2004 CHRYSLER VOYAGER transmission fluid
[x] Cancel search: transmission fluidPage 1713 of 2585

41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
DESCRIPTION........................117
OPERATION..........................119
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - 41TE
TRANSAXLE GENERAL DIAGNOSIS......119
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD TEST . . 119
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
PRESSURE TESTS...................120
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CLUTCH AIR
PRESSURE TESTS...................122
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TORQUE
CONVERTER HOUSING FLUID LEAKAGE . . 123
REMOVAL............................124
DISASSEMBLY........................125
ASSEMBLY...........................144
INSTALLATION........................166
SCHEMATICS AND DIAGRAMS
41TE TRANSAXLE HYDRAULIC
SCHEMATICS.......................169
SPECIFICATIONS - 41TE TRANSAXLE......181
SPECIAL TOOLS
41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE.........183
ACCUMULATOR
DESCRIPTION........................188
OPERATION..........................189
AUTOSTICK SWITCH
DESCRIPTION........................189
OPERATION..........................189
DRIVING CLUTCHES
DESCRIPTION........................190
OPERATION..........................190
FINAL DRIVE
DISASSEMBLY........................190
ASSEMBLY...........................195
ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT - DIFFERENTIAL BEARING
PRELOAD..........................199
FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE
FLUID LEVEL AND CONDITION CHECK . . . 201
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID AND
FILTER SERVICE.....................203
GEAR SHIFT CABLE
REMOVAL............................204
INSTALLATION........................205
ADJUSTMENTS
GEARSHIFT CABLE ADJUSTMENT.......206HOLDING CLUTCHES
DESCRIPTION........................207
OPERATION..........................207
INPUT CLUTCH ASSEMBLY
DISASSEMBLY........................208
ASSEMBLY...........................216
OIL PUMP
DESCRIPTION........................230
OPERATION..........................230
DISASSEMBLY........................230
ASSEMBLY...........................232
PLANETARY GEARTRAIN
DESCRIPTION........................232
OPERATION..........................232
SEAL - OIL PUMP
REMOVAL............................232
INSTALLATION........................233
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION........................233
OPERATION..........................233
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE/
TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK
SOLENOID..........................235
REMOVAL............................235
INSTALLATION........................236
SOLENOID/PRESSURE SWITCH ASSY
DESCRIPTION........................237
OPERATION..........................237
REMOVAL............................238
INSTALLATION........................239
SPEED SENSOR - INPUT
DESCRIPTION........................239
OPERATION..........................240
REMOVAL............................240
INSTALLATION........................240
SPEED SENSOR - OUTPUT
DESCRIPTION........................241
OPERATION..........................241
REMOVAL............................241
INSTALLATION........................242
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION........................242
OPERATION..........................245
REMOVAL............................247
INSTALLATION........................247
TRANSMISSION CONTROL RELAY
DESCRIPTION........................247
OPERATION..........................248
21 - 116 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
Page 1714 of 2585

TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION........................248
OPERATION..........................248
REMOVAL............................249
INSTALLATION........................249
TRD LINK
DESCRIPTION........................249
OPERATION..........................249VALVE BODY
DESCRIPTION........................250
OPERATION..........................250
REMOVAL............................251
DISASSEMBLY........................252
ASSEMBLY...........................257
INSTALLATION........................262
41TE AUTOMATIC
TRANSAXLE
DESCRIPTION
The 41TE (Fig. 1) is a four-speed transaxle that is
a conventional hydraulic/mechanical assembly with
an integral differential, and is controlled with adap-
tive electronic controls and monitors. The hydraulic
system of the transaxle consists of the transaxle
fluid, fluid passages, hydraulic valves, and various
line pressure control components. An input clutch
assembly which houses the underdrive, overdrive,
and reverse clutches is used. It also utilizes separate
holding clutches: 2nd/4th gear and Low/Reverse. The
primary mechanical components of the transaxle con-
sist of the following:
²Three multiple disc input clutches
²Two multiple disc holding clutches
²Four hydraulic accumulators
²Two planetary gear sets
²Hydraulic oil pump
²Valve body
²Solenoid/Pressure switch assembly
²Integral differential assemblyControl of the transaxle is accomplished by fully
adaptive electronics. Optimum shift scheduling is
accomplished through continuous real-time sensor
feedback information provided to the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) or Transmission Control Mod-
ule (TCM).
The PCM/TCM is the heart of the electronic control
system and relies on information from various direct
and indirect inputs (sensors, switches, etc.) to deter-
mine driver demand and vehicle operating condi-
tions. With this information, the PCM/TCM can
calculate and perform timely and quality shifts
through various output or control devices (solenoid
pack, transmission control relay, etc.).
The PCM/TCM also performs certain self-diagnos-
tic functions and provides comprehensive information
(sensor data, DTC's, etc.) which is helpful in proper
diagnosis and repair. This information can be viewed
with the DRB scan tool.
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 117
Page 1716 of 2585
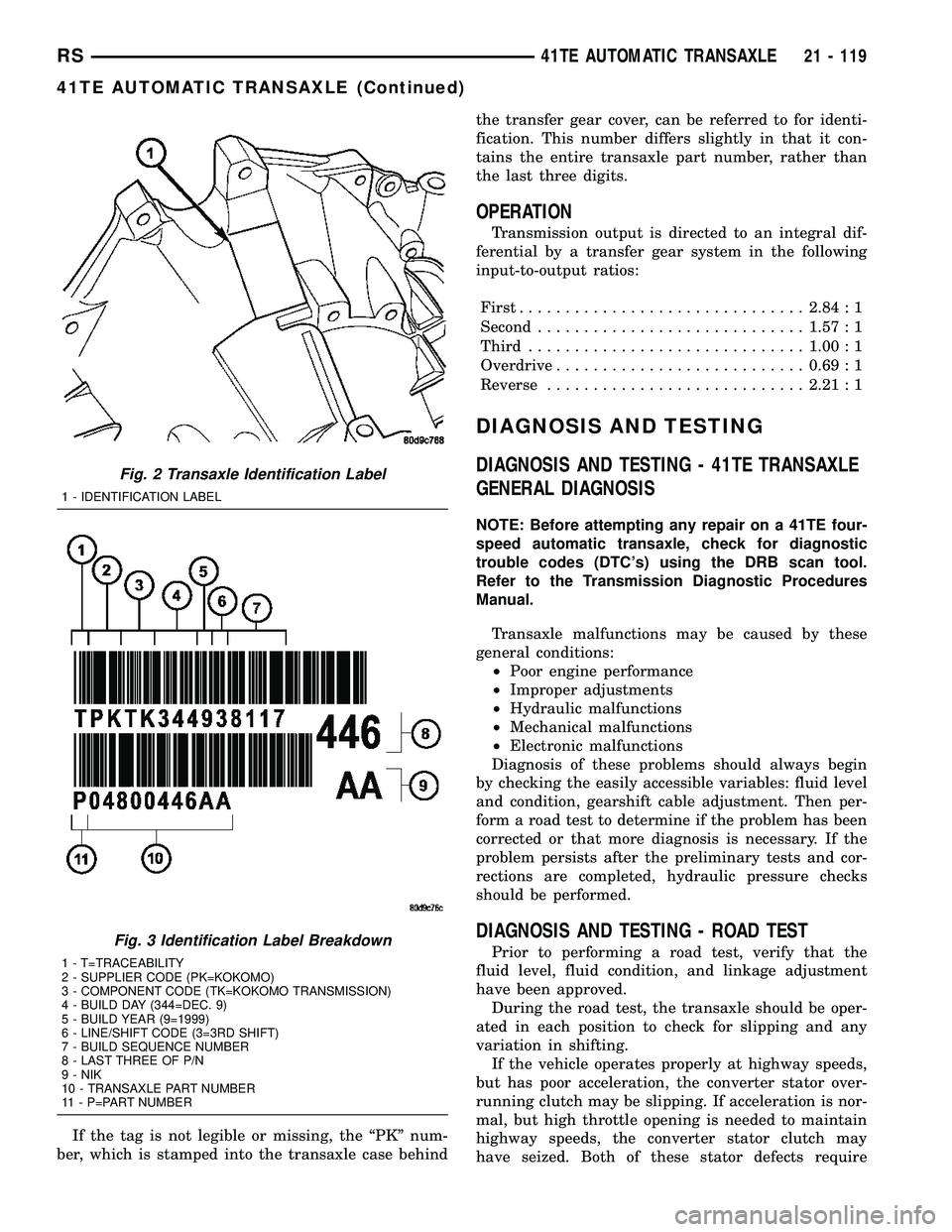
If the tag is not legible or missing, the ªPKº num-
ber, which is stamped into the transaxle case behindthe transfer gear cover, can be referred to for identi-
fication. This number differs slightly in that it con-
tains the entire transaxle part number, rather than
the last three digits.
OPERATION
Transmission output is directed to an integral dif-
ferential by a transfer gear system in the following
input-to-output ratios:
First...............................2.84 : 1
Second.............................1.57 : 1
Third..............................1.00 : 1
Overdrive...........................0.69 : 1
Reverse............................2.21 : 1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - 41TE TRANSAXLE
GENERAL DIAGNOSIS
NOTE: Before attempting any repair on a 41TE four-
speed automatic transaxle, check for diagnostic
trouble codes (DTC's) using the DRB scan tool.
Refer to the Transmission Diagnostic Procedures
Manual.
Transaxle malfunctions may be caused by these
general conditions:
²Poor engine performance
²Improper adjustments
²Hydraulic malfunctions
²Mechanical malfunctions
²Electronic malfunctions
Diagnosis of these problems should always begin
by checking the easily accessible variables: fluid level
and condition, gearshift cable adjustment. Then per-
form a road test to determine if the problem has been
corrected or that more diagnosis is necessary. If the
problem persists after the preliminary tests and cor-
rections are completed, hydraulic pressure checks
should be performed.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD TEST
Prior to performing a road test, verify that the
fluid level, fluid condition, and linkage adjustment
have been approved.
During the road test, the transaxle should be oper-
ated in each position to check for slipping and any
variation in shifting.
If the vehicle operates properly at highway speeds,
but has poor acceleration, the converter stator over-
running clutch may be slipping. If acceleration is nor-
mal, but high throttle opening is needed to maintain
highway speeds, the converter stator clutch may
have seized. Both of these stator defects require
Fig. 2 Transaxle Identification Label
1 - IDENTIFICATION LABEL
Fig. 3 Identification Label Breakdown
1 - T=TRACEABILITY
2 - SUPPLIER CODE (PK=KOKOMO)
3 - COMPONENT CODE (TK=KOKOMO TRANSMISSION)
4 - BUILD DAY (344=DEC. 9)
5 - BUILD YEAR (9=1999)
6 - LINE/SHIFT CODE (3=3RD SHIFT)
7 - BUILD SEQUENCE NUMBER
8 - LAST THREE OF P/N
9 - NIK
10 - TRANSAXLE PART NUMBER
11 - P=PART NUMBER
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 119
41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 1720 of 2585
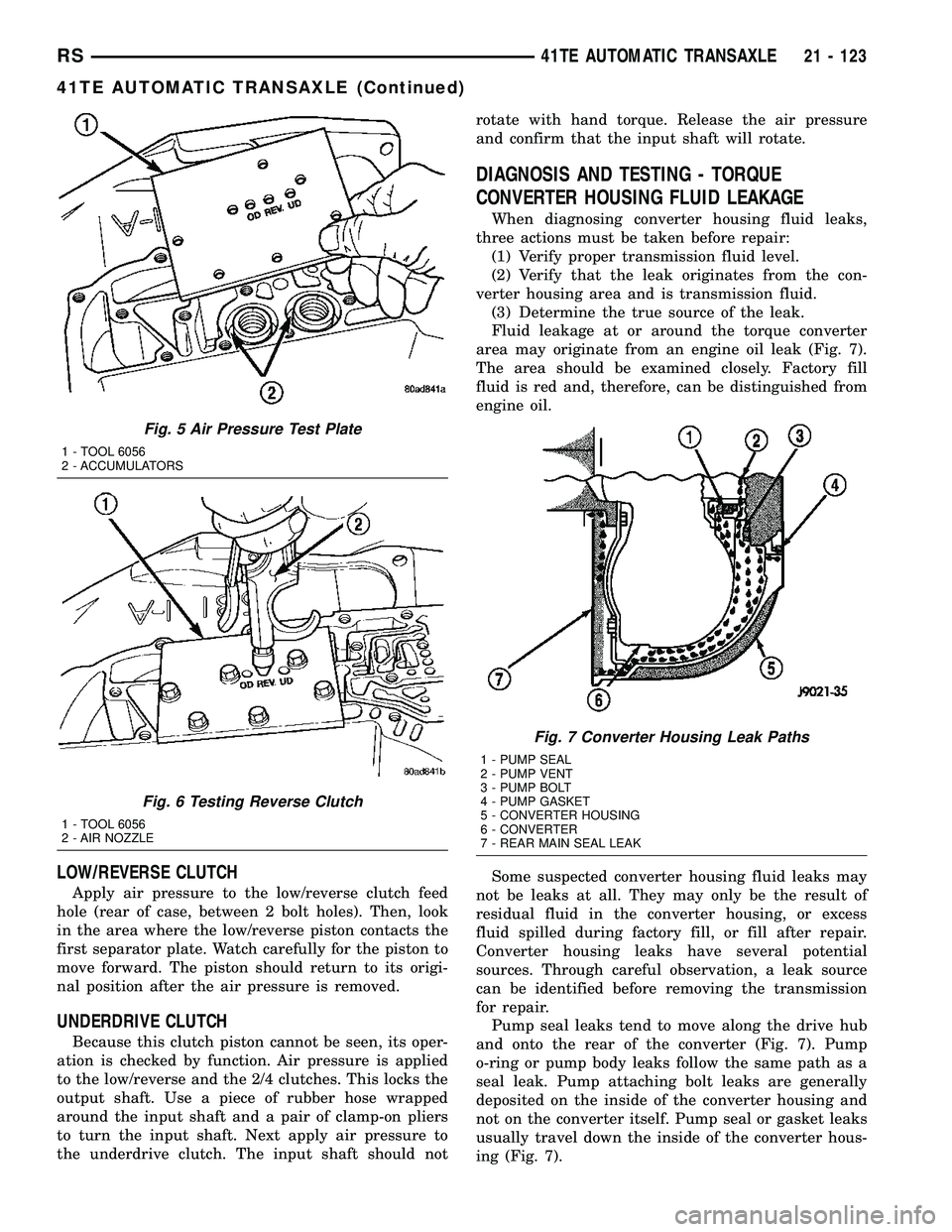
LOW/REVERSE CLUTCH
Apply air pressure to the low/reverse clutch feed
hole (rear of case, between 2 bolt holes). Then, look
in the area where the low/reverse piston contacts the
first separator plate. Watch carefully for the piston to
move forward. The piston should return to its origi-
nal position after the air pressure is removed.
UNDERDRIVE CLUTCH
Because this clutch piston cannot be seen, its oper-
ation is checked by function. Air pressure is applied
to the low/reverse and the 2/4 clutches. This locks the
output shaft. Use a piece of rubber hose wrapped
around the input shaft and a pair of clamp-on pliers
to turn the input shaft. Next apply air pressure to
the underdrive clutch. The input shaft should notrotate with hand torque. Release the air pressure
and confirm that the input shaft will rotate.
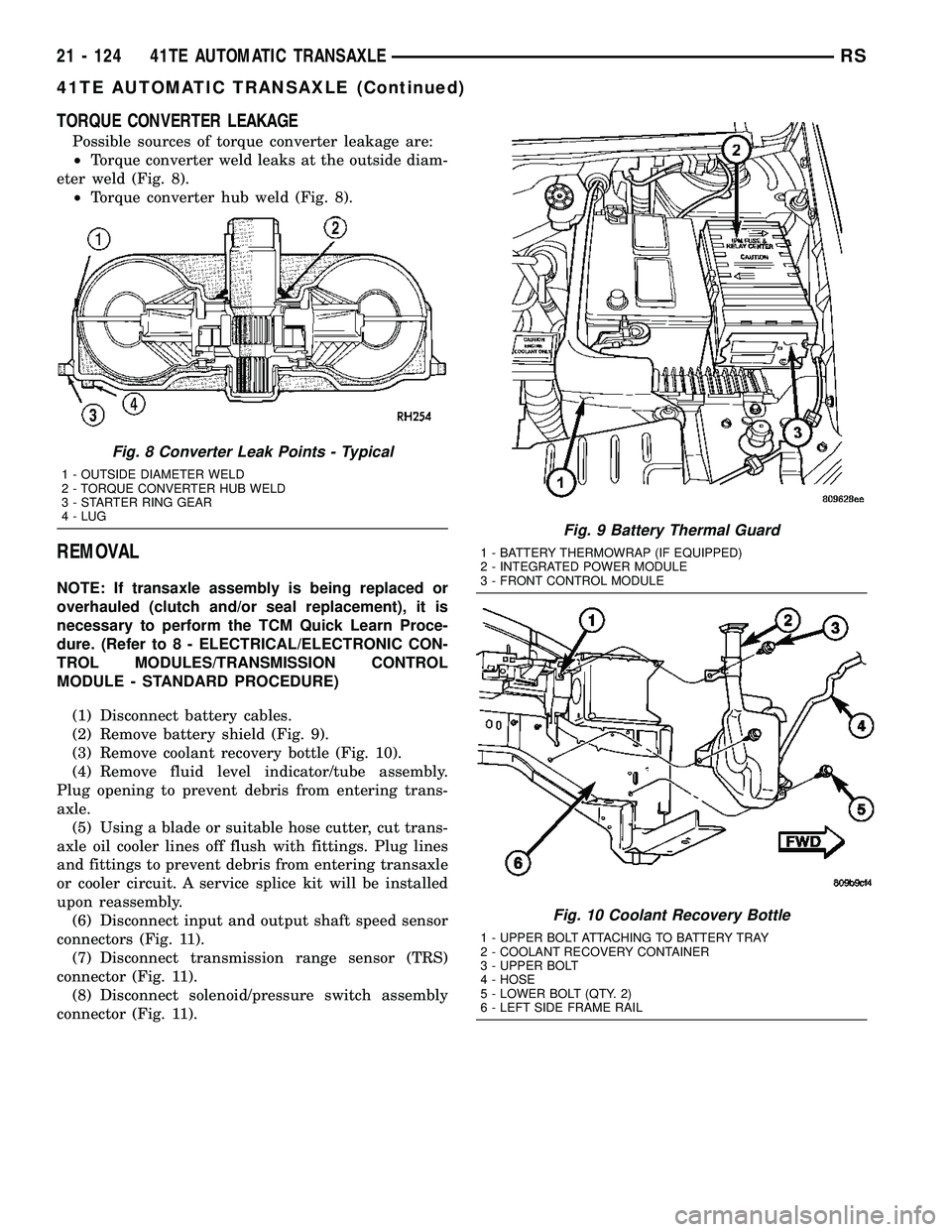
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TORQUE
CONVERTER HOUSING FLUID LEAKAGE
When diagnosing converter housing fluid leaks,
three actions must be taken before repair:
(1) Verify proper transmission fluid level.
(2) Verify that the leak originates from the con-
verter housing area and is transmission fluid.
(3) Determine the true source of the leak.
Fluid leakage at or around the torque converter
area may originate from an engine oil leak (Fig. 7).
The area should be examined closely. Factory fill
fluid is red and, therefore, can be distinguished from
engine oil.
Some suspected converter housing fluid leaks may
not be leaks at all. They may only be the result of
residual fluid in the converter housing, or excess
fluid spilled during factory fill, or fill after repair.
Converter housing leaks have several potential
sources. Through careful observation, a leak source
can be identified before removing the transmission
for repair.
Pump seal leaks tend to move along the drive hub
and onto the rear of the converter (Fig. 7). Pump
o-ring or pump body leaks follow the same path as a
seal leak. Pump attaching bolt leaks are generally
deposited on the inside of the converter housing and
not on the converter itself. Pump seal or gasket leaks
usually travel down the inside of the converter hous-
ing (Fig. 7).
Fig. 5 Air Pressure Test Plate
1 - TOOL 6056
2 - ACCUMULATORS
Fig. 6 Testing Reverse Clutch
1 - TOOL 6056
2 - AIR NOZZLE
Fig. 7 Converter Housing Leak Paths
1 - PUMP SEAL
2 - PUMP VENT
3 - PUMP BOLT
4 - PUMP GASKET
5 - CONVERTER HOUSING
6 - CONVERTER
7 - REAR MAIN SEAL LEAK
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 123
41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 1721 of 2585
TORQUE CONVERTER LEAKAGE
Possible sources of torque converter leakage are:
²Torque converter weld leaks at the outside diam-
eter weld (Fig. 8).
²Torque converter hub weld (Fig. 8).
REMOVAL
NOTE: If transaxle assembly is being replaced or
overhauled (clutch and/or seal replacement), it is
necessary to perform the TCM Quick Learn Proce-
dure. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CON-
TROL MODULES/TRANSMISSION CONTROL
MODULE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(1) Disconnect battery cables.
(2) Remove battery shield (Fig. 9).
(3) Remove coolant recovery bottle (Fig. 10).
(4) Remove fluid level indicator/tube assembly.
Plug opening to prevent debris from entering trans-
axle.
(5) Using a blade or suitable hose cutter, cut trans-
axle oil cooler lines off flush with fittings. Plug lines
and fittings to prevent debris from entering transaxle
or cooler circuit. A service splice kit will be installed
upon reassembly.
(6) Disconnect input and output shaft speed sensor
connectors (Fig. 11).
(7) Disconnect transmission range sensor (TRS)
connector (Fig. 11).
(8) Disconnect solenoid/pressure switch assembly
connector (Fig. 11).
Fig. 8 Converter Leak Points - Typical
1 - OUTSIDE DIAMETER WELD
2 - TORQUE CONVERTER HUB WELD
3 - STARTER RING GEAR
4 - LUG
Fig. 9 Battery Thermal Guard
1 - BATTERY THERMOWRAP (IF EQUIPPED)
2 - INTEGRATED POWER MODULE
3 - FRONT CONTROL MODULE
Fig. 10 Coolant Recovery Bottle
1 - UPPER BOLT ATTACHING TO BATTERY TRAY
2 - COOLANT RECOVERY CONTAINER
3 - UPPER BOLT
4 - HOSE
5 - LOWER BOLT (QTY. 2)
6 - LEFT SIDE FRAME RAIL
21 - 124 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 1722 of 2585
(9) Disconnect gear shift cable from manual valve
lever and upper mount bracket (Fig. 12).
(10) Disconnect crankshaft position sensor (if
equipped). Remove sensor from bellhousing.(11) Reposition leak detection pump harness and
hoses.
(12) Remove rear mount bracket-to-transaxle case
bolts (Fig. 13).
(13) Remove transaxle upper bellhousing-to-block
bolts.
(14) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(15) Remove transaxle oil pan and drain fluid into
suitable container.
(16) Remove front wheel/tire assemblies.
(17) Remove left and right halfshaft assemblies.
(Refer to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/HALF
SHAFT - REMOVAL)
(18) AWD models: Remove power transfer unit.
(Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/
POWER TRANSFER UNIT - REMOVAL)
(19) Remove rear mount bracket-to-transaxle case
lower (horizontal) bolt (Fig. 13).
(20) Remove front mount/bracket assembly.
(21) Remove starter motor.
(22) Remove lateral bending brace.
(23) Remove inspection cover.
(24) Remove torque converter-to-drive plate bolts.
(25) Support engine/transaxle assembly at engine
oil pan with screw jack and wood block.
(26) Partially remove left wheelhouse splash shield
to gain access to and remove upper mount thru-bolt
(Fig. 14).
(27) Lower engine/transaxle assembly with screw
jack.
(28) Obtain helper and/or transmission jack.
Secure transmission jack to transaxle assembly.
(29) Remove upper mount bracket from transaxle
(Fig. 14).
(30) Remove remaining transaxle bellhousing-to-
engine bolts.
(31) Remove transaxle assembly from vehicle.
DISASSEMBLY
NOTE: If transaxle is being overhauled (clutch
and/or seal replacement) or replaced, it is neces-
sary to perform the PCM/TCM Quick Learn Proce-
dure. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC
CONTROL MODULES/POWERTRAIN/TRANSMIS-
SION CONTROL MODULE - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE)
NOTE: This procedure does not include final drive
(differential) disassembly.
(1) Remove input and output speed sensors.
(2) Remove three (3) solenoid/pressure switch
assembly-to-case bolts.
(3) Remove solenoid/pressure switch assembly and
gasket (Fig. 15).
Fig. 11 Component Connector LocationÐTypical
1 - SOLENOID/PRESSURE SWITCH ASSY. CONNECTOR
2 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
3 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
4 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR CONNECTOR
Fig. 12 Gearshift Cable at Transaxle - Typical
1 - MANUAL VALVE LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT CABLE
3 - UPPER MOUNT BRACKET
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 125
41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 1765 of 2585
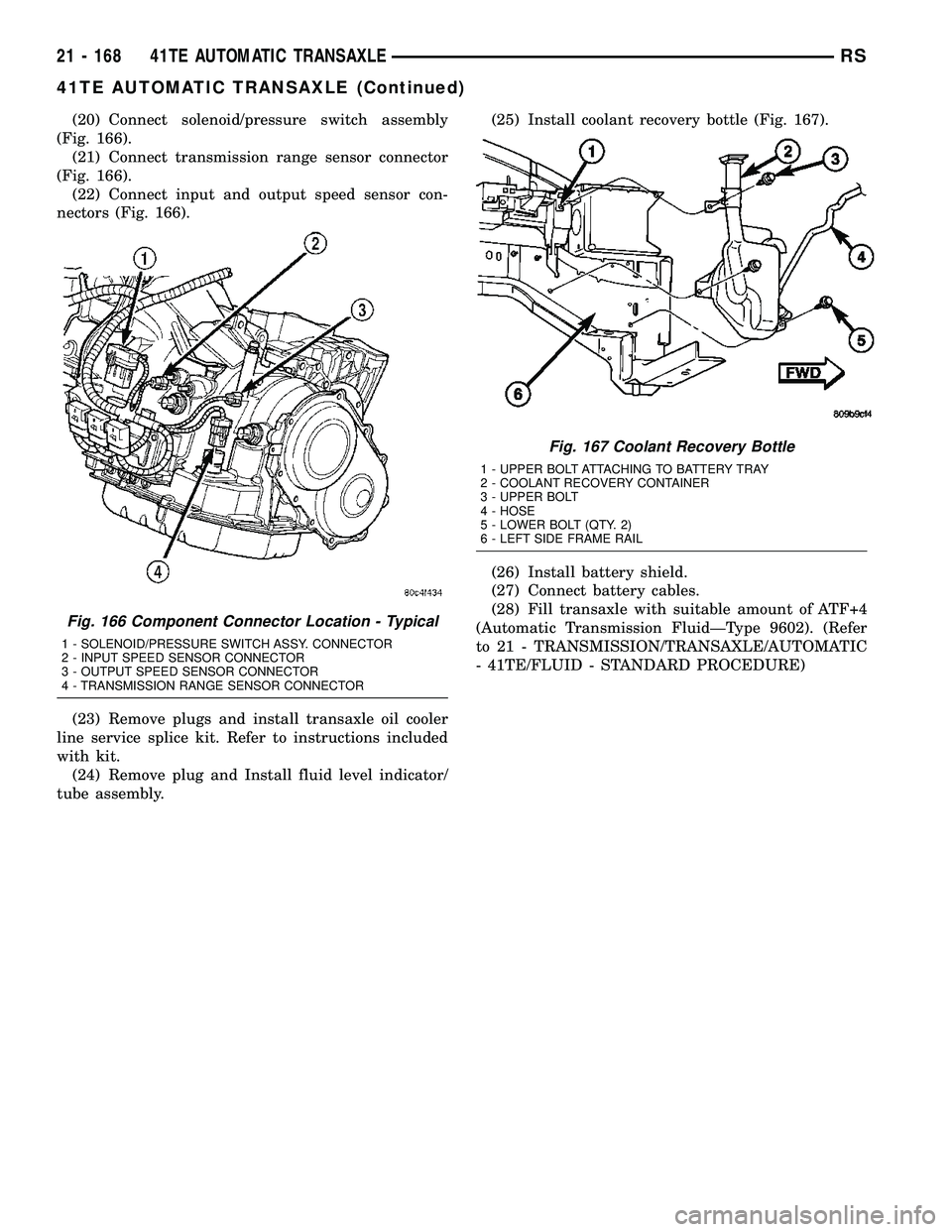
(20) Connect solenoid/pressure switch assembly
(Fig. 166).
(21) Connect transmission range sensor connector
(Fig. 166).
(22) Connect input and output speed sensor con-
nectors (Fig. 166).
(23) Remove plugs and install transaxle oil cooler
line service splice kit. Refer to instructions included
with kit.
(24) Remove plug and Install fluid level indicator/
tube assembly.(25) Install coolant recovery bottle (Fig. 167).
(26) Install battery shield.
(27) Connect battery cables.
(28) Fill transaxle with suitable amount of ATF+4
(Automatic Transmission FluidÐType 9602). (Refer
to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC
- 41TE/FLUID - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
Fig. 166 Component Connector Location - Typical
1 - SOLENOID/PRESSURE SWITCH ASSY. CONNECTOR
2 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
3 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
4 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR CONNECTOR
Fig. 167 Coolant Recovery Bottle
1 - UPPER BOLT ATTACHING TO BATTERY TRAY
2 - COOLANT RECOVERY CONTAINER
3 - UPPER BOLT
4 - HOSE
5 - LOWER BOLT (QTY. 2)
6 - LEFT SIDE FRAME RAIL
21 - 168 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)
Page 1798 of 2585

PRELOAD ADJUSTMENT W/O SHIM
(1) Remove the bearing cup from the differential
bearing retainer using Miller special Tool 6062A.
(2) Remove existing shim from under bearing cup.
(3) Reinstall the bearing cup into the retainer
using Miller Special Tool 6061, and C-4171.
NOTE: Oil baffle is not required when making the
shim calculation.
(4) Install the bearing retainer into the case.
Torque bolts to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.).
(5) Position the transaxle assembly vertically on
the support stand and install Miller Special Tool
L-4436-A into the bearing retainer.
(6) Rotate the differential at least one full revolu-
tion to ensure the tapered roller bearings are fully
seated.
(7) Attach a dial indicator to the case and zero the
dial. Place the tip on the end of Special Tool
L-4436-A.
(8) Place a large screwdriver to each side of the
ring gear and lift. Check the dial indicator for the
amount of end play.
CAUTION: Do not damage the transaxle case and/or
differential retainer sealing surface.
(9) Using the end play measurement that was
determined, add 0.18mm (0.007 inch). This should
give you between 5-18 inch pounds of bearing pre-
load. Refer to the Differential Bearing Shim Chart to
determine which shim to use.
(10) Remove the differential bearing retainer.
Remove the bearing cup.
(11) Install the oil baffle. Install the proper shim
combination under the bearing cup.
(12) Install the differential bearing retainer. Seal
the retainer to the housing with MopartSilicone
Rubber Adhesive Sealant. Torque bolts to 28 N´m
(250 in. lbs.).
(13) Using Miller Special Tool L-4436-A and an
inch-pound torque wrench, check the turning torque
of the differential (Fig. 208). The turning torque
should be between 5-18 inch-pounds.
NOTE: If turning torque is too high install a 0.05mm
(0.002 inch) thicker shim. If the turning torque is too
low, install a 0.05mm (0.002 inch) thinner shim.
Repeat until 5-18 inch-pounds of turning torque is
obtained.
FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE
FLUID LEVEL AND CONDITION CHECK
NOTE: Only transmission fluid of the type labeled
Mopar ATF+4 (Automatic Transmission Fluid)
should be used in this transaxle.
FLUID LEVEL CHECK
The transmission sump has a fluid level indicator
(dipstick) to check oil similar to most automatic
transmissions. It is located on the left side of the
engine. Be sure to wipe all dirt from dipstick handle
before removing.
The torque converter fills in both the P Park and N
Neutral positions. Place the selector lever in P Park
to be sure that the fluid level check is accurate.The
engine should be running at idle speed for at
least one minute, with the vehicle on level
ground.At normal operating temperature 82É C
(180É F), the fluid level is correct if it is in the HOT
region on the oil level indicator (Fig. 209). The fluid
level should be within the COLD region of the dip-
stick at 27É C (80É F) fluid temperature.
FLUID LEVEL CHECK USING DRB
NOTE: Engine and Transaxle should be at normal
operating temperature before performing this proce-
dure.
(1) Start engine and apply parking brake.
(2) Hook up DRB scan tool and select transmis-
sion.
Fig. 209 Fluid Level Indicator
1 - FLUID LEVEL INDICATOR
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 201
FINAL DRIVE (Continued)