
/ OBD/MOBD / DATA LIST / ALL / DPNR DIFF PRESS ” using the hand−held tester.
Reference:
Engine ConditionDifferential Pressure OutputSensor Condition
Ignition Switch ONApproximately 0 kPaNormal
Always3 kPaOpen or short circuit
3,000 rpm (No engine load)Negative outputIncorrect arrangement of hose piping
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
In order to detect abnormality in the differential pressure sensor at any time, the ECM always monitors output
voltage from the sensor. When the sensor output voltage deviates from the normal operating range (between
0.4 V and 4.8 V) for more than 3 seconds, the ECM interprets this as malfunction of the sensor circuit and
illuminates the CHK ENG.
WIRING DIAGRAM
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Read freeze frame data usingthe hand−held tester.Freeze frame data records the engine conditions when
a malfunction is detected. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can help determine if the vehicle was
running or stopped, if the engine was warmed up or not, if the air−fuel ratio was lean or rich, and other data
from the time the malfunction occurred.
Page 4400 of 5135
05−460
−
DIAGNOSTICS ECD SYSTEM (1CD −FTV)(From September, 2003)
AVENSIS Supplement (RM 1045E)
1 READ VALUE OF HAND −HELD TESTER(DIFFERENTIAL PRESSURE)
(a) Connect the hand −held tester to the DLC3.
(b) Turn the ignition switch to ON and turn the hand −held tester ON.
(c) Select the item ”DIAGNOSIS / OBD/MOBD / DATA LIST / ALL / DPNR DIFF PRESS”.
(d) Check that differential pressure is within the specification below.
Result:
ConditionDifferential PressureProceed to
Always−5 kPa or lessA
Ignition Switch ON−4 kPa to 98 kPaB
Always99 kPaC
B CHECK FOR INTERMITTENT PROBLEMS
(See page 05 −270)
C Go to step 3
A
2 CHECK CONNECTION OF VACUUM HOSE(DIFFERENTIAL PRESSURE SENSOR −
VACUUM TRANSMITTING PIPE)
(a) Check if vacuum hose arrangement between the differential pressure sensor and the vacuum trans-
mitting pipe is not incorrect arrangement (see page 14−1 08).
(b) Check that there is no exhaust gas leak between the differential pressure sensor and the vacuum transmitting pipe (see page 14−1 08).
NG CORRECT TO NORMAL CONNECTION
OK
3 CHECK BLOCKAGE(DIFFERENTIAL PRESSURE SENSOR)
CAUTION:
Be careful for being burned by exhaust gases during the following inspection.
(a) Disconnect the vacuum hose (both up −and downstream) on the differential pressure sensor side.
(b) Start the engine.
(c) Check if there is exhaust gas pulsations from both vacuum hoses during idling.
NG REPLACE CLOGGED PARTS(See page 14−1 08)
OK
Page 4401 of 5135

A90876
D22
Front View
Wire Harness Side:
Differential pressure
Sensor Connector
VP
VC
GND
A8 1088
E 13
ECM Connector
E
12
PEX
VC
−
DIAGNOSTICS ECD SYSTEM (1CD −FTV)(From September, 2003)
05 −46 1
AVENSIS Supplement (RM 1045E)
4 CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR(DIFFERENTIAL PRESSURE SENSOR −
ECM)
(a) Disconnect the D22 differential pressure sensor connec-
tor.
(b) Disconnect the E 12 and E 13 ECM connectors.
(c) Check the resistance between the wire harness side con- nectors.
Standard (Check for open):
Tester ConnectionSpecified Condition
PEX (E 12− 20) − VP (D22 −2)
VC (E 13−1 8)− VC (D22 −3)Below 1�
E2 (E 13− 28) − GND (D22 −1 )
Standard (Check for short):
Tester ConnectionSpecified Condition
PEX (E 12− 20) or VP (D22 −2) − Body ground10 k � or higherVC (E 13−1 8) or VC (D22 −3) − Body ground10k � or higher
(d) Reconnect the differential pressure sensor connector.
(e) Reconnect the ECM connectors.
NG REPAIR OR REPLACE HARNESS OR CONNECTOR
OK
REPLACE DIFFERENTIAL PRESSURE SENSOR ASSY (See page 14−1 08)
Page 4402 of 5135
05−444
−
DIAGNOSTICS ECD SYSTEM (1CD −FTV)(From September, 2003)
AVENSIS Supplement (RM 1045E)
DTC P 1386 INJECTOR FOR EXHAUST FUEL ADDITION
HINT:
S For more information on the exhaust fuel addition injector and TOYOTA D −CAT (* 1), see page
05 −255.
S If P 1386 is present, refer to the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) table for TOYOTA D −CAT on page
05 −255.
S”Learning value” used in here represents a correction learning value of the fuel addition volume to raise
the DPNR (*2) catalyst temperature to a target range.
* 1 : Diesel Clean Advanced Technology.
*2: Diesel Particulate −NOx Reduction system.
05I8 1−01
Page 4403 of 5135
A85355
Exhaust Fuel
Addition Injector
Injector Spray Supply PumpExhaust Gas
Temperature
Sensor (on up stream)
ECM Exhaust
Gas
Exhaust Gas Temperature
Sensor (on down stream)
Exhaust Fuel Addition InjectorA/F Sensor DPNR Catalytic
Converter
Turbocharger
− DIAGNOSTICSECD SYSTEM (1CD−FTV)(From September, 2003)
05−445
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E)
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The exhaust fuel addition injector is mounted on the exhaust port of the cylinder head, and low pressure is
provided to the injector by the feed pump in the supply pump. This injector adds fuel by a control signal from
the ECM.
This injector is used for two different controls: DPNR catalyst regeneration and nitrogen oxides (NOx) reduc-
tion.
Under the DPNR catalyst regeneration control, the injector adds fuel to raise a catalyst temperature.
In the other control, the injector helps the air−fuel ratio become RICH. As a result, NOx in the exhaust gas
will be reduced in response to the RICH air−fuel ratio.