Page 530 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE MECHANICAL (M13 ENGINE) 6A1-49
REMOVAL
1) Relieve fuel pressure referring to “Fuel Pressure Relief Pro-
cedure” in Section 6.
2) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
3) Drain engine oil.
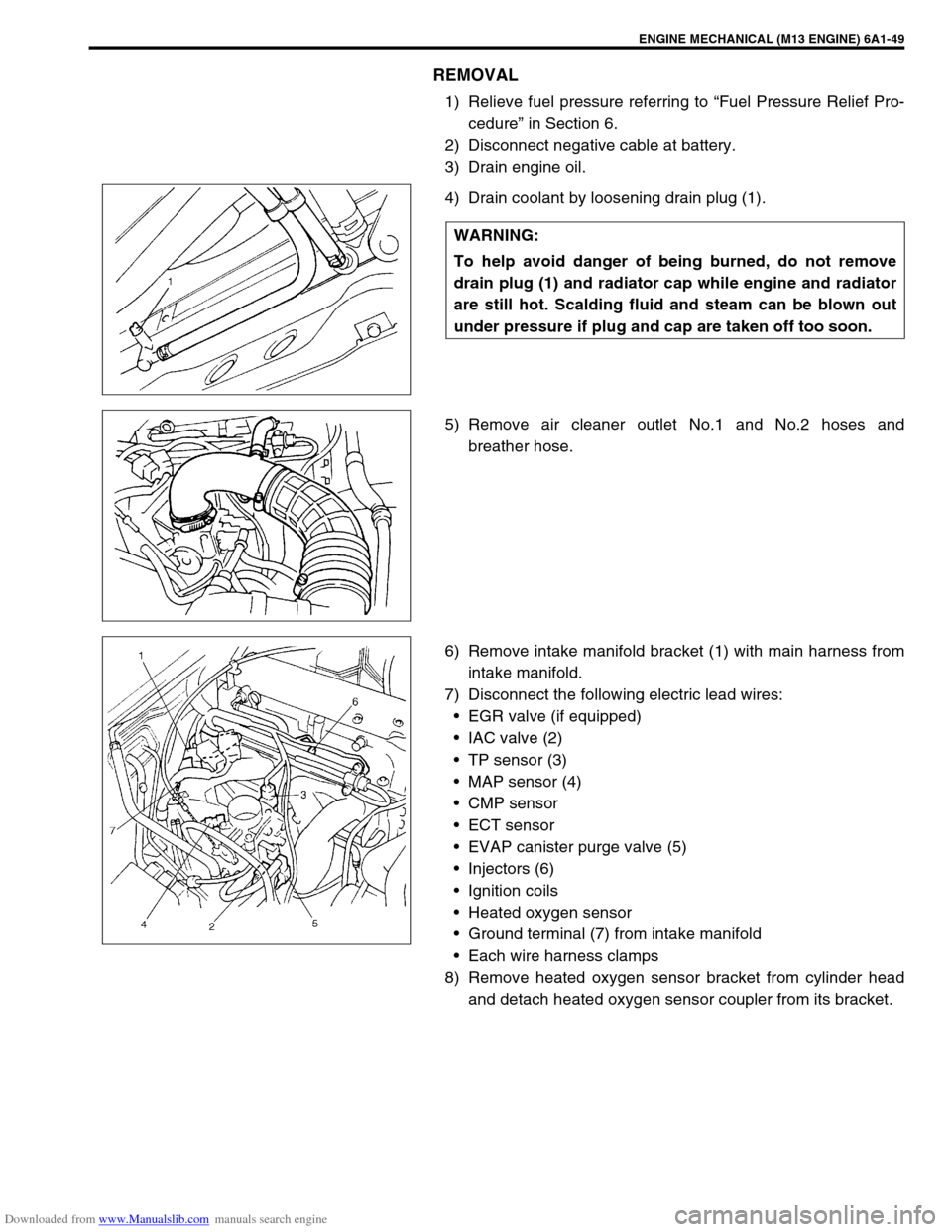
4) Drain coolant by loosening drain plug (1).
5) Remove air cleaner outlet No.1 and No.2 hoses and
breather hose.
6) Remove intake manifold bracket (1) with main harness from
intake manifold.
7) Disconnect the following electric lead wires:
EGR valve (if equipped)
IAC valve (2)
TP sensor (3)
MAP sensor (4)
CMP sensor
ECT sensor
EVAP canister purge valve (5)
Injectors (6)
Ignition coils
Heated oxygen sensor
Ground terminal (7) from intake manifold
Each wire harness clamps
8) Remove heated oxygen sensor bracket from cylinder head
and detach heated oxygen sensor coupler from its bracket. WARNING:
To help avoid danger of being burned, do not remove
drain plug (1) and radiator cap while engine and radiator
are still hot. Scalding fluid and steam can be blown out
under pressure if plug and cap are taken off too soon.
Page 531 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6A1-50 ENGINE MECHANICAL (M13 ENGINE)
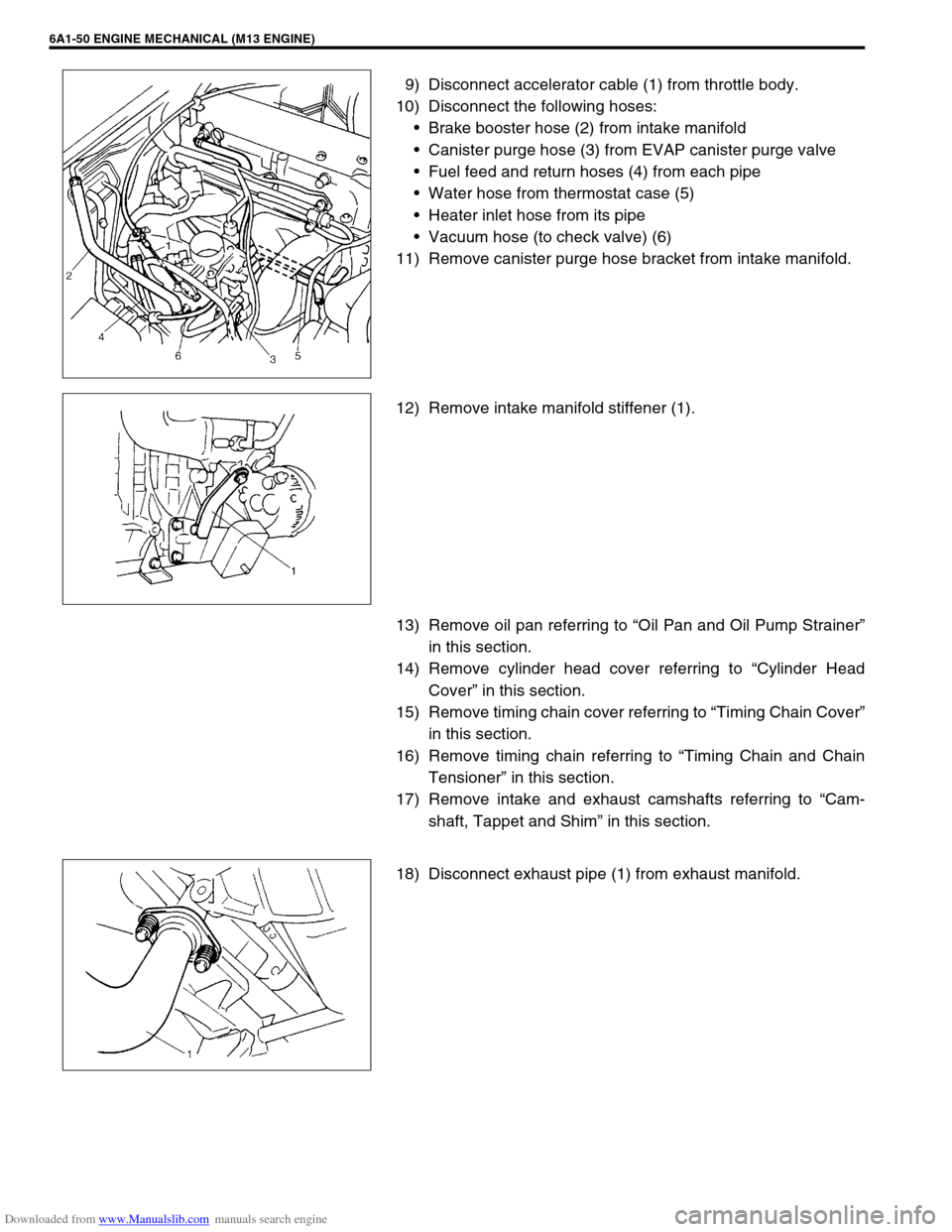
9) Disconnect accelerator cable (1) from throttle body.
10) Disconnect the following hoses:
Brake booster hose (2) from intake manifold
Canister purge hose (3) from EVAP canister purge valve
Fuel feed and return hoses (4) from each pipe
Water hose from thermostat case (5)
Heater inlet hose from its pipe
Vacuum hose (to check valve) (6)
11) Remove canister purge hose bracket from intake manifold.
12) Remove intake manifold stiffener (1).
13) Remove oil pan referring to “Oil Pan and Oil Pump Strainer”
in this section.
14) Remove cylinder head cover referring to “Cylinder Head
Cover” in this section.
15) Remove timing chain cover referring to “Timing Chain Cover”
in this section.
16) Remove timing chain referring to “Timing Chain and Chain
Tensioner” in this section.
17) Remove intake and exhaust camshafts referring to “Cam-
shaft, Tappet and Shim” in this section.
18) Disconnect exhaust pipe (1) from exhaust manifold.
Page 532 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE MECHANICAL (M13 ENGINE) 6A1-51
19) Remove exhaust manifold stiffener (1).
20) Loosen cylinder head bolts in such order as indicated in fig-
ure by using a 12 corner socket wrenches and remove them.
21) Check all around cylinder head for any other parts required
to be removed or disconnected and remove or disconnect
whatever necessary.
22) Remove cylinder head with intake manifold and exhaust
manifold. Use lifting device, if necessary.
NOTE:
Don’t forget to remove bolt (M8) (1) as shown in figure.
Page 535 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6A1-54 ENGINE MECHANICAL (M13 ENGINE)
Valves
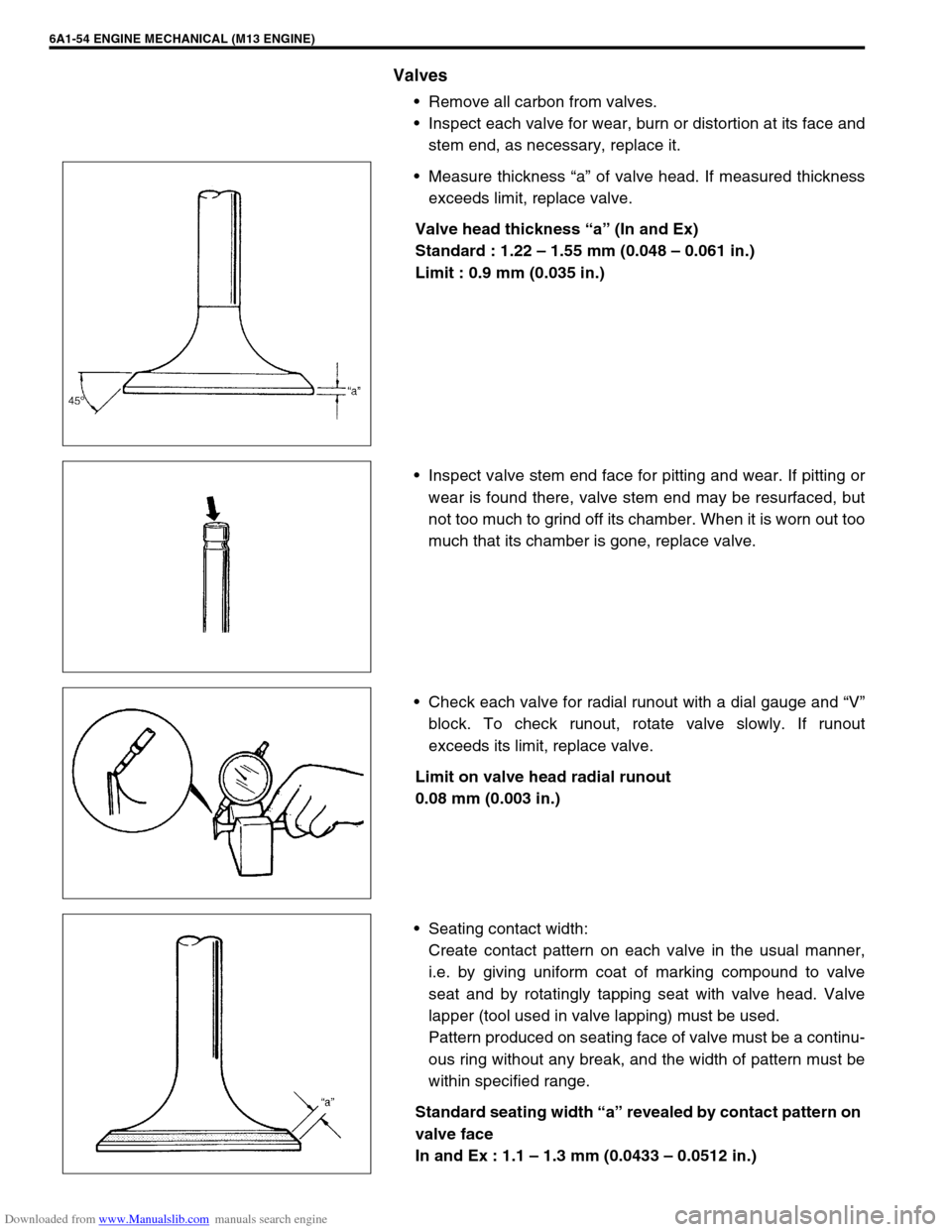
Remove all carbon from valves.
Inspect each valve for wear, burn or distortion at its face and
stem end, as necessary, replace it.
Measure thickness “a” of valve head. If measured thickness
exceeds limit, replace valve.
Valve head thickness “a” (In and Ex)
Standard : 1.22 – 1.55 mm (0.048 – 0.061 in.)
Limit : 0.9 mm (0.035 in.)
Inspect valve stem end face for pitting and wear. If pitting or
wear is found there, valve stem end may be resurfaced, but
not too much to grind off its chamber. When it is worn out too
much that its chamber is gone, replace valve.
Check each valve for radial runout with a dial gauge and “V”
block. To check runout, rotate valve slowly. If runout
exceeds its limit, replace valve.
Limit on valve head radial runout
0.08 mm (0.003 in.)
Seating contact width:
Create contact pattern on each valve in the usual manner,
i.e. by giving uniform coat of marking compound to valve
seat and by rotatingly tapping seat with valve head. Valve
lapper (tool used in valve lapping) must be used.
Pattern produced on seating face of valve must be a continu-
ous ring without any break, and the width of pattern must be
within specified range.
Standard seating width “a” revealed by contact pattern on
valve face
In and Ex : 1.1 – 1.3 mm (0.0433 – 0.0512 in.)
Page 536 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE MECHANICAL (M13 ENGINE) 6A1-55
Valve seat repair:
A valve seat not producing a uniform contact with its valve or
showing width of seating contact that is out of specified
range must be repaired by regrinding or by cutting and
regrinding and finished by lapping.
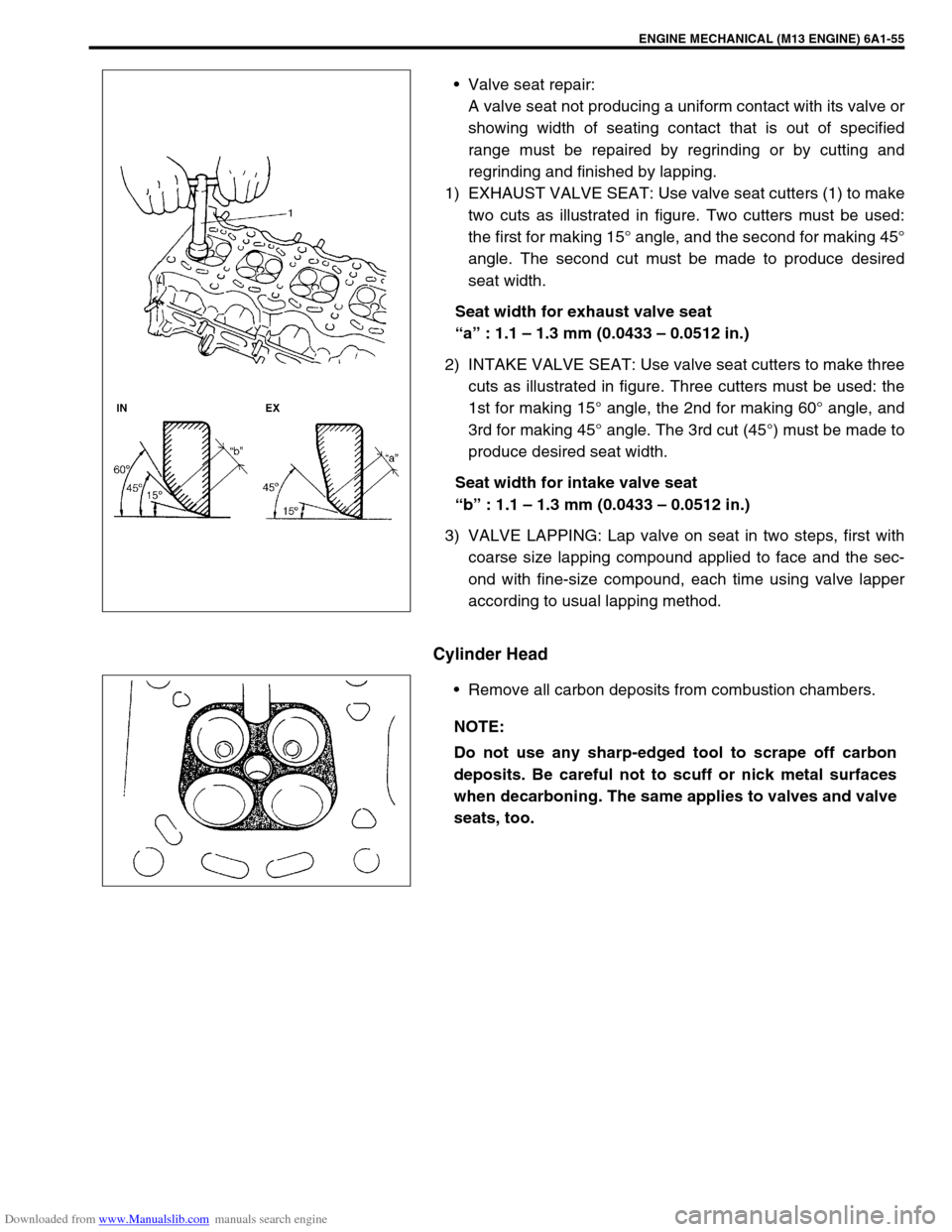
1) EXHAUST VALVE SEAT: Use valve seat cutters (1) to make
two cuts as illustrated in figure. Two cutters must be used:
the first for making 15° angle, and the second for making 45°
angle. The second cut must be made to produce desired
seat width.
Seat width for exhaust valve seat
“a” : 1.1 – 1.3 mm (0.0433 – 0.0512 in.)
2) INTAKE VALVE SEAT: Use valve seat cutters to make three
cuts as illustrated in figure. Three cutters must be used: the
1st for making 15° angle, the 2nd for making 60° angle, and
3rd for making 45° angle. The 3rd cut (45°) must be made to
produce desired seat width.
Seat width for intake valve seat
“b” : 1.1 – 1.3 mm (0.0433 – 0.0512 in.)
3) VALVE LAPPING: Lap valve on seat in two steps, first with
coarse size lapping compound applied to face and the sec-
ond with fine-size compound, each time using valve lapper
according to usual lapping method.
Cylinder Head
Remove all carbon deposits from combustion chambers.
NOTE:
Do not use any sharp-edged tool to scrape off carbon
deposits. Be careful not to scuff or nick metal surfaces
when decarboning. The same applies to valves and valve
seats, too.
Page 537 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6A1-56 ENGINE MECHANICAL (M13 ENGINE)
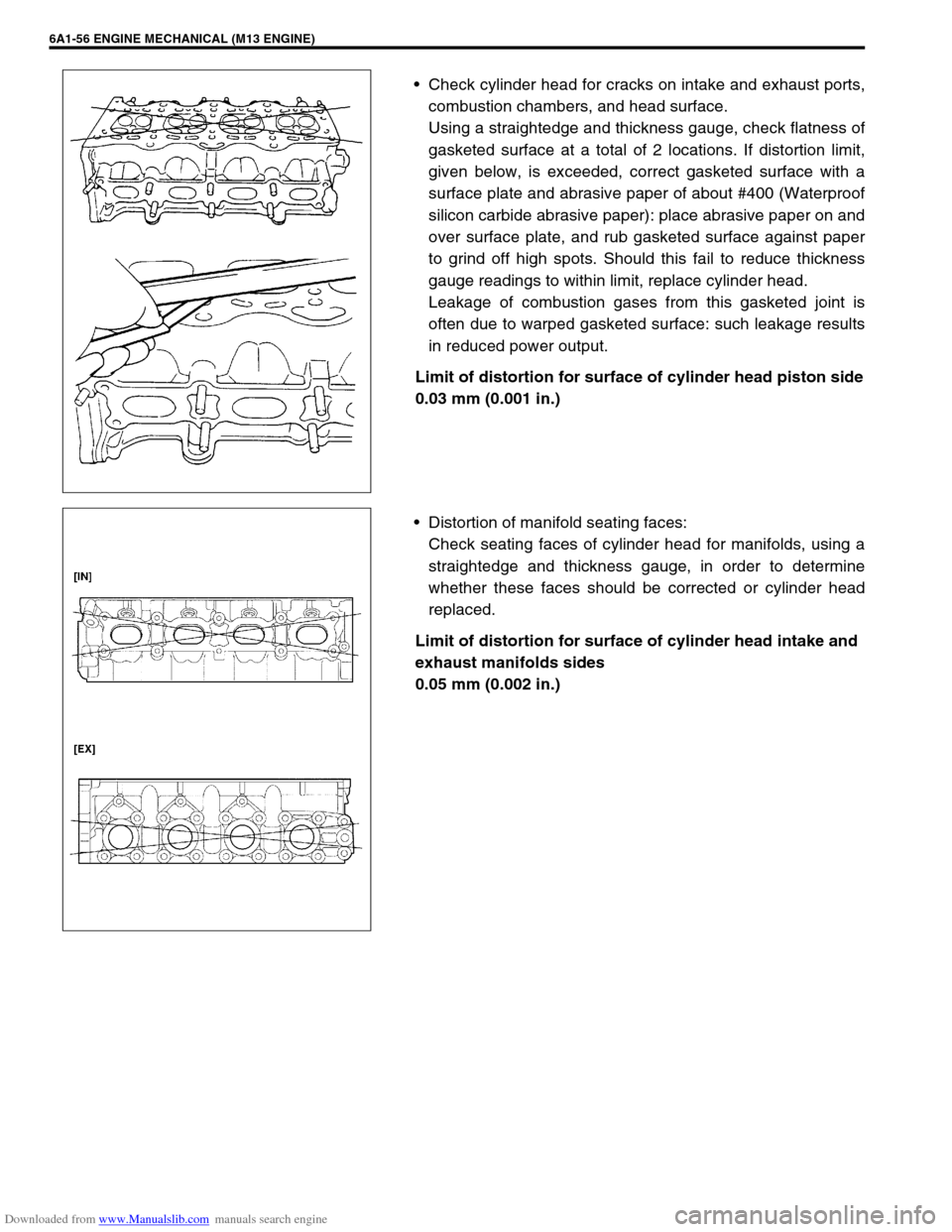
Check cylinder head for cracks on intake and exhaust ports,
combustion chambers, and head surface.
Using a straightedge and thickness gauge, check flatness of
gasketed surface at a total of 2 locations. If distortion limit,
given below, is exceeded, correct gasketed surface with a
surface plate and abrasive paper of about #400 (Waterproof
silicon carbide abrasive paper): place abrasive paper on and
over surface plate, and rub gasketed surface against paper
to grind off high spots. Should this fail to reduce thickness
gauge readings to within limit, replace cylinder head.
Leakage of combustion gases from this gasketed joint is
often due to warped gasketed surface: such leakage results
in reduced power output.
Limit of distortion for surface of cylinder head piston side
0.03 mm (0.001 in.)
Distortion of manifold seating faces:
Check seating faces of cylinder head for manifolds, using a
straightedge and thickness gauge, in order to determine
whether these faces should be corrected or cylinder head
replaced.
Limit of distortion for surface of cylinder head intake and
exhaust manifolds sides
0.05 mm (0.002 in.)
Page 538 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE MECHANICAL (M13 ENGINE) 6A1-57
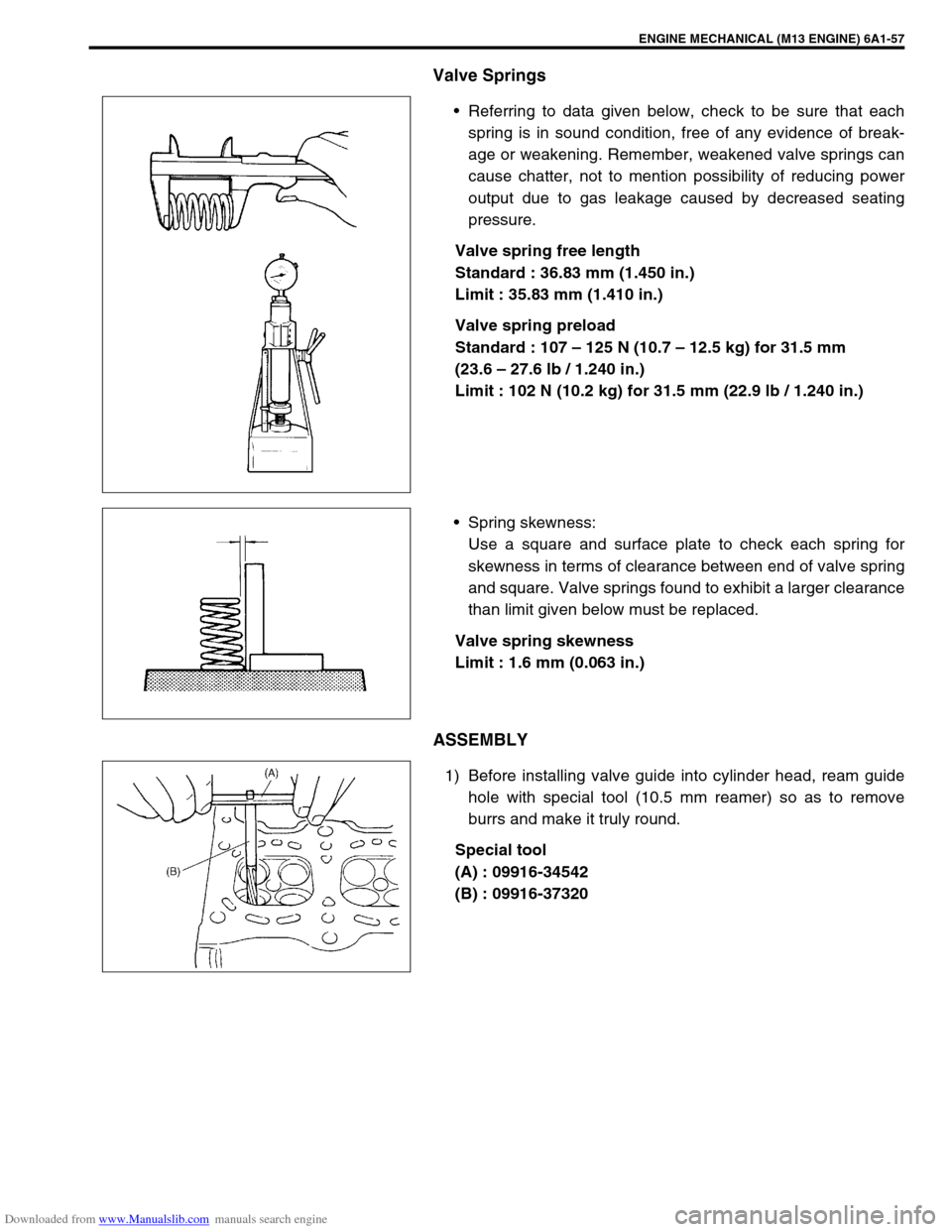
Valve Springs
Referring to data given below, check to be sure that each
spring is in sound condition, free of any evidence of break-
age or weakening. Remember, weakened valve springs can
cause chatter, not to mention possibility of reducing power
output due to gas leakage caused by decreased seating
pressure.
Valve spring free length
Standard : 36.83 mm (1.450 in.)
Limit : 35.83 mm (1.410 in.)
Valve spring preload
Standard : 107 – 125 N (10.7 – 12.5 kg) for 31.5 mm
(23.6 – 27.6 lb / 1.240 in.)
Limit : 102 N (10.2 kg) for 31.5 mm (22.9 lb / 1.240 in.)
Spring skewness:
Use a square and surface plate to check each spring for
skewness in terms of clearance between end of valve spring
and square. Valve springs found to exhibit a larger clearance
than limit given below must be replaced.
Valve spring skewness
Limit : 1.6 mm (0.063 in.)
ASSEMBLY
1) Before installing valve guide into cylinder head, ream guide
hole with special tool (10.5 mm reamer) so as to remove
burrs and make it truly round.
Special tool
(A) : 09916-34542
(B) : 09916-37320
Page 541 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6A1-60 ENGINE MECHANICAL (M13 ENGINE)
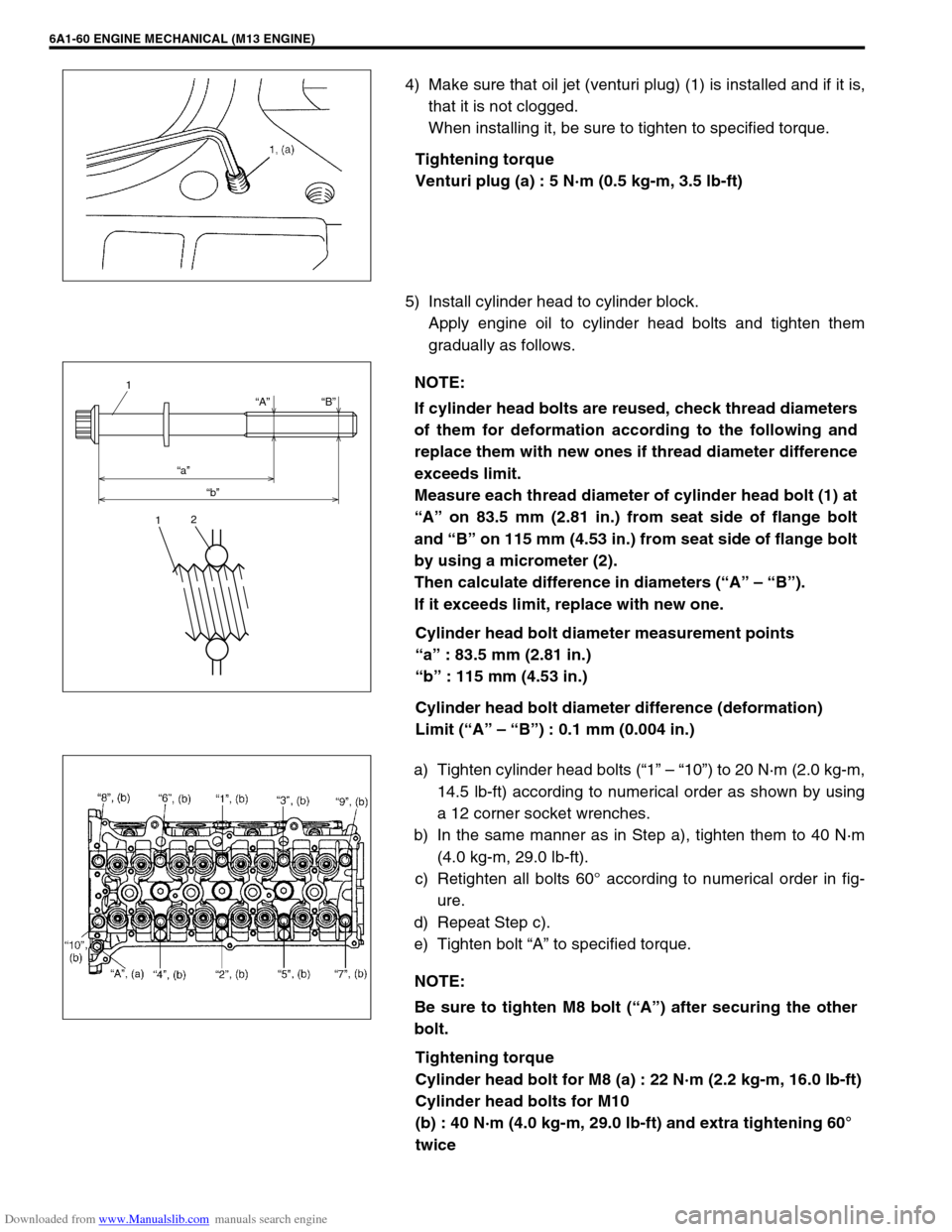
4) Make sure that oil jet (venturi plug) (1) is installed and if it is,
that it is not clogged.
When installing it, be sure to tighten to specified torque.
Tightening torque
Venturi plug (a) : 5 N·m (0.5 kg-m, 3.5 lb-ft)
5) Install cylinder head to cylinder block.
Apply engine oil to cylinder head bolts and tighten them
gradually as follows.
Cylinder head bolt diameter measurement points
“a” : 83.5 mm (2.81 in.)
“b” : 115 mm (4.53 in.)
Cylinder head bolt diameter difference (deformation)
Limit (“A” – “B”) : 0.1 mm (0.004 in.)
a) Tighten cylinder head bolts (“1” – “10”) to 20 N·m (2.0 kg-m,
14.5 lb-ft) according to numerical order as shown by using
a 12 corner socket wrenches.
b) In the same manner as in Step a), tighten them to 40 N·m
(4.0 kg-m, 29.0 lb-ft).
c) Retighten all bolts 60° according to numerical order in fig-
ure.
d) Repeat Step c).
e) Tighten bolt “A” to specified torque.
Tightening torque
Cylinder head bolt for M8 (a) : 22 N·m (2.2 kg-m, 16.0 lb-ft)
Cylinder head bolts for M10
(b) : 40 N·m (4.0 kg-m, 29.0 lb-ft) and extra tightening 60°
twice
NOTE:
If cylinder head bolts are reused, check thread diameters
of them for deformation according to the following and
replace them with new ones if thread diameter difference
exceeds limit.
Measure each thread diameter of cylinder head bolt (1) at
“A” on 83.5 mm (2.81 in.) from seat side of flange bolt
and “B” on 115 mm (4.53 in.) from seat side of flange bolt
by using a micrometer (2).
Then calculate difference in diameters (“A” – “B”).
If it exceeds limit, replace with new one.
“A”
“a”
“b”“B”
1
12
NOTE:
Be sure to tighten M8 bolt (“A”) after securing the other
bolt.