Page 1580 of 2870
ME(H4DOTC)-120
MECHANICAL
Engine Trouble in General
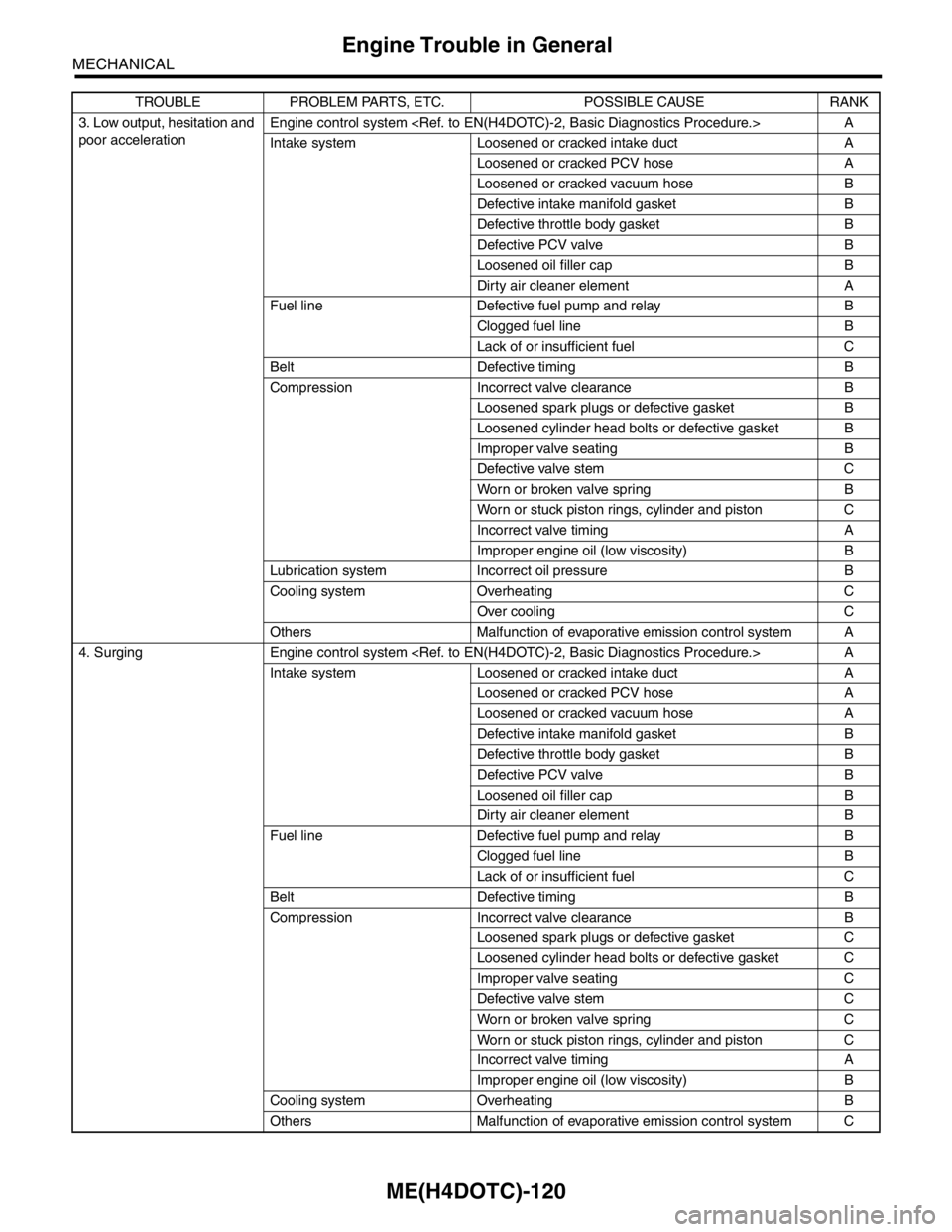
3. Low output, hesitation and
poor accelerationEngine control system A
Intake system Loosened or cracked intake duct A
Loosened or cracked PCV hose A
Loosened or cracked vacuum hose B
Defective intake manifold gasket B
Defective throttle body gasket B
Defective PCV valve B
Loosened oil filler cap B
Dirty air cleaner element A
Fuel line Defective fuel pump and relay B
Clogged fuel line B
Lack of or insufficient fuel C
Belt Defective timing B
Compression Incorrect valve clearance B
Loosened spark plugs or defective gasket B
Loosened cylinder head bolts or defective gasket B
Improper valve seating B
Defective valve stem C
Worn or broken valve spring B
Worn or stuck piston rings, cylinder and piston C
Incorrect valve timing A
Improper engine oil (low viscosity) B
Lubrication system Incorrect oil pressure B
Cooling system Overheating C
Over cooling C
Others Malfunction of evaporative emission control system A
4. Surging Engine control system A
Intake system Loosened or cracked intake duct A
Loosened or cracked PCV hose A
Loosened or cracked vacuum hose A
Defective intake manifold gasket B
Defective throttle body gasket B
Defective PCV valve B
Loosened oil filler cap B
Dirty air cleaner element B
Fuel line Defective fuel pump and relay B
Clogged fuel line B
Lack of or insufficient fuel C
Belt Defective timing B
Compression Incorrect valve clearance B
Loosened spark plugs or defective gasket C
Loosened cylinder head bolts or defective gasket C
Improper valve seating C
Defective valve stem C
Worn or broken valve spring C
Worn or stuck piston rings, cylinder and piston C
Incorrect valve timing A
Improper engine oil (low viscosity) B
Cooling system Overheating B
Others Malfunction of evaporative emission control system C TROUBLE PROBLEM PARTS, ETC. POSSIBLE CAUSE RANK
Page 1581 of 2870
ME(H4DOTC)-121
MECHANICAL
Engine Trouble in General
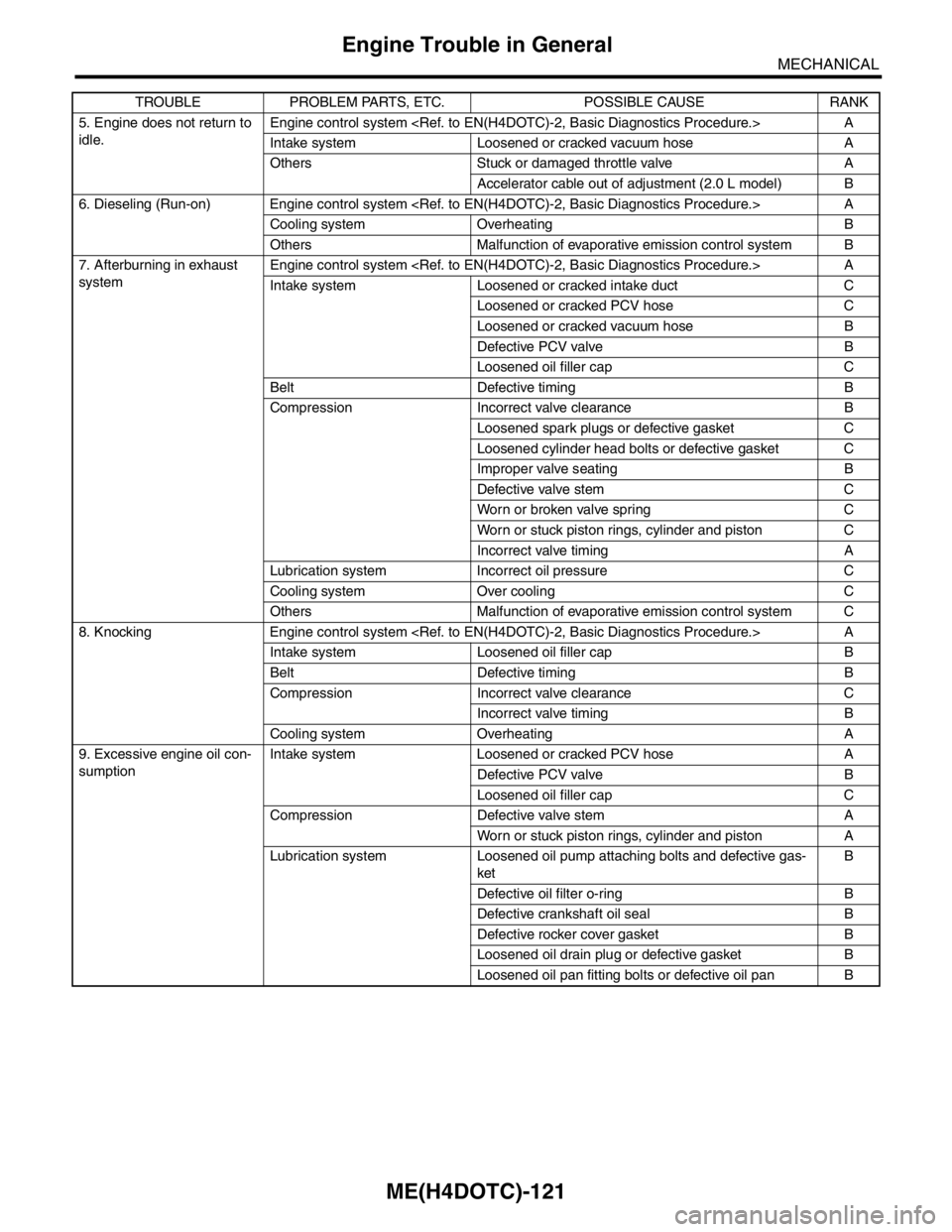
5. Engine does not return to
idle.Engine control system A
Intake system Loosened or cracked vacuum hose A
Others Stuck or damaged throttle valve A
Accelerator cable out of adjustment (2.0 L model) B
6. Dieseling (Run-on) Engine control system A
Cooling system Overheating B
Others Malfunction of evaporative emission control system B
7. Afterburning in exhaust
systemEngine control system A
Intake system Loosened or cracked intake duct C
Loosened or cracked PCV hose C
Loosened or cracked vacuum hose B
Defective PCV valve B
Loosened oil filler cap C
Belt Defective timing B
Compression Incorrect valve clearance B
Loosened spark plugs or defective gasket C
Loosened cylinder head bolts or defective gasket C
Improper valve seating B
Defective valve stem C
Worn or broken valve spring C
Worn or stuck piston rings, cylinder and piston C
Incorrect valve timing A
Lubrication system Incorrect oil pressure C
Cooling system Over cooling C
Others Malfunction of evaporative emission control system C
8. Knocking Engine control system A
Intake system Loosened oil filler cap B
Belt Defective timing B
Compression Incorrect valve clearance C
Incorrect valve timing B
Cooling system Overheating A
9. Excessive engine oil con-
sumptionIntake system Loosened or cracked PCV hose A
Defective PCV valve B
Loosened oil filler cap C
Compression Defective valve stem A
Worn or stuck piston rings, cylinder and piston A
Lubrication system Loosened oil pump attaching bolts and defective gas-
ketB
Defective oil filter o-ring B
Defective crankshaft oil seal B
Defective rocker cover gasket B
Loosened oil drain plug or defective gasket B
Loosened oil pan fitting bolts or defective oil pan B TROUBLE PROBLEM PARTS, ETC. POSSIBLE CAUSE RANK
Page 1582 of 2870
ME(H4DOTC)-122
MECHANICAL
Engine Trouble in General
10. Excessive fuel consump-
tionEngine control system A
Intake system Dirty air cleaner element A
Belt Defective timing B
Compression Incorrect valve clearance B
Loosened spark plugs or defective gasket C
Loosened cylinder head bolts or defective gasket C
Improper valve seating B
Defective valve stem C
Worn or broken valve spring C
Worn or stuck piston rings, cylinder and piston B
Incorrect valve timing B
Lubrication system Incorrect oil pressure C
Cooling system Over cooling C
Others Accelerator cable out of adjustment (2.0 L model) B TROUBLE PROBLEM PARTS, ETC. POSSIBLE CAUSE RANK
Page 1621 of 2870
IG(H4DOTC)-5
IGNITION
Spark Plug
2. Spark Plug
A: REMOVAL
CAUTION:
All spark plugs installed on an engine, must be
of the same heat range.
General Description.>
1. RH SIDE
1) Disconnect the ground cable from battery.
2) Remove the air cleaner lower case.
IN(H4DOTC)-7, REMOVAL, Air Cleaner.>
3) Disconnect the connector from ignition coil.
4) Remove the ignition coil.5) Remove the spark plugs with the spark plug
sockets.
2. LH SIDE
1) Disconnect the battery cables, and then remove
the battery and battery carrier.
2) Disconnect the washer motor connector.
3) Disconnect the rear window glass washer hose
from washer motor, then plug connection with a
suitable cap.
4) Remove the two bolts which hold washer tank,
then take the tank away from working area.
FU-00009
FU-01307
IG-00003
IG-00004
FU-00009
IG-00005
IG-00006
Page 1622 of 2870

IG(H4DOTC)-6
IGNITION
Spark Plug
5) Disconnect the connector from ignition coil.
6) Remove the ignition coil.
7) Remove the spark plugs with the spark plug
sockets.
B: INSTALLATION
1. RH SIDE
Install in the reverse order of removal.
Tightening torque (Spark plug):
21 N
⋅m (2.1 kgf-m, 15.2 ft-lb)
Tightening torque (Ignition coil):
16 N
⋅m (1.6 kgf-m, 11.7 ft-lb)
NOTE:
The above torque should be only applied to new
spark plugs without oil on their threads.
In case their threads are lubricated, the torque
should be reduced by approx. 1/3 of the specified
torque in order to avoid over-stressing.
2. LH SIDE
Install in the reverse order of removal.
Tightening torque (Spark plug):
21 N
⋅m (2.1 kgf-m, 15.2 ft-lb)
Tightening torque (Ignition coil):
16 N
⋅m (1.6 kgf-m, 11.7 ft-lb)
NOTE:
The above torque should be only applied to new
spark plugs without oil on their threads.
In case their threads are lubricated, the torque
should be reduced by approx. 1/3 of the specified
torque in order to avoid over-stressing.
C: INSPECTION
Check the electrodes and inner and ceramic insu-
lator of plugs, noting the type of deposits and the
degree of electrode erosion.
1) Normal:
Brown to grayish-tan deposits and slight electrode
wear indicates correct spark plug heat range.
FU-01308
IG-00008
IG-00009
(A) Electrode gap
(B) Carbon accumulation or wear
(C) Cracks
(D) Damage
(E) Damaged gasket
IG-00010
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
(E)
IG-00011
Page 1623 of 2870
IG(H4DOTC)-7
IGNITION
Spark Plug
2) Carbon fouled:
Dry fluffy carbon deposits on insulator and elec-
trode are mostly caused by slow speed driving in
city, weak ignition, too rich fuel mixture, dirty air
cleaner, etc.
It is advisable to replace with plugs having hotter
heat range.
3) Oil fouled:
Wet black deposits show excessive oil entrance
into combustion chamber through worn rings and
pistons or excessive clearance between valve
guides and stems. If the same condition remains
after repair, use a hotter plug.
4) Overheating:
White or light gray insulator with black or gray
brown spots and bluish burnt electrodes indicates
engine overheating. Moreover, the appearance re-
sults from incorrect ignition timing, loose spark
plugs, wrong selection of fuel, hotter range plug,
etc. It is advisable to replace with plugs having
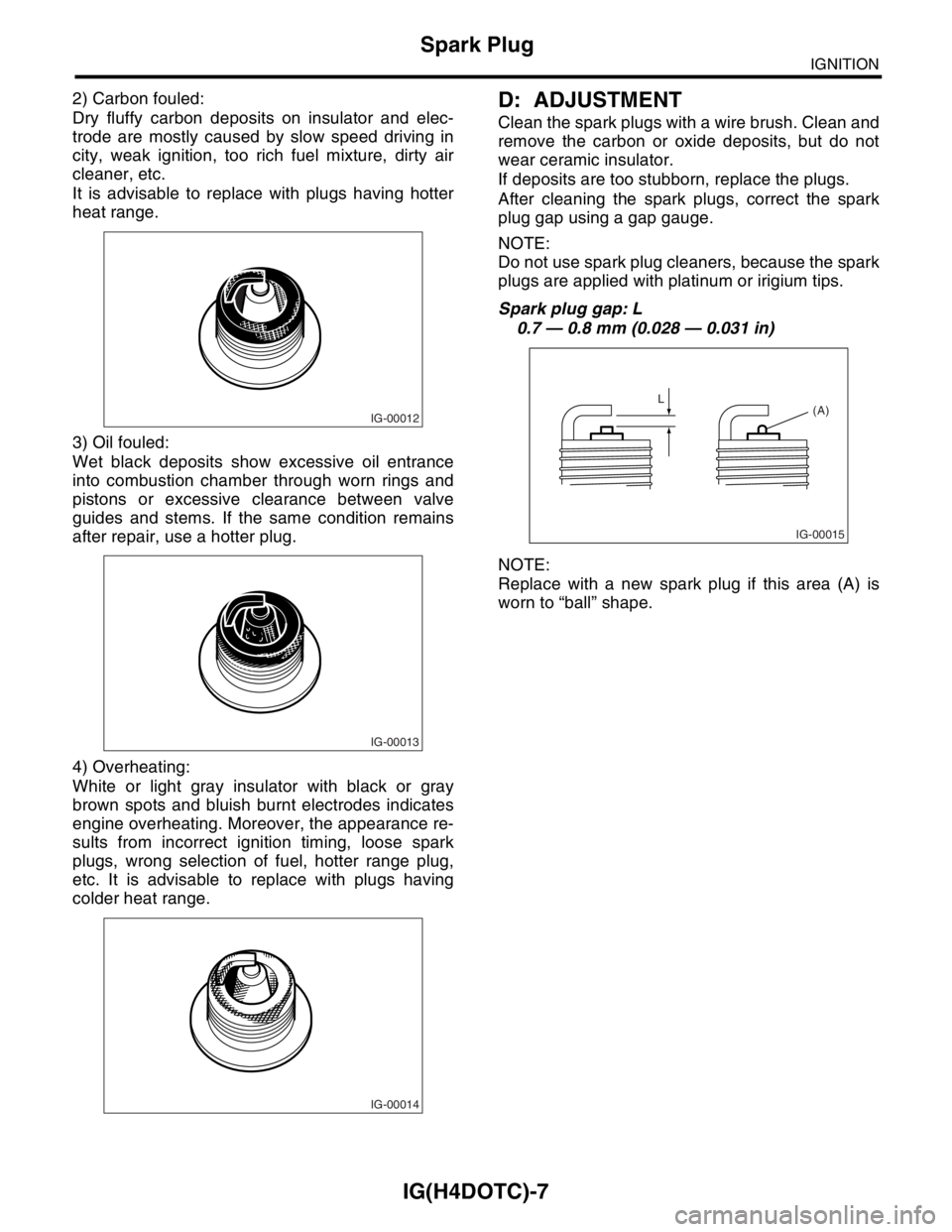
colder heat range.D: ADJUSTMENT
Clean the spark plugs with a wire brush. Clean and
remove the carbon or oxide deposits, but do not
wear ceramic insulator.
If deposits are too stubborn, replace the plugs.
After cleaning the spark plugs, correct the spark
plug gap using a gap gauge.
NOTE:
Do not use spark plug cleaners, because the spark
plugs are applied with platinum or irigium tips.
Spark plug gap: L
0.7 — 0.8 mm (0.028 — 0.031 in)
NOTE:
Replace with a new spark plug if this area (A) is
worn to “ball” shape.
IG-00012
IG-00013
IG-00014
IG-00015
L
(A)