2004 DAEWOO NUBIRA coolant temperature
[x] Cancel search: coolant temperaturePage 134 of 2643

1C2 – 14I1.8L DOHC ENGINE MECHANICAL
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
6. Disconnect the manifold air temperature (MAT)
sensor connector.
7. Disconnect the breather tube from the camshaft
cover.
8. Disconnect the air cleaner outlet hose from the
throttle body.
9. Disconnect the direct ignition system (DIS) coil con-
nector.
10. Disconnect the oxygen (O2) sensor connector, if
equipped.
11. Disconnect the idle air control (IAC) valve connec-
tor.
12. Disconnect the throttle position sensor (TPS) con-
nector.
13. Disconnect the engine coolant temperature (ECT)
sensor connector.
14. Disconnect the coolant temperature sensor (CTS)
connector.
15. Remove the air cleaner housing bolts.
16. Remove the air cleaner housing.
17. Remove the right front wheel. Refer to Section 2E,
Tires and Wheels.
18. Remove the right front wheel well splash shield.
19. Install the engine assembly support fixture
J–28467–B.
20. Remove the right engine mount bracket and bolts.
21. Disconnect the upper radiator hose at the thermo-
stat housing.
22. Remove the serpentine accessory drive belt. Refer
to Section 6B, Power Steering Pump.
23. Remove the crankshaft pulley bolts.
24. Remove the crankshaft pulley.
Page 158 of 2643

1C2 – 38I1.8L DOHC ENGINE MECHANICAL
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
3. Install the timing belt idler pulleys.
4. Install the timing belt idler pulley bolt and nut.
Tighten
Tighten the timing belt idler pulley bolt and nut to 25
NSm (18 lb–ft).
5. Tension the timing belt by turning the timing belt
automatic tensioner hex–key tab counterclockwise
until the pointer is aligned to the indicator.
Tighten
Tighten the timing belt automatic tensioner bolt to 25
NSm (18 lb–ft).
6. Install the front timing belt cover.
7. Install the front timing belt cover bolts.
Tighten
Tighten the front timing belt cover bolts to 6 NSm (53
lb–in).
8. Install the engine mount bracket and retaining bolts.
Tighten
Tighten the engine mount bracket retaining bolts to 55
NSm (41 lb–ft).
9. Remove the engine assembly support fixture
J–28467–B, and the channel X–28467–560.
10. Install the serpentine accessory drive belt. Refer to
Section 6B, Power Steering Pump.
11. Connect the negative battery cable.
INTAKE MANIFOLD
Removal Procedure
1. Remove the fuel pump fuse.
2. Start the engine. After it stalls, crank the engine for
10 seconds to rid the fuel system of fuel pressure.
3. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
4. Disconnect the charcoal canister purge (CCP) and
exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) solenoid from the
intake manifold and loosen the bracket bolt.
5. Drain the engine coolant. Refer to Section 1D, En-
gine Cooling.
6. Disconnect the manifold air temperature sensor
(MAT) connector.
7. Disconnect the air cleaner outlet hose from the
throttle body.
Page 166 of 2643

1C2 – 46I1.8L DOHC ENGINE MECHANICAL
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
7. Install the timing belt automatic tensioner and bolt.
8. Install the camshaft gears. Refer to ”Camshaft
Gears” in this section.
9. Install the timing belt and timing belt cover. Refer to
”Timing Belt” in this section.
10. Connect the negative battery cable.
ENGINE
Removal Procedure
1. Remove the fuel pump fuse.
2. Start the engine. After it stalls, crank the engine for
10 seconds to rid the fuel system of fuel pressure.
3. Remove the hood. Refer to Section 9R, Body Front
End.
4. Drain the engine oil.
5. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
6. Discharge the air conditioning (A/C) system, if
equipped. Refer to Section 7B, Manual Control
Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning Systems.
7. Disconnect the manifold air temperature (MAT)
sensor connector.
8. Remove the air cleaner outlet hose from the throttle
body and air cleaner housing.
9. Disconnect the breather tubes from the camshaft
cover.
10. Remove the right front wheel. Refer to Section 2E,
Tires and Wheels.
11. Remove the right front wheel well splash shield.
Refer to Section 9R, Body Font End.
12. Remove the serpentine accessory drive belt. Refer
to Section 6B, Power Steering Pump.
13. Drain the engine coolant. Refer to Section 1D, En-
gine Cooling.
14. Remove the cooling system radiator and the engine
cooling fans. Refer to Section 1D, Engine Cooling.
15. Disconnect the upper radiator hose from the ther-
mostat housing.
16. Disconnect the power steering return hose from the
power steering pump.
17. Disconnect the power steering pressure hose from
the power steering pump.
18. Disconnect the electrical connector at the direct
ignition system (DIS) coil and the electronic control
module (ECM) ground terminal and at the starter
motor.
Page 167 of 2643

1.8L DOHC ENGINE MECHANICAL 1C2 – 47
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
19. Disconnect the oxygen (O2) sensor connector, if
equipped.
20. Disconnect the idle air control (IAC) valve connec-
tor.
21. Disconnect the throttle position sensor (TPS) con-
nector.
22. Disconnect the engine coolant temperature sensor
(CTS) connector.
23. Disconnect the CTS connector.
24. Disconnect the generator voltage regulator connec-
tor and power lead.
25. Disconnect all of the necessary vacuum lines, in-
cluding the brake booster vacuum hose.
26. Disconnect the fuel return line at the fuel rail.
27. Disconnect the fuel feed line at the fuel rail.
28. Remove the fuel rail and injector channel cover as
an assembly. Refer to Section 1F, Engine Controls.
29. Disconnect the throttle cable from the throttle body
and the intake manifold bracket.
30. Disconnect the coolant hose at the throttle body.
31. Disconnect the heater outlet hose at the coolant
pipe.
32. Disconnect the coolant bypass hose from the cylin-
der head.
33. Disconnect the surge tank coolant hose from the
coolant pipe.
34. Disconnect the lower radiator hose from the coolant
pipe.
35. Disconnect the starter solenoid ”S” terminal wire
and power lead.
36. Remove the A/C compressor. Refer to Section 7B,
Manual Control Heating, Ventilation, and Air Condi-
tioning Systems.
37. Remove the exhaust flex pipe retaining nuts from
the exhaust manifold studs.
38. Remove the exhaust flex pipe retaining nuts from
the catalytic converter or the connecting pipe.
39. Remove the exhaust flex pipe.
Page 198 of 2643
ENGINE COOLING 1D – 3
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSIS
THERMOSTAT TEST
1. Remove the thermostat from the vehicle. Refer to
”Thermostat” in this section.
2. Make sure the valve spring is tight when the ther-
mostat is fully closed. If the spring is not tight, re-
place the thermostat.
3. Suspend the thermostat and a thermometer in a
pan of 50/50 mixture of ethylene glycol and water.
Do not let the thermostat or the thermometer rest
on the bottom of the pan because the uneven con-
centration of heat on the bottom could result in in-
accurate temperature measurements.
4. Heat the pan on a burner.
5. Use the thermometer to measure the temperature
of the heated solution.
6. The thermostat should begin to open at 87°C
(189°F) and it should be fully open at 102°C
(216°F). If it does not open at these temperatures,
replace the thermostat.
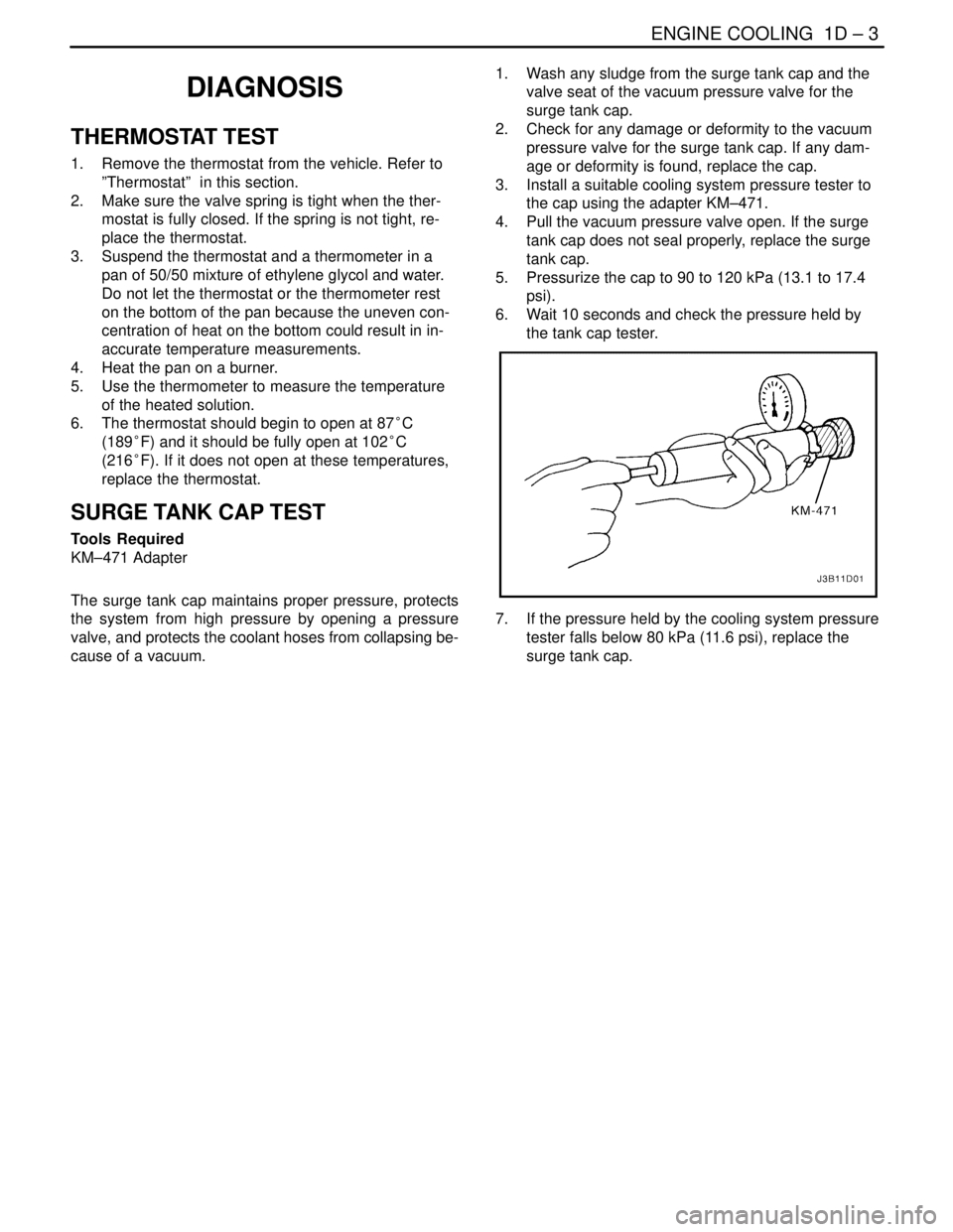
SURGE TANK CAP TEST
Tools Required
KM–471 Adapter
The surge tank cap maintains proper pressure, protects
the system from high pressure by opening a pressure
valve, and protects the coolant hoses from collapsing be-
cause of a vacuum.1. Wash any sludge from the surge tank cap and the
valve seat of the vacuum pressure valve for the
surge tank cap.
2. Check for any damage or deformity to the vacuum
pressure valve for the surge tank cap. If any dam-
age or deformity is found, replace the cap.
3. Install a suitable cooling system pressure tester to
the cap using the adapter KM–471.
4. Pull the vacuum pressure valve open. If the surge
tank cap does not seal properly, replace the surge
tank cap.
5. Pressurize the cap to 90 to 120 kPa (13.1 to 17.4
psi).
6. Wait 10 seconds and check the pressure held by
the tank cap tester.
7. If the pressure held by the cooling system pressure
tester falls below 80 kPa (11.6 psi), replace the
surge tank cap.
Page 199 of 2643
1D – 4IENGINE COOLING
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
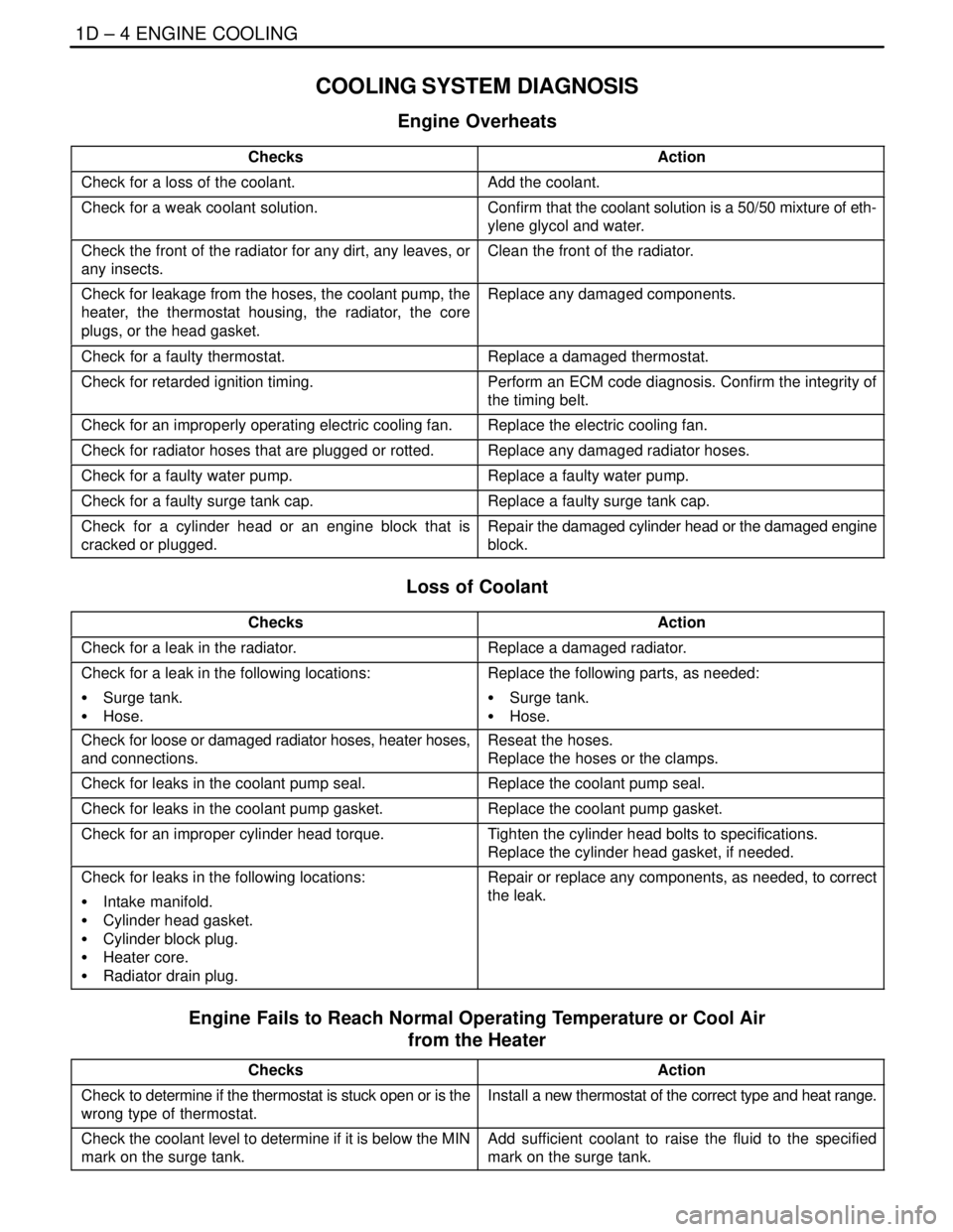
COOLING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
Engine Overheats
ChecksAction
Check for a loss of the coolant.Add the coolant.
Check for a weak coolant solution.Confirm that the coolant solution is a 50/50 mixture of eth-
ylene glycol and water.
Check the front of the radiator for any dirt, any leaves, or
any insects.Clean the front of the radiator.
Check for leakage from the hoses, the coolant pump, the
heater, the thermostat housing, the radiator, the core
plugs, or the head gasket.Replace any damaged components.
Check for a faulty thermostat.Replace a damaged thermostat.
Check for retarded ignition timing.Perform an ECM code diagnosis. Confirm the integrity of
the timing belt.
Check for an improperly operating electric cooling fan.Replace the electric cooling fan.
Check for radiator hoses that are plugged or rotted.Replace any damaged radiator hoses.
Check for a faulty water pump.Replace a faulty water pump.
Check for a faulty surge tank cap.Replace a faulty surge tank cap.
Check for a cylinder head or an engine block that is
cracked or plugged.Repair the damaged cylinder head or the damaged engine
block.
Loss of Coolant
ChecksAction
Check for a leak in the radiator.Replace a damaged radiator.
Check for a leak in the following locations:
S Surge tank.
S Hose.Replace the following parts, as needed:
S Surge tank.
S Hose.
Check for loose or damaged radiator hoses, heater hoses,
and connections.Reseat the hoses.
Replace the hoses or the clamps.
Check for leaks in the coolant pump seal.Replace the coolant pump seal.
Check for leaks in the coolant pump gasket.Replace the coolant pump gasket.
Check for an improper cylinder head torque.Tighten the cylinder head bolts to specifications.
Replace the cylinder head gasket, if needed.
Check for leaks in the following locations:
S Intake manifold.
S Cylinder head gasket.
S Cylinder block plug.
S Heater core.
S Radiator drain plug.Repair or replace any components, as needed, to correct
the leak.
Engine Fails to Reach Normal Operating Temperature or Cool Air
from the Heater
ChecksAction
Check to determine if the thermostat is stuck open or is the
wrong type of thermostat.Install a new thermostat of the correct type and heat range.
Check the coolant level to determine if it is below the MIN
mark on the surge tank.Add sufficient coolant to raise the fluid to the specified
mark on the surge tank.
Page 213 of 2643

1D – 18IENGINE COOLING
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
AND SYSTEM OPERATION
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The cooling system maintains the engine temperature at
an efficient level during all engine operating conditions.
When the engine is cold, the cooling system cools the en-
gine slowly or not at all. This slow cooling of the engine al-
lows the engine to warm up quickly.
The cooling system includes a radiator and recovery sub-
system, cooling fans, a thermostat and housing, a coolant
pump, and a coolant pump drive belt. The timing belt
drives the coolant pump.
All components must function properly in order for the
cooling system to operate. The coolant pump draws the
coolant from the radiator. The coolant then circulates
through water jackets in the engine block, the intake man-
ifold, and the cylinder head. When the coolant reaches the
operating temperature of the thermostat, the thermostat
opens. The coolant then goes back to the radiator where
it cools.
This system directs some coolant through the hoses to the
heater core. This provides for heating and defrosting. The
surge tank is connected to the radiator to recover the cool-
ant displaced by expansion from the high temperatures.
The surge tank maintains the correct coolant level.
The cooling system for this vehicle has no radiator cap or
filler neck. The coolant is added to the cooling system
through the surge tank.
RADIATOR
This vehicle has a lightweight tube–and–fin aluminum ra-
diator. Plastic tanks are mounted on the right and the left
sides of the radiator core.
On vehicles equipped with automatic transaxles, the
transaxle fluid cooler lines run through the left radiator
tank. A radiator drain cock is on this radiator.
To drain the cooling system, open the drain cock.
SURGE TANK
The surge tank is a transparent plastic reservoir, similar to
the windshield washer reservoir.
The surge tank is connected to the radiator by a hose and
to the engine cooling system by another hose. As the ve-
hicle is driven, the engine coolant heats and expands. The
portion of the engine coolant displaced by this expansion
flows from the radiator and the engine into the surge tank.
The air trapped in the radiator and the engine is degassed
into the surge tank.When the engine stops, the engine coolant cools and con-
tracts. The displaced engine coolant is then drawn back
into the radiator and the engine. This keeps the radiator
filled with the coolant to the desired level at all times and
increases the cooling efficiency.
Maintain the coolant level between the MIN and the MAX
marks on the surge tank when the system is cold.
WATER PUMP
The belt–driven centrifugal water pump consists of an im-
peller, a drive shaft, and a belt pulley. The water pump is
mounted on the front of the transverse–mounted engine,
and is driven by the timing belt.
The impeller is supported by a completely sealed bearing.
The water pump is serviced as an assembly and, there-
fore, cannot be disassembled.
THERMOSTAT
A wax pellet–type thermostat controls the flow of the en-
gine coolant through the engine cooling system. The ther-
mostat is mounted in the thermostat housing to the front
of the cylinder head.
The thermostat stops the flow of the engine coolant from
the engine to the radiator in order to provide faster warm–
up, and to regulate the coolant temperature. The thermo-
stat remains closed while the engine coolant is cold, pre-
venting circulation of the engine coolant through the
radiator. At this point, the engine coolant is allowed to cir-
culate only throughout the heater core to warm it quickly
and evenly.
As the engine warms, the thermostat opens. This allows
the engine coolant to flow through the radiator, where the
heat is dissipated through the radiator. This opening and
closing of the thermostat permits enough engine coolant
to enter the radiator to keep the engine within proper en-
gine temperature operating limits.
The wax pellet in the thermostat is hermetically sealed in
a metal case. The wax element of the thermostat expands
when it is heated and contracts when it is cooled.
As the vehicle is driven and the engine warms, the engine
coolant temperature increases. When the engine coolant
reaches a specified temperature, the wax pellet element
in the thermostat expands and exerts pressure against the
metal case, forcing the valve open. This allows the engine
coolant to flow through the engine cooling system and cool
the engine.
As the wax pellet cools, the contraction allows a spring to
close the valve.
The thermostat begins to open at 87°C (189°F) and is fully
open at 102°C (216°F). The thermostat closes at 86°C
(187°F).
Page 214 of 2643

ENGINE COOLING 1D – 19
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
ELECTRIC COOLING FAN
CAUTION : Keep hands, tools, and clothing away
from the engine cooling fans to help prevent personal
injury. This fan is electric and can turn ON whether or
not the engine is running.
CAUTION : If a fan blade is bent or damaged in any
way, no attempt should be made to repair or reuse the
damaged part. A bent or damaged fan assembly
should always be replaced with a new one. Failure to
do so can result in personal injury.
The cooling fans are mounted behind the radiator in the
engine compartment. The electric cooling fans increase
the flow of air across the radiator fins and across the con-
denser on air condition (A/C)–equipped vehicles. This
helps to speed cooling when the vehicle is at idle or moving
at low speeds.
1.4L DOHC engine fan size is 340mm (13.4 in.) and
1.6L/1.8L DOHC engine main fan size is 300 mm (11.8
inches) in diameter with five blades to aid the air flow
through the radiator and the condenser. An electric motor
attached to the radiator support drives the fan.
A/C models have two fans – the main fan and the auxiliary
fan. The auxiliary fan is 300 mm (11.8 inches) in diameter.
Non–A/C models have only the main fan.
A/C OFF or Non–A/C Model (1.4L/1.6L)
S The cooling fans are actuated by the electronic
control module (ECM) using a low–speed cooling
fan relay and a high–speed cooling fan relay. On
A/C–equipped vehicles, a series/parallel cooling fan
relay is also used.
S The ECM will turn the cooling fans on at low speed
when the coolant temperature reaches 97.5°C
(207.5°F) and the cooling fans off at 95.25°C
(203.4°F).
A/C OFF or Non–A/C Model (1.8L)
S The cooling fans are actuated by the electronic
control module (ECM) using a low–speed cooling
fan relay and a high–speed cooling fan relay. On
A/C–equipped vehicles, a series/parallel cooling fan
relay is also used.
S The ECM will turn the cooling fans on at low speed
when the coolant temperature reaches 93°C
(199°F) and the cooling fans off at 90°C (194°F).
A/C ON (1.4L/1.6L)
S The ECM will turn the cooling fans on at low speed
when the A/C system is on. The ECM will change
to high speed when the coolant temperature reach-
es 101.25°C (214°F) or the high side A/C pressure
reaches 1859 kPa (270 psi).
S The cooling fans will return to low speed when the
coolant temperature reaches 99°C (210°F) and the
high side A/C pressure reaches 1449 kPa (210 psi).
A/C ON (1.8L)
S The ECM will turn the cooling fans on at low speed
when the A/C system is on. The ECM will change
to high speed when the coolant temperature reach-
es 97°C (207°F) or the high side A/C pressure
reaches 1859 kPa (270 psi).
S The cooling fans will return to low speed when the
coolant temperature reaches 94°C (201°F) and the
high side A/C pressure reaches 1449 kPa (210 psi).
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER
The vehicle is designed to accept an engine block heater
that helps to warm the engine and to improve starting in
cold weather. It also can help to reduce fuel consumption
while a cold engine warms up.
The engine block heater is located under the intake man-
ifold and uses an existing expansion plug for installation.