2005 SUZUKI JIMNY turn
[x] Cancel search: turnPage 635 of 687
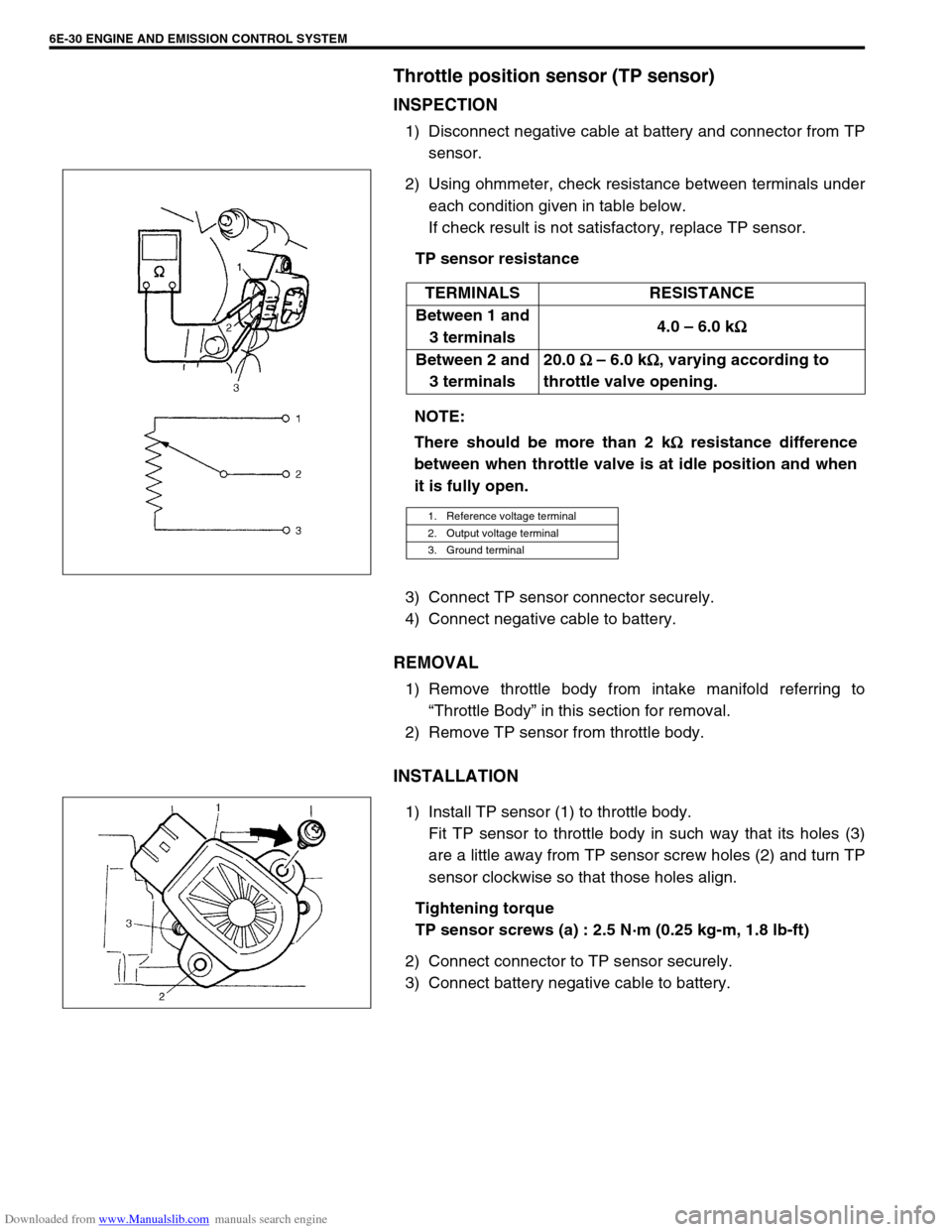
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6E-30 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
Throttle position sensor (TP sensor)
INSPECTION
1) Disconnect negative cable at battery and connector from TP
sensor.
2) Using ohmmeter, check resistance between terminals under
each condition given in table below.
If check result is not satisfactory, replace TP sensor.
TP sensor resistance
3) Connect TP sensor connector securely.
4) Connect negative cable to battery.
REMOVAL
1) Remove throttle body from intake manifold referring to
“Throttle Body” in this section for removal.
2) Remove TP sensor from throttle body.
INSTALLATION
1) Install TP sensor (1) to throttle body.
Fit TP sensor to throttle body in such way that its holes (3)
are a little away from TP sensor screw holes (2) and turn TP
sensor clockwise so that those holes align.
Tightening torque
TP sensor screws (a) : 2.5 N·m (0.25 kg-m, 1.8 lb-ft)
2) Connect connector to TP sensor securely.
3) Connect battery negative cable to battery.TERMINALS RESISTANCE
Between 1 and
3 terminals4.0 – 6.0 k
Ω
ΩΩ Ω
Between 2 and
3 terminals20.0
Ω
ΩΩ Ω – 6.0 k
Ω
ΩΩ Ω, varying according to
throttle valve opening.
NOTE:
There should be more than 2 k
Ω
ΩΩ Ω resistance difference
between when throttle valve is at idle position and when
it is fully open.
1. Reference voltage terminal
2. Output voltage terminal
3. Ground terminal
Page 643 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6E-38 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
2) Connect battery (3) to A/C condenser fan motor coupler (2)
as shown in figure, then check that the A/C condenser fan
motor (1) operates smoothly.
If A/C condenser fan motor does not operate smoothly,
replace motor.
Reference current data of A/C condenser fan motor
Approx. 6.7 – 8.3 A at 12 V
Output signals of throttle valve opening and engine
coolant temp. (Vehicle with A/T only)
THROTTLE VALVE OPENING SIGNAL INSPECTION
Check throttle valve opening (throttle position) signal referring to
step 1 of “DTC P1700 (No.32 or 33) Flow Table” in Section 7B.
If check result is not satisfactory, check each wire harness, circuit
connections and TP sensor.
ENGINE COOLANT TEMP. SIGNAL INSPECTION
Check engine coolant temp. signal referring to step 1 of “DTC
P1709 (No.51) Flow Table” in Section 7B.
If check result is not satisfactory, check each wire harness, circuit
connection and ECT sensor.
Emission Control System
EGR system (If equipped)
SYSTEM INSPECTION (USING SUZUKI SCAN TOOL)
1) Connect SUZUKI scan tool to DLC with ignition switch OFF.
2) Turn ignition switch ON and then select “DATA LIST” mode
on scan tool.
3) Make sure that vehicle condition is as following.
Vehicle speed = 0 km/h (0 KPH)
Engine speed ≤ 3000 rpm
4) Clear DTC by using “CLEAR INFO” mode.
5) With engine idling (without depressing accelerator pedal),
open EGR valve by using “STEP EGR” mode in “MISC
TEST” menu.
In this state, according as EGR valve opening increases
engine idle speed drops. If not, possible cause is clogged
EGR gas passage, stuck or faulty EGR valve, poor perfor-
mance of ECT sensor or TP sensor or DTC and/or pending
DTC is (are) stored in ECM memory.
1. SUZUKI scan tool display
2. EGR valve opening (0: Close, 100: Full Open)
Page 645 of 687
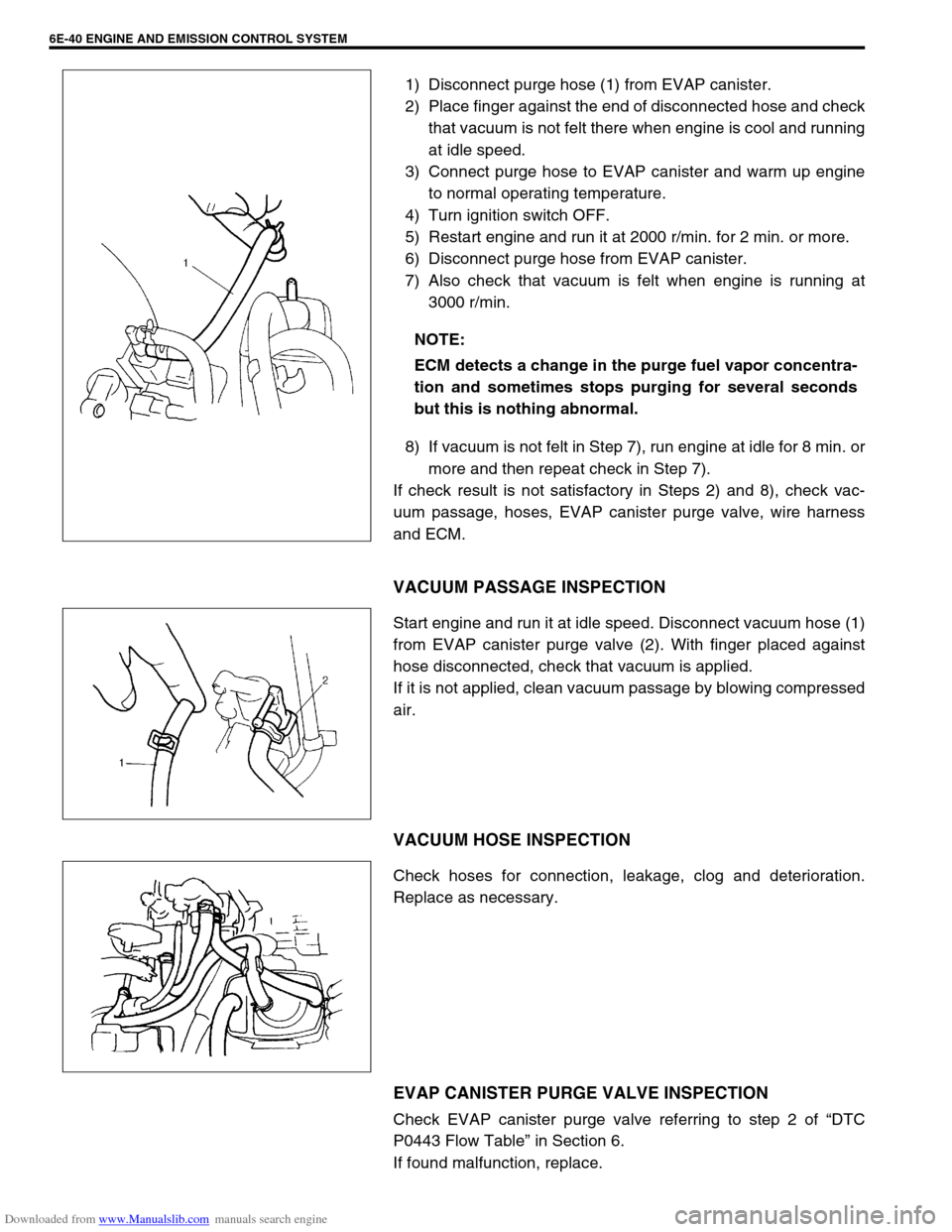
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6E-40 ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
1) Disconnect purge hose (1) from EVAP canister.
2) Place finger against the end of disconnected hose and check
that vacuum is not felt there when engine is cool and running
at idle speed.
3) Connect purge hose to EVAP canister and warm up engine
to normal operating temperature.
4) Turn ignition switch OFF.
5) Restart engine and run it at 2000 r/min. for 2 min. or more.
6) Disconnect purge hose from EVAP canister.
7) Also check that vacuum is felt when engine is running at
3000 r/min.
8) If vacuum is not felt in Step 7), run engine at idle for 8 min. or
more and then repeat check in Step 7).
If check result is not satisfactory in Steps 2) and 8), check vac-
uum passage, hoses, EVAP canister purge valve, wire harness
and ECM.
VACUUM PASSAGE INSPECTION
Start engine and run it at idle speed. Disconnect vacuum hose (1)
from EVAP canister purge valve (2). With finger placed against
hose disconnected, check that vacuum is applied.
If it is not applied, clean vacuum passage by blowing compressed
air.
VACUUM HOSE INSPECTION
Check hoses for connection, leakage, clog and deterioration.
Replace as necessary.
EVAP CANISTER PURGE VALVE INSPECTION
Check EVAP canister purge valve referring to step 2 of “DTC
P0443 Flow Table” in Section 6.
If found malfunction, replace.NOTE:
ECM detects a change in the purge fuel vapor concentra-
tion and sometimes stops purging for several seconds
but this is nothing abnormal.
Page 648 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM 6E-43
Tightening Torque Specifications
09931-76030
16/14 pin DLC cable Tech 2 kit (SUZUKI scan
tool) (See NOTE “C”.)
NOTE:
“A”: This kit includes the following items.
1. Tool body & washer, 2. Body plug, 3. Body attachment-1, 4. Holder, 5. Return hose & clamp,
6. Body attachment-2 & washer, 7. Hose attachment-1, 8. Hose attachment-2
“B”: This kit includes the following items and substitutes for the Tech 2 kit.
1. Storage case, 2. Operator’s manual, 3. Tech 1A, 4. DLC cable (14/26 pin, 09931-76040),
5. Test lead / probe, 6. Power source cable, 7. DLC cable adaptor, 8. Self-test adaptor
“C”: This kit includes the following items and substitutes for the Tech 1A kit.
1. Tech 2, 2. PCMCIA card, 3. DLC cable, 4. SAE 16/19 adapter, 5. Cigarette cable,
6. DLC loopback adapter, 7. Battery power cable, 8. RS232 cable, 9. RS232 adapter,
10. RS232 loopback connector, 11. Storage case, 12. Power supply
Fastening partTightening torque
Nm kg-m lb-ft
TP sensor mounting screw 2.5 0.25 1.8
IAC valve screw 3.5 0.35 2.5
ECT sensor 15 1.5 11.5
Heated oxygen sensor-1 and -2 45 4.5 32.5
Camshaft position sensor 10 1.0 7.5
Fuel pressure regulator bolt 10 1.0 7.5
Page 650 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine IGNITION SYSTEM (ELECTRONIC IGNITION SYSTEM) 6F-1
6G
6F2
6G
6H
7D
7E
7F
7A1
7A1
7D
7E
7F
8A
8B
8C
8D
8E
6K
6F
7A
10
10A
10B
SECTION 6F
IGNITION SYSTEM
(ELECTRONIC IGNITION SYSTEM)
CONTENTS
General Description ........................................ 6F-2
Diagnosis ......................................................... 6F-3
On-Vehicle Service.......................................... 6F-5
Ignition Spark Test ........................................ 6F-5
High-tension Cords ....................................... 6F-5
Spark Plugs ................................................... 6F-6Ignition Coil Assembly (Including Ignitor) ...... 6F-7
Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKP Sensor) ... 6F-8
Ignition Timing............................................... 6F-8
Special Tools ................................................. 6F-10
Tightening Torque Specification ................. 6F-10
WARNING:
For vehicles equipped with Supplemental Restraint (Air Bag) System:
Service on and around the air bag system components or wiring must be performed only by an
authorized SUZUKI dealer. Refer to “Air Bag System Components and Wiring Location View” under
“General Description” in air bag system section in order to confirm whether you are performing ser-
vice on or near the air bag system components or wiring. Please observe all WARNINGS and “Ser-
vice Precautions” under “On-Vehicle Service” in air bag system section before performing service
on or around the air bag system components or wiring. Failure to follow WARNINGS could result in
unintentional activation of the system or could render the system inoperative. Either of these two
conditions may result in severe injury.
Technical service work must be started at least 90 seconds after the ignition switch is turned to the
“LOCK” position and the negative cable is disconnected from the battery. Otherwise, the system
may be activated by reserve energy in the Sensing and Diagnostic Module (SDM).
Page 651 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6F-2 IGNITION SYSTEM (ELECTRONIC IGNITION SYSTEM)
General Description
The ignition system is an electronic (distributorless) ignition system. It consists of the parts as described below
and has an electronic ignition control system.
ECM
It detects the engine and vehicle conditions through the signals from the sensors, determines the most suit-
able ignition timing and time for electricity to flow to the primary coil and sends a signal to the ignitor (power
unit) in the ignition coil assembly.
Ignition coil assembly (including an ignitor)
The ignition coil assembly has a built-in ignitor which turns ON and OFF the current flow to the primary coil
according to the signal from ECM. When the current flow to the primary coil is turned OFF, a high voltage is
induced in the secondary coil.
High tension cords and spark plugs.
CMP sensor (Camshaft position sensor) and CKP sensor (Crankshaft position sensor)
Using signals from these sensors, ECM identifies the specific cylinder whose piston is in the compression
stroke, detects the crank angle and adjust initial ignition timing automatically.
TP sensor, ECT sensor, MAP sensor and other sensors/switches
Refer to “Electronic Control System” in Section 6E for details.
Although this ignition system does not have a distributor, it has two ignition coil assemblies (one is for No.1 and
No.4 spark plugs and the other is for No.2 and No.3 spark plugs). When an ignition signal is sent from ECM to
the ignitor in the ignition coil assembly for No.1 and No.4 spark plugs, a high voltage is induced in the secondary
coil and that passes through the high-tension cords and causes No.1 and No.4 spark plugs to spark simulta-
neously. Likewise, when an ignition signal is sent to the ignitor in the other ignition coil assembly, No.2 and No.3
spark plugs spark simultaneously.
SYSTEM COMPONENTS
1. ECM 7. ECT sensor 13. Monitor connector
2. Ignition coil assembly for No.1 and No.4 spark plugs 8. IAT sensor 14. Knock sensor
3. Ignition coil assembly for No.2 and No.3 spark plugs 9. TP sensor 15. DLC
4. CMP sensor 10. VSS 16. Spark plugs
5. CKP sensor 11. Transmission range switch (A/T)
6. MAP sensor 12. High-tension cords
Page 660 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine CRANKING SYSTEM 6G-1
6F1
6F2
6H
7C1
7D
7E
7C1
7B1
7C1
7D
7E
7F
8A
8B
8C
8D
8E
6G
7A1
10A
10B
SECTION 6G
CRANKING SYSTEM
CONTENTS
General Description ....................................... 6G-2
Cranking Circuit ............................................ 6G-2
Diagnosis ........................................................ 6G-2
Diagnosis Table ........................................... 6G-2Performance Test .........................................6G-4
On-Vehicle Service .........................................6G-5
Starting Motor ...............................................6G-5
Specifications..................................................6G-7
WARNING:
For vehicles equipped with Supplemental Restraint (Air Bag) System:
Service on and around the air bag system components or wiring must be performed only by an
authorized SUZUKI dealer. Refer to “Air Bag System Components and Wiring Location View” under
“General Description” in air bag system section in order to confirm whether you are performing ser-
vice on or near the air bag system components or wiring. Please observe all WARNINGS and “Ser-
vice Precautions” under “On-Vehicle Service” in air bag system section before performing service
on or around the air bag system components or wiring. Failure to follow WARNINGS could result in
unintentional activation of the system or could render the system inoperative. Either of these two
conditions may result in severe injury.
Technical service work must be started at least 90 seconds after the ignition switch is turned to the
“LOCK” position and the negative cable is disconnected from the battery. Otherwise, the system
may be activated by reserve energy in the Sensing and Diagnostic Module (SDM).
NOTE:
Starting motor varies depending on specifications, etc. Therefore, be sure to check model and speci-
fication of vehicle being serviced before replacing parts.
Page 662 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine CRANKING SYSTEM 6G-3
Condition Possible Cause Correction
Motor not running
(No operating sound of
magnetic switch)Shift lever switch is not in P or N, or not adjusted
(A/T)Shift in P or N, or adjust switch.
Battery run down Recharge battery.
Battery voltage too low due to battery deteriora-
tionReplace battery.
Poor contact in battery terminal connection Retighten or replace.
Loose grounding cable connection Retighten.
Fuse set loose or blown off Tighten or replace.
Poor contacting action of ignition switch and mag-
netic switchReplace.
Lead wire coupler loose in place Retighten.
Open-circuit between ignition switch and magnetic
switchRepair.
Open-circuit in pull-in coil Replace magnetic switch.
Brushes are seating poorly or worn down Repair or replace.
Poor sliding of plunger and/or pinion Repair.
Motor not running
(Operating sound of
magnetic switch
heard)Battery run down Recharge battery.
Battery voltage too low due to battery deteriora-
tionReplace battery.
Loose battery cable connections Retighten.
Burnt main contact point, or poor contacting action
of magnetic switchReplace magnetic switch.
Brushes are seating poorly or worn down Repair or replace.
Weakened brush spring Replace.
Burnt commutator Replace armature.
Layer short-circuit of armature Replace.
Crankshaft rotation obstructed Repair.
Starting motor running
but too slow (small
torque) (If battery and
wiring are satisfac-
tory, inspect starting
motor)Insufficient contact of magnetic switch main con-
tactsReplace magnetic switch.
Layer short-circuit of armature Replace.
Disconnected, burnt or worn commutator Repair commutator or replace
armature.
Worn brushes Replace brush.
Weakened brush springs Replace spring.
Burnt or abnormally worn end bush Replace bush.
Starting motor run-
ning, but not cranking
engineWorn pinion tip Replace over-running clutch.
Poor sliding of over-running clutch Repair.
Over-running clutch slipping Replace over-running clutch.
Worn teeth of ring gear Replace flywheel (M/T) or drive
plate (A/T).
Noise
Abnormally worn bush Replace bush.
Worn pinion or worn teeth of ring gear Replace pinion or flywheel
(M/T) or drive plate (A/T).
Poor sliding of pinion (failure in return movement) Repair or replace.
Worn internal or planetary gear teeth Replace.
Lack of oil in each part Lubricate.