2004 ISUZU TF SERIES content
[x] Cancel search: contentPage 2627 of 4264

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–51
Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
The IAT sensor is a thermistor. A temperature changes
the resistance value. And it changes voltage. In other
words it measures a temperature value. Low air
temperature produces a high resistance.
The ECM supplies 5 volts signal to the IAT sensor
through resisters in the ECM and measures the voltage.
The signal voltage will be high when the air temperature
is cold, and it will be low when the air temperature is
hot.
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS)
The VSS is a magnet rotated by the transmission output
shaft. The VSS uses a hall element. It interacts with the
magnetic field treated by the rotating magnet. It outputs
pulse signal. The 12 volts operating supply from the
meter fuse.
Heated Oxygen (O2) Sensor
The heated ox ygen sensor consists of a 4-wire low
temperature activated zirconia ox ygen analyzer element
with heater for operating temperature of 315°C, and
there is one mounted on each ex haust pipe.
A constant 450millivolt is supplied by the ECM between
the two supply terminals, and oxygen concentration in
the ex haust gas is reported to the ECM as returned
signal voltage.
The ox ygen present in the ex haust gas reacts with the
sensor to produce a voltage output. This voltage should
constantly fluctuate from approx imately 100mV to
1000mV and the ECM calculates the pulse width
commanded for the injectors to produce the proper
combustion chamber mix ture.
Low ox ygen sensor output voltage is a lean mix ture
which will result in a rich commanded to compensate.
High ox ygen sensor output voltage is a rich mix ture
which result in a lean commanded to compensate.
When the engine is first started the system is in “Open
Loop” operation. In “Open Loop”, the ECM ignores the
signal from the ox ygen sensors. When various
conditions (ECT, time from start, engine speed &
ox ygen sensor output) are met, the system enters
“Closed Loop” operation. In “Closed Loop”, the ECM
calculates the air fuel ratio based on the signal from the
ox ygen sensors.
Heated ox ygen sensors are used to minimize the
amount of time required for closed loop fuel control to
begin operation and allow accurate catalyst monitoring.
The ox ygen sensor heater greatly decreases the
amount of time required for fuel control sensors to
become active.
Oxygen sensor heaters are required by catalyst monitor
and sensors to maintain a sufficiently high temperature
which allows accurate ex haust ox ygen content readings
further away from the engine.
C haract erist ic of I A T Sen sor -Ref erence-
10 100 1000 10000 100000
- 20 - 10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120
I nt ake A i r T emp. ( deg . C ) ( Tec h2 R eadi ng )
Resistance (ohm) (Solid Line)
Page 2739 of 4264
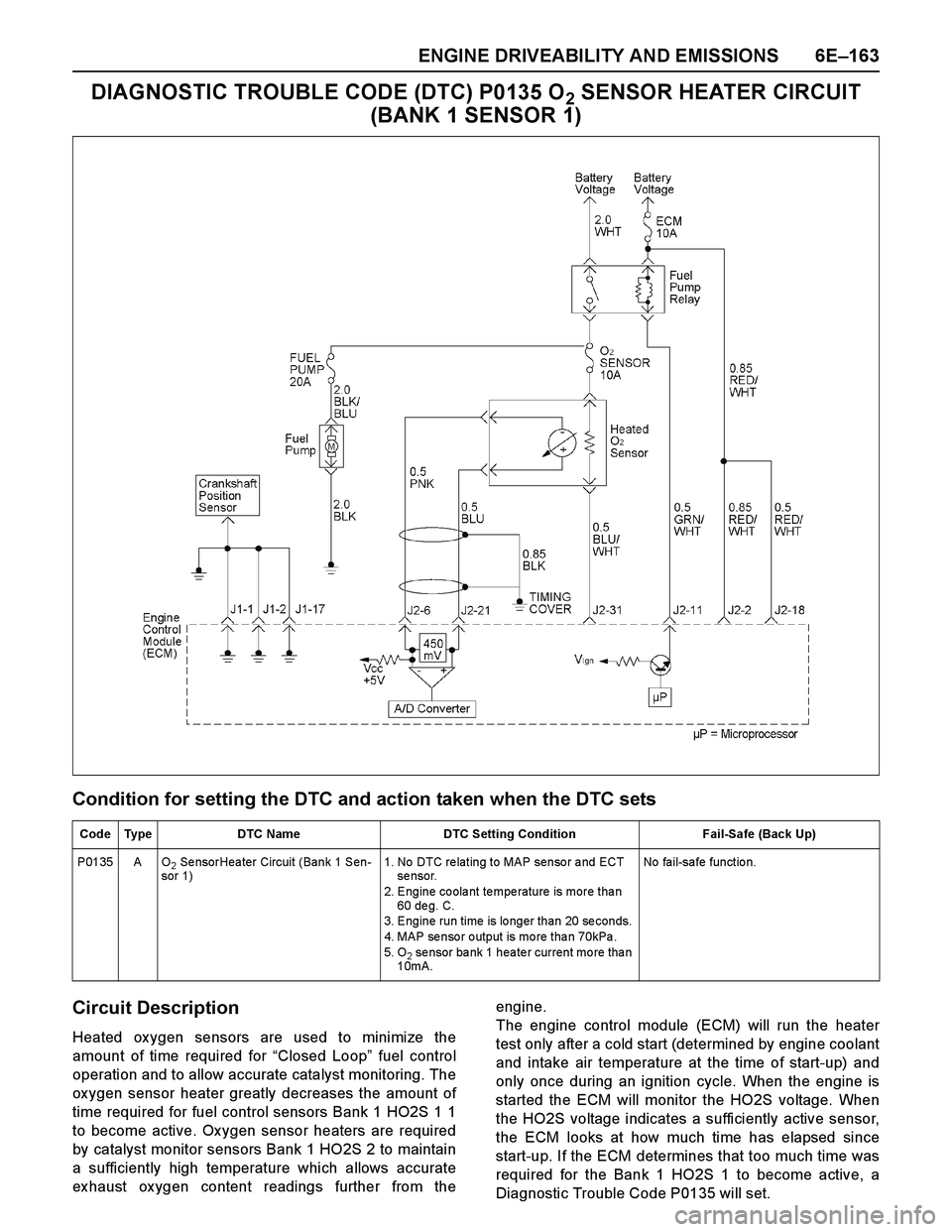
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–163
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0135 O2 SENSOR HEATER CIRCUIT
(BANK 1 SENSOR 1)
Condition for setting the DTC and action taken when the DTC sets
Circuit Description
Heated ox ygen sensors are used to minimize the
amount of time required for “Closed Loop” fuel control
operation and to allow accurate catalyst monitoring. The
ox ygen sensor heater greatly decreases the amount of
time required for fuel control sensors Bank 1 HO2S 1 1
to become active. Ox ygen sensor heaters are required
by catalyst monitor sensors Bank 1 HO2S 2 to maintain
a sufficiently high temperature which allows accurate
ex haust ox ygen content readings further from theengine.
The engine control module (ECM) will run the heater
test only after a cold start (determined by engine coolant
and intake air temperature at the time of start-up) and
only once during an ignition cycle. When the engine is
started the ECM will monitor the HO2S voltage. When
the HO2S voltage indicates a sufficiently active sensor,
the ECM looks at how much time has elapsed since
start-up. If the ECM determines that too much time was
required for the Bank 1 HO2S 1 to become active, a
Diagnostic Trouble Code P0135 will set.
Code Type DTC Name DTC Setting Condition Fail-Safe (Back Up)
P0135 A O
2 Se nsorHea ter Circuit (Bank 1 Sen-
sor 1)1. No DTC re lating to MAP senso r a nd ECT
se nsor.
2. Engine coolant temperature is more than
60 de g. C.
3. Engine run time is longer than 20 seconds.
4. MAP se nso r o utput is mo re tha n 70kPa .
5. O
2 se nsor ba nk 1 hea te r current mo re tha n
10mA.No fail-safe function.
Page 2782 of 4264
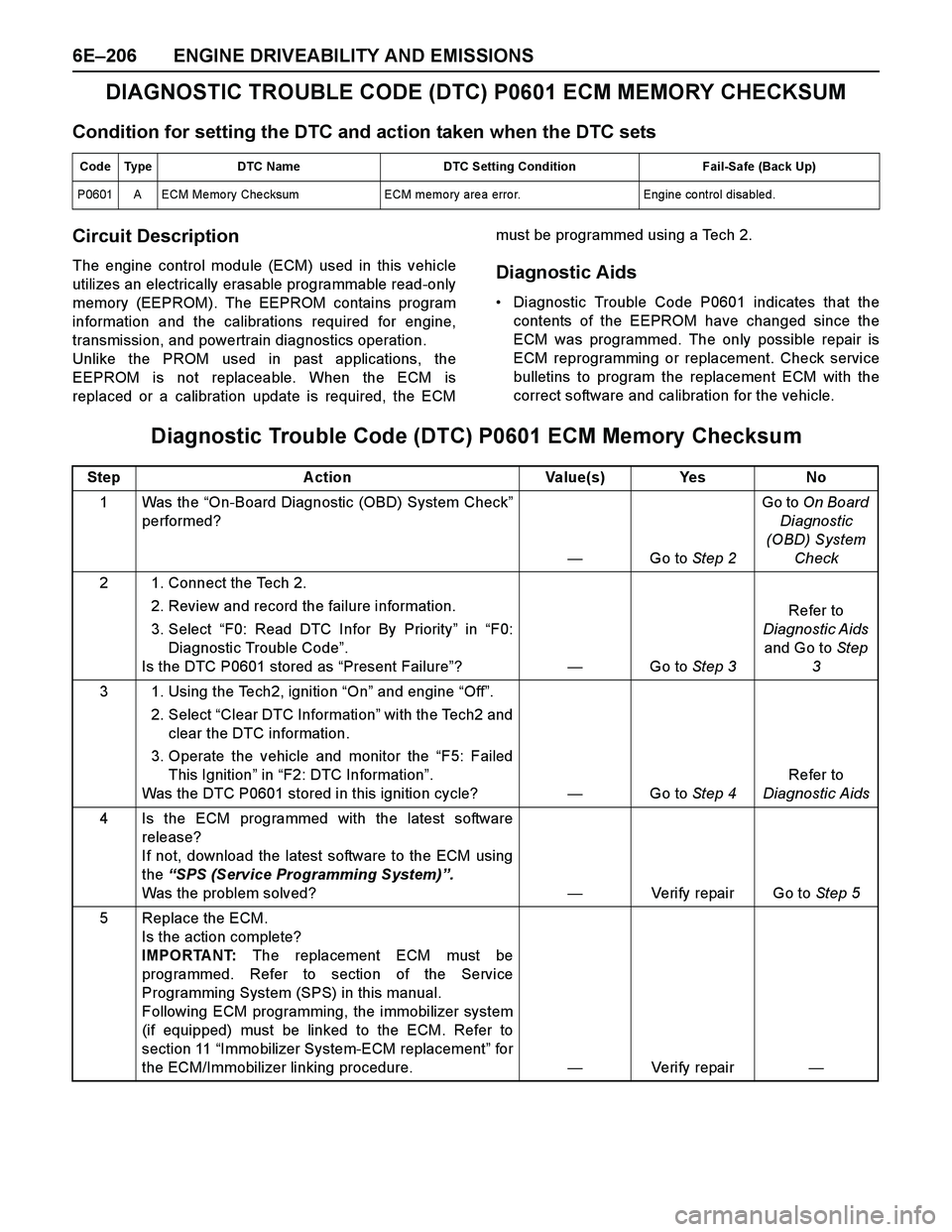
6E–206 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0601 ECM MEMORY CHECKSUM
Condition for setting the DTC and action taken when the DTC sets
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) used in this vehicle
utilizes an electrically erasable programmable read-only
memory (EEPROM). The EEPROM contains program
information and the calibrations required for engine,
transmission, and powertrain diagnostics operation.
Unlike the PROM used in past applications, the
EEPROM is not replaceable. When the ECM is
replaced or a calibration update is required, the ECMmust be programmed using a Tech 2.Diagnostic Aids
Diagnostic Trouble Code P0601 indicates that the
contents of the EEPROM have changed since the
ECM was programmed. The only possible repair is
ECM reprogramming or replacement. Check service
bulletins to program the replacement ECM with the
correct software and calibration for the vehicle.
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0601 ECM Memory Checksum
Code Type DTC Name DTC Setting Condition Fail-Safe (Back Up)
P0601 A ECM Me mo ry Che cksum ECM memo ry are a erro r. Engine co ntrol disabled.
Step A ction Value(s) Yes No
1 Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2Go to On Board
Diagnostic
(OBD) System
Check
2 1. Connect the Tech 2.
2. Review and record the failure information.
3. Select “F0: Read DTC Infor By Priority” in “F0:
Diagnostic Trouble Code”.
Is the DTC P0601 stored as “Present Failure”?—Go to Step 3Refer to
Diagnostic Aids
and Go to Step
3
3 1. Using the Tech2, ignition “On” and engine “Off”.
2. Select “Clear DTC Information” with the Tech2 and
clear the DTC information.
3. Operate the vehicle and monitor the “F5: Failed
This Ignition” in “F2: DTC Information”.
Was the DTC P0601 stored in this ignition cycle?—Go to Step 4Refer to
Diagnostic Aids
4 Is the ECM programmed with the latest software
release?
If not, download the latest software to the ECM using
the “SPS (Service Programming System)”.
Was the problem solved?—Verify repair Go to Step 5
5 Replace the ECM.
Is the action complete?
IMPORTANT: The replacement ECM must be
programmed. Refer to section of the Service
Programming System (SPS) in this manual.
Following ECM programming, the immobilizer system
(if equipped) must be linked to the ECM. Refer to
section 11 “Immobilizer System-ECM replacement” for
the ECM/Immobilizer linking procedure.—Veri fy repai r—
Page 2808 of 4264

6E–232 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS
PRELIMINARY CHECKS
Before using this section, perform the “On-Board
Diagnostic (OBD) System Check” and verify all of the
following items:
The engine control module (ECM) and malfunction
indicator lamp (MIL = Check Engine Lamp) are
operating correctly.
There are no Diagnostic Trouble Code(s) stored.
Tech 2 data is within normal operating range. Refer to
Typical Scan Data Values.
Verify the customer complaint and locate the correct
symptom in the table of contents. Perform the
procedure included in the symptom chart.
VISUAL/PHYSICAL CHECK
Several of the symptom procedures call for a careful
visual/physical check. This can lead to correcting a
problem without further checks and can save valuable
time. This check should include the following items:
ECM grounds for cleanliness, tightness and proper
location.
Vacuum hoses for splits, kinks, and proper
connection, shown on the “Emission Control System
Schematics”. Check thoroughly for any type of leak or
restriction.
Air intake ducts for collapsed or damaged areas.
Air leaks at throttle body mounting area, manifold
absolute pressure (MAP) sensor and intake manifold
sealing surfaces.
Ignition wires for cracking, harness, and carbon
tracking.
Wiring for proper connections, pinches and cuts.
INTERMITTENT
Important: An intermittent problem may or may not turn
on the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) or store a
Diagnostic Trouble Code. Do NOT use the Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) charts for intermittent problems.
The fault must be present to locate the problem.
Most intermittent problems are cased by faulty electrical
connections or wiring. Perform a careful visual/physical
check for the following conditions.
Poor mating of the connector halves or a terminal not
fully seated in the connector (backed out).
Improperly formed or damaged terminal.
All connector terminals in the problem circuit should
be carefully checked for proper contact tension.
Poor terminal-to-wire connection. This requires
removing the terminal form the connector body to
check.
Ignition coils shorted to ground and arcing at ignition
wires or plugs.MIL (Check Engine Lamp) wire to ECM shorted to
ground.
Poor ECM grounds. Refer to the ECM wiring
diagrams.
Road test the vehicle with a Digital Multimeter
connected to a suspected circuit. An abnormal voltage
when the malfunction occurs is a good indication that
there is a fault in the circuit being monitored.
Using Tech 2 to help detect intermittent conditions. The
Tech 2 has several features that can be used to located
an intermittent condition.
An intermittent MIL (Check Engine Lamp) with no stored
Diagnostic Trouble Code may be caused by the
follow ing:
Ignition coil shorted to ground and arcing at ignition
wires or plugs.
MIL (Check Engine Lamp) wire to ECM short to
ground.
Poor ECM grounds. Refer to the ECM wiring
diagrams.
Check for improper installation of electrical options such
as light, cellular phones, etc. Check all wires from ECM
to the ignition control module for poor connections.
Check for an open diode across the A/C compressor
clutch and check for other open diodes (refer to wiring
diagrams in Electrical Diagnosis).
If problem has not been found, refer to ECM connector
symptom tables.
Check the “Broadcast Code” of the ECM, and
compare it with the latest Isuzu service bulletins and/
or Isuzu EEPROM reprogramming equipment to
determine if an update to the ECM’s reprogrammable
memory has been released.
To check the “Broadcast Code”, connect the Tech 2,
then look for “ID info.” then select “Broadcast Code”.
This should display a 4 character code, such as “XBYA”
(ex ample only).
This identifies the contents of the reprogrammable
software and calibration contained in the ECM.
If the “Broadcast Code” is not the most current
available, it is advisable to reprogram the ECM’s
EEPROM memory, which may either help identify a
hard-to find problem or may fix the problem.
The Service Programming System (SPS) will not allow
incorrect software programming or incorrect calibration
changes.
Page 2857 of 4264
ENGINE EXHAUST 6F-1
SECTION 6F
ENGINE EXHAUST
CONTENTS
PAGE
General Description........................................................................................................ 6F- 2
Service Precaution ......................................................................................................... 6F- 4
Exhaust Pipe ................................................................................................................... 6F- 5
Exhaust pipe and Associated parts.......................................................................... 6F- 5
Removal ...................................................................................................................... 6F- 5
Installation .................................................................................................................. 6F- 6
Inspection ................................................................................................................... 6F- 6
Front Exhaust Pipe ......................................................................................................... 6F- 7
Front Exhaust Pipe and Associated Parts ............................................................... 6F- 7
Removal ...................................................................................................................... 6F- 7
Installation .................................................................................................................. 6F- 7
Mid Pipe ........................................................................................................................... 6F- 8
Mid Pipe and associated Parts ................................................................................. 6F- 8
Removal ...................................................................................................................... 6F- 8
Installation .................................................................................................................. 6F- 8
Catalytic Converter (If applicable) ................................................................................. 6F- 9
Catalytic Converter and Associated Parts ............................................................... 6F- 9
Removal ...................................................................................................................... 6F- 9
Installation .................................................................................................................. 6F- 9
3 way Catalytic Converter System ............................................................................ 6F- 10
Exhaust Silencer ............................................................................................................. 6F- 12
Exhaust Silencer and Associated Parts ................................................................... 6F- 12
Removal ...................................................................................................................... 6F- 12
Installation .................................................................................................................. 6F- 13
Main Data and Specifications ........................................................................................ 6F- 14
Torque Specification.................................................................................................. 6F- 15
Page 2873 of 4264
ENGINE LUBRICATION 6G-1
SECTION 6G
ENGINE LUBRICATION
CONTENTS
PAGE
General Description........................................................................................................ 6G- 2
Service Precaution ......................................................................................................... 6G- 3
Oil Pump .......................................................................................................................... 6G- 4
Oil Pump and Associated Parts ................................................................................ 6G- 4
Disassembly ............................................................................................................... 6G- 4
Inspection and Repair................................................................................................ 6G- 5
Reassembly ................................................................................................................ 6G- 5
Oil Pan ............................................................................................................................. 6G- 6
Oil Pan and Associated Parts ................................................................................... 6G- 6
Disassembly ............................................................................................................... 6G- 6
Inspection and Repair................................................................................................ 6G- 7
Reassembly ................................................................................................................ 6G- 7
Page 2881 of 4264

ENGINE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM (C24SE) 6H-1
ENGINE
ENGINE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM (C24SE)
CONTENTS
Service Precaution............................................... 6H-1
Accelerator Pedal Control Cable...................... 6H-2
Removal.............................................................. 6H-2
Inspection........................................................... 6H-3
Installation.......................................................... 6H-3
Service Precaution
WARNING: THIS VEHICLE HAS A SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINT SYSTEM (SRS). REFER TO THE SRS
COMPONENT AND WIRING LOCATION VIEW IN
ORDER TO DETERMINE WHETHER YOU ARE
PERFORMING SERVICE ON OR NEAR THE SRS
COMPONENTS OR THE SRS WIRING. WHEN YOU
ARE PERFORMING SERVICE ON OR NEAR THE
SRS COMPONENTS OR THE SRS WIRING, REFE
R
TO THE SRS SERVICE INFORMATION. FAILURE TO
FOLLOW WARNINGS COULD RESULT IN
POSSIBLE AIR BAG DEPLOYMENT, PERSONAL
INJURY, OR OTHERWISE UNNEEDED SRS SYSTEM
REPAIRS.
CAUTION: Always use the correct fastener in the
proper location. When you replace a fastener, use
ONLY the exact part number for that application.
ISUZU will call out those fasteners that require a
replacement after removal. ISUZU will also call out
the fasteners that require thread lockers or thread
sealant. UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED, do not
use supplemental coatings (Paints, greases, o
r
other corrosion inhibitors) on threaded fasteners o
r
fastener joint interfaces. Generally, such coatings
adversely affect the fastener torque and the joint
clamping force, and may damage the fastener.
When you install fasteners, use the correct
tightening sequence and specifications. Following
these instructions can help you avoid damage to
parts and systems.
Page 2885 of 4264

INDUCTION 6J-1
SECTION 6J
INDUCTION
CONTENTS
PAGE
Service Precaution ......................................................................................................... 6J- 2
Air Cleaner Filter ............................................................................................................. 6J- 2
Removal ...................................................................................................................... 6J- 2
Inspection ................................................................................................................... 6J- 2
Installation .................................................................................................................. 6J- 3