2003 FORD ESCAPE lock
[x] Cancel search: lockPage 87 of 240

12 years old and under should be properly restrained in the rear seat
whenever possible. Refer toSafety restraints for childrenorSafety
seats for childrenlater in this chapter.
How to use the automatic locking mode
•Buckle the combination lap and
shoulder belt.
•Grasp the shoulder portion and
pull downward until the entire
belt is pulled out.
•Allow the belt to retract. As the belt retracts, you will hear a clicking
sound. This indicates the safety belt is now in the automatic locking
mode.
How to disengage the automatic locking mode
Disconnect the combination lap/shoulder belt and allow it to retract
completely to disengage the automatic locking mode and activate the
vehicle sensitive (emergency) locking mode.
After any vehicle collision, the safety belt systems at all outboard
seating positions (except the driver position, which doesn’t have
this feature) must be checked by a qualified technician to verify that
the automatic locking retractor feature for child seats is still
functioning properly. In addition, all seat belts should be checked for
proper function.
Seating and Safety Restraints
87
Page 88 of 240

BELT AND RETRACTOR ASSEMBLY MUST BE REPLACED if
the seat belt assembly“automatic locking retractor”feature or
any other seat belt function is not operating properly when checked
according to the procedures in Workshop Manual. Failure to replace
the Belt and Retractor assembly could increase the risk of injury in
collisions.
Front safety belt height adjustment
Adjust the height of the shoulder
belt so the belt rests across the
middle of your shoulder.
To adjust the shoulder belt height,
push the button and slide the height
adjuster up or down. Release the
button and pull down on the height
adjuster to make sure it is locked in
place.
Position the safety belt
height adjusters so that the
belt rests across the middle of
your shoulder. Failure to adjust
the safety belt properly could
reduce the effectiveness of the
seat belt and increase the risk of
injury in a collision.
Safety belt pretensioner
Your vehicle is equipped with safety belt pretensioners at the driver and
front passenger seating positions.
The safety belt pretensioners are designed to activate during certain
frontal or near-frontal collisions with sufficient longitudinal deceleration.
A safety belt pretensioner is a device which tightens the webbing of the
lap and shoulder belts in such a way that they fit more snugly against
the body.
The driver and front outboard passenger safety belt system (including
retractors, buckles and height adjusters) must be replaced if the vehicle
Seating and Safety Restraints
88
Page 106 of 240

When installing a child safety seat:
•Review and follow the information
presented in theAir bag
supplemental restraint system
(SRS) section in this chapter.
•Use the correct safety belt buckle
for that seating position (the
buckle closest to the direction the
tongue is coming from).
•Insert the belt tongue into the
proper buckle until you hear a
snap and feel it latch. Make sure the tongue is securely fastened in the
buckle.
•Keep the buckle release button pointing up and away from the safety
seat, with the tongue between the child seat and the release button,
to prevent accidental unbuckling.
•Place seat back in upright position.
•Put the safety belt in the automatic locking mode. Refer toAutomatic
locking mode(passenger side front and outboard rear seating
positions) (if equipped) section in this chapter.
Ford recommends the use of a child safety seat having a top tether
strap. Install the child safety seat in a seating position with a tether
anchor. For more information on top tether straps, refer toAttaching
child safety seats with tether straps.in this chapter.
Carefully follow all of the manufacturer’s instructions included
with the safety seat you put in your vehicle. If you do not install
and use the safety seat properly, the child may be injured in a sudden
stop or collision.
Rear-facing child seats or infant carriers should never be placed
in the front seats.
Seating and Safety Restraints
106
Page 108 of 240
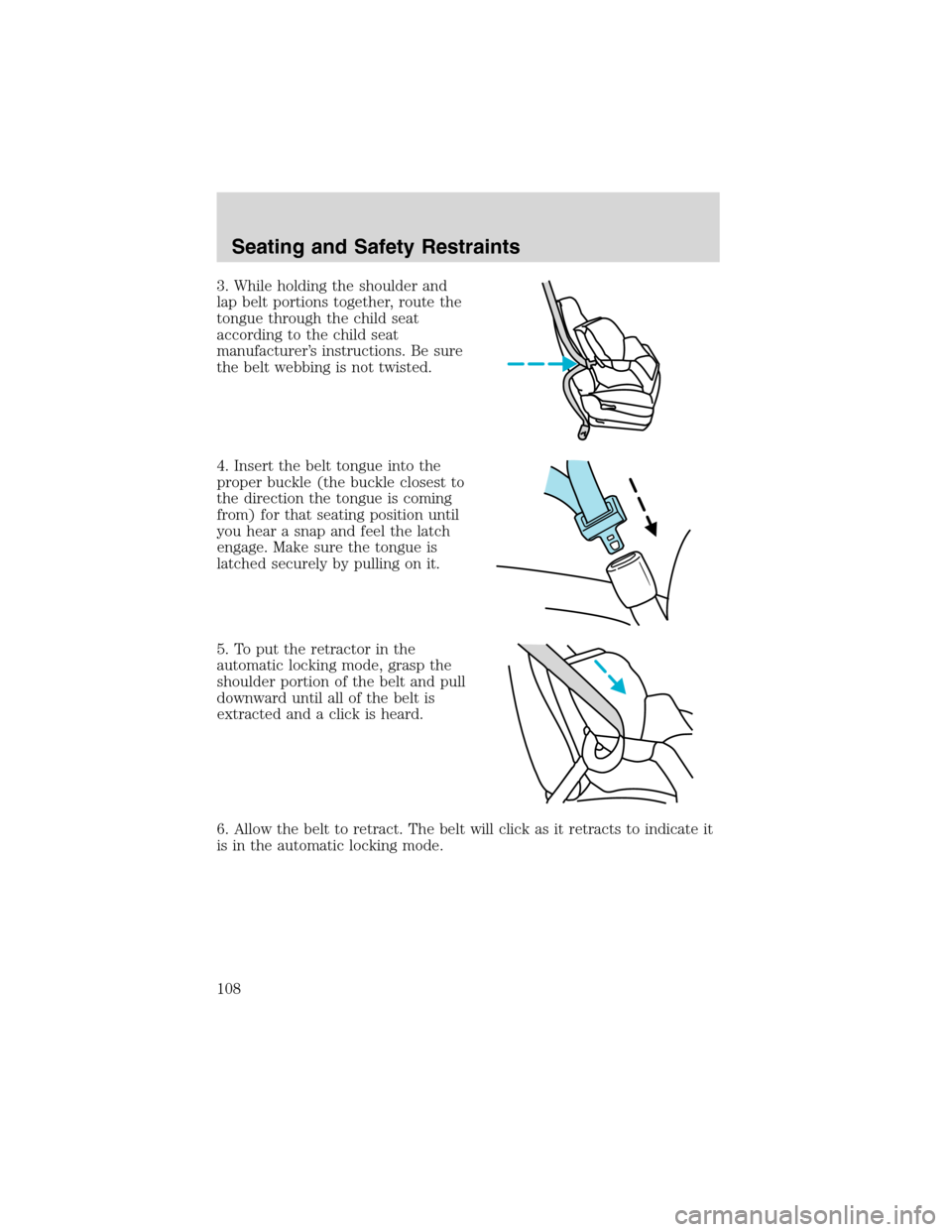
3. While holding the shoulder and
lap belt portions together, route the
tongue through the child seat
according to the child seat
manufacturer’s instructions. Be sure
the belt webbing is not twisted.
4. Insert the belt tongue into the
proper buckle (the buckle closest to
the direction the tongue is coming
from) for that seating position until
you hear a snap and feel the latch
engage. Make sure the tongue is
latched securely by pulling on it.
5. To put the retractor in the
automatic locking mode, grasp the
shoulder portion of the belt and pull
downward until all of the belt is
extracted and a click is heard.
6. Allow the belt to retract. The belt will click as it retracts to indicate it
is in the automatic locking mode.
Seating and Safety Restraints
108
Page 109 of 240

7. Pull the lap belt portion across
the child seat toward the buckle and
pull up on the shoulder belt while
pushing down with your knee on the
child seat.
8. Allow the safety belt to retract to
remove any slack in the belt.
9. Before placing the child in the
seat, forcibly tilt the seat forward
and back to make sure the seat is
securely held in place. To check
this, grab the seat at the belt path
and attempt to move it side to side
and forward and back. There should
be no more than one inch of
movement for proper installation.
10. Try to pull the belt out of the retractor to make sure the retractor is
in the automatic locking mode (you should not be able to pull more belt
out). If the retractor is not locked, unbuckle the belt and repeat steps
two through nine.
Check to make sure the child seat is properly secured before each use.
Attaching child safety seats with tether straps
Most new forward-facing child safety seats include a tether strap which
goes over the back of the seat and hooks to an anchoring point. Tether
straps are available as an accessory for many older safety seats. Contact
the manufacturer of your child seat for information about ordering a
tether strap.
The rear seating positions of your vehicle are equipped with built-in
tether strap anchors located behind the seats on the roof panel in the
cargo area.
Seating and Safety Restraints
109
Page 114 of 240

STARTING
Positions of the ignition
1. LOCK, locks the gearshift lever
and allows key removal.
2. ACCESSORY, allows the electrical
accessories such as the radio to
operate while the engine is not
running.
3. RUN, all electrical circuits
operational and warning lights will
illuminate. This is the position the
key is in when you’re driving.
4. START, cranks the engine. Release the key as soon as the engine
starts.
Preparing to start your vehicle
Engine starting is controlled by the powertrain control system. This
system meets all Canadian Interference-Causing Equipment standard
requirements regulating the impulse electrical field strength of radio
noise.
When starting a fuel-injected engine, don’t press the accelerator before
or during starting. Only use the accelerator when you have difficulty
starting the engine. For more information on starting the vehicle, refer to
Starting the enginein this chapter.
Extended idling at high engine speeds can produce very high
temperatures in the engine and exhaust system, creating the risk
of fire or other damage.
Do not park, idle, or drive your vehicle in dry grass or other dry
ground cover. The emission system heats up the engine
compartment and exhaust system, which can start a fire.
Do not start your vehicle in a closed garage or in other enclosed
areas. Exhaust fumes can be toxic. Always open the garage door
before you start the engine. SeeGuarding against exhaust fumesin
this chapter for more instructions.
Driving
114
Page 117 of 240

Starting the engine
1. Turn the key to 3 (RUN) without
turning the key to 4 (START). If
there is difficulty in turning the key,
rotate the steering wheel until the
key turns freely. This condition may
occur when:
•the front wheels are turned
•a front wheel is against the curb
Turn the key to 4 (START), then
release the key as soon as the
engine starts. Excessive cranking could damage the starter.
Note:If the engine does not start within five seconds on the first try,
turn the key to 1 (LOCK), wait 10 seconds and try again.
Using the engine block heater (if equipped)
An engine block heater warms the engine coolant which aids in starting
and heater/defroster performance. Use of an engine block heater is
strongly recommended if you live in a region where temperatures reach
-23°C (-10°F) or below. For best results, plug the heater in at least
three hours before starting the vehicle. The heater can be plugged in the
night before starting the vehicle.
To prevent electrical shock, do not use your heater with
ungrounded electrical systems or two-pronged (cheater)
adapters.
Guarding against exhaust fumes
Carbon monoxide is present in exhaust fumes. Take precautions to avoid
its dangerous effects.
If you smell exhaust fumes inside your vehicle, have your dealer
inspect your vehicle immediately. Do not drive if you smell
exhaust fumes.
Important ventilating information
If the engine is idling while the vehicle is stopped for a long period of
time, open the windows at least 2.5 cm (one inch) or adjust the heating
or air conditioning to bring in fresh air.
Driving
117
Page 118 of 240

BRAKES
Occasional brake noise is normal. If a metal-to-metal, continuous grinding
or continuous squeal sound is present, the brake linings may be worn-out
and should be inspected by a qualified service technician. If the vehicle
has continuous vibration or shudder in the steering wheel while braking,
the vehicle should be inspected by a qualified service technician.
Brakes
Under normal operating conditions, brake dust may accumulate on the
wheels. Some brake dust is inevitable as brakes wear and does not
contribute to brake noise. The use of modern friction materials with
emphasis on improved performance and environmental considerations
can lead to more dust than in the past. Brake dust can be cleaned by
weekly washing with soapy water and a soft sponge. Heavier deposits can
be removed with Motorcraft Wheel and Tire Cleaner (ZC-37–A).
Four-wheel anti-lock brake system (ABS) (if equipped)
Your vehicle may be equipped with an Anti-lock Braking System (ABS).
This system helps you maintain steering control during emergency stops
by keeping the brakes from locking. Noise from the ABS pump motor
and brake pedal pulsation may be observed during ABS braking; any
pulsation or mechanical noise you may feel or hear is normal.
Using ABS
When hard braking is required, apply continuous force on the brake
pedal; do not pump the brake pedal since this will reduce the
effectiveness of the ABS and will increase your vehicle’s stopping
distance. The ABS will be activated immediately, allowing you to retain
full steering control during hard braking and on slippery surfaces.
However, the ABS does not decrease stopping distance.
ABS warning lamp
ABS
TheABSlamp in the instrument cluster momentarily illuminates when
the ignition is turned to ON. If the light does not illuminate during start
up, remains on or flashes, the ABS may be disabled and the ABS may
need to be serviced
Even when the ABS is disabled,
normal braking is still effective. (If
your BRAKE warning lamp
illuminates with the parking brake
released, have your brake system
serviced immediately.)
!
BRAKE
Driving
118