2003 DODGE RAM diagram
[x] Cancel search: diagramPage 434 of 2895

open switch prevents the starter relay from being
energized and the starter motor from operating
unless the automatic transmission gear selector is in
the Neutral or Park positions.
When the starter relay coil is energized, the nor-
mally open relay contacts close. The relay contacts
connect the relay common feed terminal to the relay
normally open terminal. The closed relay contacts
energize the starter solenoid coil windings.
The energized solenoid pull-in coil pulls in the sole-
noid plunger. The solenoid plunger pulls the shift
lever in the starter motor. This engages the starter
overrunning clutch and pinion gear with the starter
ring gear.
As the solenoid plunger reaches the end of its
travel, the solenoid contact disc completes the high-
amperage starter feed circuit and energizes the sole-
noid plunger hold-in coil. Current now flows between
the solenoid battery terminal and the starter motor,
energizing the starter.
Once the engine starts, the overrunning clutch pro-
tects the starter motor from damage by allowing thestarter pinion gear to spin faster than the pinion
shaft. When the ignition switch is released to the On
position, the starter relay coil is de-energized. This
causes the relay contacts to open. When the relay
contacts open, the starter solenoid plunger hold-in
coil is de-energized.
When the solenoid plunger hold-in coil is de-ener-
gized, the solenoid plunger return spring returns the
plunger to its relaxed position. This causes the con-
tact disc to open the starter feed circuit, and the shift
lever to disengage the overrunning clutch and pinion
gear from the starter ring gear.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STARTING
SYSTEM
The battery, starting, and charging systems oper-
ate in conjunction with one another, and must be
tested as a complete system. For correct starting/
charging system operation, all of the components
involved in these 3 systems must perform within
specifications.
Starting System Diagnosis
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
STARTER FAILS TO
OPERATE.1. Battery discharged or
faulty.1. Refer to Battery. Charge or replace battery, if required.
2. Starting circuit wiring
faulty.2. Refer to 8, Wiring Diagrams. Test and repair starter
feed and/or control circuits, if required.
3. Starter relay faulty. 3. Refer to Starter Relay in Diagnosis and Testing.
Replace starter relay if required.
4. Ignition switch faulty. 4. Refer to Ignition Switch and Key Lock Cylinder.
Replace ignition switch if required.
5. Clutch pedal position
switch faulty.5. Refer to Clutch Pedal Position Switch.
6. Park/Neutral position
switch faulty or
misadjusted.6. Refer to Park/Neutral Position Switch. Replace
park/neutral position switch if required.
7. Starter solenoid faulty. 7. Refer to Starter Motor. Replace starter motor assembly
if required.
8. Starter motor faulty. 8. If all other starting system components and circuits test
OK, replace starter motor.
STARTER ENGAGES,
FAILS TO TURN
ENGINE.1. Battery discharged or
faulty.1. Refer to Battery. Charge or replace battery if required.
2. Starting circuit wiring
faulty.2. Refer to 8, Wiring Diagrams. Test and repair starter
feed and/or control circuits if required.
3. Starter motor faulty. 3. If all other starting system components and circuits test
OK, replace starter motor assembly.
4. Engine seized. 4. Refer to Engine Diagnosis in the Diagnosis and Testing
section of 9, Engine.
DRSTARTING 8F - 29
STARTING (Continued)
Page 435 of 2895

Starting System Diagnosis
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
STARTER ENGAGES,
SPINS OUT BEFORE
ENGINE STARTS.1. Starter ring gear faulty. 1. Refer to Starter Motor Removal and Installation.
Remove starter motor to inspect starter ring gear.
Replace starter ring gear if required.
2. Starter motor faulty. 2. If all other starting system components and circuits test
OK, replace starter motor assembly.
STARTER DOES NOT
DISENGAGE.1. Starter motor
improperly installed.1. Refer to Starter Motor Removal and Installation.
Tighten starter mounting hardware to correct torque
specifications.
2. Starter relay faulty. 2. Refer to Starter Relay Diagnosis and Testing. Replace
starter relay if required.
3. Ignition switch faulty. 3. Refer to Ignition Switch and Key Lock Cylinder.
Replace ignition switch if required.
4. Starter motor faulty. 4. If all other starting system components and circuits test
OK, replace starter motor.
INSPECTION
For complete starter wiring circuit diagrams, refer
to 8, Wiring Diagrams. Before removing any unit
from starting system for repair or diagnosis, perform
the following inspections:
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, REFER TO 8, PASSIVE RESTRAINT SYS-
TEMS, BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING
WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT
PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE.
FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRECAUTIONS
COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOY-
MENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL INJURY.
²Battery- Visually inspect battery for indica-
tions of physical damage and loose or corroded cable
connections. Determine state-of-charge and cranking
capacity of battery. Charge or replace battery if
required. Refer toBatteryin 8, Battery.Note: If
equipped with diesel engine, a dual battery sys-
tem may be used, and both batteries must be
inspected.
²Ignition Switch- Visually inspect ignition
switch for indications of physical damage and loose
or corroded wire harness connections. Refer toIgni-
tion Switch and Key Lock Cylinder.
²Clutch Pedal Position Switch- If equipped
with manual transmission, visually inspect clutch
pedal position switch for indications of physical dam-
age and loose or corroded wire harness connections.
Refer toClutch Pedal Position Switchin 6,
Clutch.
²Park/Neutral Position Switch- If equipped
with automatic transmission, visually inspect park/
neutral position switch for indications of physical
damage and loose or corroded wire harness connec-tions. Refer toPark/Neutral Position Switchin
21, Transmission.
²Starter Relay- Visually inspect starter relay
for indications of physical damage and loose or cor-
roded wire harness connections.
²Starter Motor- Visually inspect starter motor
for indications of physical damage and loose or cor-
roded wire harness connections.
²Starter Solenoid- Visually inspect starter sole-
noid for indications of physical damage and loose or
corroded wire harness connections.
²Wiring- Visually inspect wire harnesses for
damage. Repair or replace any faulty wiring, as
required. Refer to 8, Wiring Diagrams.
TESTING
COLD CRANKING TEST
For complete starter wiring circuit diagrams, refer
to 8, Wiring Diagrams. The battery must be fully-
charged and load-tested before proceeding. Refer to
Batteryin 8, Battery.
(1) Connect volt-ampere tester to battery terminals
(Fig. 1). See instructions provided by manufacturer of
volt-ampere tester being used.Note: Certain diesel
equipped models use dual batteries. If equipped
with dual battery system, tester should be con-
nected to battery on left side of vehicle only.
Also, tester current reading must be taken from
positive battery cable lead that connects to
starter motor.
(2) Fully engage parking brake.
(3) If equipped with manual transmission, place
gearshift selector lever in Neutral position and block
clutch pedal in fully depressed position. If equipped
8F - 30 STARTINGDR
STARTING (Continued)
Page 436 of 2895

with automatic transmission, place gearshift selector
lever in Park position.
(4) Verify that all lamps and accessories are
turned off.
(5) To prevent a gasoline engine from starting,
remove Automatic ShutDown (ASD) relay. To prevent
a diesel engine from starting, remove Fuel Pump
Relay. These relays are located in Power Distribution
Center (PDC). Refer to label on PDC cover for relay
location.
WARNING: IF EQUIPPED WITH DIESEL ENGINE,
ATTEMPT TO START ENGINE A FEW TIMES
BEFORE PROCEEDING WITH FOLLOWING STEP.
(6) Rotate and hold ignition switch in Start posi-
tion. Note cranking voltage and current (amperage)
draw readings shown on volt-ampere tester.
(a) If voltage reads below 9.6 volts, refer to
Starter Motorin Diagnosis and Testing. If starter
motor is OK, refer toEngine Diagnosisin 9,
Engine for further testing of engine. If starter
motor is not OK, replace faulty starter motor.
(b) If voltage reads above 9.6 volts and current
(amperage) draw reads below specifications, refer
toFeed Circuit Testin this section.
(c) If voltage reads 12.5 volts or greater and
starter motor does not turn, refer toControl Cir-
cuit Testingin this section.
(d) If voltage reads 12.5 volts or greater and
starter motor turns very slowly, refer toFeed Cir-
cuit Testin this section.
NOTE: A cold engine will increase starter current
(amperage) draw reading, and reduce battery volt-
age reading.FEED CIRCUIT TEST
The starter feed circuit test (voltage drop method)
will determine if there is excessive resistance in
high-amperage feed circuit. For complete starter wir-
ing circuit diagrams, refer 8, Wiring Diagrams.
When performing these tests, it is important to
remember that voltage drop is giving an indication of
resistance between two points at which voltmeter
probes are attached.
Example:When testing resistance of positive bat-
tery cable, touch voltmeter leads to positive battery
cable clamp and cable connector at starter solenoid.
If you probe positive battery terminal post and cable
connector at starter solenoid, you are reading com-
bined voltage drop in positive battery cable clamp-to-
terminal post connection and positive battery cable.
The following operation will require a voltmeter
accurate to 1/10 (0.10) volt. Before performing tests,
be certain that following procedures are accom-
plished:
²Battery is fully-charged and load-tested. Refer to
Batteryin 8, Battery.
²Fully engage parking brake.
²If equipped with manual transmission, place
gearshift selector lever in Neutral position and block
clutch pedal in fully depressed position. If equipped
with automatic transmission, place gearshift selector
lever in Park position.
²Verify that all lamps and accessories are turned
off.
²To prevent a gasoline engine from starting,
remove Automatic ShutDown (ASD) relay. To prevent
a diesel engine from starting, remove Fuel Pump
Relay. These relays are located in Power Distribution
Center (PDC). Refer to label on PDC cover for relay
location.
(1) Connect positive lead of voltmeter to negative
battery cable terminal post. Connect negative lead of
voltmeter to negative battery cable clamp (Fig. 2).
Rotate and hold ignition switch in Start position.
Observe voltmeter. If voltage is detected, correct poor
contact between cable clamp and terminal post.
Note: Certain diesel equipped models use dual
batteries. If equipped with dual battery system,
procedure must be performed twice, once for
each battery.
(2) Connect positive lead of voltmeter to positive
battery terminal post. Connect negative lead of volt-
meter to battery positive cable clamp (Fig. 3). Rotate
and hold ignition switch in Start position. Observe
voltmeter. If voltage is detected, correct poor contact
between cable clamp and terminal post.Note: Cer-
tain diesel equipped models use dual batteries.
If equipped with dual battery system, this pro-
cedure must be performed twice, once for each
battery.
Fig. 1 VOLTS-AMPS TESTER CONNECTIONS -
TYPICAL
1 - POSITIVE CLAMP
2 - NEGATIVE CLAMP
3 - INDUCTION AMMETER CLAMP
DRSTARTING 8F - 31
STARTING (Continued)
Page 438 of 2895
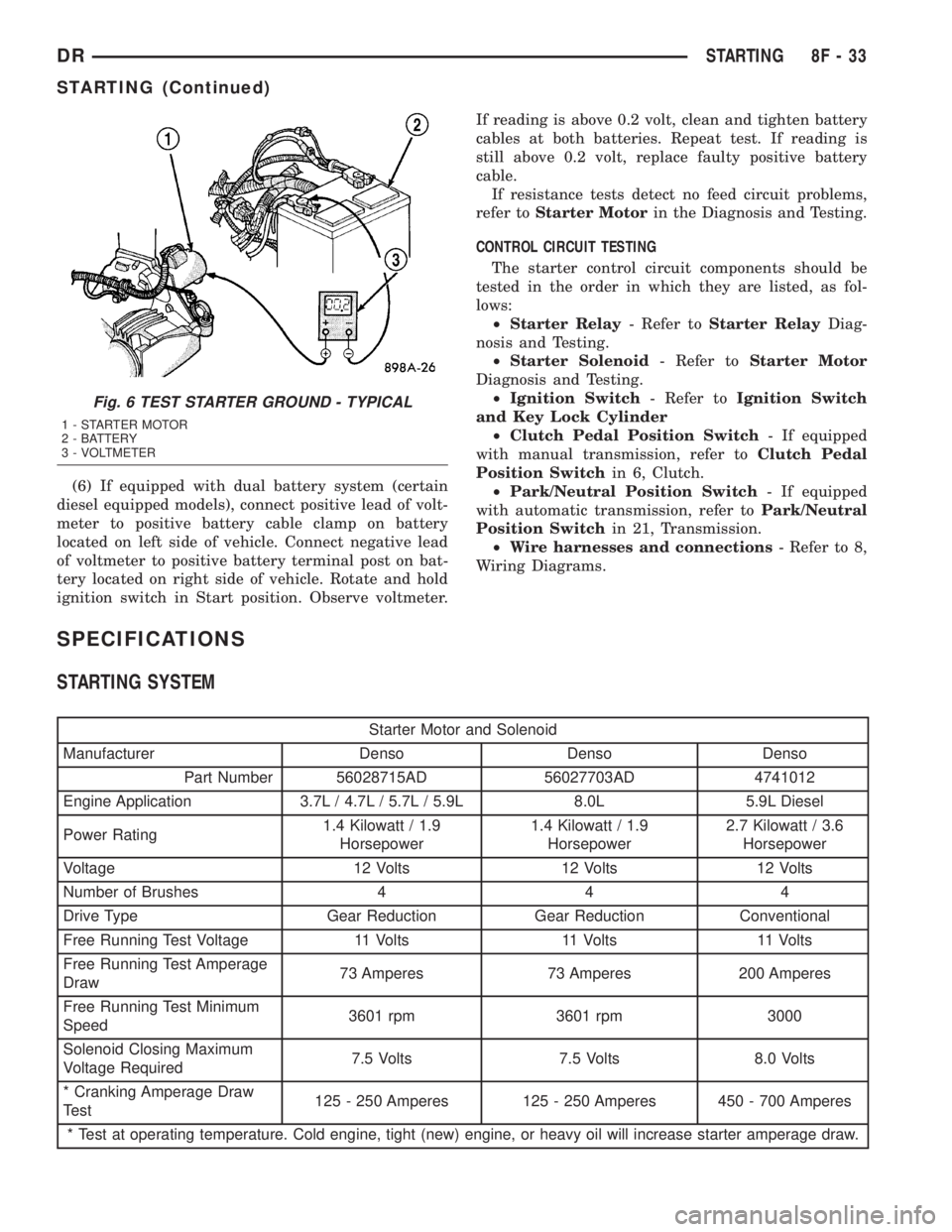
(6) If equipped with dual battery system (certain
diesel equipped models), connect positive lead of volt-
meter to positive battery cable clamp on battery
located on left side of vehicle. Connect negative lead
of voltmeter to positive battery terminal post on bat-
tery located on right side of vehicle. Rotate and hold
ignition switch in Start position. Observe voltmeter.If reading is above 0.2 volt, clean and tighten battery
cables at both batteries. Repeat test. If reading is
still above 0.2 volt, replace faulty positive battery
cable.
If resistance tests detect no feed circuit problems,
refer toStarter Motorin the Diagnosis and Testing.
CONTROL CIRCUIT TESTING
The starter control circuit components should be
tested in the order in which they are listed, as fol-
lows:
²Starter Relay- Refer toStarter RelayDiag-
nosis and Testing.
²Starter Solenoid- Refer toStarter Motor
Diagnosis and Testing.
²Ignition Switch- Refer toIgnition Switch
and Key Lock Cylinder
²Clutch Pedal Position Switch- If equipped
with manual transmission, refer toClutch Pedal
Position Switchin 6, Clutch.
²Park/Neutral Position Switch- If equipped
with automatic transmission, refer toPark/Neutral
Position Switchin 21, Transmission.
²Wire harnesses and connections- Refer to 8,
Wiring Diagrams.
SPECIFICATIONS
STARTING SYSTEM
Starter Motor and Solenoid
Manufacturer Denso Denso Denso
Part Number 56028715AD 56027703AD 4741012
Engine Application 3.7L / 4.7L / 5.7L / 5.9L 8.0L 5.9L Diesel
Power Rating1.4 Kilowatt / 1.9
Horsepower1.4 Kilowatt / 1.9
Horsepower2.7 Kilowatt / 3.6
Horsepower
Voltage 12 Volts 12 Volts 12 Volts
Number of Brushes 4 4 4
Drive Type Gear Reduction Gear Reduction Conventional
Free Running Test Voltage 11 Volts 11 Volts 11 Volts
Free Running Test Amperage
Draw73 Amperes 73 Amperes 200 Amperes
Free Running Test Minimum
Speed3601 rpm 3601 rpm 3000
Solenoid Closing Maximum
Voltage Required7.5 Volts 7.5 Volts 8.0 Volts
* Cranking Amperage Draw
Test125 - 250 Amperes 125 - 250 Amperes 450 - 700 Amperes
* Test at operating temperature. Cold engine, tight (new) engine, or heavy oil will increase starter amperage draw.
Fig. 6 TEST STARTER GROUND - TYPICAL
1 - STARTER MOTOR
2 - BATTERY
3 - VOLTMETER
DRSTARTING 8F - 33
STARTING (Continued)
Page 443 of 2895

STARTER MOTOR RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The starter relay is an electromechanical device
that switches battery current to the pull-in coil of the
starter solenoid when ignition switch is turned to
Start position. The starter relay is located in the
Power Distribution Center (PDC) in the engine com-
partment. See PDC cover for relay identification and
location.
The starter relay is a International Standards
Organization (ISO) relay. Relays conforming to ISO
specifications have common physical dimensions, cur-
rent capacities, terminal patterns, and terminal func-
tions.
The starter relay cannot be repaired or adjusted. If
faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
OPERATION
The ISO relay consists of an electromagnetic coil, a
resistor or diode, and three (two fixed and one mov-
able) electrical contacts. The movable (common feed)
relay contact is held against one of the fixed contacts
(normally closed) by spring pressure. When electro-
magnetic coil is energized, it draws the movable con-
tact away from normally closed fixed contact, and
holds it against the other (normally open) fixed con-
tact.
When electromagnetic coil is de-energized, spring
pressure returns movable contact to normally closed
position. The resistor or diode is connected in parallel
with electromagnetic coil within relay, and helps to
dissipate voltage spikes produced when coil is de-en-
ergized.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STARTER RELAY
The starter relay (Fig. 15) is located in Power Dis-
tribution Center (PDC). Refer to PDC cover for relay
identification and location. For complete starter relay
wiring circuit diagrams, refer to 8, Wiring Diagrams.
(1) Remove starter relay from PDC.
(2) A relay in de-energized position should have
continuity between terminals 87A and 30, and no
continuity between terminals 87 and 30. If OK, go to
Step 3. If not OK, replace faulty relay.
(3) Resistance between terminals 85 and 86 (elec-
tromagnet) should be 75 5 ohms. If OK, go to Step
4. If not OK, replace faulty relay.
(4) Connect 12V battery to terminals 85 and 86.
There should now be continuity between terminals
30 and 87, and no continuity between terminals 87A
and 30. If OK, perform Relay Circuit Test that fol-
lows. If not OK, replace faulty relay.RELAY CIRCUIT TEST
(1) The relay common feed terminal cavity (30) is
connected to battery voltage and should be hot at all
times. If OK, go to Step 2. If not OK, repair open cir-
cuit to fuse in PDC as required.
(2) The relay normally closed terminal (87A) is
connected to terminal 30 in the de-energized position,
but is not used for this application. Go to Step 3.
(3) The relay normally open terminal (87) is con-
nected to common feed terminal (30) in the energized
position. This terminal supplies battery voltage to
starter solenoid field coils. There should be continu-
ity between cavity for relay terminal 87 and starter
solenoid terminal at all times. If OK, go to Step 4. If
not OK, repair open circuit to starter solenoid as
required.
(4) The coil battery terminal (86) is connected to
electromagnet in relay. It is energized when ignition
switch is held in Start position. On vehicles with
manual transmission, clutch pedal must be fully
depressed for this test. Check for battery voltage at
cavity for relay terminal 86 with ignition switch in
Start position, and no voltage when ignition switch is
released to On position. If OK, go to Step 5. If not
OK with automatic transmission, check for open or
short circuit to ignition switch and repair, if required.
If circuit to ignition switch is OK, refer toIgnition
Switch and Key Lock Cylinder. If not OK with a
manual transmission, check circuit between relay
and clutch pedal position switch for open or a short.
If circuit is OK, refer toClutch Pedal Position
Switchin 6 , Clutch.
Fig. 15 TYPE 1 RELAY
TERMINAL LEGEND
NUMBER IDENTIFICATION
30 COMMON FEED
85 COIL GROUND
86 COIL BATTERY
87 NORMALLY OPEN
87A NORMALLY CLOSED
8F - 38 STARTINGDR
Page 449 of 2895

OPERATION
The heated seat module receives fused battery cur-
rent through the Integrated Power Module only when
the engine is running. The heated seat switches
receive battery current through fuse #48 in the Inte-
grated Power Module only when the ignition switch
is in the On position. The heated seat module shares
a common ground circuit with each of the heated seat
elements. The heated seat system will only operate
when the surface temperature of the seat cushion is
below the designed temperature set points of the sys-
tem.
The heated seat system will also automatically
turn off whenever the ignition switch is turned to
any position except On, or if the engine quits run-
ning. If the ignition switch is turned to the Off posi-
tion or if the engine quits running while a heated
seat is ON, the heated seat will remain Off after the
engine is restarted until a heated seat switch is
depressed again. This helps prevent the vehicles bat-
tery from being drained by the heated seat system.The heated seat module monitors inputs from the
heated seat sensors and the heated seat switches. In
response to these inputs the heated seat module uses
its internal programming to control 12v to the heated
seat elements in both front seats and to control the
heated seat LED indicator lamps located in both of
the heated seat switches. The heated seat module is
also programmed to provide self-diagnostics, if a
problem with the heated seat system is detected. If
the module detects certain failures within the heated
seat system, it will provide a visual indication of the
failure by flashing the indicator lamps in the appro-
priate heated seat switch. The heated seat module
will automatically turn off the heated seat elements
if it detects a short or open in the heated seat ele-
ment circuit or a heated seat sensor value that is out
of range.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATED SEAT
SYSTEM
HEATED SEAT SYSTEM SELF-DIAGNOSIS
The heated seat system is capable of performing
some self-diagnostics. The following table depicts the
various monitored failures which will be reported to
the vehicle operator or technician by flashing the
individual heated seat switch Light Emitting Diode
(LED) indicator lamps. Refer to the HEATED SEAT
SYSTEM SELF-DIAGNOSIS table for failure identi-
fication. The drivers heated seat switch indicator
lamps will flash if a failure occurs in the driver
heated seat, and the passengers heated seat switch
indicator lamps will flash for a passenger heated seat
failure. If a monitored heated seat system failure
occurs, the switch indicator lamps will flash at a
pulse rate of about one-half second on, followed by
about one-half second off for a duration of about one
minute after the switch for the faulty heated seat is
depressed in either the Low or High direction. This
process will repeat every time the faulty heated seat
switch is actuated until the problem has been cor-
rected.
HEATED SEAT SYSTEM SELF-DIAGNOSIS
Monitored FailureSwitch High
Indicator LampSwitch Low
Indicator Lamp
Heated Seat
Element ShortedFlashing Flashing
Heated Seat
Element OpenFlashing Off
Heated Seat
Sensor Value Out
of RangeOff Flashing
Fig. 1 DR Heated Seat System Diagram
1 - WIRE HARNESS
2 - DRIVER HEATED SEAT SWITCH
3 - PASSENGER HEATED SEAT SWITCH
4 - PASSENGER HEATED SEAT CUSHION ELEMENT
5 - SEAT CUSHION/BACK ELEMENT ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
LOCATION
6 - DRIVER HEATED SEAT BACK ELEMENT
7 - DRIVER HEATED SEAT CUSHION ELEMENT
8 - HEATED SEAT MODULE
8G - 4 HEATED SEAT SYSTEMDR
HEATED SEAT SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 450 of 2895

Diagnostic logic is built into the heated seat mod-
ule to help the person trying to locate the problem by
the most efficient means possible. Anytime a problem
is suspected, locate the diagnosis and testing proce-
dure for the component in question and follow the
steps until the specific problem is located and
resolved. Once the problem is thought to be cor-
rected, verify correct system operation. If the heated
seat system is functioning correctly return the vehi-
cle to service.
If a problem could not be verified such as not find-
ing anything wrong when following the diagnostic
procedure, this is a good indication that a INTER-
MITTENT problem may be present. You must then
attempt to find the intermittent problem, such as
moving the heating element within the seat while
testing continuity or wiggling the wire harness's/elec-
trical connectors under the seat while testing conti-
nuity. Always, eliminate all other potential problems
before attempting to replace the heated seat module.
PRELIMINARY TEST
Refer toWiringfor the location of complete heated
seat system wiring diagrams. Before testing the indi-
vidual components in the heated seat system, per-
form the following preliminary checks:
WARNING: DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM
BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING WHEEL,
STEERING COLUMN, OR INSTRUMENT PANEL
COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE. DISCON-
NECT AND ISOLATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE
CABLE, THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES FOR THE AIR-
BAG SYSTEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE
BEFORE PERFORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR
SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DIS-
ABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM. FAILURE TO TAKE
THE PROPER PRECAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN
ACCIDENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSI-
BLE PERSONAL INJURY.
²If the heated seat switch back lighting and the
cluster illumination lamps do not illuminate with the
headlamps or park lamps turned On, refer to the
Instrument Clustersection of the service manual
for the location of cluster illumination lamp diagnosis
and testing procedures. If the heated seat switch
back lighting does not illuminate, but the cluster illu-
mination lamps do illuminate with the headlamps or
park lamps turned On, refer toDiagnosis and Test-
ing the Heated Seat Switchin this section for the
location of the heated seat switch diagnosis and test-
ing procedures.
²If a single LED indicator lamp for one heated
seat switch does not operate and the heated seat ele-
ments do heat, refer toDiagnosis and Testing theHeated Seat Switchin this section for heated seat
switch diagnosis and testing procedures.
²If both LED indicator lamps for a heated seat
switch operate, but the heated seat elements do not
heat, refer toDiagnosis and Testing the Heated
Seat Modulein Electronic Control Modules for
heated seat module diagnosis and testing procedures.
²If the indicator lamp on either heated seat
switch remains illuminated after the heated seat has
been turned Off, refer toDiagnosis and Testing
the Heated Seat Modulein Electronic Control
Modules for heated seat module diagnosis and test-
ing procedures.
HEATED SEAT ELEMENT
DESCRIPTION
Vehicles equipped with the optional heated seat
system have two sets of electrically operated heating
element grids located in each front seat, one set for
the seat cushion and the other set for the seat back.
Each of the heated seat element grids consists of a
single length of resistor wire that is routed in a zig-
zag pattern and captured between a covering and the
adhesive foam rubber backing. Short pigtail wires
with connectors (Fig. 2) are soldered to each end of
each resistor wire element grid, which connect all of
Fig. 2 Heating Element Installed on Seat Cushion
Foam
1 - SEAT BACK WIRE HARNESS
2 - HEATED SEAT WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
3 - HEATED SEAT CUSHION ELEMENT
DRHEATED SEAT SYSTEM 8G - 5
HEATED SEAT SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 451 of 2895

the element grids to the heated seat module through
the seat wire harness.
One temperature sensor is used for each front seat,
and it is located in the center insert area of the seat
cushion element. The heated seat sensors and their
pigtail wires are also captured between a covering
and the adhesive foam rubber backing. The heated
seat sensors are Negative Thermal Coefficient (NTC)
thermistors. The sensors for both front seats receive
a voltage feed from a single output of the heated seat
module, but the module receives individual sensor
inputs from the driver side and passenger side sen-
sors.
The heated seat elements and sensors should not
be repaired. If damaged or faulty, the heated seat ele-
ment assembly must be replaced.
OPERATION
One end of the heated seat element resistor wire is
connected to ground at all times through a splice in
the heated seat module ground circuit. Battery cur-
rent is directed to the other end of the heated seat
element resistor wire by the energized N-channel
Field Effect Transistor (N-FET) located within the
heated seat module. The heated seat module will
energize the N-FET only when the heated seat
switch is in the Low or High position and the heated
seat sensor indicates that the seat cushion surface
temperature is below the selected (Low or High) tem-
perature set point. As electrical current passes
through the heating element grid, the resistance of
the wire used in the element disperses some of that
electrical current in the form of heat. The heat pro-
duced by the heated seat element grid then radiates
through the seat trim cover, warming its occupant.
The resistance of the heated seat sensor increases
and decreases as the surface temperature of the seat
cushion cover changes. The heated seat module sup-
plies each sensor with a 5v voltage feed, then uses
the sensor resistance to determine when the heated
seat element grids need to be cycled on or off in order
to maintain the selected temperature set point.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEATED SEAT
ELEMENT
The heated seat module will self-diagnose shorted
or open heated seat element circuits and sensor cir-
cuits. Refer to Heated Seat System Diagnosis and
Testing in this section for additional diagnosis and
testing procedures. To manually check the heated
seat element, proceed as follows. The wire harness
connectors for the seat cushion and seat back heating
elements and sensor are located on the right side of
the seat, near the edge of the seat cushion frame.
The proper connector can be identified by the foam
wrapping.NOTE: When checking heated seat elements for
continuity, be certain to move the heating element
being checked. Moving the element, such as sitting
in the seat will eliminate the possibility of an inter-
mittent open in the element which would only be
evident if the element was in a certain position.
Failure to check the element in various positions
could result in an incomplete test.
(1) Position the appropriate seat in the full for-
ward position.
(2) Make certain the ignition switch is in the OFF
position.
(3) Disconnect the heated seat element connector
which requires testing. Check for continuity between
the two heated seat element circuit cavities while
moving the appropriate seat cushion. Refer toWir-
ingfor the location of complete heated seat system
wiring diagrams. There should be continuity. If OK,
the elements within the seat assembly test OK, go to
Step 4. If not OK, replace the faulty seat heating ele-
ment, refer to the procedure in this section.
(4) Test the seat wire harness between the heated
seat module connector and the appropriate heated
seat wire harness connector for shorted or open cir-
cuits. If OK, element is OK, proceed with testing the
heated seat sensor and module. If not OK, repair the
shorted or open seat wire harness as required.
REMOVAL
Do not remove the heating element from the seat
or seat back cushion. The original element is perma-
nently attached to the seat cushions and cannot be
removed without damaging the cushion. The replace-
ment heating element is designed to be applied
directly over the original seat heating element.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the negative battery
cable.
(2) Remove the appropriate seat cushion or seat
back trim cover. Refer to the Body section of this
manual for the procedures.
(3) Disconnect the inoperative heated seat cushion
or seat back element electrical connectors.
(4) Locate the wires leading from the inoperative
heating element and cut them off flush with the edge
of the original heating element.
INSTALLATION
(1) Peel off the adhesive backing on the back of the
replacement heating element and stick directly over
the original heating element (Fig. 3).
CAUTION: During the installation of the replace-
ment heating element, be careful not to fold or
crease the element assembly. Folds or creases will
cause premature failure.
8G - 6 HEATED SEAT SYSTEMDR
HEATED SEAT ELEMENT (Continued)