2004 CHRYSLER VOYAGER Ignition lock
[x] Cancel search: Ignition lockPage 1563 of 2585
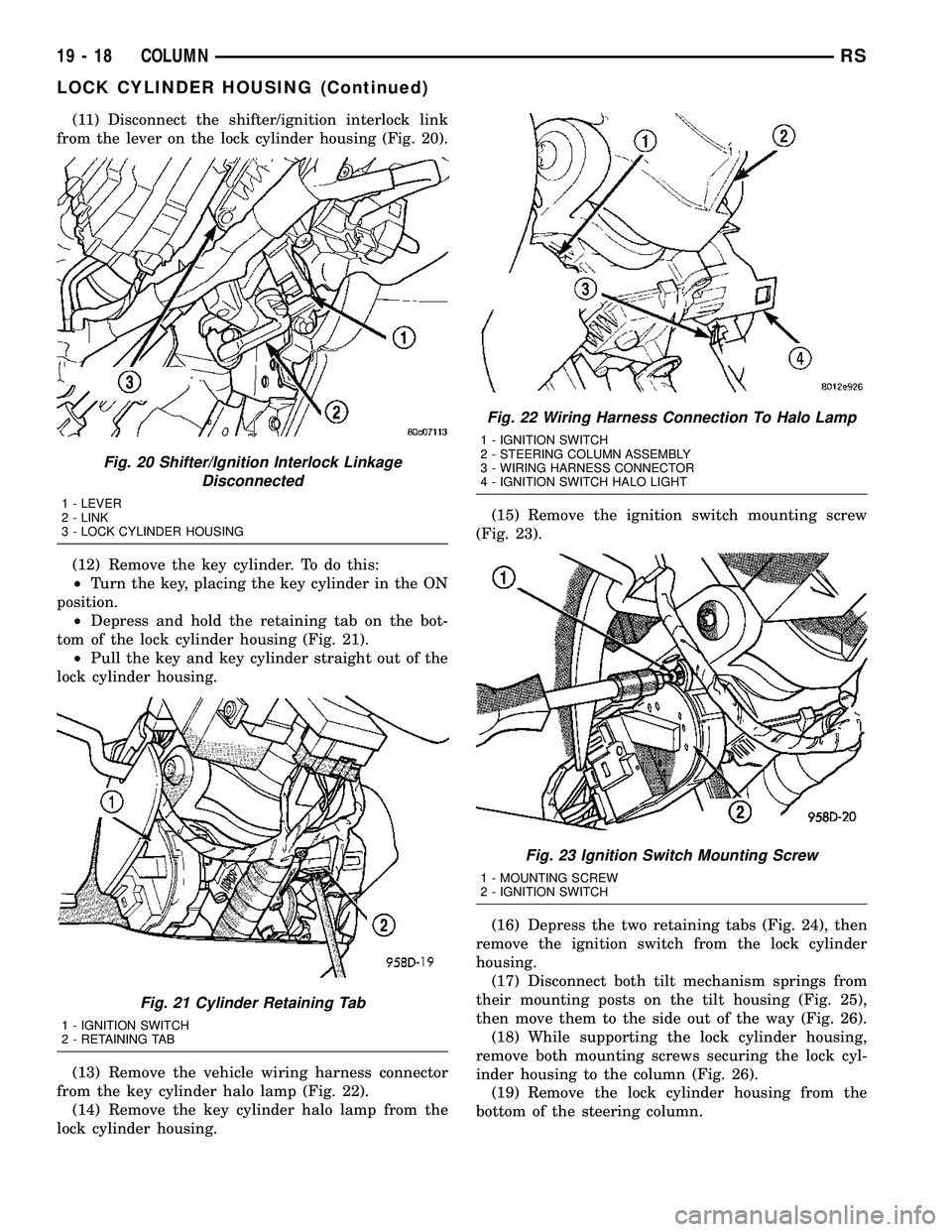
(11) Disconnect the shifter/ignition interlock link
from the lever on the lock cylinder housing (Fig. 20).
(12) Remove the key cylinder. To do this:
²Turn the key, placing the key cylinder in the ON
position.
²Depress and hold the retaining tab on the bot-
tom of the lock cylinder housing (Fig. 21).
²Pull the key and key cylinder straight out of the
lock cylinder housing.
(13) Remove the vehicle wiring harness connector
from the key cylinder halo lamp (Fig. 22).
(14) Remove the key cylinder halo lamp from the
lock cylinder housing.(15) Remove the ignition switch mounting screw
(Fig. 23).
(16) Depress the two retaining tabs (Fig. 24), then
remove the ignition switch from the lock cylinder
housing.
(17) Disconnect both tilt mechanism springs from
their mounting posts on the tilt housing (Fig. 25),
then move them to the side out of the way (Fig. 26).
(18) While supporting the lock cylinder housing,
remove both mounting screws securing the lock cyl-
inder housing to the column (Fig. 26).
(19) Remove the lock cylinder housing from the
bottom of the steering column.
Fig. 20 Shifter/Ignition Interlock Linkage
Disconnected
1 - LEVER
2 - LINK
3 - LOCK CYLINDER HOUSING
Fig. 21 Cylinder Retaining Tab
1 - IGNITION SWITCH
2 - RETAINING TAB
Fig. 22 Wiring Harness Connection To Halo Lamp
1 - IGNITION SWITCH
2 - STEERING COLUMN ASSEMBLY
3 - WIRING HARNESS CONNECTOR
4 - IGNITION SWITCH HALO LIGHT
Fig. 23 Ignition Switch Mounting Screw
1 - MOUNTING SCREW
2 - IGNITION SWITCH
19 - 18 COLUMNRS
LOCK CYLINDER HOUSING (Continued)
Page 1564 of 2585
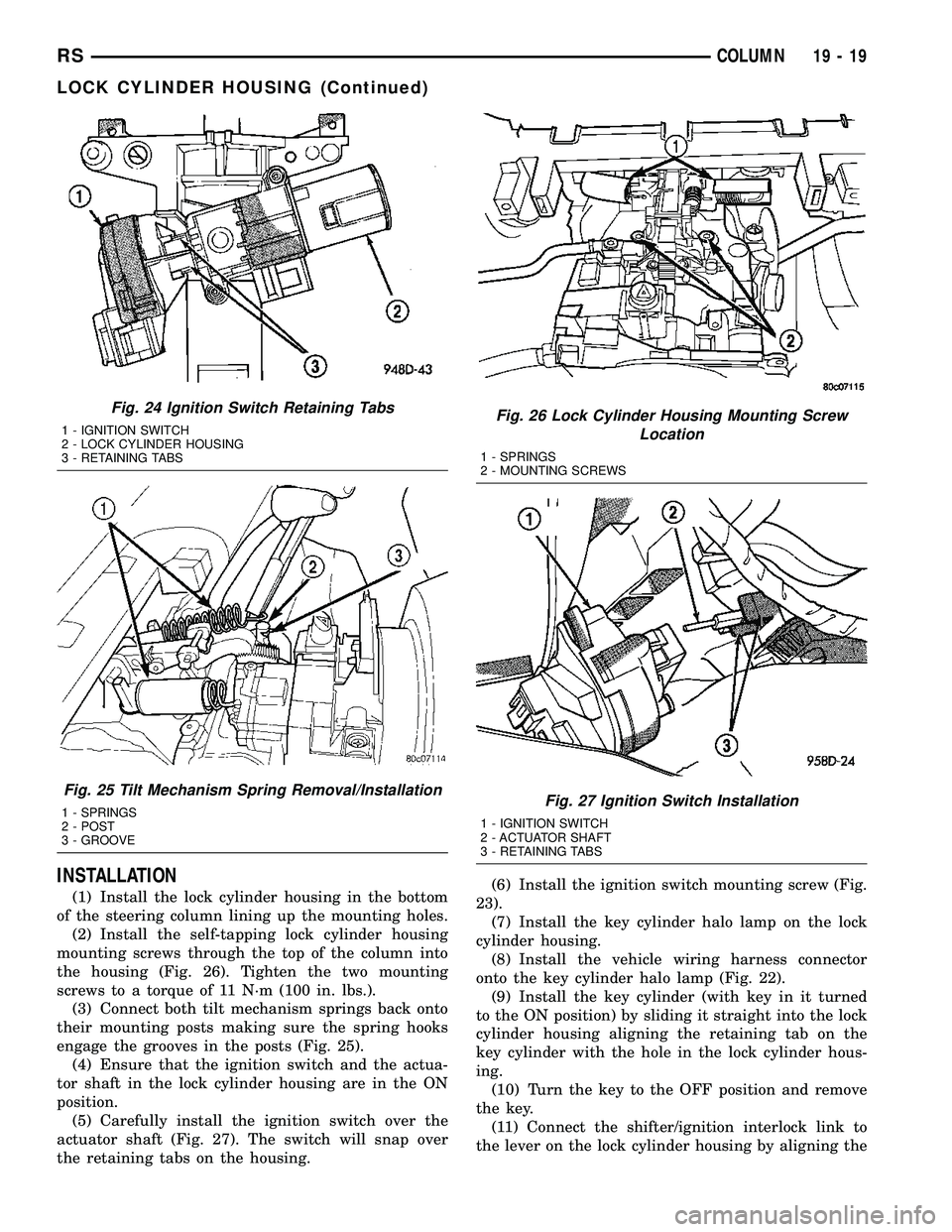
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the lock cylinder housing in the bottom
of the steering column lining up the mounting holes.
(2) Install the self-tapping lock cylinder housing
mounting screws through the top of the column into
the housing (Fig. 26). Tighten the two mounting
screws to a torque of 11 N´m (100 in. lbs.).
(3) Connect both tilt mechanism springs back onto
their mounting posts making sure the spring hooks
engage the grooves in the posts (Fig. 25).
(4) Ensure that the ignition switch and the actua-
tor shaft in the lock cylinder housing are in the ON
position.
(5) Carefully install the ignition switch over the
actuator shaft (Fig. 27). The switch will snap over
the retaining tabs on the housing.(6) Install the ignition switch mounting screw (Fig.
23).
(7) Install the key cylinder halo lamp on the lock
cylinder housing.
(8) Install the vehicle wiring harness connector
onto the key cylinder halo lamp (Fig. 22).
(9) Install the key cylinder (with key in it turned
to the ON position) by sliding it straight into the lock
cylinder housing aligning the retaining tab on the
key cylinder with the hole in the lock cylinder hous-
ing.
(10) Turn the key to the OFF position and remove
the key.
(11) Connect the shifter/ignition interlock link to
the lever on the lock cylinder housing by aligning the
Fig. 24 Ignition Switch Retaining Tabs
1 - IGNITION SWITCH
2 - LOCK CYLINDER HOUSING
3 - RETAINING TABS
Fig. 25 Tilt Mechanism Spring Removal/Installation
1 - SPRINGS
2 - POST
3 - GROOVE
Fig. 26 Lock Cylinder Housing Mounting Screw
Location
1 - SPRINGS
2 - MOUNTING SCREWS
Fig. 27 Ignition Switch Installation
1 - IGNITION SWITCH
2 - ACTUATOR SHAFT
3 - RETAINING TABS
RSCOLUMN19-19
LOCK CYLINDER HOUSING (Continued)
Page 1565 of 2585
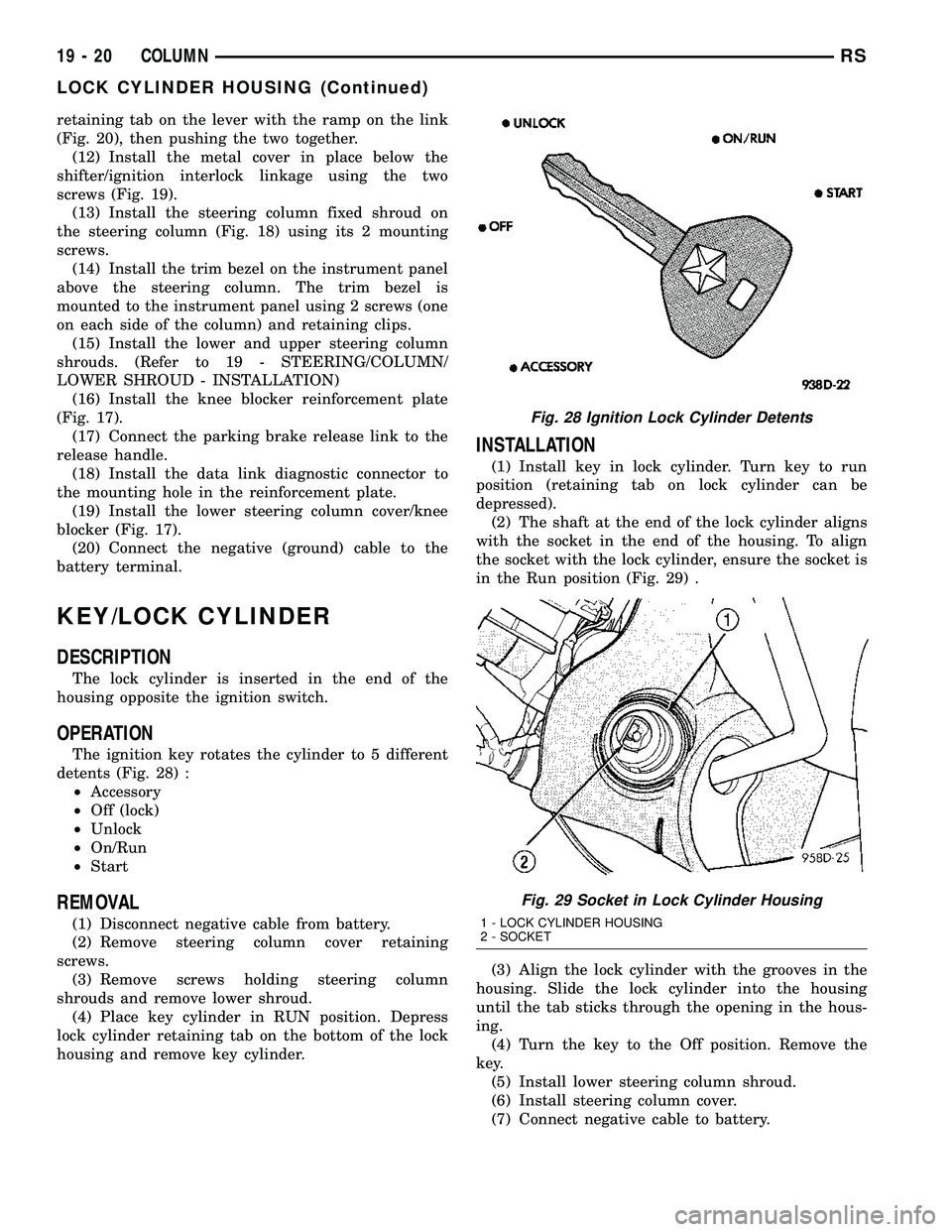
retaining tab on the lever with the ramp on the link
(Fig. 20), then pushing the two together.
(12) Install the metal cover in place below the
shifter/ignition interlock linkage using the two
screws (Fig. 19).
(13) Install the steering column fixed shroud on
the steering column (Fig. 18) using its 2 mounting
screws.
(14) Install the trim bezel on the instrument panel
above the steering column. The trim bezel is
mounted to the instrument panel using 2 screws (one
on each side of the column) and retaining clips.
(15) Install the lower and upper steering column
shrouds. (Refer to 19 - STEERING/COLUMN/
LOWER SHROUD - INSTALLATION)
(16) Install the knee blocker reinforcement plate
(Fig. 17).
(17) Connect the parking brake release link to the
release handle.
(18) Install the data link diagnostic connector to
the mounting hole in the reinforcement plate.
(19) Install the lower steering column cover/knee
blocker (Fig. 17).
(20) Connect the negative (ground) cable to the
battery terminal.
KEY/LOCK CYLINDER
DESCRIPTION
The lock cylinder is inserted in the end of the
housing opposite the ignition switch.
OPERATION
The ignition key rotates the cylinder to 5 different
detents (Fig. 28) :
²Accessory
²Off (lock)
²Unlock
²On/Run
²Start
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove steering column cover retaining
screws.
(3) Remove screws holding steering column
shrouds and remove lower shroud.
(4) Place key cylinder in RUN position. Depress
lock cylinder retaining tab on the bottom of the lock
housing and remove key cylinder.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install key in lock cylinder. Turn key to run
position (retaining tab on lock cylinder can be
depressed).
(2) The shaft at the end of the lock cylinder aligns
with the socket in the end of the housing. To align
the socket with the lock cylinder, ensure the socket is
in the Run position (Fig. 29) .
(3) Align the lock cylinder with the grooves in the
housing. Slide the lock cylinder into the housing
until the tab sticks through the opening in the hous-
ing.
(4) Turn the key to the Off position. Remove the
key.
(5) Install lower steering column shroud.
(6) Install steering column cover.
(7) Connect negative cable to battery.
Fig. 28 Ignition Lock Cylinder Detents
Fig. 29 Socket in Lock Cylinder Housing
1 - LOCK CYLINDER HOUSING
2 - SOCKET
19 - 20 COLUMNRS
LOCK CYLINDER HOUSING (Continued)
Page 1576 of 2585
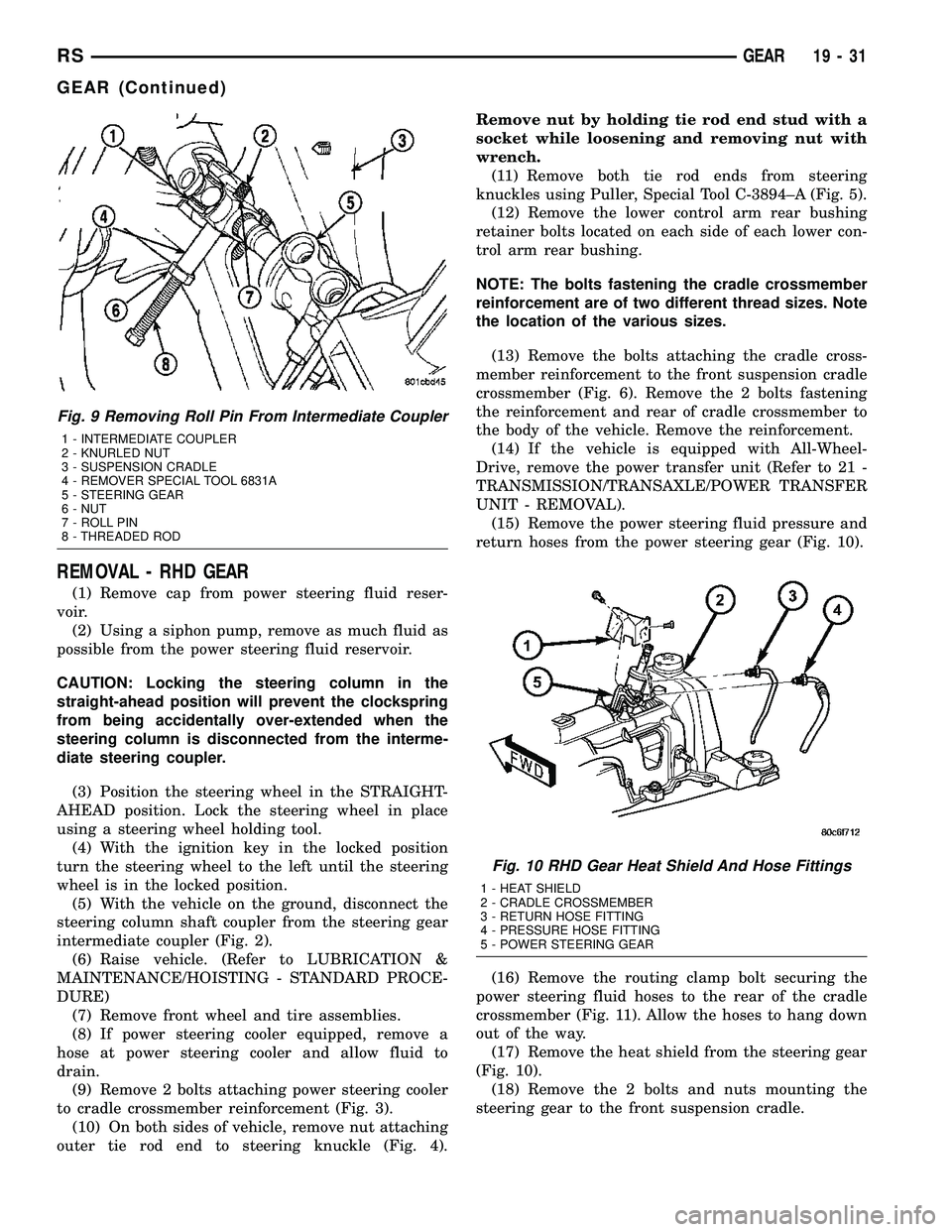
REMOVAL - RHD GEAR
(1) Remove cap from power steering fluid reser-
voir.
(2) Using a siphon pump, remove as much fluid as
possible from the power steering fluid reservoir.
CAUTION: Locking the steering column in the
straight-ahead position will prevent the clockspring
from being accidentally over-extended when the
steering column is disconnected from the interme-
diate steering coupler.
(3) Position the steering wheel in the STRAIGHT-
AHEAD position. Lock the steering wheel in place
using a steering wheel holding tool.
(4) With the ignition key in the locked position
turn the steering wheel to the left until the steering
wheel is in the locked position.
(5) With the vehicle on the ground, disconnect the
steering column shaft coupler from the steering gear
intermediate coupler (Fig. 2).
(6) Raise vehicle. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/HOISTING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE)
(7) Remove front wheel and tire assemblies.
(8) If power steering cooler equipped, remove a
hose at power steering cooler and allow fluid to
drain.
(9) Remove 2 bolts attaching power steering cooler
to cradle crossmember reinforcement (Fig. 3).
(10) On both sides of vehicle, remove nut attaching
outer tie rod end to steering knuckle (Fig. 4).Remove nut by holding tie rod end stud with a
socket while loosening and removing nut with
wrench.
(11) Remove both tie rod ends from steering
knuckles using Puller, Special Tool C-3894±A (Fig. 5).
(12) Remove the lower control arm rear bushing
retainer bolts located on each side of each lower con-
trol arm rear bushing.
NOTE: The bolts fastening the cradle crossmember
reinforcement are of two different thread sizes. Note
the location of the various sizes.
(13) Remove the bolts attaching the cradle cross-
member reinforcement to the front suspension cradle
crossmember (Fig. 6). Remove the 2 bolts fastening
the reinforcement and rear of cradle crossmember to
the body of the vehicle. Remove the reinforcement.
(14) If the vehicle is equipped with All-Wheel-
Drive, remove the power transfer unit (Refer to 21 -
TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/POWER TRANSFER
UNIT - REMOVAL).
(15) Remove the power steering fluid pressure and
return hoses from the power steering gear (Fig. 10).
(16) Remove the routing clamp bolt securing the
power steering fluid hoses to the rear of the cradle
crossmember (Fig. 11). Allow the hoses to hang down
out of the way.
(17) Remove the heat shield from the steering gear
(Fig. 10).
(18) Remove the 2 bolts and nuts mounting the
steering gear to the front suspension cradle.
Fig. 9 Removing Roll Pin From Intermediate Coupler
1 - INTERMEDIATE COUPLER
2 - KNURLED NUT
3 - SUSPENSION CRADLE
4 - REMOVER SPECIAL TOOL 6831A
5 - STEERING GEAR
6 - NUT
7 - ROLL PIN
8 - THREADED ROD
Fig. 10 RHD Gear Heat Shield And Hose Fittings
1 - HEAT SHIELD
2 - CRADLE CROSSMEMBER
3 - RETURN HOSE FITTING
4 - PRESSURE HOSE FITTING
5 - POWER STEERING GEAR
RSGEAR19-31
GEAR (Continued)
Page 1830 of 2585
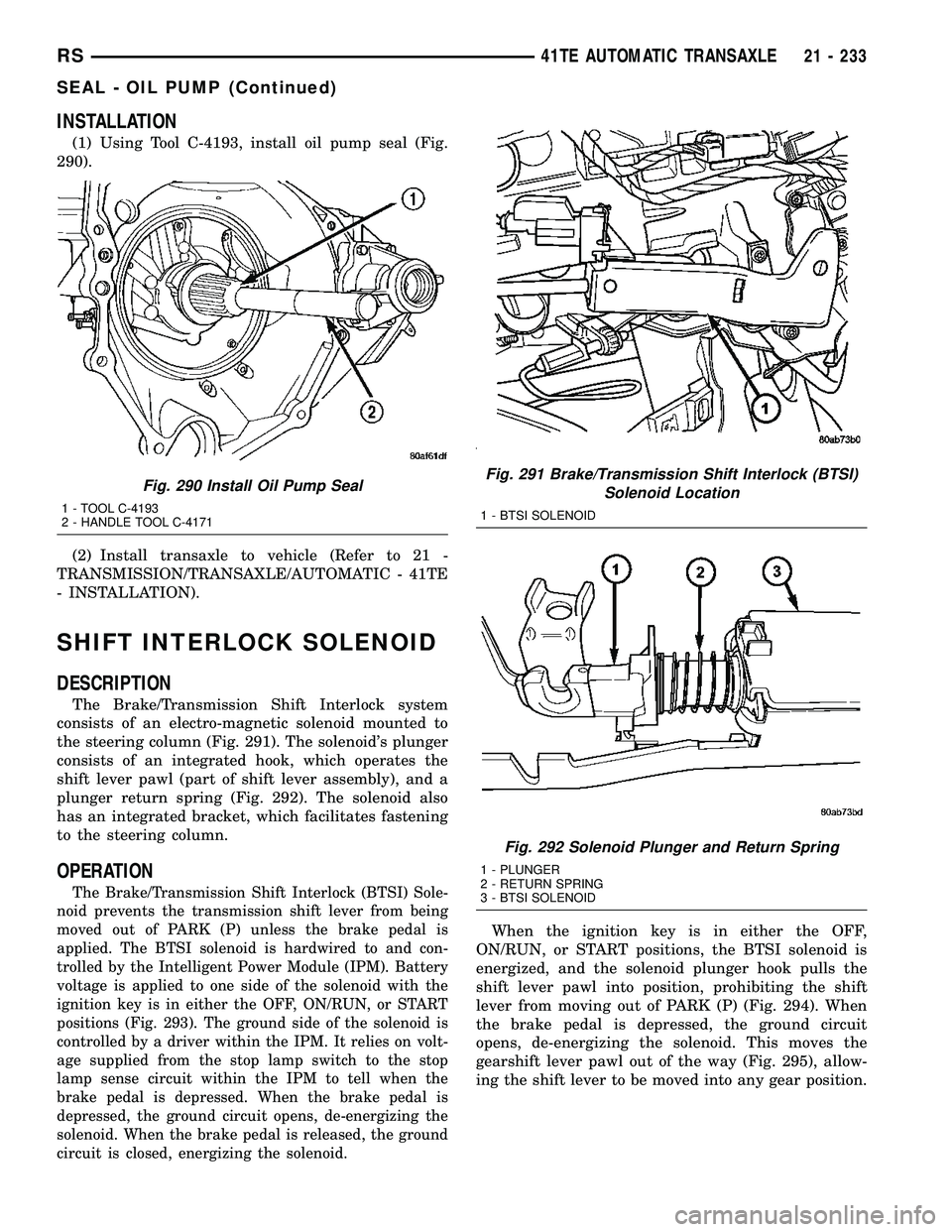
INSTALLATION
(1) Using Tool C-4193, install oil pump seal (Fig.
290).
(2) Install transaxle to vehicle (Refer to 21 -
TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC - 41TE
- INSTALLATION).
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION
The Brake/Transmission Shift Interlock system
consists of an electro-magnetic solenoid mounted to
the steering column (Fig. 291). The solenoid's plunger
consists of an integrated hook, which operates the
shift lever pawl (part of shift lever assembly), and a
plunger return spring (Fig. 292). The solenoid also
has an integrated bracket, which facilitates fastening
to the steering column.
OPERATION
The Brake/Transmission Shift Interlock (BTSI) Sole-
noid prevents the transmission shift lever from being
moved out of PARK (P) unless the brake pedal is
applied. The BTSI solenoid is hardwired to and con-
trolled by the Intelligent Power Module (IPM). Battery
voltage is applied to one side of the solenoid with the
ignition key is in either the OFF, ON/RUN, or START
positions (Fig. 293). The ground side of the solenoid is
controlled by a driver within the IPM. It relies on volt-
age supplied from the stop lamp switch to the stop
lamp sense circuit within the IPM to tell when the
brake pedal is depressed. When the brake pedal is
depressed, the ground circuit opens, de-energizing the
solenoid. When the brake pedal is released, the ground
circuit is closed, energizing the solenoid.
When the ignition key is in either the OFF,
ON/RUN, or START positions, the BTSI solenoid is
energized, and the solenoid plunger hook pulls the
shift lever pawl into position, prohibiting the shift
lever from moving out of PARK (P) (Fig. 294). When
the brake pedal is depressed, the ground circuit
opens, de-energizing the solenoid. This moves the
gearshift lever pawl out of the way (Fig. 295), allow-
ing the shift lever to be moved into any gear position.
Fig. 290 Install Oil Pump Seal
1 - TOOL C-4193
2 - HANDLE TOOL C-4171
Fig. 291 Brake/Transmission Shift Interlock (BTSI)
Solenoid Location
1 - BTSI SOLENOID
Fig. 292 Solenoid Plunger and Return Spring
1 - PLUNGER
2 - RETURN SPRING
3 - BTSI SOLENOID
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 233
SEAL - OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1831 of 2585
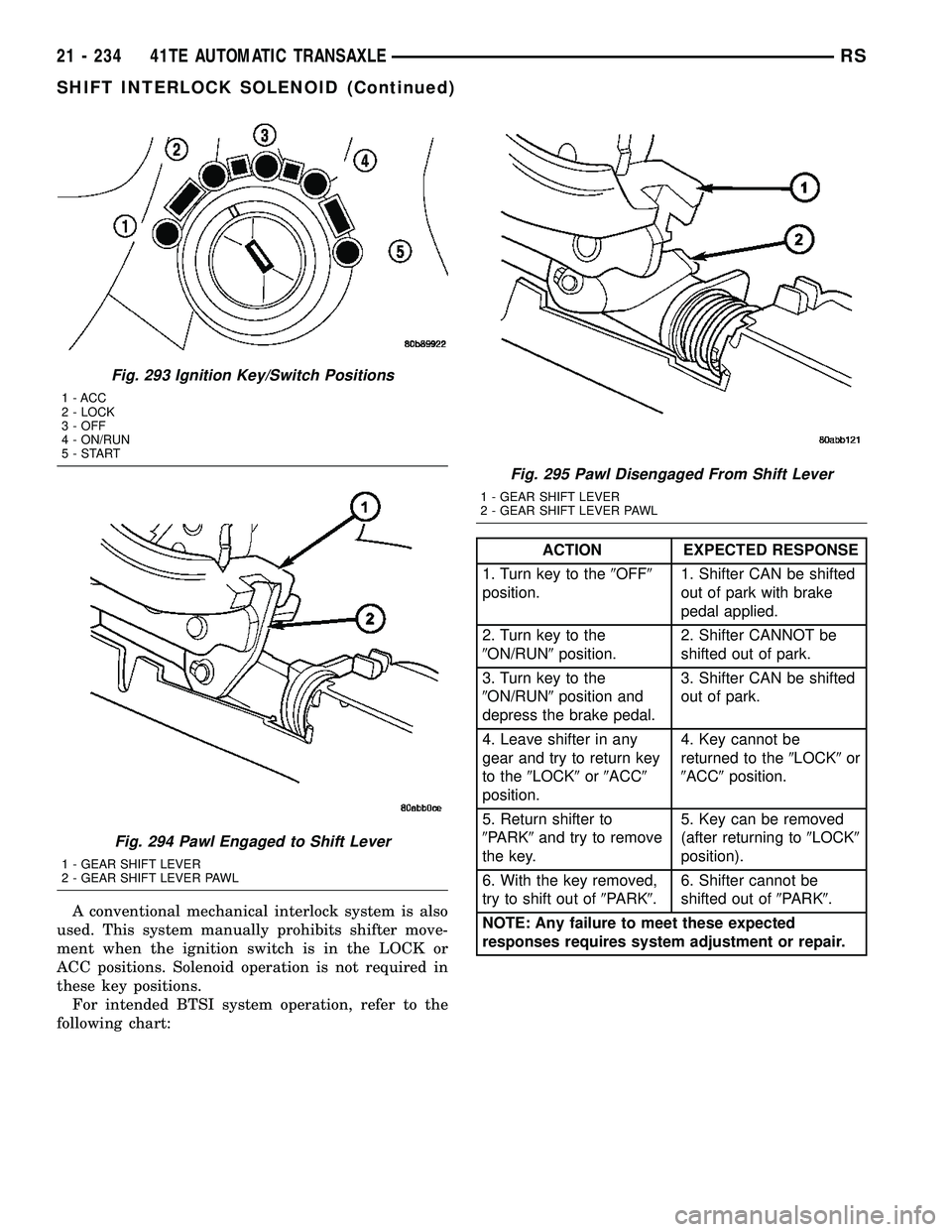
A conventional mechanical interlock system is also
used. This system manually prohibits shifter move-
ment when the ignition switch is in the LOCK or
ACC positions. Solenoid operation is not required in
these key positions.
For intended BTSI system operation, refer to the
following chart:
ACTION EXPECTED RESPONSE
1. Turn key to the9OFF9
position.1. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park with brake
pedal applied.
2. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position.2. Shifter CANNOT be
shifted out of park.
3. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position and
depress the brake pedal.3. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park.
4. Leave shifter in any
gear and try to return key
to the9LOCK9or9ACC9
position.4. Key cannot be
returned to the9LOCK9or
9ACC9position.
5. Return shifter to
9PARK9and try to remove
the key.5. Key can be removed
(after returning to9LOCK9
position).
6. With the key removed,
try to shift out of9PARK9.6. Shifter cannot be
shifted out of9PARK9.
NOTE: Any failure to meet these expected
responses requires system adjustment or repair.
Fig. 293 Ignition Key/Switch Positions
1 - ACC
2 - LOCK
3 - OFF
4 - ON/RUN
5-START
Fig. 294 Pawl Engaged to Shift Lever
1 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER PAWL
Fig. 295 Pawl Disengaged From Shift Lever
1 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER PAWL
21 - 234 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID (Continued)
Page 1846 of 2585
Since there are four switches, there are 16 possible
combinations of open and closed switches (codes).
Seven of these codes are related to gear position and
three are recognized as ªbetween gearº codes. This
results in six codes which should never occur. These
are called ªinvalidº codes. An invalid code will result
in a DTC, and the PCM/TCM will then determine the
shift lever position based on pressure switch data.
This allows reasonably normal transmission opera-
tion with a TRS failure.
TRS SWITCH STATES
SLP T42 T41 T3 T1
PCL CL CL OP
RCL OP OP OP
NCL CL OP CL
ODOP OP OP CL
3OP OP CL OP
LCL OP CL CL
TRANSMISSION TEMPERATURE SENSOR
The TRS has an integrated thermistor (Fig. 329)
that the PCM/TCM uses to monitor the transmis-
sion's sump temperature. Since fluid temperature
can affect transmission shift quality and convertor
lock up, the PCM/TCM requires this information to
determine which shift schedule to operate in. The
PCM also monitors this temperature data so it can
energize the vehicle cooling fan(s) when a transmis-
sion ªoverheatº condition exists. If the thermistor cir-
cuit fails, the PCM/TCM will revert to calculated oil
temperature usage.
CALCULATED TEMPERATURE
A failure in the temperature sensor or circuit will
result in calculated temperature being substituted for
actual temperature. Calculated temperature is a pre-
dicted fluid temperature which is calculated from a
combination of inputs:
²Battery (ambient) temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²In-gear run time since start-up
REMOVAL
(1) Remove valve body assembly from transaxle.
(Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTO-
MATIC - 41TE/VALVE BODY - REMOVAL)
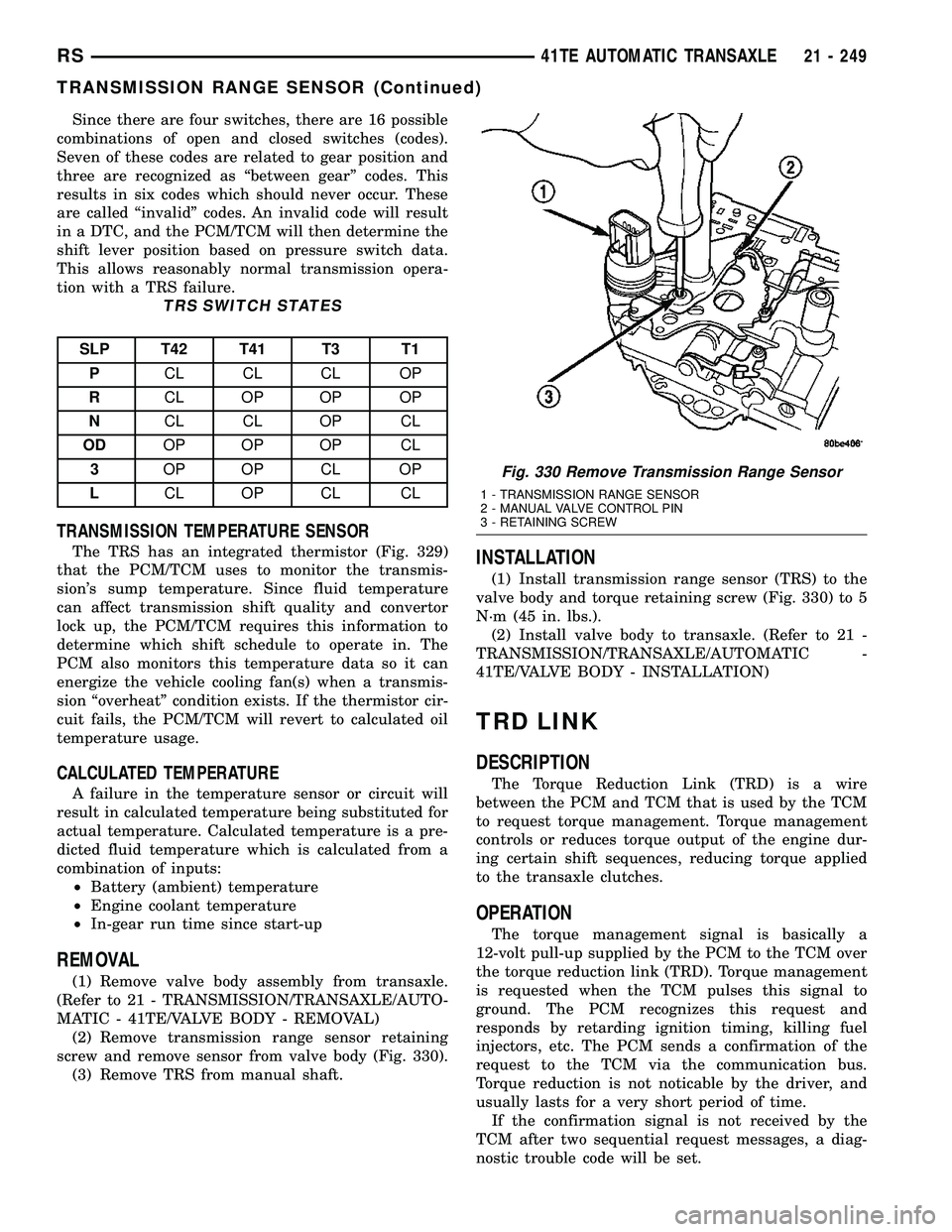
(2) Remove transmission range sensor retaining
screw and remove sensor from valve body (Fig. 330).
(3) Remove TRS from manual shaft.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install transmission range sensor (TRS) to the
valve body and torque retaining screw (Fig. 330) to 5
N´m (45 in. lbs.).
(2) Install valve body to transaxle. (Refer to 21 -
TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC -
41TE/VALVE BODY - INSTALLATION)
TRD LINK
DESCRIPTION
The Torque Reduction Link (TRD) is a wire
between the PCM and TCM that is used by the TCM
to request torque management. Torque management
controls or reduces torque output of the engine dur-
ing certain shift sequences, reducing torque applied
to the transaxle clutches.
OPERATION
The torque management signal is basically a
12-volt pull-up supplied by the PCM to the TCM over
the torque reduction link (TRD). Torque management
is requested when the TCM pulses this signal to
ground. The PCM recognizes this request and
responds by retarding ignition timing, killing fuel
injectors, etc. The PCM sends a confirmation of the
request to the TCM via the communication bus.
Torque reduction is not noticable by the driver, and
usually lasts for a very short period of time.
If the confirmation signal is not received by the
TCM after two sequential request messages, a diag-
nostic trouble code will be set.
Fig. 330 Remove Transmission Range Sensor
1 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
2 - MANUAL VALVE CONTROL PIN
3 - RETAINING SCREW
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 249
TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1995 of 2585
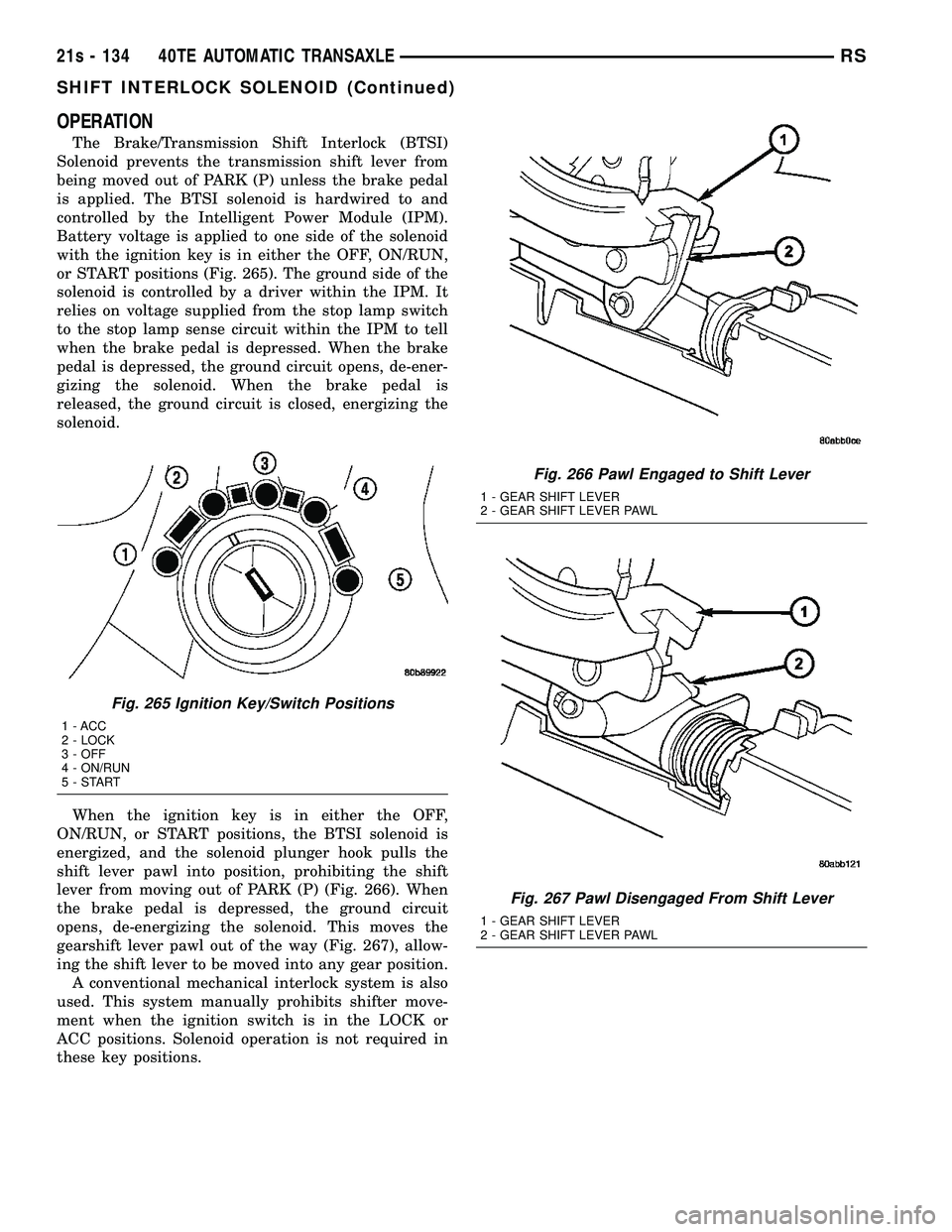
OPERATION
The Brake/Transmission Shift Interlock (BTSI)
Solenoid prevents the transmission shift lever from
being moved out of PARK (P) unless the brake pedal
is applied. The BTSI solenoid is hardwired to and
controlled by the Intelligent Power Module (IPM).
Battery voltage is applied to one side of the solenoid
with the ignition key is in either the OFF, ON/RUN,
or START positions (Fig. 265). The ground side of the
solenoid is controlled by a driver within the IPM. It
relies on voltage supplied from the stop lamp switch
to the stop lamp sense circuit within the IPM to tell
when the brake pedal is depressed. When the brake
pedal is depressed, the ground circuit opens, de-ener-
gizing the solenoid. When the brake pedal is
released, the ground circuit is closed, energizing the
solenoid.
When the ignition key is in either the OFF,
ON/RUN, or START positions, the BTSI solenoid is
energized, and the solenoid plunger hook pulls the
shift lever pawl into position, prohibiting the shift
lever from moving out of PARK (P) (Fig. 266). When
the brake pedal is depressed, the ground circuit
opens, de-energizing the solenoid. This moves the
gearshift lever pawl out of the way (Fig. 267), allow-
ing the shift lever to be moved into any gear position. A conventional mechanical interlock system is also
used. This system manually prohibits shifter move-
ment when the ignition switch is in the LOCK or
ACC positions. Solenoid operation is not required in
these key positions.
Fig. 265 Ignition Key/Switch Positions
1 - ACC
2 - LOCK
3 - OFF
4 - ON/RUN
5-START
Fig. 266 Pawl Engaged to Shift Lever
1 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER PAWL
Fig. 267 Pawl Disengaged From Shift Lever
1 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT LEVER PAWL
21s - 134 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID (Continued)