2003 DODGE RAM Heating and cooling
[x] Cancel search: Heating and coolingPage 2040 of 2895

FLUID AND FILTER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - EFFECTS OF
INCORRECT FLUID LEVEL
A low fluid level allows the pump to take in air
along with the fluid. Air in the fluid will cause fluid
pressures to be low and develop slower than normal.
If the transmission is overfilled, the gears churn the
fluid into foam. This aerates the fluid and causing
the same conditions occurring with a low level. In
either case, air bubbles cause fluid overheating, oxi-
dation and varnish buildup which interferes with
valve and clutch operation. Foaming also causes fluid
expansion which can result in fluid overflow from the
transmission vent or fill tube. Fluid overflow can eas-
ily be mistaken for a leak if inspection is not careful.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CAUSES OF
BURNT FLUID
Burnt, discolored fluid is a result of overheating
which has two primary causes.
(1) A result of restricted fluid flow through the
main and/or auxiliary cooler. This condition is usu-
ally the result of a faulty or improperly installed
drainback valve, a damaged main cooler, or severe
restrictions in the coolers and lines caused by debris
or kinked lines.
(2) Heavy duty operation with a vehicle not prop-
erly equipped for this type of operation. Trailer tow-
ing or similar high load operation will overheat the
transmission fluid if the vehicle is improperly
equipped. Such vehicles should have an auxiliary
transmission fluid cooler, a heavy duty cooling sys-
tem, and the engine/axle ratio combination needed to
handle heavy loads.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLUID
CONTAMINATION
Transmission fluid contamination is generally a
result of:
²adding incorrect fluid
²failure to clean dipstick and fill tube when
checking level
²engine coolant entering the fluid
²internal failure that generates debris
²overheat that generates sludge (fluid break-
down)
²failure to replace contaminated converter after
repair
The use of non-recommended fluids can result in
transmission failure. The usual results are erratic
shifts, slippage, abnormal wear and eventual failuredue to fluid breakdown and sludge formation. Avoid
this condition by using recommended fluids only.
The dipstick cap and fill tube should be wiped
clean before checking fluid level. Dirt, grease and
other foreign material on the cap and tube could fall
into the tube if not removed beforehand. Take the
time to wipe the cap and tube clean before withdraw-
ing the dipstick.
Engine coolant in the transmission fluid is gener-
ally caused by a cooler malfunction. The only remedy
is to replace the radiator as the cooler in the radiator
is not a serviceable part. If coolant has circulated
through the transmission, an overhaul is necessary.
The torque converter should be replaced whenever
a failure generates sludge and debris. This is neces-
sary because normal converter flushing procedures
will not remove all contaminants.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID LEVEL
CHECK
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows the pump to take in air along with
the fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles
make the fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be
low and build up slowly.
Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too
high. When the transmssion has too much fluid, the
geartrain churns up foam and cause the same condi-
tions which occur with a low fluid level.
In either case, air bubbles can cause overheating
and/or fluid oxidation, and varnishing. This can
interfere with normal valve, clutch, and accumulator
operation. Foaming can also result in fluid escaping
from the transmission vent where it may be mis-
taken for a leak.
After the fluid has been checked, seat the dipstick
fully to seal out water and dirt.
The transmission has a dipstick to check oil level.
It is located on the right side of the engine. Be sure
to wipe all dirt from dipstick handle before removing.
Fluid level is checked with the engine running at
curb idle speed, the transmission in NEUTRAL and
the transmission fluid at normal operating tempera-
ture.The engine should be running at idle
speed for at least one minute, with the vehicle
on level ground.
The transmission fluid level can be checked two
ways.
PROCEDURE ONE
(1) Transmission fluid must be at normal operat-
ing temperature for accurate fluid level check. Drive
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 46RE 21 - 201
Page 2220 of 2895

FLUID AND FILTER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - EFFECTS OF
INCORRECT FLUID LEVEL
A low fluid level allows the pump to take in air
along with the fluid. Air in the fluid will cause fluid
pressures to be low and develop slower than normal.
If the transmission is overfilled, the gears churn the
fluid into foam. This aerates the fluid and causing
the same conditions occurring with a low level. In
either case, air bubbles cause fluid overheating, oxi-
dation and varnish buildup which interferes with
valve and clutch operation. Foaming also causes fluid
expansion which can result in fluid overflow from the
transmission vent or fill tube. Fluid overflow can eas-
ily be mistaken for a leak if inspection is not careful.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CAUSES OF
BURNT FLUID
Burnt, discolored fluid is a result of overheating
which has two primary causes.
(1) A result of restricted fluid flow through the
main and/or auxiliary cooler. This condition is usu-
ally the result of a faulty or improperly installed
drainback valve, a damaged main cooler, or severe
restrictions in the coolers and lines caused by debris
or kinked lines.
(2) Heavy duty operation with a vehicle not prop-
erly equipped for this type of operation. Trailer tow-
ing or similar high load operation will overheat the
transmission fluid if the vehicle is improperly
equipped. Such vehicles should have an auxiliary
transmission fluid cooler, a heavy duty cooling sys-
tem, and the engine/axle ratio combination needed to
handle heavy loads.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLUID
CONTAMINATION
Transmission fluid contamination is generally a
result of:
²adding incorrect fluid
²failure to clean dipstick and fill tube when
checking level
²engine coolant entering the fluid
²internal failure that generates debris
²overheat that generates sludge (fluid break-
down)
²failure to replace contaminated converter after
repair
The use of non-recommended fluids can result in
transmission failure. The usual results are erratic
shifts, slippage, abnormal wear and eventual failuredue to fluid breakdown and sludge formation. Avoid
this condition by using recommended fluids only.
The dipstick cap and fill tube should be wiped
clean before checking fluid level. Dirt, grease and
other foreign material on the cap and tube could fall
into the tube if not removed beforehand. Take the
time to wipe the cap and tube clean before withdraw-
ing the dipstick.
Engine coolant in the transmission fluid is gener-
ally caused by a cooler malfunction. The only remedy
is to replace the radiator as the cooler in the radiator
is not a serviceable part. If coolant has circulated
through the transmission, an overhaul is necessary.
The torque converter should be replaced whenever
a failure generates sludge and debris. This is neces-
sary because normal converter flushing procedures
will not remove all contaminants.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID LEVEL
CHECK
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows the pump to take in air along with
the fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles
make the fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be
low and build up slowly.
Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too
high. When the transmssion has too much fluid, the
geartrain churns up foam and cause the same condi-
tions which occur with a low fluid level.
In either case, air bubbles can cause overheating
and/or fluid oxidation, and varnishing. This can
interfere with normal valve, clutch, and accumulator
operation. Foaming can also result in fluid escaping
from the transmission vent where it may be mis-
taken for a leak.
After the fluid has been checked, seat the dipstick
fully to seal out water and dirt.
The transmission has a dipstick to check oil level.
It is located on the right side of the engine. Be sure
to wipe all dirt from dipstick handle before removing.
Fluid level is checked with the engine running at
curb idle speed, the transmission in NEUTRAL and
the transmission fluid at normal operating tempera-
ture.The engine should be running at idle
speed for at least one minute, with the vehicle
on level ground.
The transmission fluid level can be checked two
ways.
PROCEDURE ONE
(1) Transmission fluid must be at normal operat-
ing temperature for accurate fluid level check. Drive
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 48RE 21 - 381
Page 2380 of 2895

BTSI FUNCTION CHECK
(1) Verify removal of ignition key allowed in PARK
position only.
(2) When the shift lever is in PARK, the ignition
key cylinder should rotate freely from off to lock.
When the shifter is in any other position, the ignition
key should not rotate from off to lock.
(3) Shifting out of PARK should be possible when
the ignition key cylinder is in the off position.
(4) Shifting out of PARK should not be possible
while applying normal force, and ignition key cylin-
der is in the run or start positions, unless the foot
brake pedal is depressed approximately 1/2 inch
(12mm).
(5) Shifting out of PARK should not be possible
when the ignition key cylinder is in the accessory or
lock position.
(6) Shifting between any gear and NEUTRAL, or
PARK, may be done without depressing foot brake
with ignition switch in run or start positions.
(7) Engine starts must be possible with shifter
lever in PARK or NEUTRAL positions only. Engine
starts must not be possible in any position other than
PARK or NEUTRAL.
(8) With shifter lever in the:
²PARK position - Apply upward force on the shift
arm and remove pressure. Engine starts must be
possible.
²PARK position - Apply downward force on the
shift arm and remove pressure. Engine starts must
be possible.
²NEUTRAL position - Normal position. Engine
starts must be possible.²NEUTRAL position - Engine running and brakes
applied, apply upward force on the shift arm. Trans-
mission shall not be able to shift from neutral to
reverse.
FLUID AND FILTER
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - EFFECTS OF
INCORRECT FLUID LEVEL
A low fluid level allows the pump to take in air
along with the fluid. Air in the fluid will cause fluid
pressures to be low and develop slower than normal.
If the transmission is overfilled, the gears churn the
fluid into foam. This aerates the fluid and causing
the same conditions occurring with a low level. In
either case, air bubbles cause fluid overheating, oxi-
dation and varnish buildup which interferes with
valve and clutch operation. Foaming also causes fluid
expansion which can result in fluid overflow from the
transmission vent or fill tube. Fluid overflow can eas-
ily be mistaken for a leak if inspection is not careful.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CAUSES OF
BURNT FLUID
Burnt, discolored fluid is a result of overheating
which has three primary causes.
(1) Internal clutch slippage, usually caused by low
line pressure, inadequate clutch apply pressure, or
clutch seal failure.
(2) A result of restricted fluid flow through the
main and/or auxiliary cooler. This condition is usu-
ally the result of a faulty or improperly installed
drainback valve, a damaged main cooler, or severe
restrictions in the coolers and lines caused by debris
or kinked lines.
(3) Heavy duty operation with a vehicle not prop-
erly equipped for this type of operation. Trailer tow-
ing or similar high load operation will overheat the
transmission fluid if the vehicle is improperly
equipped. Such vehicles should have an auxiliary
transmission fluid cooler, a heavy duty cooling sys-
tem, and the engine/axle ratio combination needed to
handle heavy loads.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FLUID
CONTAMINATION
Transmission fluid contamination is generally a
result of:
²adding incorrect fluid
²failure to clean dipstick and fill tube when
checking level
²engine coolant entering the fluid
Fig. 65 Brake Transmission Interlock Mechanism
1 - STEERING COLUMN
2 - GEARSHIFT CABLE
3 - GEARSHIFT CABLE LOCK TAB
4 - BTSI SOLENOID LOCK TAB
5 - BTSI CONNECTOR
DRAUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION - 45RFE/545RFE 21 - 541
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 2776 of 2895

HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - HEATER AND AIR
CONDITIONER........................1
DESCRIPTION - COOLING SYSTEM
REQUIREMENTS.......................1
DESCRIPTION - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM
SERVICE PORT........................1
OPERATION
OPERATION - HEATER AND AIR
CONDITIONER........................1
OPERATION - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM
SERVICE PORT........................2DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C
PERFORMANCE.......................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATER
PERFORMANCE.......................5
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DIODE
REPLACEMENT.......................7
SPECIFICATIONS
A/C APPLICATION TABLE................7
SPECIFICATIONS......................8
CONTROLS.............................9
DISTRIBUTION..........................24
PLUMBING.............................31
HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - HEATER AND AIR
CONDITIONER
All vehicles are equipped with a common HVAC
housing assembly (Fig. 1). The system combines air
conditioning, heating, and ventilating capabilities in
a single unit housing mounted under the instrument
panel.
DESCRIPTION - COOLING SYSTEM
REQUIREMENTS
To maintain the performance level of the HVAC
system, the engine cooling system must be properly
maintained. The use of a bug screen is not recom-
mended. Any obstructions in front of the radiator or
condenser will reduce the performance of the air con-
ditioning and engine cooling systems.
The engine cooling system includes the heater core
and the heater hoses. Refer to Engine Cooling for
more information before the opening of, or attempt-
ing any service to the engine cooling system.
DESCRIPTION - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM
SERVICE PORT
The two refrigerant system service ports are used
to charge, recover/recycle, evacuate, and test the air
conditioning refrigerant system. Unique service port
coupler sizes are used on the R-134a system, toensure that the refrigerant system is not accidentally
contaminated by the use of the wrong refrigerant
(R-12), or refrigerant system service equipment.
OPERATION
OPERATION - HEATER AND AIR CONDITIONER
The heater air conditioner are blend-air type sys-
tems. In a blend-air system, a blend door controls the
amount of unconditioned air (or cooled air from the
evaporator on models with air conditioning) that is
allowed to flow through, or around, the heater core. A
temperature control knob on the A/C Heater control
panel determines the discharge air temperature by
controlling an electric actuator, which moves the
blend door. This allows an almost immediate control
of the output air temperature of the system.
The mode control knob on the A/C Heater control
panel is used to direct the conditioned air to the
selected system outlets. Both mode control switches
use electric actuators to control the mode doors.
On all vehicles, the outside air intake can be shut
off by selecting the Recirculation Mode with the
mode control knob. This will operate a electric actu-
ated recirculation door that closes off the outside
fresh air intake and recirculates the air that is
already inside the vehicle.
The air conditioner for all models is designed for
the use of non-CFC, R-134a refrigerant. The air con-
ditioning system has an evaporator to cool and dehu-
midify the incoming air prior to blending it with the
heated air. This air conditioning system uses a fixed
orifice tube in the liquid line near the condenser out-
let tube to meter refrigerant flow to the evaporator
DRHEATING & AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 1
Page 2779 of 2895
Pressure Diagnosis
Condition Possible Causes Correction
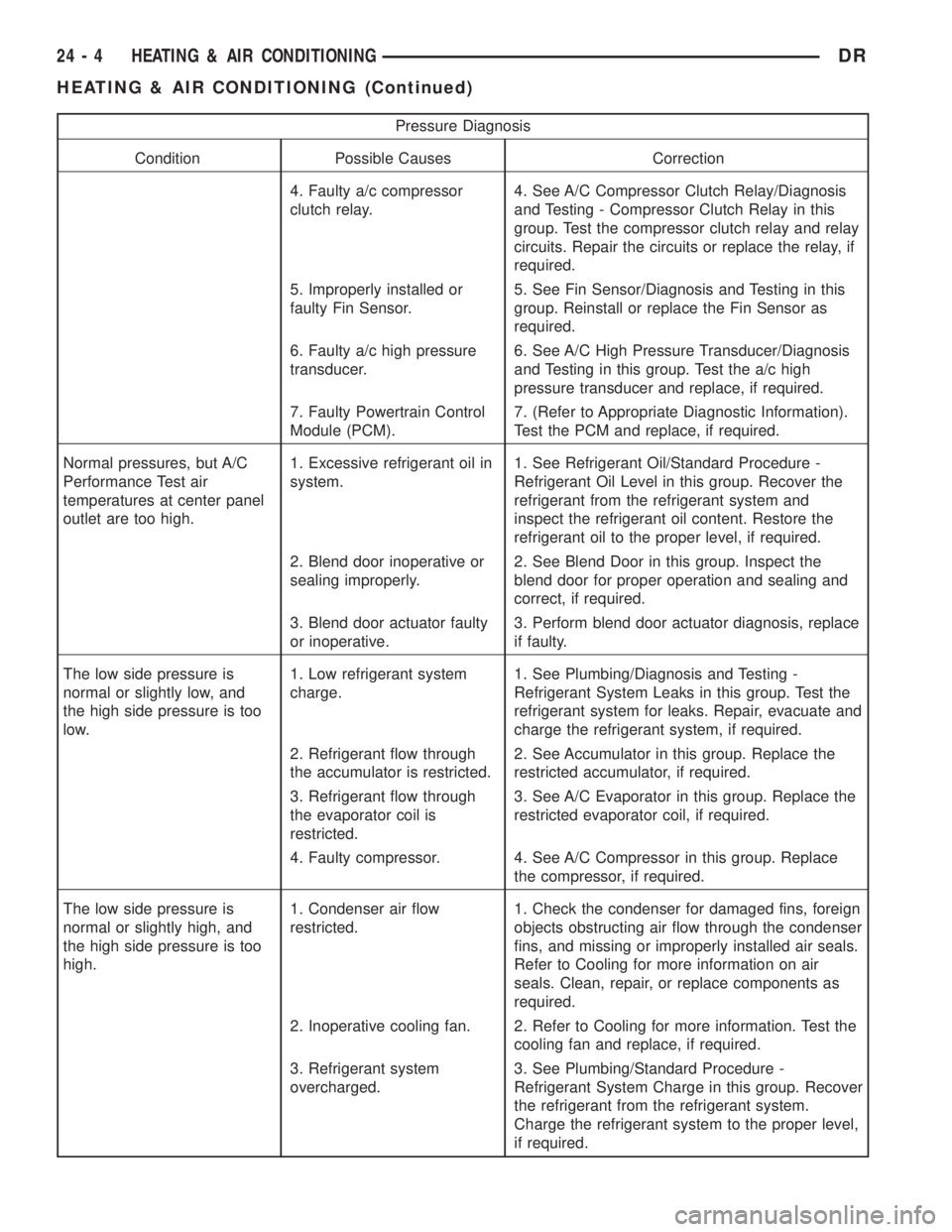
4. Faulty a/c compressor
clutch relay.4. See A/C Compressor Clutch Relay/Diagnosis
and Testing - Compressor Clutch Relay in this
group. Test the compressor clutch relay and relay
circuits. Repair the circuits or replace the relay, if
required.
5. Improperly installed or
faulty Fin Sensor.5. See Fin Sensor/Diagnosis and Testing in this
group. Reinstall or replace the Fin Sensor as
required.
6. Faulty a/c high pressure
transducer.6. See A/C High Pressure Transducer/Diagnosis
and Testing in this group. Test the a/c high
pressure transducer and replace, if required.
7. Faulty Powertrain Control
Module (PCM).7. (Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic Information).
Test the PCM and replace, if required.
Normal pressures, but A/C
Performance Test air
temperatures at center panel
outlet are too high.1. Excessive refrigerant oil in
system.1. See Refrigerant Oil/Standard Procedure -
Refrigerant Oil Level in this group. Recover the
refrigerant from the refrigerant system and
inspect the refrigerant oil content. Restore the
refrigerant oil to the proper level, if required.
2. Blend door inoperative or
sealing improperly.2. See Blend Door in this group. Inspect the
blend door for proper operation and sealing and
correct, if required.
3. Blend door actuator faulty
or inoperative.3. Perform blend door actuator diagnosis, replace
if faulty.
The low side pressure is
normal or slightly low, and
the high side pressure is too
low.1. Low refrigerant system
charge.1. See Plumbing/Diagnosis and Testing -
Refrigerant System Leaks in this group. Test the
refrigerant system for leaks. Repair, evacuate and
charge the refrigerant system, if required.
2. Refrigerant flow through
the accumulator is restricted.2. See Accumulator in this group. Replace the
restricted accumulator, if required.
3. Refrigerant flow through
the evaporator coil is
restricted.3. See A/C Evaporator in this group. Replace the
restricted evaporator coil, if required.
4. Faulty compressor. 4. See A/C Compressor in this group. Replace
the compressor, if required.
The low side pressure is
normal or slightly high, and
the high side pressure is too
high.1. Condenser air flow
restricted.1. Check the condenser for damaged fins, foreign
objects obstructing air flow through the condenser
fins, and missing or improperly installed air seals.
Refer to Cooling for more information on air
seals. Clean, repair, or replace components as
required.
2. Inoperative cooling fan. 2. Refer to Cooling for more information. Test the
cooling fan and replace, if required.
3. Refrigerant system
overcharged.3. See Plumbing/Standard Procedure -
Refrigerant System Charge in this group. Recover
the refrigerant from the refrigerant system.
Charge the refrigerant system to the proper level,
if required.
24 - 4 HEATING & AIR CONDITIONINGDR
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 2780 of 2895

Pressure Diagnosis
Condition Possible Causes Correction
4. Air in the refrigerant
system.4. See Plumbing/Diagnosis and Testing -
Refrigerant System Leaks in this group. Test the
refrigerant system for leaks. Repair, evacuate and
charge the refrigerant system, if required.
5. Engine overheating. 5. Refer to Cooling for more information. Test the
cooling system and repair, if required.
The low side pressure is too
high, and the high side
pressure is too low.1. Accessory drive belt
slipping.1. Refer to Cooling for more information. Inspect
the accessory drive belt condition and tension.
Tighten or replace the accessory drive belt, if
required.
2. Fixed orifice tube not
installed.2. See A/C Orifice Tube in this group. Replace
the liquid line, if required.
3. Faulty compressor. 3. See A/C Compressor in this group. Replace
the compressor, if required.
The low side pressure is too
low, and the high side
pressure is too high.1. Restricted refrigerant flow
through the refrigerant lines.1. See Liquid, Suction, and Discharge Line in this
group. Inspect the refrigerant lines for kinks, tight
bends or improper routing. Correct the routing or
replace the refrigerant line, if required.
2. Restricted refrigerant flow
through the fixed orifice tube.2. See A/C Orifice Tube in this group. Replace
the liquid line, if required.
3. Restricted refrigerant flow
through the condenser.3. See A/C Condenser in this group. Replace the
restricted condenser, if required.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATER
PERFORMANCE
Before performing the following tests, refer to Cool-
ing for the procedures to check the engine coolant
level and flow, engine coolant reserve/recovery sys-
tem operation, accessory drive belt condition and ten-
sion, radiator air flow and the fan drive operation.
Also be certain that the accessory vacuum supply
line is connected at the engine vacuum source.
MAXIMUM HEATER OUTPUT
Engine coolant is delivered to the heater core
through two heater hoses. With the engine idling at
normal operating temperature, set the temperature
control knob in the full hot position, the mode control
switch knob in the floor position, and the blower
motor switch knob in the highest speed position.
Using a test thermometer, check the temperature of
the air being discharged at the HVAC housing floor
outlets. Compare the test thermometer reading to the
Temperature Reference chart.
Temperature Reference
Ambient Air Temperature15.5É C
(60É F)21.1É C
(70É F)26.6É C
(80É F)32.2É C
(90É F)
Minimum Air Temperature at
Floor Outlet62.2É C
(144É F)63.8É C
(147É F)65.5É C
(150É F)67.2É C
(153É F)
DRHEATING & AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 5
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 2781 of 2895

If the floor outlet air temperature is too low, refer
to Cooling to check the engine coolant temperature
specifications. Both of the heater hoses should be hot
to the touch. The coolant return heater hose should
be slightly cooler than the coolant supply heater
hose. If the return hose is much cooler than the sup-
ply hose, locate and repair the engine coolant flow
obstruction in the cooling system. Refer to Cooling
for the procedures.
An alternate method of checking heater perfor-
mance is to use a DRBIIItscan tool to monitor the
engine coolant temperature. The floor outlet air tem-
perature reading should be no more than 4.5É C (40É
F) lower than the engine coolant temperature read-
ing.
OBSTRUCTED COOLANT FLOW Possible loca-
tions or causes of obstructed coolant flow:
²Faulty water pump.
²Faulty thermostat.
²Pinched or kinked heater hoses.
²Improper heater hose routing.
²Plugged heater hoses or supply and return ports
at the cooling system connections.
²A plugged heater core.If proper coolant flow through the cooling system is
verified, and heater outlet air temperature is still
low, a mechanical problem may exist.
MECHANICAL PROBLEMS Possible locations or
causes of insufficient heat:
²An obstructed cowl air intake.
²Obstructed heater system outlets.
²A faulty, obstructed or improperly installed
blend door.
²A faulty blower system.
²A faulty a/c heater control.
TEMPERATURE CONTROL
If the heater outlet air temperature cannot be
adjusted with the temperature control knob on the
a/c heater control panel, the following could require
service:
²A faulty a/c heater control.
²A faulty blend door actuator.
²A faulty, obstructed or improperly installed
blend door.
²An obstructed cowl air intake.
²The engine cooling system.
Heater Diagnosis
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
INSUFFICIENT HEATER
OUTPUT.1. Incorrect engine
coolant level.1. Check the engine coolant level. Refer to Cooling for
the procedures.
2. Air trapped in engine
cooling system.2. Check the operation of the coolant reserve/recovery
system. Refer to Cooling for the procedures.
3. Incorrect engine
coolant temperature.3. Check the performance and operation of the engine
cooling system including: thermostat, water pump, fan
drive, accessory drive belt, coolant flow (plugged radiator
or heater core, plugged or kinked coolant hoses), air flow
(missing or improperly installed radiator air seals or fan
shroud). Refer to Cooling for the procedures.
4. Blend door actuator
inoperative or defective.4. (Refer to Controls/Blend Door Actuator) in this group.
5. Blend door not
operating properly.5. Check for a damaged, obstructed or improperly
installed blend door or seals. (Refer to Controls/Blend
Door Actuator) in this group.
6. Insufficient air flow
through heater housing.6. Remove foreign material or obstructions from cowl air
intake.
7. Improper blower motor
operation.7. (Refer to Distribution/Blower Motor/ Diagnosis and
Testing) in this group.
24 - 6 HEATING & AIR CONDITIONINGDR
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)
Page 2782 of 2895

STANDARD PROCEDURE - DIODE
REPLACEMENT
(1) Disconnect the battery negative cable and iso-
late it. If vehicle has a dual batterys remove both
negative cables.
(2) Locate the diode in the harness, and remove
the protective covering.
(3) Remove the diode from the harness, pay atten-
tion to the current flow direction (Fig. 2).
(4) Remove the insulation from the wires in the
harness. Only remove enough insulation to solder in
the new diode.
(5) Install the new diode in the harness, making
sure current flow is correct. If necessary refer to the
appropriate wiring diagram for current flow.
(6) Solder the connections together using rosin
core type solder only.Do not use acid core solder.
(7) Tape the diode to the harness using electrical
tape making, sure the diode is completely sealed
from the elements.
(8) Re-connect the battery negative cable(s), and
test affected systems.
SPECIFICATIONS
A/C APPLICATION TABLE
Item Description Notes
Vehicle DR- Ram Truck
System R134a w/ fixed
orifice tube
Compressor Saden SD-7 SP-15 PAG oil
Freeze±up
ControlA/C Fin Sensor Evaporator
mounted
High psi Control 475 psi A/C cut
outdischarge line
Control Head electronic Software -
J2190
Mode Door electric
Blend Door electric
Recirculation
Doorelectric
Blower Motor hardwired to
control headresistor block
Cooling Fan Viscous for
cooling with a
single speed
electric for A/C
for 3.7, 4.7 and
5.7L gas
engines.
Viscous for
both cooling
and A/C with
5.9L diesel
engine and
8.0L gas
engine.
Clutch Electro-
mechanical
Control relay PCM
Draw 2 - 3.7 amps @
12V 0.5V @ 70É F
Gap 0.0169- 0.0319
DRB IIIT
Reads TPS, RPM, A/C
switch test
Actuators clutch and fan
relay
Fig. 2 DIODE IDENTIFICATION
1 - CURRENT FLOW
2 - BAND AROUND DIODE INDICATES CURRENT FLOW
3 - DIODE AS SHOWN IN THE DIAGRAMS
DRHEATING & AIR CONDITIONING 24 - 7
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING (Continued)