2004 DAEWOO LACETTI Rod
[x] Cancel search: RodPage 229 of 2643

ENGINE ELECTRICAL 1E – 15
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
4. Position the starter electrical wire on the solenoid
terminals and the ground wire on the lower stud.
5. Install the starter solenoid nuts and the ground wire
nut.
Tighten
Tighten the starter solenoid terminal–to–battery cable
terminal nut to 5.5 NSm (49 lb–in), and the starter sole-
noid terminal–to–ignition solenoid terminal nut to 5.5
NSm (49 lb–in).
Tighten the starter lower mounting stud ground wire
nut to 12 NSm (106 lb–in).
BATTERY AND BATTERY TRAY
Removal Procedure
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable and then dis-
connect the positive battery cable.
2. Remove the nuts from the battery rods that fasten
the battery hold–down bar clamp.
3. Check the battery carrier tray for obvious cracks or
damage. Unclip the lead to the negative battery
cable from the side of the battery tray (if applica-
ble). Detach the carrier tray if necessary by remov-
ing the upper battery carrier tray bolts, and the side
bolt that connects the hydraulic clutch hose bracket
to the battery carrier tray (if applicable).
4. Remove the lower battery tray bolts.
Installation Procedure
1. Install the battery carrier by fastening the carrier
tray upper, lower, and side bolts.
Tighten
Tighten the battery carrier tray upper, lower and side
bolts (if applicable) to 20 NSm (15 lb–ft).
2. Push in the clip of the negative battery lead to the
hole in the side of the battery tray (if applicable and
as shown).
Page 230 of 2643

1E – 16IENGINE ELECTRICAL
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
3. Install the battery into the tray.
4. Fasten the bar clamp to the battery by loosely at-
taching the battery rods from the battery tray cut-
outs through the bar clamp holes, and loosely tight-
ening the nuts.
Tighten
Tighten the battery retainer clamp–to–battery rod
nuts to 5 NSm (44 lb–in).
5. Connect the negative and the positive battery
cables.
Tighten
Tighten the battery cable nuts to 5 NSm (44 lb–in).
Page 244 of 2643

1E – 30IENGINE ELECTRICAL
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
AND SYSTEM OPERATION
BATTERY
The sealed battery is standard on all cars. There are no
vent plugs in the cover. The battery is completely sealed,
except for two small vent holes in the sides. These vent
holes allow the small amount of gas produced in the bat-
tery to escape. The battery has the following advantages
over conventional batteries:
S No water addition for the life of the battery.
S Overcharge protection. If too much voltage is ap-
plied to the battery, it will not accept as much cur-
rent as a conventional battery. In a conventional
battery, the excess voltage will still try to charge the
battery, leading to gassing, which causes liquid
loss.
S Not as liable to self–discharge as compared to a
conventional battery. This is particularly important
when a battery is left standing for long periods of
time.
S More power available in a lighter and smaller case.
The battery has three major functions in the electrical sys-
tem. First, the battery provides a source of energy for
cranking the engine. Second, the battery acts as a voltage
stabilizer for the electrical system. Finally, the battery can,
for a limited time, provide energy when the electrical de-
mand exceeds the output of the generator.
RATINGS
A battery has two ratings: (1) a reserve capacity rating
designated at 27°C (80°F), which is the time a fully
charged battery will provide 25 amperes current flow at or
above 10.5 volts; (2) a cold cranking amp rating deter-
mined under testing at –18°C (0°F), which indicates the
cranking load capacity.
RESERVE CAPACITY
The reserve capacity is the maximum length of time it is
possible to travel at night with the minimum electrical load
and no generator output. Expressed in minutes, Reserve
Capacity (or RC rating) is the time required for a fully
charged battery, at a temperature of 27°C (80°F) and be-
ing discharged at a current of 25 amperes, to reach a ter-
minal voltage of 10.5 volts.
COLD CRANKING AMPERAGE
The cold cranking amperage test is expressed at a battery
temperature of –18°C (0°F). The current rating is the mini-
mum amperage, which must be maintained by the battery
for 30 seconds at the specified temperature, while meeting
a minimum voltage requirement of 7.2 volts. This rating is
a measure of cold cranking capacity.The battery is not designed to last indefinitely. However,
with proper care, the battery will provide many years of
service.
If the battery tests well, but fails to perform satisfactorily
in service for no apparent reason, the following factors
may point to the cause of the trouble:
S Vehicle accessories are left on overnight.
S Slow average driving speeds are used for short pe-
riods.
S The vehicle’s electrical load is more than the gener-
ator output, particularly with the addition of after-
market equipment.
S Defects in the charging system, such as electrical
shorts, a slipping generator belt, a faulty generator,
or a faulty voltage regulator.
S Battery abuse, including failure to keep the battery
cable terminals clean and tight, or a loose battery
hold–down clamp.
S Mechanical problems in the electrical system, such
as shorted or pinched wires.
BUILT – IN HYDROMETER
The sealed battery has a built–in, temperature–compen-
sated hydrometer in the top of the battery. This hydrome-
ter is to be used with the following diagnostic procedure:
1. When observing the hydrometer, make sure that
the battery has a clean top.
2. Under normal operation, two indications can be ob-
served:
S GREEN DOT VISIBLE – Any green appearance
is interpreted as a ”green dot,” meaning the bat-
tery is ready for testing.
S DARK GREEN DOT IS NOT VISIBLE – If there
is a cranking complaint, the battery should be
tested. The charging and electrical systems
should also be checked at this time.
3. Occasionally, a third condition may appear:
S CLEAR OR BRIGHT YELLOW – This means
the fluid level is below the bottom of the hydrom-
eter. This may have been caused by excessive
or prolonged charging, a broken case, excessive
tipping, or normal battery wear. Finding a battery
in this condition may indicate high charging by a
faulty charging system. Therefore, the charging
and the electrical systems may need to be
checked if a cranking complaint exists. If the
cranking complaint is caused by the battery, re-
place the battery.
CHARGING PROCEDURE
1. Batteries with the green dot showing do not require
charging unless they have just been discharged
(such as in cranking a vehicle).
2. When charging sealed–terminal batteries out of the
vehicle, install the adapter kit. Make sure all the
charger connections are clean and tight. For best
results, batteries should be charged while the elec-
Page 257 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 11
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
FUEL SYSTEM SPECIFICATIONS
Gasoline
All engines are designed to use unleaded fuel only. Un-
leaded fuel must be used for proper emission control sys-
tem operation. Its use will also minimize spark plug fouling
and extend engine oil life. Using leaded fuel can damage
the emission warranty coverage. The fuel should meet
specification ASTM D4814 for the U.S. or CGSB 3.5 M93
for Canada. All engines are designed to use unleaded fuel
with a minimum U(R+M)/2e (pump) octane number of 87,
where R=research octane number, and M=motor octane
number.
Ethanol
You may use fuel containing ethanol (ethyl alcohol) orgrain alcohol providing that there is no more than 10 per-
cent ethyl alcohol by volume.
Methanol
Do not use fuels containing methanol. Methanol can cor-
rode metal parts and cause damage to plastic and rubber
parts in the fuel system.
Methyl Tertiary–Butyl Ether (MTBE)
You may use fuel containing Methyl Tertiary–Butyl Ether
(MTBE) providing there is no more than 15 percent MTBE
by volume.
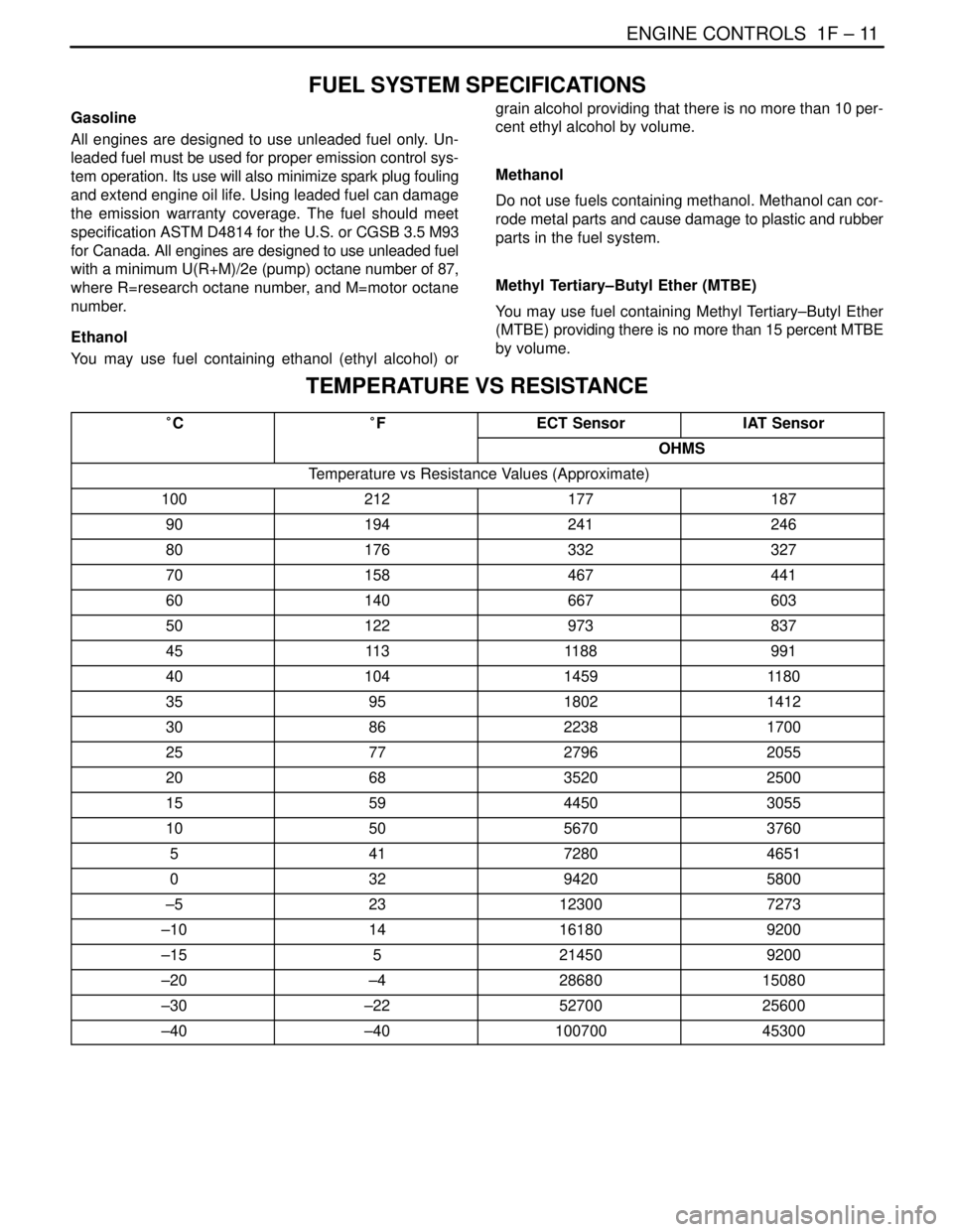
TEMPERATURE VS RESISTANCE
°C°FECT SensorIAT Sensor
OHMS
Temperature vs Resistance Values (Approximate)
100212177187
90194241246
80176332327
70158467441
60140667603
50122973837
4511 31188991
4010414591180
359518021412
308622381700
257727962055
206835202500
155944503055
105056703760
54172804651
03294205800
–523123007273
–1014161809200
–155214509200
–20–42868015080
–30–225270025600
–40–4010070045300
Page 331 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 85
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
IGNITION SYSTEM CHECK (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
Circuit Description
The Electronic Ignition (EI) system uses a waste spark
method of spark distribution. In this type of EI system, the
Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor is mounted to the oil
pump near a slotted wheel that is a part of the crankshaft
pulley. The CKP sensor sends reference pulses to the en-
gine control module (ECM). The ECM then triggers the EI
system ignition coil. Once the ECM triggers the EI system
ignition coil, both of the connected spark plugs fire at the
same time. One cylinder is on its compression stroke at
the same time that the other is on the exhaust stroke, re-
sulting in lower energy needed to fire the spark plug in the
cylinder on its exhaust stroke.
This leaves the remainder of the high voltage to be used
to fire the spark plug in the cylinder on its compression
stroke. Since the CKP sensor is in a fixed position, timing
adjustments are not possible or needed.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostictable.
2. It is important to check for the presence of spark to
all of the cylinders to isolate the problem to either
EI system ignition coil inputs or outputs.
5. In checking the ECM outputs for the electronic
spark timing signal, it recommended to use an os-
cilloscope to view the varying voltage signals. In
measuring these outputs with a voltmeter, intermit-
tent errors may occur that cannot be seen by a volt-
meter.
6. After confirming ECM inputs for the electronic spark
timing to the EI system ignition coil are OK, it can
be determined that a faulty EI system ignition coil is
at fault.
11. After confirming proper CKP sensor inputs to the
ECM and no wiring problems present, it can be de-
termined that the ECM is at fault.
24. This step, along with step 25, checks for battery
voltage and a ground to the EI system ignition coil.
Ignition System Check (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
CAUTION : Use only electrically insulated pliers when handling ignition wires with the engine running to prevent
an electrical shock.
Step
ActionValue(s)YesNo
11. Remove the spark plugs.
2. Inspect for wet spark plugs, cracks, wear, im-
proper gap, burned electrodes, or heavy de-
posits.
3. Replace the spark plugs as needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OKGo to Step 2
2Check for the presence of spark from all of the igni-
tion wires while cranking the engine.
Is spark present from all of the ignition wires?–System OKGo to Step 3
31. Measure the resistance of the ignition wires.
2. Replace any ignition wire(s) with a resistance
above the value specified.
3. Check for the presence of spark from all of the
ignition wires.
Is spark present from all of the ignition wires?30,000 WSystem OKGo to Step 4
4Is spark present from at least one of the ignition
wires, but not all of the ignition wires?–Go to Step 5Go to Step 12
51. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the Electronic Ignition (EI) system
ignition coil connector.
3. While cranking the engine, measure the volt-
age at the EI system ignition coil connector
terminal 1.
Does the voltage fluctuate within the values speci-
fied?0.2–2.0 vGo to Step 6Go to Step 7
Page 335 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 89
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Ignition System Check (1.8L DOHC)
CAUTION : Use only electrically insulated pliers when handling ignition wires with the engine running to prevent
an electrical shock.
Step
ActionValue(s)YesNo
11. Remove the spark plugs.
2. Inspect for wet spark plugs, cracks, wear, im-
proper gap, burned electrodes, or heavy de-
posits.
3. Replace the spark plugs as needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OKGo to Step 2
2Check for the presence of spark from all of the igni-
tion wires while cranking the engine.
Is spark present from all of the ignition wires?–System OKGo to Step 3
31. Measure the resistance of the ignition wires.
2. Replace any ignition wire(s) with a resistance
above the value specified.
3. Check for the presence of spark from all of the
ignition wires.
Is spark present from all of the ignition wires?30,000 WSystem OKGo to Step 4
4Is spark present from at least one of the ignition
wires, but not all of the ignition wires?–Go to Step 5Go to Step 12
51. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the Electronic Ignition (EI) system
ignition coil connector.
3. While cranking the engine, measure the volt-
age at the EI system ignition coil connector
terminal 1.
Does the voltage fluctuate within the values speci-
fied?0.2–2.0 vGo to Step 6Go to Step 7
6While cranking the engine, measure the voltage at
the EI system ignition coil connector terminal 3
Does the voltage fluctuate within the values speci-
fied?0.2–2.0 vGo to Step 10Go to Step 8
7Check for an open in the wire from the EI system
ignition coil connector terminal 1 to the engine con-
trol module (ECM) connector terminal M35 or M51.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 9Go to Step 11
8Check for an open in the wire from the EI system
ignition coil connector terminal 3 to the ECM connec-
tor terminal M1 or M33.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 9Go to Step 11
91. Repair the wiring as needed.
2. Connect the EI system ignition coil connector.
3. Check for the presence of spark from all of the
ignition wires.
Is spark present from all of the ignition wires?–System OK–
Page 383 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 137
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0131
FRONT HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR LOW VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) supplies a voltage of
about 450mm volts between the ECM terminals 44 and 13.
The oxygen (O2) sensor varies the voltage within a range
of about 1volt if the exhaust is rich, down to about 100mm
volts if the exhaust is lean. The O2 sensor is like an open
circuit and produces no voltage when it is below
360°C(600°F). An open O2 sensor circuit or a cold O2
sensor causes ”open loop” operation.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
(Case A)
S The engine controls system is in closed loop.
S Engine speed is less than 6,000rpm.
S The oxygen sensor voltage is below 0.07V for at
least 40seconds.
S DTCs P0107, P0108, P0117, P0118, P0122,
P0123, P0335, P0336, P0341, P0342, P0400,
P0404, P0405, P0406 are NOT SET.
(Case B)
S The engine controls system is in closed loop.
S Engine speed is less than 6,000rpm.
S The oxygen sensor voltage is between 0.352 and
0.499 at least 10 seconds.Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
S The coolant fan turns ON.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
Normal scan tool voltage varies between 0.1volts and 0.9
volts while in closed loop.
Inspect the oxygen (O2) sensor wire. The O2 sensor may
be positioned incorrectly and contacting the exhaust man-
ifold.
Page 386 of 2643

1F – 140IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0132
FRONT HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR HIGH VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) supplies a voltage of
about 450mm volts between the ECM terminals 44 and 13.
The oxygen (O2) sensor varies the voltage within a range
of about 1volt if the exhaust is rich, down to about 100mm
volts if the exhaust is lean. The O2 sensor is like an open
circuit and produces no voltage when it is below
360°C(600°F). An open O2 sensor circuit or a cold O2
sensor causes ”open loop” operation.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S The oxygen sensor voltage is more than 1.2V.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
S The coolant fan turns ON.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTCS The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for 10 sec-
onds.
Diagnostic Aids
Normal scan tool voltage varies between 0.1volts and 0.9
volts while in closed loop.
Inspect the oxygen (O2) sensor wire. The O2 sensor may
be positioned incorrectly and contacting the exhaust man-
ifold.
Check for an intermittent ground in the wire between the
O2 sensor and the engine control module.
Perform an injector 2alance test to determine if a restricted
fuel injector may be causing the lean condition.
Vacuum of crankcase leaks will cause a lean running con-
dition.
An exhaust manifold gasket leak of a cracked exhaust
manifold may cause outside air to be pulled into the ex-
haust and past the sensor.