2004 NISSAN PATROL sensor
[x] Cancel search: sensorPage 257 of 579

System Description
OUTLINE
The navigation system periodically calculates the vehicle's current
position according to the following three signals: Travel distance of
the vehicle as determined by the vehicle speed sensor, turning
angle of the vehicle as determined by the gyroscope (angular
velocity sensor), and the direction of vehicle travel as determined
by the GPS antenna (GPS information).
The current position of the vehicle is then identi®ed by comparing
the calculated vehicle position with map data read from the map
DVD-ROM, which is stored in the DVD-ROM drive (map-matching),
and indicated on the screen with a current location mark.
By comparing the vehicle position detection results found by the
GPS and by map-matching, more accurate vehicle position data
can be used.
The current vehicle position will be calculated by detecting the dis-
tance the vehicle moved from the previous calculation point and its
direction.
TRAVEL DISTANCE
Travel distance calculations are based on the vehicle speed sen-
sor input signal. Therefore, the calculation may become incorrect
as the tires wear down. To prevent this, an automatic distance ®ne
adjustment function has been adopted.
TRAVEL DIRECTION
Change in the travel direction of the vehicle is calculated by a
gyroscope (angular velocity sensor) and a GPS antenna (GPS
information). As the gyroscope and GPS antenna have both merit
and demerit, input signals from them are prioritized in each situa-
tion. However, this order of priority may change in accordance with
more detailed travel conditions so that the travel direction is
detected more accurately.
Type Advantage Disadvantage
Gyroscope (angular velocity sensor) +
Can detect the vehicle's turning angle
quite accurately. +
Direction errors may accumulate when
the vehicle is driven for long distances
without stopping.
GPS antenna (GPS information) +
Can detect the vehicle's travel direction
(North/South/East/West). +
Correct direction cannot be detected
when the vehicle speed is low.
SKIA0370E
SEL684V
NAVIGATION SYSTEM
EL-4162
Page 259 of 579

GPS (GLOBAL POSITIONING SYSTEM)
GPS (Global Positioning System) has been developed and con-
trolled by the US Department of Defense. The system utilizes GPS
satellite (NAVSTAR), sending out radio waves while ¯ying on an
orbit around the earth at the height of approx. 21,000 km (13,000
miles).
The GPS receiver calculates the vehicle's position in three dimen-
sions (latitude/longitude/altitude) according to the time lag of the
radio waves received from four or more GPS satellites (three-di-
mensional positioning). If radio waves were received only from
three GPS satellites, the GPS receiver calculates the vehicle's
position in two dimensions (latitude/longitude), utilizing the altitude
data calculated previously by using radio waves from four or more
GPS satellites (two-dimensional positioning).
Accuracy of the GPS will deteriorate under the following conditions.
+In two-dimensional positioning, the GPS accuracy will deterio-
rate when the altitude of the vehicle position changes.
+ There may be an error of approximately 10 m (30 ft.) in posi-
tion detected by three-dimensional positioning, which is more
accurate than two-dimensional positioning. The accuracy can
be even lower depending on the arrangement of the GPS sat-
ellites utilized for the positioning.
+ Position detection is not possible when the vehicle is in an area
where radio waves from the GPS satellite do not reach, such
as in a tunnel, parking lot in a building, and under an elevated
highway. Radio waves from the GPS satellites may not be
received when some object is located over the GPS antenna.
+ Position correction by GPS is not available while the vehicle is
stopped.
COMPONENT DESCRIPTION
NAVI control unit
+The gyro (angular speed sensor) and the DVD-ROM drive are
built-in units that control the navigation functions.
+ Signals are received from the gyro, the vehicle speed sensor,
and the GPS antenna. Vehicle location is determined by com-
bining this data with the data contained in the DVD-ROM map.
Locational information is shown on liquid crystal display panel.
DVD-ROM drive
Maps, traffic control regulations, and other pertinent information
can be easily read from the DVD-ROM disc.
Map DVD-ROM
+The map DVD-ROM has maps, traffic control regulations, and
other pertinent information.
+ To improve DVD-ROM map matching and route determination
functions, the DVD-ROM uses an exclusive Nissan format.
Therefore, the use of a DVD-ROM provided by other manufac-
turers cannot be used.
SEL526V
PKIA0248E
PKIA0249E
NAVIGATION SYSTEM
System Description (Cont'd)
EL-4164
Page 260 of 579

Gyro (Angular speed sensor)
+The oscillator gyro sensor is used to detect changes in vehicle
steering angle.
+ The gyro is built into the navigation (NAVI) control unit.
BIRDVIEW T
The BIRDVIEW Tprovides a detailed and easily seen display of
road conditions covering the vehicle's immediate to distant area.
+ MAP DISPLAY
+ BIRDVIEW T
Description
+Display area: Trapezoidal representation showing approximate
distances (Wn, D, and Wd).
+ Ten horizontal grid lines indicate display width while six vertical
grid lines indicate display depth and direction.
+ Drawing line area shows open space, depth, and immediate
front area. Each area is to a scale of approximately 5:6:25.
+ Pushing the ªZOOM INº button during operation displays the
scale change and the view point height on the left side of the
screen.
The height of the view point increases or decreases when
ªZOOMº or ªWIDEº is selected.
SKIA1377E
SKIA1378E
SEL691V
NAVIGATION SYSTEM
System Description (Cont'd)
EL-4165
Page 291 of 579

DIAGNOSIS BY HISTORY OF ERRORS
The ªSelf-diagnosisº results indicate whether an error occurred during the period from when the ignition switch
is turned to ON until ªSelf-diagnosisº is completed.
If an error occurred before the ignition switch was turned to ON and does not occur again until the ªSelf-di-
agnosisº is completed, the diagnosis result will be judged normal. Therefore, those errors in the past, which
cannot be found by the ªSelf-diagnosisº, must be found by diagnosing the ªHistory of Errorsº.
The History of Errors displays the time and place of the most recent occurrence of that error. However, take
note of the following points.
+Correct time of the error occurrence may not be displayed when the GPS antenna substrate within the
NAVI control unit has malfunctioned.
+ Place of the error occurrence is represented by the position of the current location mark at the time when
the error occurred. If the current location mark has deviated from the correct position, then the place of
the error occurrence may be located correctly.
+ The maximum number of occurrences which can be stored is 50. For the 51st and later occurrences, the
displayed number remains 50.
When a reproducible malfunction occurred but its cause cannot be identi®ed because several errors are
present, record the item, number and place (longitude/latitude) of error occurrence (or delete the History of
Errors), then turn the ignition switch from OFF to ON to reproduce the malfunction. Check the History of Errors
to ®nd the items which show an increased number of occurrences, and diagnose the item.
Error item Possible causes
Example of symptom
Action/symptom
Gyro sensor
disconnected Communications malfunction between NAVI control unit
and internal gyro
+Navigation location detection performance has dete-
riorated. (Angular velocity cannot be detected.)
+
Perform self-diagnosis.
+ When the NAVI control unit is judged normal by self-
diagnosis, the symptom may be intermittent, caused
by strong radio interference.
GPS discon-
nected Communication error between NAVI control unit and
internal GPS substrate
+Navigation location detection performance has dete-
riorated. (Location correction using GPS is not per-
formed.)
+ GPS receiving status remains gray.
+
Perform self-diagnosis.
+ When the NAVI control unit is judged normal by self-
diagnosis, the symptom may be intermittent, caused
by strong radio interference.
GPS transmis-
sion cable
malfunction Malfunctioning transmission wires to NAVI control unit
and internal GPS substrate
+During self-diagnosis, GPS diagnosis is not per-
formed.
+
Perform self-diagnosis.
+ When the NAVI control unit is judged normal by self-
diagnosis, the symptom may be intermittent, caused
by strong radio interference.
GPS input line
connection
error Malfunctioning receiving wires to NAVI control unit and
internal GPS substrate
+Navigation location detection performance has dete-
riorated. (Location correction using GPS is not per-
formed.)
+ GPS receiving status remains gray.
+
Perform self-diagnosis.
+ When the NAVI control unit is judged normal by self-
diagnosis, the symptom may be intermittent, caused
by strong radio interference.
GPS TCX0
over
GPS TCX0
under Oscillating frequency of the GPS substrate frequency
synchronizing oscillation circuit exceeded (or below) the
speci®cation
+Navigation location detection performance has dete-
riorated. (Location correction using GPS is not per-
formed.)
+ GPS receiving status remains gray.
+
Perform self-diagnosis.
+ When the NAVI control unit is judged normal by self-
diagnosis, the symptom may be intermittent, caused
by strong radio interference, or the control unit may
have been subjected to excessively high or low tem-
peratures.
NAVIGATION SYSTEM
Con®rmation/Adjustment Mode (Cont'd)
EL-4196
Page 312 of 579

DRIVING TEST
1. DRIVING TEST 1
1. Scroll the map screen to display the area to make correction. Push ªENTERº and select ªCURRENT LOCATION COR-RECTIONº.
2. Correct direction of the vehicle mark.
3. Perform the distance correction of the ªCONFIRMATION/ADJUSTMENTº mode. NOTE:
Normally, adjustment is not necessary because this system has automatic distance correction function. However, when
a tire chain is ®tted, adjustment in accordance with the tire diameter ratio must be made.
4. Are symptoms applicable to the Example of Symptoms Judged Not Malfunction (EL-4218) present after driving the vehicle? YesorNo
Ye s ©Limit of the location detection capacity of the navigation system.
No ©GO TO 2.
2. DRIVING TEST 2
+Did any malfunction occur when the proper test in the following test patterns is performed?
+ Test pattern
Driving test ®nds the difference between the symptoms monitored with and without each sensor.
Ð Test pattern 1: Test method with no GPS location correction Disconnect the GPS antenna connector connected to the NAVI control unit. Accurately adjust the current location and
the direction, then drive the vehicle.
Ð Test pattern 2: Test method with no map-matching Accurately adjust the current location and the direction. Eject the map DVD-ROM from the NAVI control unit with the
ignition switch turned to OFF, then drive the vehicle. After driving, insert the map DVD-ROM back in the unit, display
the track of the vehicle on the map screen and compare it with the actual road con®guration.
+ Sample tests
Ð
Perform test pattern 1.
Ð
Compare the track of the vehicle on the map screen and the actual road con®guration. For fairly accurate tracking,
plotting shall be made every several hundred meters.
Ð
Drive on a road of which distance is accurately known (by utilizing distance posts on a highway). Calculate the rate of
change (increased/decreased) of the distance by comparing with the actual distance.
Correctio n=1ÐA/B
A: Distance shown on the screen
B: Actual distance YesorNo
Ye s ©+If adjustment is insufficient, perform adjustment again.
+ If any error is found in the map, please let us know.
+ Replace NAVI control unit.
No ©Limit of the location detection capacity of the navigation system.
NAVIGATION SYSTEM
Trouble Diagnoses (Cont'd)
EL-4217
Page 317 of 579
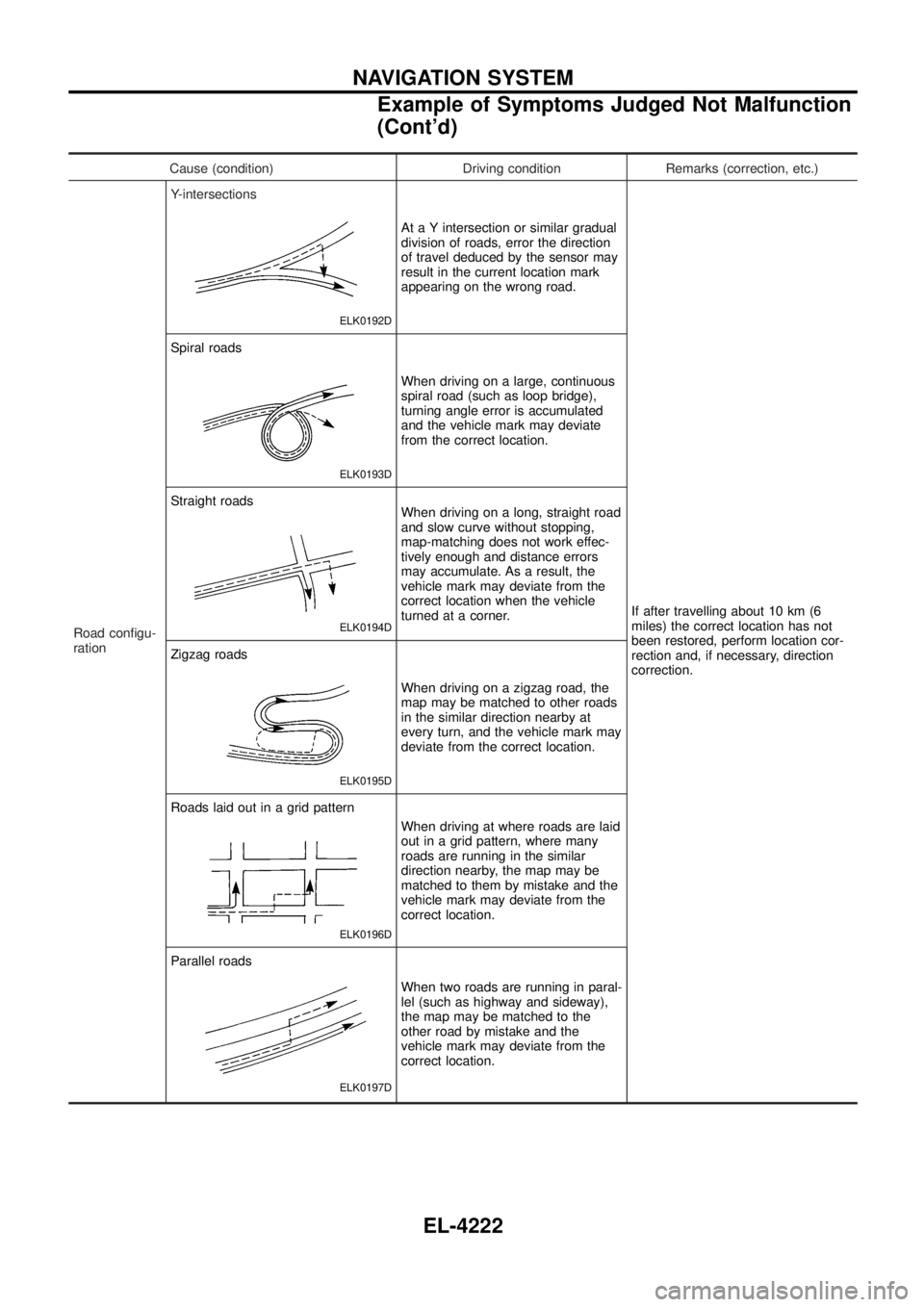
Cause (condition) Driving condition Remarks (correction, etc.)
Road con®gu-
ration Y-intersections
ELK0192D
At a Y intersection or similar gradual
division of roads, error the direction
of travel deduced by the sensor may
result in the current location mark
appearing on the wrong road.
If after travelling about 10 km (6
miles) the correct location has not
been restored, perform location cor-
rection and, if necessary, direction
correction.
Spiral roads
ELK0193D
When driving on a large, continuous
spiral road (such as loop bridge),
turning angle error is accumulated
and the vehicle mark may deviate
from the correct location.
Straight roads
ELK0194D
When driving on a long, straight road
and slow curve without stopping,
map-matching does not work effec-
tively enough and distance errors
may accumulate. As a result, the
vehicle mark may deviate from the
correct location when the vehicle
turned at a corner.
Zigzag roads
ELK0195D
When driving on a zigzag road, the
map may be matched to other roads
in the similar direction nearby at
every turn, and the vehicle mark may
deviate from the correct location.
Roads laid out in a grid pattern
ELK0196D
When driving at where roads are laid
out in a grid pattern, where many
roads are running in the similar
direction nearby, the map may be
matched to them by mistake and the
vehicle mark may deviate from the
correct location.
Parallel roads
ELK0197D
When two roads are running in paral-
lel (such as highway and sideway),
the map may be matched to the
other road by mistake and the
vehicle mark may deviate from the
correct location.
NAVIGATION SYSTEM
Example of Symptoms Judged Not Malfunction
(Cont'd)
EL-4222
Page 318 of 579
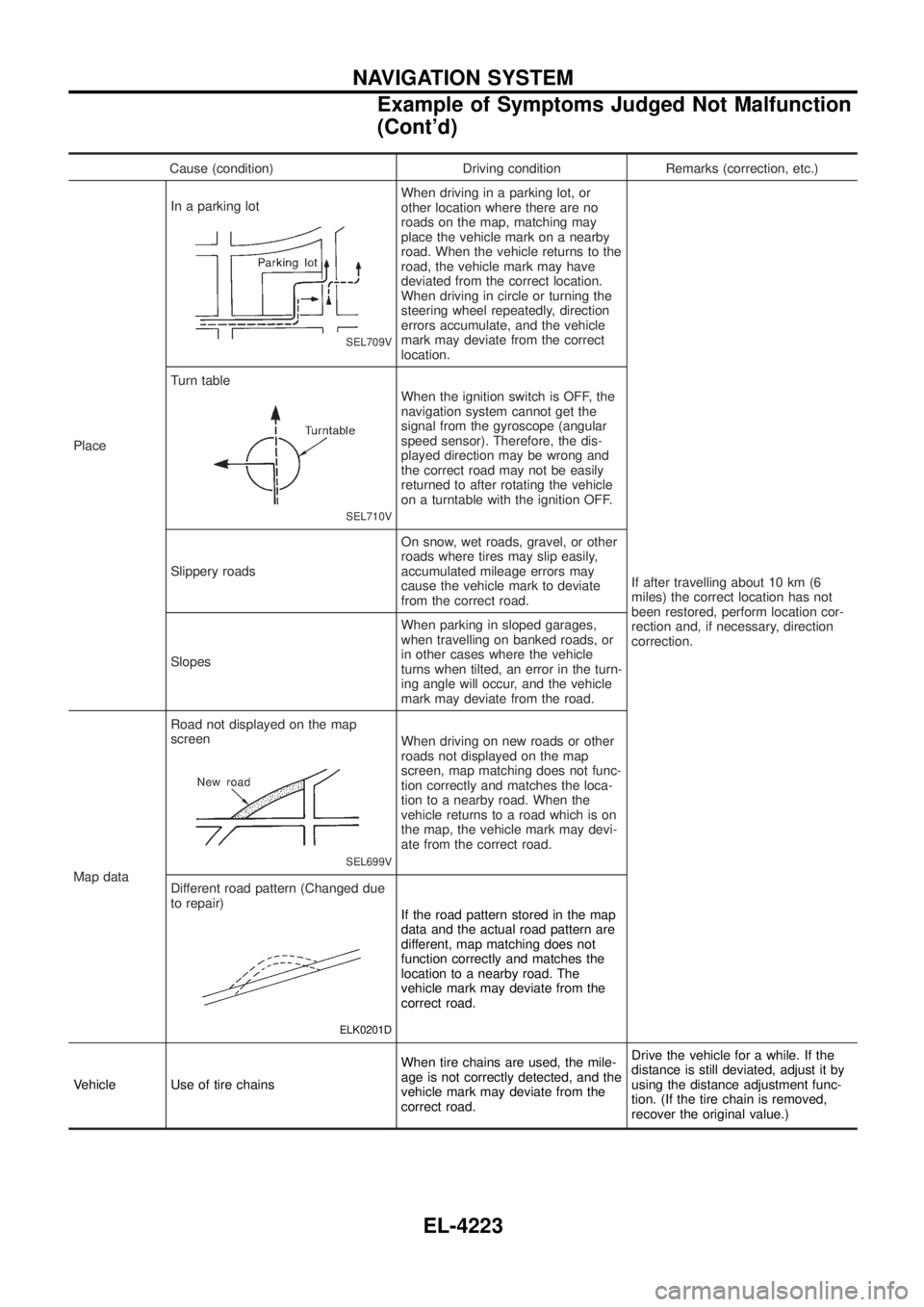
Cause (condition) Driving condition Remarks (correction, etc.)
Place In a parking lot
SEL709V
When driving in a parking lot, or
other location where there are no
roads on the map, matching may
place the vehicle mark on a nearby
road. When the vehicle returns to the
road, the vehicle mark may have
deviated from the correct location.
When driving in circle or turning the
steering wheel repeatedly, direction
errors accumulate, and the vehicle
mark may deviate from the correct
location.
If after travelling about 10 km (6
miles) the correct location has not
been restored, perform location cor-
rection and, if necessary, direction
correction.
Turn table
SEL710V
When the ignition switch is OFF, the
navigation system cannot get the
signal from the gyroscope (angular
speed sensor). Therefore, the dis-
played direction may be wrong and
the correct road may not be easily
returned to after rotating the vehicle
on a turntable with the ignition OFF.
Slippery roads On snow, wet roads, gravel, or other
roads where tires may slip easily,
accumulated mileage errors may
cause the vehicle mark to deviate
from the correct road.
Slopes When parking in sloped garages,
when travelling on banked roads, or
in other cases where the vehicle
turns when tilted, an error in the turn-
ing angle will occur, and the vehicle
mark may deviate from the road.
Map data Road not displayed on the map
screen
SEL699V
When driving on new roads or other
roads not displayed on the map
screen, map matching does not func-
tion correctly and matches the loca-
tion to a nearby road. When the
vehicle returns to a road which is on
the map, the vehicle mark may devi-
ate from the correct road.
Different road pattern (Changed due
to repair)
ELK0201D
If the road pattern stored in the map
data and the actual road pattern are
different, map matching does not
function correctly and matches the
location to a nearby road. The
vehicle mark may deviate from the
correct road.
Vehicle Use of tire chains When tire chains are used, the mile-
age is not correctly detected, and the
vehicle mark may deviate from the
correct road.Drive the vehicle for a while. If the
distance is still deviated, adjust it by
using the distance adjustment func-
tion. (If the tire chain is removed,
recover the original value.)
NAVIGATION SYSTEM
Example of Symptoms Judged Not Malfunction
(Cont'd)
EL-4223
Page 319 of 579

Cause (condition) Driving condition Remarks (correction, etc.)
Precautions
for driving Just after the engine is started
If the vehicle is driven off just after
the engine is started when the gyro-
scope (angular speed sensor) cor-
rection is not completed, the vehicle
can lose its direction and may have
deviated from the correct location.Wait for a short while before driving
after starting the engine.
Continuous driving without stopping When driving long distances without
stopping, direction errors may
accumulate, and the current location
mark may deviate from the correct
road.Stop and adjust the orientation.
Abusive driving Spinning the wheels or engaging in
other kinds of abusive driving may
result in the system being unable to
perform correct detection, and may
cause the vehicle mark to deviate
from the correct road.If after travelling about 10 km (6
miles) the correct location has not
been restored, perform location cor-
rection and, if necessary, direction
correction.
How to correct
location Position correction accuracy
SEL699V
If the accuracy of location settings is
poor, accuracy may be reduced
when the correct road cannot be
found, particularly in places where
there are many roads.
Enter in the road displayed on the
screen with an accuracy of approx. 1
mm.
NOTE:
Whenever possible, use detailed
map for the correction.
Direction when location is corrected
SEL702V
If the accuracy of location settings
during correction is poor, accuracy
may be reduced afterwards. Perform direction correction.
THE CURRENT POSITION MARK SHOWS A POSITION WHICH IS COMPLETELY WRONG
In the following cases, the current location mark may appear on completely different position in the map
depending on the GPS satellite signal receiving conditions. In this case, perform location correction and
direction correction.
+
When location correction has not been done
Ð If the receiving conditions of the GPS satellite signal is poor, if the current location mark becomes out of place, it may move to a completely different location and not come back if location correction is not done.
The position will be corrected if the GPS signal can be received.
+ When the vehicle has traveled by ferry, or when the vehicle has been being towed
Ð Because calculation of the current location cannot be done when travelling with the ignition OFF, for example when travelling by ferry or when being towed, the location before travel is displayed. If the pre-
cise location can be detected with GPS, the location will be corrected.
THE CURRENT POSITION MARK JUMPS
In the following cases, the current location mark may appear to jump as a result of automatic correction of the
current location.
+When map matching has been done
Ð If the current location and the current location mark are different when map matching is done, the current location mark may seem to jump. At this time, the location may be ªcorrectedº to the wrong road or to a
location which is not on a road.
+ When GPS location correction has been done
Ð If the current location and the current location mark are different when the location is corrected using GPS measurements, the current location mark may seem to jump. At this time, the location may be ªcorrectedº
to a location which is not on a road.
NAVIGATION SYSTEM
Example of Symptoms Judged Not Malfunction
(Cont'd)
EL-4224