2005 MITSUBISHI 380 stop start
[x] Cancel search: stop startPage 1088 of 1500

Page 1169 of 1500

BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM35A-4
STEP 2. Check disc brake pistons for smooth
operation.
(1) With engine not running, depress the brake pedal
rapidly several times to deplete booster vacuum
reserves.
(2) Test each disc brake assembly one at a time.
a. Remove the lower caliper bolt, then remove
caliper from mount.
b. Have an assistant slowly depress the brake
pedal. Confirm piston(s) extend slowly and
smoothly with no jumpiness. Repeat for each
disc brake assembly.
Q: Do (does) the piston(s) move correctly?
YES :
Go to Step 3.
NO : Disassemble and inspect the brake
assembly (Front: refer to P.35A-33, Rear:
refer to P.35A-36). Then go to Step 5.
STEP 3. Check brake disc(s) for runout.
Refer to P.35A-19.
Q: Is runout outside of specifications?
YES :
Repair or replace the brake disc(s) as
necessary. Then go to Step 5.
NO : Go to Step 4.
STEP 4. Check brake discs for correct thickness.
Refer to P.35A-19.
Q: Is the thickness outside of specifications?
YES :
Repair or replace the brake disc(s) as
necessary. Then go to Step 5.
NO : Perform the brake line bleeding. Then go to
St e p 5.
STEP 5. Retest the system.
Q: Is the symptom eliminated?
YES :
The procedure is complete.
NO : Start over at Step 1. If a new symptom
appears, refer to the appropriate symptom
chart.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 2: Insufficient Braking Power
.
DIAGNOSIS
STEP 1. Check that the specified brake fluid is
used, its level is correct, and no contamination is
found.
Q: Is there a fault?
YES :
Refill or replace with the specified brake
fluid DOT 3 or DOT 4. Bleed the brakes if
necessary (Refer to P.35A-16). Then go to
Step 7.
NO : Go to Step 2.
STEP 2. Check for spongy (not firm) brakes.
(1) With engine not running, depress the brake pedal
rapidly several times to deplete the booster
vacuum reserve.
(2) With the brake pedal fully released, depress the
brake pedal slowly until it stops.
(3) With a measuring device (ruler, etc.) next to the
brake pedal, depress the pedal firmly and
measure the distance the pedal traveled.
Q: Is the distance greater than 20 mm (0.8 inch)?
YES :
Bleed the brakes to remove air in the fluid
(Refer to P.35A-16). Then go to Step 7.
NO : Go to Step 3.
STEP 3. Check the brake booster function.
Refer to P.35A-14.
Q: Is there a fault?
YES :
Replace the brake booster. Then go to Step
7.
NO : Go to Step 4.
Page 1170 of 1500

BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM35A-5
STEP 4. Check for pinched or restricted brake
tube or hose.
Q: Is there a pinched or restricted brake tube or hose?
YES :
Replace that complete section of brake tube
or brake hose. Then go to Step 7.
NO : Go to Step 5.
STEP 5. Check for oil, water, etc., on the pad
contact surfaces of all brakes.
Q: Is oil, water, etc., on the pad contact surface?
YES :
Replace the part and determine the
source/cause of foreign material. Recheck
symptom. Then go to Step 7.
NO : The procedure is complete. If condition
persists for vehicles without ABS, go to Step
6.
STEP 7. Recheck symptom.
Q: Is the symptom eliminated?
YES :
The procedure is complete.
NO : Start over at step 1. If a new symptom
surfaces, refer to the appropriate symptom
chart.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 3: Increased Pedal Stroke (Reduced Pedal-to-Floor Board Clearance)
.
DIAGNOSIS
STEP 1. Check for spongy (not firm) brakes.
(1) With engine not running, depress the brake pedal
rapidly several times to deplete booster vacuum
reserve.
(2) With the brake pedal fully released, depress the
brake pedal slowly until it stops.
(3) With a measuring device (ruler, etc.) next to the
brake pedal, depress the pedal firmly and
measure the distance the pedal traveled.
Q: Is the distance greater than 20 mm (0.8 inch)?
YES :
Bleed the brakes to remove air in the fluid
(Refer to P.35A-16). Then go to Step 7.
NO : Go to Step 2.
STEP 2. Check the pad for wear.
Refer to P.35A-17.
Q: Is the pad thickness outside of specifications?
YES :
Replace the part. Then go to Step 7.
NO : Go to Step 3.
STEP 3. Check the vacuum hose and check valve
for damage.
Refer to P.35A-15.
Q: Is there a damage?
YES :
Replace the part. Then go to Step 7.
NO : Go to Step 4.
STEP 4. Check the master cylinder function.
Refer to P.35A-23.
Q: Is there a fault?
YES :
Repair it. Then go to Step 7.
NO : Go to Step 5.
STEP 5. Check for brake fluid leaks.
Q: Is there a leak?
YES :
Check the connection for looseness,
corrosion, etc. Clean and repair as
necessary. If leaking in any tube or hose
section, replace the complete tube or hose.
Then go to Step 7 .
NO : Go to Step 6.
STEP 6. Check for excessive clearance between
the push rod and primary piston.
Refer to P.35A-26.
Q: Is the clearance outside of specifications?
YES :
Adjust the clearance. Then go to Step 7.
NO : Go to Step 7.
STEP 7. Recheck symptom.
Q: Is the symptom eliminated?
YES :
The procedure is complete.
NO : Start over at step 1. If a new symptom
surfaces, refer to the symptom chart.
Page 1179 of 1500
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM35A-14
BRAKE PEDAL FREE PLAY
1. Turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF) position, and
depress the brake pedal two or three times. After eliminating
the vacuum in the brake booster, press the pedal down by
hand, and confirm that the amount of movement before
resistance is met (free play) is within the standard value
range.
Standard value: 3
8 mm (0.12 0.31 inch)
2. If the brake pedal play is not within the standard value,
check the following, and adjust or replace if necessary:
Excessive play between the brake pedal and the clevis pin,
or between the clevis pin and the brake booster operating
rod
Brake pedal height
Installation position of the stop light switch, etc.
CLEARANCE BETWEEN BRAKE PEDAL AND
DASH PANEL
1. Turn up the carpet, etc. under the brake pedal.
2. Start the engine, depress the brake pedal with
approximately 500 N (112 pounds) of force, and measure
the clearance between the brake pedal and the dash panel.
Standard value: 110 mm (4.33 inches) or more [From
the surface of dash panel to the face of pedal pad]
3. If the clearance is outside the standard value, check for air
trapped in the brake line and check the thickness of the disc
brake pad. Andjust and replace defective parts as required.
4. Return the carpet etc. to its original position.
BRAKE BOOSTER OPERATING TESTM1351001000372
1. For simple checking of the brake booster operation, carry
out the following tests:
(1) Run the engine for one or two minutes, and then stop it. If
the pedal depresses fully the first time but gradually
becomes higher when depressed succeeding times, the
booster is operating properly. If the pedal height remains
unchanged, the booster is defective. Go to step 2.
Page 1180 of 1500
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM35A-15
(2) With the engine stopped, step on the brake pedal several
times. Then step on the brake pedal and start the engine.
If the pedal moves downward slightly, the booster is in
good condition. If there is no change, the booster is
defective. Go to step 3.
(3) With the engine running, step on the brake pedal and
then stop the engine. Hold the pedal depressed for 30
seconds. If the pedal height does not change, the booster
is in good condition, if the pedal rises, the booster is
defective.
2. If the above three tests are okay, the booster is OK. If one of
the above three tests is not okay, the check valve, vacuum
hose, or booster is defective. Check the check valve (Refer
to P.35A-15), vacuum hose for leaks, high volume engine
vacuum applied to booster. Repair or replace as necessary.
If these are OK, replace booster and repeat this test starting
at Step 1.
CHECK VALVE OPERATION CHECKM1351009000376
The check valve should not be removed from the vacuum
hose.
1. Remove the vacuum hose. (Refer to P.35A-26).
If the check valve is defective, replace it as an assembly
together with the vacuum hose.
2. Check the operation of the check valve by using a vacuum
pump.
VACUUM PUMP
CONNECTIONCRITERIA
Connection at the brake
booster side (A)A negative pressure
(vacuum) is created and
held.
Connection at the intake
manifold side (B)A negative pressure
(vacuum) is not created.
Page 1196 of 1500
DISC BRAKE ASSEMBLY
BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM35A-31
INSTALLATION SERVICE POINT
.
>>A<< BRAKE DRAG FORCE CHECK
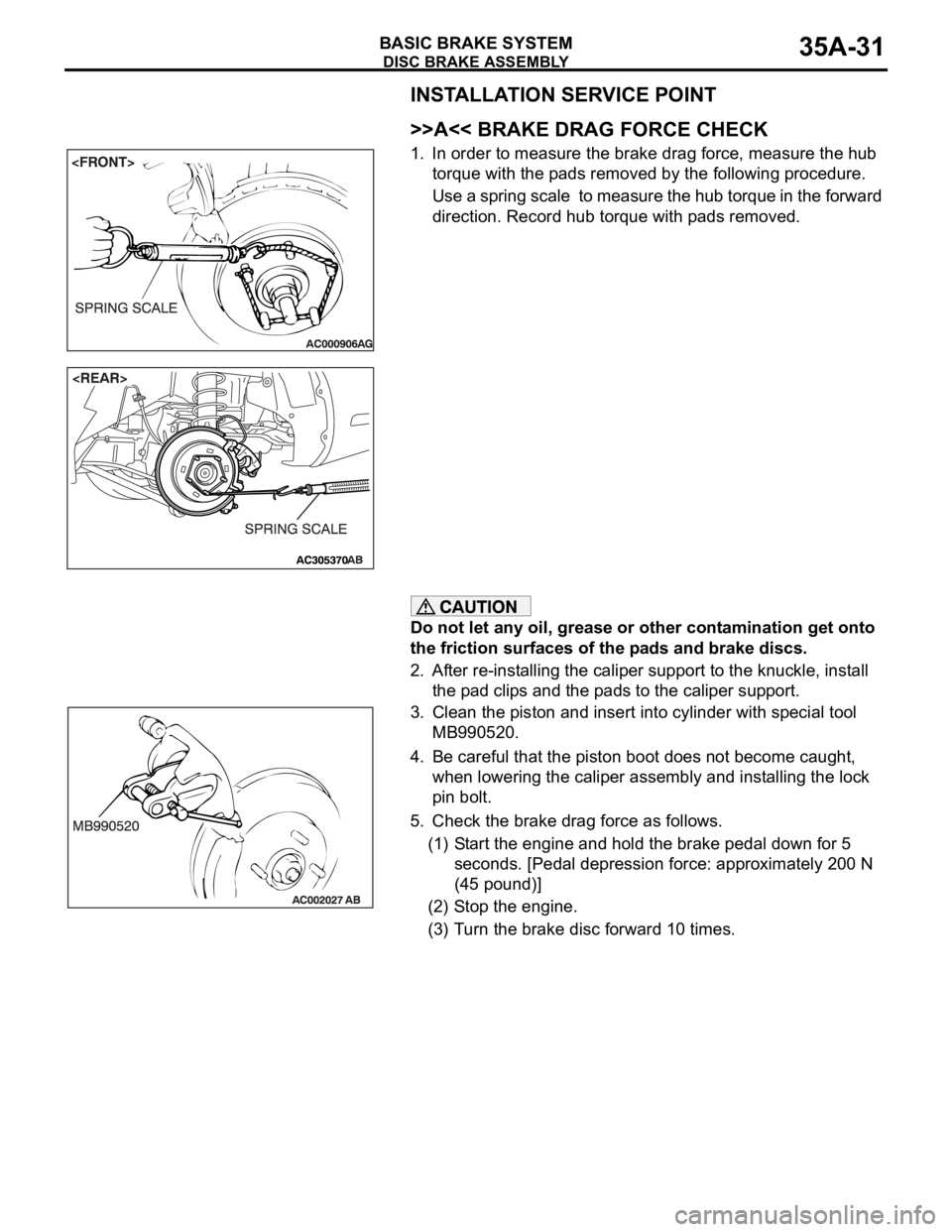
1. In order to measure the brake drag force, measure the hub
torque with the pads removed by the following procedure.
Use a spring scale to measure the hub torque in the forward
direction. Record hub torque with pads removed.
Do not let any oil, grease or other contamination get onto
the friction surfaces of the pads and brake discs.
2. After re-installing the caliper support to the knuckle, install
the pad clips and the pads to the caliper support.
3. Clean the piston and insert into cylinder with special tool
MB990520.
4. Be careful that the piston boot does not become caught,
when lowering the caliper assembly and installing the lock
pin bolt.
5. Check the brake drag force as follows.
(1) Start the engine and hold the brake pedal down for 5
seconds. [Pedal depression force: approximately 200 N
(45 pound)]
(2) Stop the engine.
(3) Turn the brake disc forward 10 times.
Page 1269 of 1500
MAINTENANCE SERVICE
GENERAL00-48
4. Drain the water in the water jacket by unplugging the drain
plug of the cylinder block.
5. Remove the radiator condenser tank assembly and drain the
coolant.
6. Drain the coolant then clean the path of the coolant by
injecting water into the radiator from the radiator cap area.
7. Apply the designated sealant to the screw area of the
cylinder block drain plug, and then tighten to the standard
torque.
Specified sealant: Loctite 577 or equivalent
Tightening torque:
<3.8L Engine> 39
5 Nm
8. Securely tighten the radiator drain plug.
9. Assemble the radiator condenser tank assembly.
Do not use alcohol or methanol anti-freeze or any engine
coolants mixed with alcohol or methanol anti-freeze. The
use of an improper anti-freeze can cause corrosion of the
aluminum components.
10.By referring to the section on coolant, select an appropriate
concentration for safe operating temperature within the
range of 30 to 60%. Use special tool MB991871 to refill the
coolant. A convenient mixture is a 50% water and 50%
antifreeze solution [freezing point:
31C (32.8 F)].
Recommended antifreeze: Long Life Antifreeze
Coolant or an equivalent
Quantity:
<3.8L Engine> 8.7 Litres
NOTE: For how to use special tool MB991871, refer to its
manufacturer’s instructions.
11.Reinstall the radiator cap.
12.Start the engine and let it warm up until the thermostat
opens.
13.After repeatedly revving the engine up to 3,000 r/min
several times, stop the engine.
Page 1302 of 1500
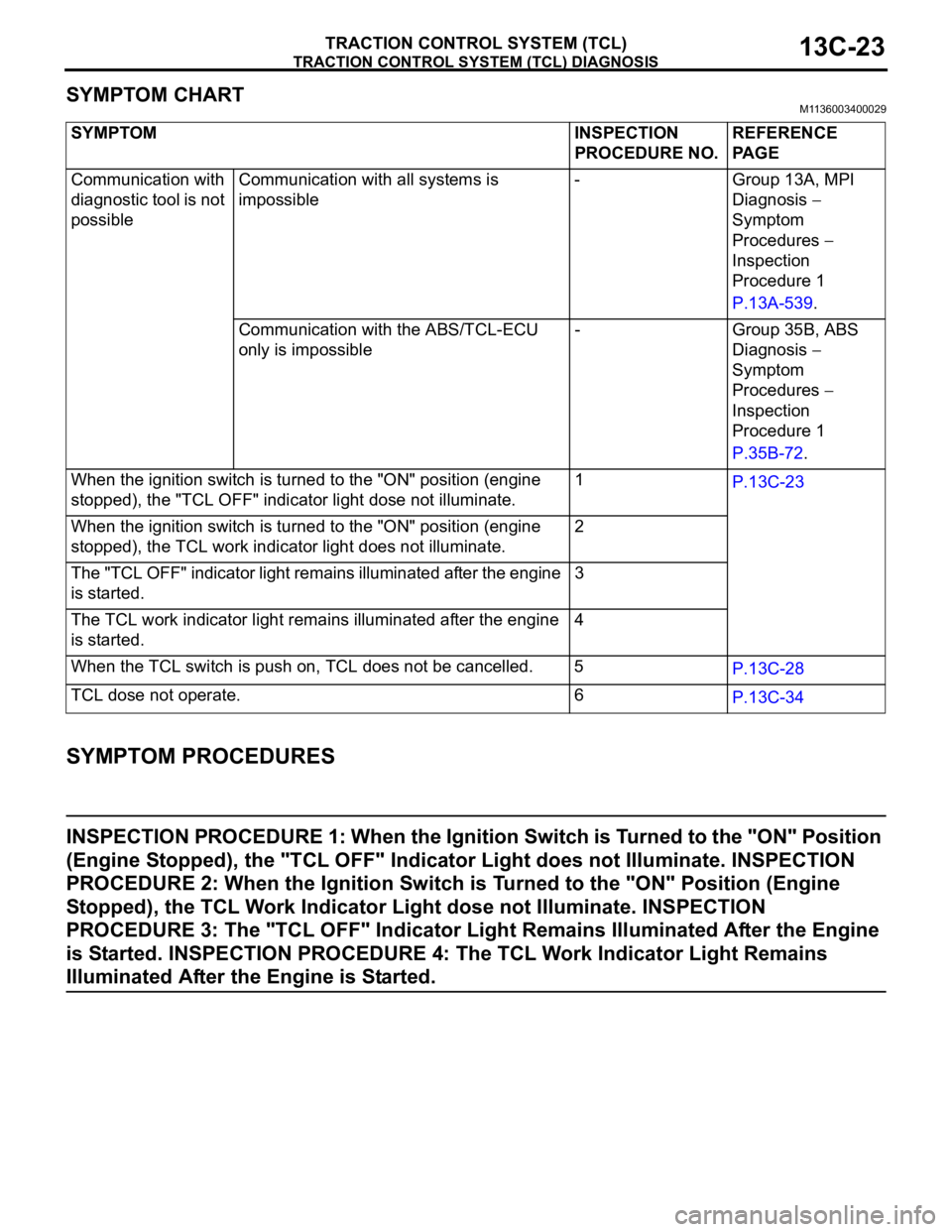
TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM (TCL) DIAGNOSIS
TRACTION CONTROL SYSTEM (TCL)13C-23
SYMPTOM CHARTM1136003400029
SYMPTOM PROCEDURES
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 1: When the Ignition Switch is Turned to the "ON" Position
(Engine Stopped), the "TCL OFF" Indicator Light does not Illuminate. INSPECTION
PROCEDURE 2: When the Ignition Switch is Turned to the "ON" Position (Engine
Stopped), the TCL Work Indicator Light dose not Illuminate. INSPECTION
PROCEDURE 3: The "TCL OFF" Indicator Light Remains Illuminated After the Engine
is Started. INSPECTION PROCEDURE 4: The TCL Work Indicator Light Remains
Illuminated After the Engine is Started.
SYMPTOM INSPECTION
PROCEDURE NO.REFERENCE
PA G E
Communication with
diagnostic tool is not
possibleCommunication with all systems is
impossible- Group 13A, MPI
Diagnosis
Symptom
Procedures
Inspection
Procedure 1
P.13A-539.
Communication with the ABS/TCL-ECU
only is impossible- Group 35B, ABS
Diagnosis
Symptom
Procedures
Inspection
Procedure 1
P.35B-72.
When the ignition switch is turned to the "ON" position (engine
stopped), the "TCL OFF" indicator light dose not illuminate.1
P.13C-23
When the ignition switch is turned to the "ON" position (engine
stopped), the TCL work indicator light does not illuminate.2
The "TCL OFF" indicator light remains illuminated after the engine
is started.3
The TCL work indicator light remains illuminated after the engine
is started.4
When the TCL switch is push on, TCL does not be cancelled. 5
P.13C-28
TCL dose not operate. 6
P.13C-34