Page 1908 of 4378

1. To maintain the integrity of the coolant and the cooling system:
1. Add Motorcraft Premium Engine Coolant VC-4- A (in Oregon VC-5, in Canada CXC-10)
or equivalent meeting Ford specification ESE-M97B44- A (green color), or Motorcraft
Premium Gold Engine Coolant VC-7- A or equivalent meeting Ford specification WSS-
M97B51- A1 (yellow color). Use the same coolant that was drained from the cooling
system. Do not mix coolant types.
2. Do not add/mix orange-colored Motorcraft Speciality Orange Engine Coolant VC- 2 or
equivalent meeting Ford specification WSS-M97B44- D. Mixing coolants may degrade the
coolant's corrosion protection.
3. Do not add alcohol, methanol, brine, or any engine coolants mixed with alcohol or
methanol antifreeze. These can cause engine damage from overheating or freezing.
4. Do not mix with recycled coolant unless it meets the requirements of Ford specification ESE- M97B44- A or WSS-M97B51- A1. Not all coolant recycling processes meet these
Ford specifications. Use of such coolants can harm the engine and cooling system
components.
2. Fill the degas bottle. Use Motorcraft Premium Engine Coolant VC-4- A (in Oregon VC-5, in
Canada CXC- 10) or equivalent meeting Ford specification ESE-M97B44- A (green color), or
Motorcraft Premium Gold Engine Coolant VC-7- A or equivalent meeting Ford specification
WSS- M97B51- A1 (yellow color). Use the same coolant that was drained from the cooling
system. Do not mix coolant types.
3. Start the engine and allow to run until coolant circulation is observed in the intercooler degas bottle. Absence of circulation indicates air is trapped in the system.
�zTurn the engine off.
4. Add coolant as needed. Use Motorcraft Premium Engine Coolant VC -4-A (in Oregon VC-5, in
Canada CXC- 10) or equivalent meeting Ford specification ESE-M97B44- A (green color), or
Motorcraft Premium Gold Engine Coolant VC-7- A or equivalent meeting Ford specification
WSS- M97B51- A1 (yellow color). Use the same coolant that was drained from the cooling
system. Do not mix coolant types.
5. Repeat the above procedure to make sure all entrapped air is released. �K�l�j . 2 �b�a
22003 Mustang Workshop Manual
18. 11. 2011file:///C:/Ford/2000 - 2004/tsocache/SHEF_4464/S3B~us~en~ ...
Page 1949 of 4378
26. Disconnect the vacuum lines
27. Squeeze the two locking tabs, and remove the accelerator cable and the speed control cable (if
equipped) from the bracket and position aside.
28. Separate the fuel charging wiring (9D930) from the rear of the intake manifold (9424) and remove from the vehicle.
Installation 1. Position the fuel charging wiring in the vehicle and attach to the rear of the intake manifold. �K�l�j . 7 �b�a
142003 Mustang Workshop Manual
18. 11. 2011file:///C:/Ford/2000 - 2004/tsocache/SHEF_4464/S3B~us~en~ ...
Page 1958 of 4378
8. Disconnect the four RH fuel injector electrical connectors.
9. Disconnect the IAC electrical connector and the main chassis vacuum hose.
10. Remove the hose.
11. Squeeze the two locking tabs, and remove the accelerator cable and the speed control cable (if equipped) and position aside.
12. Disconnect the fuel pressure sensor electrical connector and the vacuum hose. �K�l�j . 2 �b�a
82003 Mustang Workshop Manual
18. 11. 2011file:///C:/Ford/2000 - 2004/tsocache/SHEF_4464/S3B~us~en~ ...
Page 2150 of 4378

To start the testing, conditions of stable purging and vehicle speed must be satisfied. During the first
stage, the canister vent solenoid is closed, while the EVAP canister purge valve remains open,
applying and building vacuum in the system as indicated by the FTP sensor. This phase checks for
major leaks in the EVAP system.
In the second stage, the EVAP canister purge valve closes and the system looks for minimal decay
rate in the EVAP vacuum, indicating the absence of any small EVAP system leaks.
The last stage is entered only if stage two of the leak test has failed and checks whether the failed test
was due to excess vapor generation. It monitors fuel vapor generation rate. Initially, the canister vent
solenoid is opened to equalize EVAP system pressure to atmosphere. Then the canister vent solenoid
is closed, allowing pressure to build if vapor generation is present in sufficient quantity. If the rate of
generation is found to be too high, the EVAP running loss system leak test is aborted. If not, then a
small leak is diagnosed.
On-
Board Refueling Vapor Recovery (ORVR) Evaporative Emission (EVAP) System
The basic elements forming the ORVR system are as follows:
�zThe fuel filler pipe forms a seal to prevent vapors from escaping the fuel tank while liquid is
entering the fuel tank. Liquid in the one inch diameter tube blocks vapors from rushing back up
the fuel filler pipe.
�z A fuel vapor control valve controls the flow of vapors out of the fuel tank. The valve closes when
the liquid level reaches a height associated with fuel tank usable capacity. The valve
accomplishes the following:
�„limits the total amount of fuel that can be dispensed into the fuel tank
�„ prevents liquid gasoline from exiting the fuel tank when submerged (as well as when
tipped well beyond a horizontal plane as part of the vehicle rollover protection in road
accidents)
�„ minimizes vapor flow resistance during anticipated refueling conditions
�z Fuel vapor tubing connects the fuel vapor control valve to the EVAP canister. This routes the
fuel tank vapors, displaced by the incoming liquid, to the EVAP canister.
�z A check valve in the fuel filling system prevents liquid from rushing back up the fuel filler pipe
during the liquid flow variations associated with the filler nozzle shut- off.
Between refueling events, the EVAP canister is purged with fresh air so that it may be used again to
store vapors accumulated during engine soaks or subsequent refueling events. The vapors drawn off
of the carbon in the EVAP canister are consumed by the engine.
Inspection and Verification 1. Verify the customer concern is with the evaporative emission (EVAP) system.
2. Visually inspect for the following obvious signs of mechanical damage.
Visual Inspection Chart Mechanical
�z
Fuel filler cap
�z EVAP test port
�z EVAP canister or canister vent solenoid �K�l�j . 3 �b�a
252003 Mustang Workshop Manual
18. 11. 2011file:///C:/Ford/2000 - 2004/tsocache/SHEF_4464/S3B~us~en~ ...
Page 2197 of 4378

DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Electronic Engine Controls —
Cobra
Most of the Cobra engine electronic controls are similar to that of the non- supercharged 4.6L (2V)
engine. These components are as follows:
�zCrankshaft position (CKP) sensor
�z Throttle position (TP) sensor
�z Idle air control (IAC) valve
�z Mass air flow (MAF) sensor
�z Heated oxygen sensors (HO2S)
�z Engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor
There are also three controls that are unique to the Cobra engine. These are as follows:
�zIntegrated temperature and manifold absolute pressure (T- MAP) sensor
�z Supercharger bypass vacuum solenoid
�z Supercharger bypass vacuum solenoid — actuator
Supercharger Bypass Vacuum Solenoid and Actuator
The Supercharger bypass vacuum solenoid will bleed off boost under the following conditions:
�zheavy engine misfire
�z engine coolant over- temperature
�z loss of intercooler fluid
�z pump failure
This prevents damage that can occur if boost were allowed under these conditions. The solenoid is
located on the upper LH side of the engine. The solenoid uses engine vacuum to operate a actuator
and linkage that connects to the pressure bleed off valve. The actuator is located near the solenoid
and is connected to it by a vacuum line.
Integrated Temperature and Manifold Absolute Pressure (TMAP) Sensor
The TMAP sensor is located on the upper LH side of the engine and is used to measure current
manifold absolute pressure and manifold air charge temperature. SECTION 303-
14: Electronic Engine Controls 2003 Mustang Workshop Manual �K�l�j . 1 �b�a
22003 Mustang Workshop Manual
18. 11. 2011file:///C:/Ford/2000 - 2004/tsocache/SHEF_4464/S3B~us~en~ ...
Page 2200 of 4378
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
Temperature and Manifold Absolute Pressure (T-
MAP)
Sensor — Cobra
Removal and Installation 1. Disconnect the temperature manifold absolute pressure (T- MAP) sensor electrical connector.
2. Remove the bolts and the T- MAP sensor.
3. To install, reverse the removal procedure.
SECTION 303-
14: Electronic Engine Controls 2003 Mustang Workshop Manual �K�l�j . 1 �b�a
22003 Mustang Workshop Manual
18. 11. 2011file:///C:/Ford/2000 - 2004/tsocache/SHEF_4464/S3B~us~en~ ...
Page 2234 of 4378
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor —
3.8L
Removal
CAUTION: The mass air flow (MAF) sensor hot wire sensing element and housing are
calibrated as a unit and must be repaired as a complete assembly. Do not damage the sensing
element (internal to housing) or possible failure to the mass air flow sensor may occur.
1. Disconnect the battery ground cable. For additional information, refer to Section 414 - 01 .
2. Remove the air cleaner and duct assembly. For additional information, refer to Section 303 - 12 .
3. Release the four tabs and remove the mass air flow (MAF) sensor.
4. Disconnect the connector.
5. Remove the mass air flow sensor (MAF). �zRemove the nuts and the MAF sensor.
SECTION 303-
14: Electronic Engine Controls 2003 Mustang Workshop Manual �K�l�j . 1 �b�a
22003 Mustang Workshop Manual
18. 11. 2011file:///C:/Ford/2000 - 2004/tsocache/SHEF_4464/S3B~us~en~ ...
Page 2295 of 4378
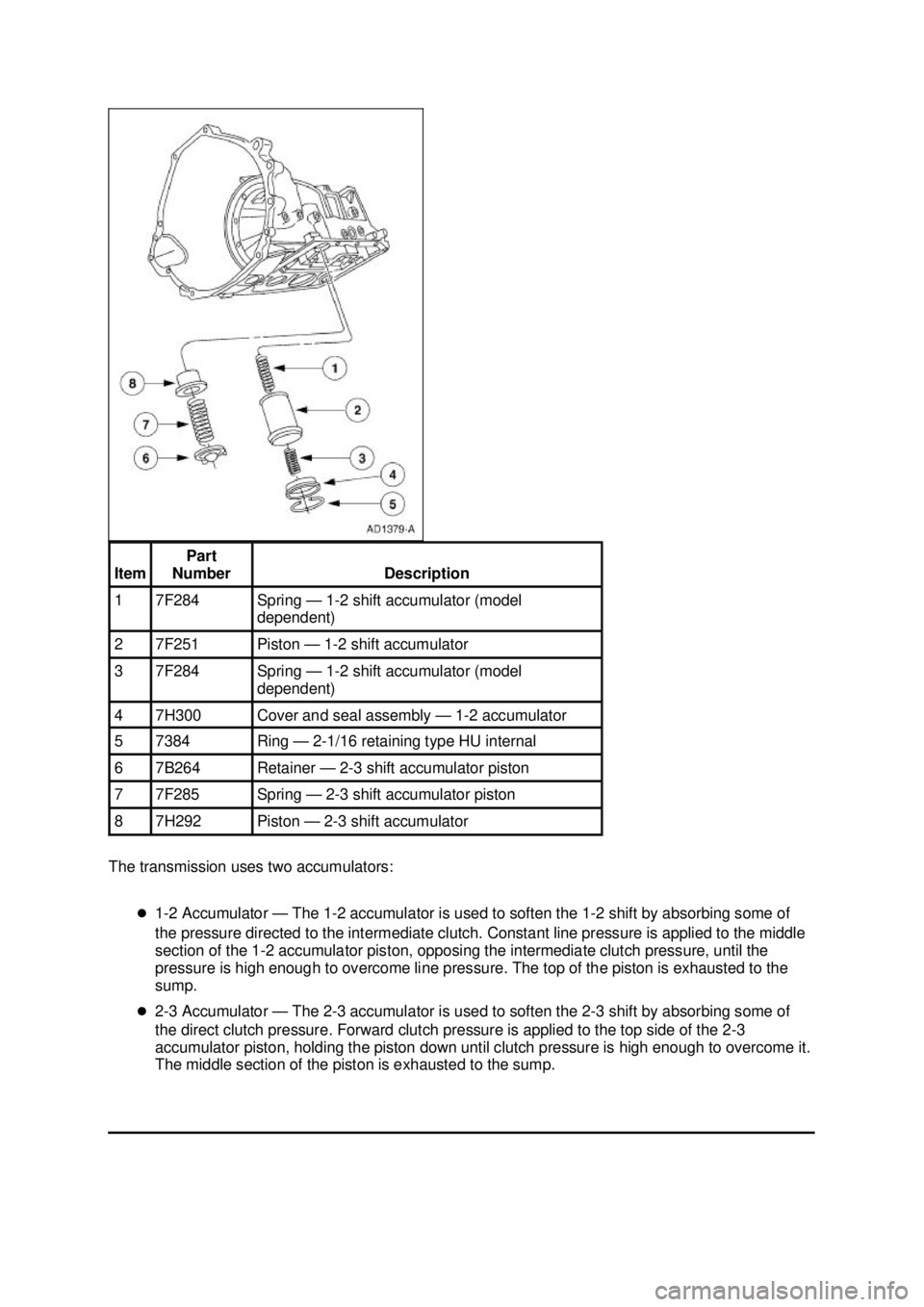
The transmission uses two accumulators:
�z1-2 Accumulator — The 1-2 accumulator is used to soften the 1- 2 shift by absorbing some of
the pressure directed to the intermediate clutch. Constant line pressure is applied to the middle
section of the 1- 2 accumulator piston, opposing the intermediate clutch pressure, until the
pressure is high enough to overcome line pressure. The top of the piston is exhausted to the
sump.
�z 2-3 Accumulator — The 2-3 accumulator is used to soften the 2- 3 shift by absorbing some of
the direct clutch pressure. Forward clutch pressure is applied to the top side of the 2- 3
accumulator piston, holding the piston down until clutch pressure is high enough to overcome it.
The middle section of the piston is exhausted to the sump. Item Part
Number Description
1 7F284 Spring — 1-
2 shift accumulator (model
dependent) 2 7F251 Piston — 1-
2 shift accumulator 3 7F284 Spring — 1-
2 shift accumulator (model
dependent) 4 7H300 Cover and seal assembly — 1-
2 accumulator 5 7384 Ring
— 2-1/16 retaining type HU internal 6 7B264 Retainer
— 2-3 shift accumulator piston 7 7F285 Spring — 2-
3 shift accumulator piston 8 7H292 Piston — 2-
3 shift accumulator �K�l�j . 3 �b�a
42003 Mustang Workshop Manual
18. 11. 2011file:///C:/Ford/2000 - 2004/tsocache/SHEF_2748/S3B~us~en~ ...